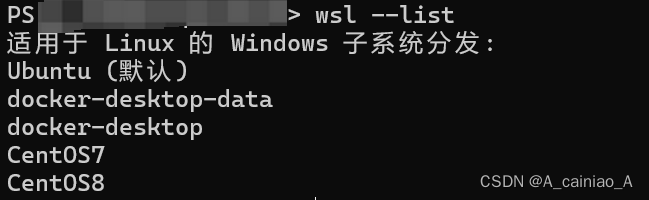
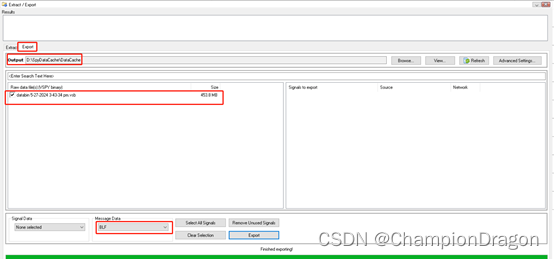
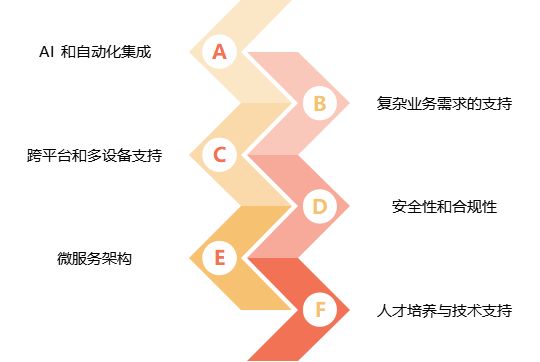
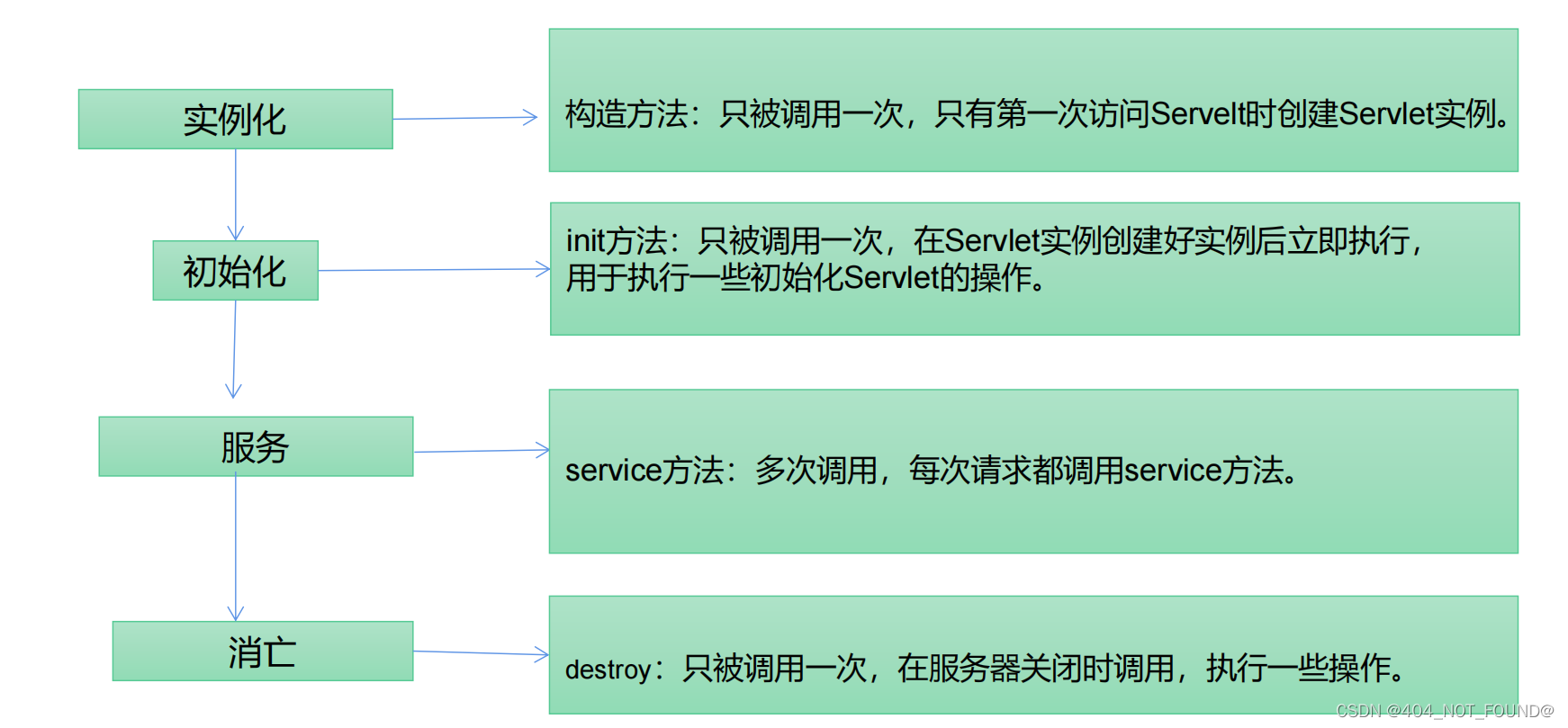
tips:有两部分的原因主要是我筛选的时候没有统一image & images
Paper1 PromptCap: Prompt-Guided Image Captioning for VQA with GPT-3
摘要原文: Knowledge-based visual question answering (VQA) involves questions that require world knowledge beyond the image to yield the correct answer. Large language models (LMs) like GPT-3 are particularly helpful for this task because of their strong knowledge retrieval and reasoning capabilities. To enable LM to understand images, prior work uses a captioning model to convert images into text. However, when summarizing an image in a single caption sentence, which visual entities to describe are often underspecified. Generic image captions often miss visual details essential for the LM to answer visual questions correctly. To address this challenge, we propose PromptCap (Prompt-guided image Captioning), a captioning model designed to serve as a better connector between images and black-box LMs. Different from generic captions, PromptCap takes a natural-language prompt to control the visual entities to describe in the generated caption. The prompt contains a question that the caption should aid in answering. To avoid extra annotation, PromptCap is trained by examples synthesized with GPT-3 and existing datasets. We demonstrate PromptCap’s effectiveness on an existing pipeline in which GPT-3 is prompted with image captions to carry out VQA. PromptCap outperforms generic captions by a large margin and achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on knowledge-based VQA tasks (60.4% on OK-VQA and 59.6% on A-OKVQA). Zero-shot results on WebQA show that PromptCap generalizes well to unseen domains.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了基于知识的视觉问答(VQA)涉及需要超越图像的世界知识才能得出正确答案的问题。大型语言模型(LMs)如GPT-3在这项任务中特别有帮助,因为它们具有强大的知识检索和推理能力。为了让LM能够理解图像,先前的工作使用一个字幕模型将图像转换为文本。然而,在用单个字幕句子总结图像时,往往会不足地描述哪些视觉实体。通用图像字幕经常错过了LM正确回答视觉问题所必需的视觉细节。为了解决这一挑战,作者提出了PromptCap(Prompt-guided image Captioning),这是一个设计为更好地连接图像和黑匣子LM的字幕模型。与通用字幕不同,PromptCap接受自然语言提示来控制生成字幕中要描述的视觉实体。提示包含一个问题,字幕应该帮助回答这个问题。为了避免额外的注释,PromptCap是通过使用GPT-3和现有数据集合成的示例进行训练的。作者展示了PromptCap在一个现有流水线上的有效性,其中GPT-3被提示使用图像字幕进行VQA。PromptCap比通用字幕表现出色,并在基于知识的VQA任务上取得了最先进的准确率(OK-VQA为60.4%,A-OKVQA为59.6%)。在WebQA上的零样本结果显示,PromptCap在未见过的领域中表现良好。
Paper2 Rethinking Fast Fourier Convolution in Image Inpainting
摘要原文: Recently proposed image inpainting method LaMa builds its network upon Fast Fourier Convolution (FFC), which was originally proposed for high-level vision tasks like image classification. FFC empowers the fully convolutional network to have a global receptive field in its early layers. Thanks to the unique character of the FFC module, LaMa has the ability to produce robust repeating texture, which can not be achieved by the previous inpainting methods. However, is the vanilla FFC module suitable for low-level vision tasks like image inpainting? In this paper, we analyze the fundamental flaws of using FFC in image inpainting, which are 1) spectrum shifting, 2) unexpected spatial activation, and 3) limited frequency receptive field. Such flaws make FFC-based inpainting framework difficult in generating complicated texture and performing faithful reconstruction. Based on the above analysis, we propose a novel Unbiased Fast Fourier Convolution (UFFC) module, which modifies the vanilla FFC module with 1) range transform and inverse transform, 2) absolute position embedding, 3) dynamic skip connection, and 4) adaptive clip, to overcome such flaws, achieving better inpainting results. Extensive experiments on several benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, outperforming the state-of-the-art methods in both texture-capturing ability and expressiveness.
中文总结: 最近提出的图像修复方法LaMa基于快速傅里叶卷积(FFC)构建其网络,FFC最初是为像图像分类这样的高级视觉任务而提出的。FFC使得完全卷积网络在早期层具有全局感受野。由于FFC模块的独特特性,LaMa具有产生稳健的重复纹理的能力,这是以前的修复方法所无法实现的。然而,香草FFC模块是否适用于像图像修复这样的低级视觉任务呢?在本文中,我们分析了在图像修复中使用FFC存在的基本缺陷,包括1)频谱偏移,2)意外的空间激活,和3)有限的频率感受野。这些缺陷使得基于FFC的修复框架难以生成复杂纹理并进行忠实的重建。基于以上分析,我们提出了一种新颖的无偏快速傅里叶卷积(UFFC)模块,通过1)范围变换和逆变换,2)绝对位置嵌入,3)动态跳过连接,和4)自适应剪辑,修改香草FFC模块,以克服这些缺陷,实现更好的修复结果。在几个基准数据集上进行的大量实验证明了我们方法的有效性,在纹理捕捉能力和表现力方面均优于现有方法。
Paper3 DDColor: Towards Photo-Realistic Image Colorization via Dual Decoders
摘要原文: Image colorization is a challenging problem due to multi-modal uncertainty and high ill-posedness. Directly training a deep neural network usually leads to incorrect semantic colors and low color richness. While transformer-based methods can deliver better results, they often rely on manually designed priors, suffer from poor generalization ability, and introduce color bleeding effects. To address these issues, we propose DDColor, an end-to-end method with dual decoders for image colorization. Our approach includes a pixel decoder and a query-based color decoder. The former restores the spatial resolution of the image, while the latter utilizes rich visual features to refine color queries, thus avoiding hand-crafted priors. Our two decoders work together to establish correlations between color and multi-scale semantic representations via cross-attention, significantly alleviating the color bleeding effect. Additionally, a simple yet effective colorfulness loss is introduced to enhance the color richness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DDColor achieves superior performance to existing state-of-the-art works both quantitatively and qualitatively. The codes and models are publicly available.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了图像着色的挑战性问题,包括多模态不确定性和高度不适定性。直接训练深度神经网络通常会导致错误的语义颜色和低色彩丰富度。虽然基于Transformer的方法可以提供更好的结果,但它们通常依赖于手动设计的先验知识,具有较差的泛化能力,并且会引入颜色渗透效应。为了解决这些问题,作者提出了DDColor,这是一种具有双解码器的端到端图像着色方法。该方法包括一个像素解码器和一个基于查询的颜色解码器。前者恢复图像的空间分辨率,而后者利用丰富的视觉特征来优化颜色查询,从而避免手工设计的先验知识。这两个解码器共同工作,通过交叉注意力在颜色和多尺度语义表示之间建立相关性,显著减轻了颜色渗透效应。此外,引入了一种简单而有效的色彩丰富度损失以增强色彩丰富度。大量实验证明,DDColor在定量和定性上均优于现有的最先进作品。代码和模型已公开发布。
Paper4 FashionNTM: Multi-turn Fashion Image Retrieval via Cascaded Memory
摘要原文: Multi-turn textual feedback-based fashion image retrieval focuses on a real-world setting, where users can iteratively provide information to refine retrieval results until they find an item that fits all their requirements. In this work, we present a novel memory-based method, called FashionNTM, for such a multi-turn system. Our framework incorporates a new Cascaded Memory Neural Turing Machine (CM-NTM) approach for implicit state management, thereby learning to integrate information across all past turns to retrieve new images, for a given turn. Unlike vanilla Neural Turing Machine (NTM), our CM-NTM operates on multiple inputs, which interact with their respective memories via individual read and write heads, to learn complex relationships. Extensive evaluation results show that our proposed method outperforms the previous state-of-the-art algorithm by 50.5%, on Multi-turn FashionIQ – the only existing multi-turn fashion dataset currently, in addition to having a relative improvement of 12.6% on Multi-turn Shoes – an extension of the single-turn Shoes dataset that we created in this work. Further analysis of the model in a real-world interactive setting demonstrates two important capabilities of our model – memory retention across turns, and agnosticity to turn order for non-contradictory feedback. Finally, user study results show that images retrieved by FashionNTM were favored by 83.1% over other multi-turn models.
中文总结: 这段话主要讲述了基于多轮文本反馈的时尚图像检索,关注于用户可以迭代提供信息以细化检索结果的真实世界设置。作者提出了一种名为FashionNTM的新型基于记忆的方法,用于这样的多轮系统。他们的框架结合了一种新的级联记忆神经图灵机(CM-NTM)方法,用于隐式状态管理,从而学习整合所有过去轮次的信息以检索给定轮次的新图像。相比于普通的神经图灵机(NTM),他们的CM-NTM操作于多个输入,这些输入通过各自的读写头与各自的记忆交互,以学习复杂关系。广泛的评估结果显示,他们提出的方法在Multi-turn FashionIQ数据集上比先前的最先进算法提高了50.5%,同时在Multi-turn Shoes数据集上相对提高了12.6%。在真实世界互动环境中对模型的进一步分析展示了模型的两个重要能力:跨轮次的记忆保持和对于非矛盾反馈的轮次顺序的不可知性。最后,用户研究结果显示,FashionNTM检索的图像比其他多轮模型受到83.1%的青睐。
Paper5 AG3D: Learning to Generate 3D Avatars from 2D Image Collections
摘要原文: While progress in 2D generative models of human appearance has been rapid, many applications require 3D avatars that can be animated and rendered. Unfortunately, most existing methods for learning generative models of 3D humans with diverse shape and appearance require 3D training data, which is limited and expensive to acquire. The key to progress is hence to learn generative models of 3D avatars from abundant unstructured 2D image collections. However, learning realistic and complete 3D appearance and geometry in this under-constrained setting remains challenging, especially in the presence of loose clothing such as dresses. In this paper, we propose a new adversarial generative model of realistic 3D people from 2D images. Our method captures shape and deformation of the body and loose clothing by adopting a holistic 3D generator and integrating an efficient, flexible, articulation module. To improve realism, we train our model using multiple discriminators while also integrating geometric cues in the form of predicted 2D normal maps. We experimentally find that our method outperforms previous 3D- and articulation-aware methods in terms of geometry and appearance. We validate the effectiveness of our model and the importance of each component via systematic ablation studies.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了目前2D人类外貌生成模型的快速进展,但许多应用需要能够进行动画和渲染的3D化身。然而,大多数现有的学习具有多样化形状和外貌的3D人类生成模型的方法需要3D训练数据,这些数据获取起来有限且昂贵。因此,进展的关键是从丰富的非结构化2D图像集合中学习3D化身的生成模型。然而,在这种不受约束的情况下学习真实和完整的3D外貌和几何仍然具有挑战性,特别是在存在松散服装(如裙子)的情况下。作者提出了一种新的对抗生成模型,可以从2D图像中生成真实的3D人物。他们的方法通过采用整体的3D生成器和整合高效、灵活的关节模块来捕捉身体和松散服装的形状和变形。为了提高真实感,他们使用多个判别器来训练模型,同时还通过预测的2D法线图形式整合几何线索。实验证明,他们的方法在几何和外貌方面优于先前的3D和关节感知方法。通过系统的消融研究,他们验证了模型的有效性和每个组件的重要性。
Paper6 Learning Non-Local Spatial-Angular Correlation for Light Field Image Super-Resolution
摘要原文: Exploiting spatial-angular correlation is crucial to light field (LF) image super-resolution (SR), but is highly challenging due to its non-local property caused by the disparities among LF images. Although many deep neural networks (DNNs) have been developed for LF image SR and achieved continuously improved performance, existing methods cannot well leverage the long-range spatial-angular correlation and thus suffer a significant performance drop when handling scenes with large disparity variations. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective method to learn the non-local spatial-angular correlation for LF image SR. In our method, we adopt the epipolar plane image (EPI) representation to project the 4D spatial-angular correlation onto multiple 2D EPI planes, and then develop a Transformer network with repetitive self-attention operations to learn the spatial-angular correlation by modeling the dependencies between each pair of EPI pixels. Our method can fully incorporate the information from all angular views while achieving a global receptive field along the epipolar line. We conduct extensive experiments with insightful visualizations to validate the effectiveness of our method. Comparative results on five public datasets show that our method not only achieves state-of-the-art SR performance, but also performs robust to disparity variations.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了光场图像超分辨率(SR)中利用空间角度相关性的重要性以及面临的挑战。尽管已经开发了许多深度神经网络(DNN)用于光场图像SR并取得了不断改进的性能,但现有方法无法很好地利用长距离的空间角度相关性,因此在处理具有大视差变化的场景时性能会显著下降。该论文提出了一种简单而有效的方法来学习光场图像SR的非局部空间角度相关性。他们采用极线平面图(EPI)表示法将4D空间角度相关性投影到多个2D EPI平面上,然后开发了一个具有重复自注意力操作的Transformer网络,通过建模每对EPI像素之间的依赖关系来学习空间角度相关性。该方法可以充分整合所有角度视图的信息,同时沿着极线获得全局感知域。通过广泛的实验和有见地的可视化验证了该方法的有效性。在五个公共数据集上的比较结果表明,该方法不仅实现了最先进的SR性能,而且对视差变化表现出鲁棒性。
Paper7 FSI: Frequency and Spatial Interactive Learning for Image Restoration in Under-Display Cameras
摘要原文: Under-display camera (UDC) systems remove the screen notch for bezel-free displays and provide a better interactive experience. The main challenge is that the pixel array of light-emitting diodes used for display diffracts and attenuates the incident light, leading to complex degradation. Existing models eliminate spatial diffraction by maximizing model capacity through complex design and ignore the periodic distribution of diffraction in the frequency domain, which prevents these approaches from satisfactory results. In this paper, we introduce a new perspective to handle various diffraction in UDC images by jointly exploring the feature restoration in the frequency and spatial domains, and present a Frequency and Spatial Interactive Learning Network (FSI). It consists of a series of well-designed Frequency-Spatial Joint (FSJ) modules for feature learning and a color transform module for color enhancement. In particular, in the FSJ module, a frequency learning block uses the Fourier transform to eliminate spectral bias, a spatial learning block uses a multi-distillation structure to supplement the absence of local details, and a dual transfer unit to facilitate the interactive learning between features of different domains. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed FSI over state-of-the-art models, through extensive quantitative and qualitative evaluations in three widely-used UDC benchmarks.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了利用Under-display camera (UDC)系统可以去除屏幕刘海,实现无边框显示,并提供更好的交互体验。主要挑战在于用于显示的发光二极管的像素阵列会衍射和衰减入射光,导致复杂的退化。现有模型通过复杂设计最大化模型容量来消除空间衍射,但忽略了频域中衍射的周期分布,从而无法取得令人满意的结果。在本文中,我们介绍了一种新的处理UDC图像中各种衍射的方法,即通过联合探索频域和空间域中的特征恢复,并提出了一个Frequency and Spatial Interactive Learning Network (FSI)。FSI由一系列经过精心设计的Frequency-Spatial Joint (FSJ)模块用于特征学习,以及一个用于颜色增强的颜色变换模块组成。特别地,在FSJ模块中,频率学习块使用傅立叶变换消除频谱偏差,空间学习块使用多蒸馏结构来补充局部细节的缺失,以及一个双转移单元来促进不同领域特征之间的交互学习。实验结果表明,所提出的FSI在三个广泛使用的UDC基准测试中通过广泛的定量和定性评估显示出优越性。
Paper8 Who Are You Referring To? Coreference Resolution In Image Narrations
摘要原文: Coreference resolution aims to identify words and phrases which refer to the same entity in a text, a core task in natural language processing. In this paper, we extend this task to resolving coreferences in long-form narrations of visual scenes. First, we introduce a new dataset with annotated coreference chains and their bounding boxes, as most existing image-text datasets only contain short sentences without coreferring expressions or labeled chains. We propose a new technique that learns to identify coreference chains using weak supervision, only from image-text pairs and a regularization using prior linguistic knowledge. Our model yields large performance gains over several strong baselines in resolving coreferences.
We also show that coreference resolution helps improve grounding narratives in images.
中文总结: 这段话主要内容是介绍了指代消解的概念,指代消解旨在识别文本中指代同一实体的单词和短语,这是自然语言处理中的一个核心任务。文章将这一任务扩展到解决视觉场景长篇叙述中的指代消解。首先,引入了一个新的数据集,其中包含带有注释的指代链和它们的边界框,因为大多数现有的图像文本数据集只包含短句,没有指代表达或标记的链。作者提出了一种新技术,通过弱监督学习,仅使用图像文本对和正则化先验语言知识来识别指代链。他们的模型在解决指代消解方面比几种强基线模型取得了很大的性能提升。文章还表明,指代消解有助于提高图像叙述的基础。
Paper9 General Image-to-Image Translation with One-Shot Image Guidance
摘要原文: Large-scale text-to-image models pre-trained on massive text-image pairs show excellent performance in image synthesis recently. However, image can provide more intuitive visual concepts than plain text. People may ask: how can we integrate the desired visual concept into an existing image, such as our portrait? Current methods are inadequate in meeting this demand as they lack the ability to preserve content or translate visual concepts effectively. Inspired by this, we propose a novel framework named visual concept translator (VCT) with the ability to preserve content in the source image and translate the visual concepts guided by a single reference image. The proposed VCT contains a content-concept inversion (CCI) process to extract contents and concepts, and a content-concept fusion (CCF) process to gather the extracted information to obtain the target image. Given only one reference image, the proposed VCT can complete a wide range of general image-to-image translation tasks with excellent results. Extensive experiments are conducted to prove the superiority and effectiveness of the proposed methods. Codes are available at https://github.com/CrystalNeuro/visual-concept-translator.
中文总结: 最近,基于大规模文本-图像对进行预训练的文本到图像模型在图像合成方面表现出色。然而,图像可以提供比纯文本更直观的视觉概念。人们可能会问:我们如何将所需的视觉概念集成到现有图像中,比如我们的肖像?当前的方法无法满足这一需求,因为它们缺乏保留内容或有效转换视觉概念的能力。受此启发,我们提出了一种名为视觉概念转换器(VCT)的新框架,具有保留源图像内容并根据单个参考图像指导转换视觉概念的能力。所提出的VCT包含内容-概念反演(CCI)过程来提取内容和概念,以及内容-概念融合(CCF)过程来收集提取的信息以获得目标图像。仅给定一个参考图像,所提出的VCT可以完成各种通用图像到图像转换任务,并取得出色的结果。我们进行了大量实验来证明所提出方法的优越性和有效性。代码可在https://github.com/CrystalNeuro/visual-concept-translator 上获得。
Paper10 uSplit: Image Decomposition for Fluorescence Microscopy
摘要原文: We present mSplit, a dedicated approach for trained image decomposition in the context of fluorescence microscopy images. We find that best results using regular deep architectures are achieved when large image patches are used during training, making memory consumption the limiting factor to further improving performance. We therefore introduce lateral contextualization (LC), a novel meta-architecture that enables the memory efficient incorporation of large image-context, which we observe is a key ingredient to solving the image decomposition task at hand. We integrate LC with U-Nets, Hierarchical AEs, and Hierarchical VAEs, for which we formulate a modified ELBO loss. Additionally, LC enables training deeper hierarchical models than otherwise possible and, interestingly, helps to reduce tiling artefacts that are inherently impossible to avoid when using tiled VAE predictions. We apply mSplit to five decomposition tasks, one on a synthetic dataset, four others derived from real microscopy data. Our method consistently achieves best results (average improvements to the best baseline of 2.25 dB PSNR), while simultaneously requiring considerably less GPU memory. Our code and datasets can be found at https://github.com/juglab/uSplit.
中文总结: 我们提出了mSplit,这是一种专门针对荧光显微镜图像中训练图像分解的方法。我们发现,使用常规深度架构在训练过程中使用大图像块时可以获得最佳结果,但内存消耗成为进一步提高性能的限制因素。因此,我们引入了横向上下文化(LC),这是一种新颖的元架构,可以实现大图像上下文的内存高效整合,我们发现这是解决图像分解任务的关键因素。我们将LC与U-Net、分层AE和分层VAE结合起来,为此我们制定了修改后的ELBO损失函数。此外,LC使得可以训练比以往更深层次的分层模型,并且有趣的是,它有助于减少瓦片VAE预测时固有的无法避免的平铺伪影。我们将mSplit应用于五个分解任务,一个是在合成数据集上,另外四个是从真实显微镜数据中得出的。我们的方法始终取得最佳结果(相对于最佳基线的平均改进为2.25 dB PSNR),同时需要的GPU内存明显较少。我们的代码和数据集可以在https://github.com/juglab/uSplit 找到。
Paper11 TIFA: Accurate and Interpretable Text-to-Image Faithfulness Evaluation with Question Answering
摘要原文: Despite thousands of researchers, engineers, and artists actively working on improving text-to-image generation models, systems often fail to produce images that accurately align with the text inputs. We introduce TIFA (Text-to-image Faithfulness evaluation with question Answering), an automatic evaluation metric that measures the faithfulness of a generated image to its text input via visual question answering (VQA). Specifically, given a text input, we automatically generate several question-answer pairs using a language model. We calculate image faithfulness by checking whether existing VQA models can answer these questions using the generated image. TIFA is a reference-free metric that allows for fine-grained and interpretable evaluations of generated images.TIFA also has better correlations with human judgments than existing metrics. Based on this approach, we introduce TIFA v1.0, a benchmark consisting of 4K diverse text inputs and 25K questions across 12 categories (object, counting, etc.). We present a comprehensive evaluation of existing text-to-image models using TIFA v1.0 and highlight the limitations and challenges of current models. For instance, we find that current text-to-image models, despite doing well on color and material, still struggle in counting, spatial relations, and composing multiple objects. We hope our benchmark will help carefully measure the research progress in text-to-image synthesis and provide valuable insights for further research.
中文总结: 尽管成千上万的研究人员、工程师和艺术家积极致力于改进文本到图像生成模型,但系统通常无法生成与文本输入准确对齐的图像。我们介绍了TIFA(Text-to-image Faithfulness evaluation with question Answering),这是一种通过视觉问答(VQA)来衡量生成图像与文本输入之间忠实性的自动评估指标。具体而言,给定一个文本输入,我们使用语言模型自动生成几个问题-答案对。我们通过检查现有的VQA模型是否能使用生成的图像回答这些问题来计算图像的忠实性。TIFA是一种无参考的指标,可以对生成的图像进行细粒度和可解释的评估。TIFA还与现有指标相比,与人类判断有更好的相关性。基于这种方法,我们推出了TIFA v1.0,这是一个基准,包括4K个不同的文本输入和12个类别(物体、计数等)的25K个问题。我们使用TIFA v1.0对现有的文本到图像模型进行了全面评估,并强调了当前模型的局限性和挑战。例如,我们发现,尽管目前的文本到图像模型在颜色和材质方面表现良好,但在计数、空间关系和组合多个对象方面仍存在困难。我们希望我们的基准能够帮助仔细衡量文本到图像合成的研究进展,并为进一步研究提供有价值的见解。
Paper12 MI-GAN: A Simple Baseline for Image Inpainting on Mobile Devices
摘要原文: In recent years, many deep learning based image inpainting methods have been developed by the research community. Some of those methods have shown impressive image completion abilities. Yet, to the best of our knowledge, there is no image inpainting model designed to run on mobile devices. In this paper we present a simple image inpainting baseline, Mobile Inpainting GAN (MI-GAN), which is approximately one order of magnitude computationally cheaper and smaller than existing state-of-the-art inpainting models, and can be efficiently deployed on mobile devices. Excessive quantitative and qualitative evaluations show that MI-GAN performs comparable or, in some cases, better than recent state-of-the-art approaches. Moreover, we perform a user study comparing MI-GAN results with results from several commercial mobile inpainting applications, which clearly shows the advantage of MI-GAN in comparison to existing apps. With the purpose of high quality and efficient inpainting, we utilize an effective combination of adversarial training, model re-parametrization, and knowledge distillation. Our models and code are publicly available at https://github.com/Picsart-AI-Research/MI-GAN.
中文总结: 近年来,研究界已经开发了许多基于深度学习的图像修复方法。其中一些方法展示了令人印象深刻的图像完成能力。然而据我们所知,目前还没有专为移动设备设计的图像修复模型。在本文中,我们提出了一个简单的图像修复基准模型Mobile Inpainting GAN(MI-GAN),其计算成本和规模大约比现有最先进的修复模型便宜一个数量级,可以高效地部署在移动设备上。过多的定量和定性评估显示,MI-GAN的表现与最近的最先进方法相媲美,甚至在某些情况下更好。此外,我们进行了一项用户研究,比较了MI-GAN的结果与几款商业移动图像修复应用的结果,清楚地展示了MI-GAN相对于现有应用的优势。为了实现高质量和高效的图像修复,我们利用了对抗训练、模型重新参数化和知识蒸馏的有效组合。我们的模型和代码可以在https://github.com/Picsart-AI-Research/MI-GAN 上公开获取。
Paper13 COOL-CHIC: Coordinate-based Low Complexity Hierarchical Image Codec
摘要原文: We introduce COOL-CHIC, a Coordinate-based Low Complexity Hierarchical Image Codec. It is a learned alternative to autoencoders with 629 parameters and 680 multiplications per decoded pixel. COOL-CHIC offers compression performance close to modern conventional MPEG codecs such as HEVC and is competitive with popular autoencoder-based systems. This method is inspired by Coordinate-based Neural Representations, where an image is represented as a learned function which maps pixel coordinates to RGB values. The parameters of the mapping function are then sent using entropy coding. At the receiver side, the compressed image is obtained by evaluating the mapping function for all pixel coordinates. COOL-CHIC implementation is made open-source.
中文总结: 这段话主要介绍了COOL-CHIC,一种基于坐标的低复杂度分层图像编解码器。它是一种学习替代方案,每个解码像素有629个参数和680次乘法。COOL-CHIC提供了接近现代传统MPEG编解码器(如HEVC)的压缩性能,并且与流行的基于自动编码器的系统相竞争。该方法受到基于坐标的神经表示的启发,其中图像被表示为将像素坐标映射到RGB值的学习函数。然后使用熵编码发送映射函数的参数。在接收端,压缩图像通过为所有像素坐标评估映射函数来获取。COOL-CHIC的实现是开源的。
Paper14 What Does a Platypus Look Like? Generating Customized Prompts for Zero-Shot Image Classification
摘要原文: Open-vocabulary models are a promising new paradigm for image classification. Unlike traditional classification models, open-vocabulary models classify among any arbitrary set of categories specified with natural language during inference. This natural language, called “prompts”, typically consists of a set of hand-written templates (e.g., "a photo of a ") which are completed with each of the category names. This work introduces a simple method to generate higher accuracy prompts, without relying on any explicit knowledge of the task domain and with far fewer hand-constructed sentences. To achieve this, we combine open-vocabulary models with large language models (LLMs) to create Customized Prompts via Language models (CuPL, pronounced “couple”). In particular, we leverage the knowledge contained in LLMs in order to generate many descriptive sentences that contain important discriminating characteristics of the image categories. This allows the model to place a greater importance on these regions in the image when making predictions. We find that this straightforward and general approach improves accuracy on a range of zero-shot image classification benchmarks, including over one percentage point gain on ImageNet. Finally, this simple baseline requires no additional training and remains completely zero-shot. Code available at https://github.com/sarahpratt/CuPL.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了开放词汇模型作为图像分类的一种新兴范式。与传统的分类模型不同,开放词汇模型在推断期间可以对任意指定的自然语言类别集进行分类。这种自然语言称为“提示”,通常由一组手写模板(例如,“一张照片的”)组成,这些模板会用每个类别名称来填充。该研究介绍了一种简单的方法来生成更高准确度的提示,而无需依赖于任何显式的任务领域知识,并且减少了手工构建的句子数量。为了实现这一目标,作者将开放词汇模型与大型语言模型(LLMs)结合起来,创建了通过语言模型定制提示(CuPL,发音为“couple”)。具体来说,他们利用LLMs中包含的知识来生成许多包含图像类别重要区分特征的描述性句子。这使得模型在进行预测时更加重视这些区域。研究发现,这种简单而通用的方法提高了一系列零样本图像分类基准的准确性,包括在ImageNet上提高了超过一个百分点。最后,这种简单的基线不需要额外的训练,并且完全是零样本的。源代码可在https://github.com/sarahpratt/CuPL找到。
Paper15 PatchCT: Aligning Patch Set and Label Set with Conditional Transport for Multi-Label Image Classification
摘要原文: Multi-label image classification is a prediction task that aims to identify more than one label from a given image. This paper considers the semantic consistency of the latent space between the visual patch and linguistic label domains and introduces the conditional transport (CT) theory to bridge the acknowledged gap. While recent cross-modal attention-based studies have attempted to align such two representations and achieved impressive performance, they required carefully-designed alignment modules and extra complex operations in the attention computation. We find that by formulating the multi-label classification as a CT problem, we can exploit the interactions between the image and label efficiently by minimizing the bidirectional CT cost. Specifically, after feeding the images and textual labels into the modality-specific encoders, we view each image as a mixture of patch embeddings and a mixture of label embeddings, which capture the local region features and the class prototypes, respectively. CT is then employed to learn and align those two semantic sets by defining the forward and backward navigators. Importantly, the defined navigators in CT distance model the similarities between patches and labels, which provides an interpretable tool to visualize the learned prototypes. Extensive experiments on three public image benchmarks show that the proposed model consistently outperforms the previous methods.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了多标签图像分类的预测任务,旨在从给定图像中识别多个标签。该论文考虑了视觉补丁和语言标签领域之间的潜在空间语义一致性,并引入了条件传输(CT)理论来弥合已知的差距。最近的跨模态注意力研究已尝试对齐这两种表示,并取得了令人印象深刻的性能,但需要精心设计的对齐模块和额外复杂的注意力计算操作。作者发现,通过将多标签分类问题表述为一个CT问题,可以通过最小化双向CT成本来高效地利用图像和标签之间的交互作用。具体而言,将图像和文本标签输入到特定编码器后,将每个图像视为补丁嵌入的混合物和标签嵌入的混合物,分别捕捉局部区域特征和类原型。然后利用CT来学习和对齐这两个语义集合,通过定义前向和后向导航器。重要的是,在CT距离模型中定义的导航器建模了补丁和标签之间的相似性,为可视化学习原型提供了一种可解释的工具。在三个公共图像基准上进行的大量实验表明,所提出的模型始终优于先前的方法。
Paper16 Learning Support and Trivial Prototypes for Interpretable Image Classification
摘要原文: Prototypical part network (ProtoPNet) methods have been designed to achieve interpretable classification by associating predictions with a set of training prototypes, which we refer to as trivial prototypes because they are trained to lie far from the classification boundary in the feature space. Note that it is possible to make an analogy between ProtoPNet and support vector machine (SVM) given that the classification from both methods relies on computing similarity with a set of training points (i.e., trivial prototypes in ProtoPNet, and support vectors in SVM). However, while trivial prototypes are located far from the classification boundary, support vectors are located close to this boundary, and we argue that this discrepancy with the well-established SVM theory can result in ProtoPNet models with inferior classification accuracy. In this paper, we aim to improve the classification of ProtoPNet with a new method to learn support prototypes that lie near the classification boundary in the feature space, as suggested by the SVM theory. In addition, we target the improvement of classification results with a new model, named ST-ProtoPNet, which exploits our support prototypes and the trivial prototypes to provide more effective classification. Experimental results on CUB-200-2011, Stanford Cars, and Stanford Dogs datasets demonstrate that ST-ProtoPNet achieves state-of-the-art classification accuracy and interpretability results. We also show that the proposed support prototypes tend to be better localised in the object of interest rather than in the background region. Code is available at https://github.com/cwangrun/ST-ProtoPNet.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了一种名为ProtoPNet的方法,旨在通过将预测与一组训练原型相关联来实现可解释的分类。这些训练原型被称为"trivial prototypes",因为它们被训练成在特征空间中远离分类边界。文章指出ProtoPNet与支持向量机(SVM)之间存在类比,因为两种方法的分类都依赖于与一组训练点的相似性计算(在ProtoPNet中是trivial prototypes,在SVM中是支持向量)。然而,trivial prototypes远离分类边界,而支持向量靠近这个边界,作者认为这种与SVM理论的不一致可能导致ProtoPNet模型具有较低的分类准确性。因此,作者提出了一种新方法,通过学习位于特征空间中接近分类边界的支持原型来改善ProtoPNet的分类。他们提出的新模型名为ST-ProtoPNet,利用支持原型和trivial prototypes提供更有效的分类。实验结果表明,ST-ProtoPNet在CUB-200-2011、Stanford Cars和Stanford Dogs数据集上实现了最先进的分类准确性和可解释性结果。作者还展示了所提出的支持原型往往更好地定位在感兴趣的对象而不是背景区域中。
Paper17 ASIC: Aligning Sparse in-the-wild Image Collections
摘要原文: We present a method for joint alignment of sparse in-the-wild image collections of an object category. Most prior works assume either ground-truth keypoint annotations or a large dataset of images of a single object category. However, neither of the above assumptions hold true for the long-tail of the objects present in the world. We present a self-supervised technique that directly optimizes on a sparse collection of images of a particular object/object category to obtain consistent dense correspondences across the collection. We use pairwise nearest neighbors obtained from deep features of a pre-trained vision transformer (ViT) model as noisy and sparse keypoint matches and make them dense and accurate matches by optimizing a neural network that jointly maps the image collection into a learned canonical grid. Experiments on CUB, SPair-71k and PF-Willow benchmarks demonstrate that our method can produce globally consistent and higher quality correspondences across the image collection when compared to existing self-supervised methods. Code and other material will be made available at https://kampta.github.io/asic.
中文总结: 我们提出了一种用于联合对齐稀疏的野外图像集合的物体类别的方法。大多数先前的工作都假设要么有地面真实关键点注释,要么有大量属于单一物体类别的图像数据集。然而,以上两种假设都不适用于世界上存在的长尾对象。我们提出了一种自监督技术,该技术直接优化特定对象/物体类别的稀疏图像集合,以获得整个集合中一致的密集对应关系。我们使用预训练视觉变换器(ViT)模型的深度特征得到的成对最近邻作为嘈杂和稀疏的关键点匹配,并通过优化神经网络将它们转换为密集和准确的匹配,从而将图像集合联合映射到学习的规范网格中。在CUB、SPair-71k和PF-Willow基准测试上的实验证明,与现有的自监督方法相比,我们的方法可以在整个图像集合中产生全局一致且更高质量的对应关系。代码和其他材料将在https://kampta.github.io/asic上提供。
Paper18 Under-Display Camera Image Restoration with Scattering Effect
摘要原文: The under-display camera (UDC) provides consumers with a full-screen visual experience without any obstruction due to notches or punched holes. However, the semi-transparent nature of the display inevitably introduces the severe degradation into UDC images. In this work, we address the UDC image restoration problem with the specific consideration of the scattering effect caused by the display. We explicitly model the scattering effect by treating the display as a piece of homogeneous scattering medium. With the physical model of the scattering effect, we improve the image formation pipeline for the image synthesis to construct a realistic UDC dataset with ground truths. To suppress the scattering effect for the eventual UDC image recovery, a two-branch restoration network is designed. More specifically, the scattering branch leverages global modeling capabilities of the channel-wise self-attention to estimate parameters of the scattering effect from degraded images. While the image branch exploits the local representation advantage of CNN to recover clear scenes, implicitly guided by the scattering branch. Extensive experiments are conducted on both real-world and synthesized data, demonstrating the superiority of the proposed method over the state-of-the-art UDC restoration techniques. The source code and dataset are available at https://github.com/NamecantbeNULL/SRUDC.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了在显示屏下方的摄像头(UDC)可以为消费者提供全屏视觉体验,无需担心由于凹口或打孔造成的遮挡。然而,由于显示屏的半透明特性,UDC 图像不可避免地会受到严重的退化影响。作者在这项工作中解决了 UDC 图像恢复问题,特别考虑了显示屏引起的散射效应。他们通过将显示屏视为一块均匀散射介质来明确建模散射效应。利用散射效应的物理模型,他们改进了图像合成的图像形成流程,以构建具有真实基准的 UDC 数据集。为了抑制散射效应以最终恢复 UDC 图像,设计了一个双分支恢复网络。具体而言,散射分支利用通道自注意力的全局建模能力来从退化图像中估计散射效应的参数。而图像分支则利用 CNN 的局部表示优势来恢复清晰的场景,隐式地受到散射分支的引导。在真实世界和合成数据上进行了大量实验,证明了该方法在 UDC 恢复技术方面优于现有技术。源代码和数据集可在 https://github.com/NamecantbeNULL/SRUDC 获取。
Paper19 Identification of Systematic Errors of Image Classifiers on Rare Subgroups
摘要原文: Despite excellent average-case performance of many image classifiers, their performance can substantially deteriorate on semantically coherent subgroups of the data that were under-represented in the training data. These systematic errors can impact both fairness for demographic minority groups as well as robustness and safety under domain shift. A major challenge is to identify such subgroups with subpar performance when the subgroups are not annotated and their occurrence is very rare. We leverage recent advances in text-to-image models and search in the space of textual descriptions of subgroups (“prompts”) for subgroups where the target model has low performance on the prompt-conditioned synthesized data. To tackle the exponentially growing number of subgroups, we employ combinatorial testing. We denote this procedure as PromptAttack as it can be interpreted as an adversarial attack in a prompt space. We study subgroup coverage and identifiability with PromptAttack in a controlled setting and find that it identifies systematic errors with high accuracy. Thereupon, we apply PromptAttack to ImageNet classifiers and identify novel systematic errors on rare subgroups.
中文总结: 尽管许多图像分类器在平均情况下表现出色,但它们在训练数据中未充分代表的语义一致子群上的表现可能会显著恶化。这些系统性错误可能会影响对人口少数群体的公平性,同时也会影响在领域转移下的鲁棒性和安全性。一个主要挑战是在这些未标注的子群中识别出表现不佳的子群,而这些子群的出现非常罕见。我们利用最近在文本到图像模型方面的进展,在子群的文本描述空间中进行搜索,以寻找目标模型在与提示条件合成数据上表现较差的子群。为了处理指数级增长的子群数量,我们采用组合测试。我们将这一过程称为PromptAttack,因为它可以被解释为在提示空间中的一种对抗攻击。我们在受控环境中研究了PromptAttack对子群覆盖率和可识别性的影响,并发现它能够高准确度地识别系统性错误。随后,我们将PromptAttack应用于ImageNet分类器,并在罕见子群上识别出新的系统性错误。
Paper20 Image-Free Classifier Injection for Zero-Shot Classification
摘要原文: Zero-shot learning models achieve remarkable results on image classification for samples from classes that were not seen during training. However, such models must be trained from scratch with specialised methods: therefore, access to a training dataset is required when the need for zero-shot classification arises. In this paper, we aim to equip pre-trained models with zero-shot classification capabilities without the use of image data. We achieve this with our proposed Image-free Classifier Injection with Semantics (ICIS) that injects classifiers for new, unseen classes into pre-trained classification models in a post-hoc fashion without relying on image data. Instead, the existing classifier weights and simple class-wise descriptors, such as class names or attributes, are used. ICIS has two encoder-decoder networks that learn to reconstruct classifier weights from descriptors (and vice versa), exploiting (cross-)reconstruction and cosine losses to regularise the decoding process. Notably, ICIS can be cheaply trained and applied directly on top of pre-trained classification models. Experiments on benchmark ZSL datasets show that ICIS produces unseen classifier weights that achieve strong (generalised) zero-shot classification performance. Code is available at https://github.com/ExplainableML/ImageFreeZSL.
中文总结: 这篇论文主要介绍了零样本学习模型在图像分类上取得了显著的成果,能够对训练过程中未见过的类别样本进行分类。然而,这些模型需要使用专门的方法从头开始训练,因此在需要进行零样本分类时需要访问一个训练数据集。本文旨在为预训练模型赋予零样本分类能力,而无需使用图像数据。作者提出了一种名为Image-free Classifier Injection with Semantics (ICIS)的方法,通过该方法可以在预训练的分类模型中后期注入用于新的未见类别的分类器,而无需依赖图像数据。ICIS包含两个编码器-解码器网络,学习从描述符到分类器权重的重构(反之亦然),利用(交叉)重构和余弦损失来规范解码过程。值得注意的是,ICIS可以便宜地训练并直接应用于预训练的分类模型之上。在基准零样本学习数据集上的实验表明,ICIS生成的未见分类器权重能够实现强大的(泛化的)零样本分类性能。源代码可在https://github.com/ExplainableML/ImageFreeZSL找到。
Paper21 Empowering Low-Light Image Enhancer through Customized Learnable Priors
摘要原文: Deep neural networks have achieved remarkable progress in enhancing low-light images by improving their brightness and eliminating noise. However, most existing methods construct end-to-end mapping networks heuristically, neglecting the intrinsic prior of image enhancement task and lacking transparency and interpretability. Although some unfolding solutions have been proposed to relieve these issues, they rely on proximal operator networks that deliver ambiguous and implicit priors. In this work, we propose a paradigm for low-light image enhancement that explores the potential of customized learnable priors to improve the transparency of the deep unfolding paradigm.Motivated by the powerful feature representation capability of Masked Autoencoder (MAE), we customize MAE-based illumination and noise priors and redevelop them from two perspectives: 1) structure flow: we train the MAE from a normal-light image to its illumination properties and then embed it into the proximal operator design of the unfolding architecture; and
- optimization flow: we train MAE from a normal-light image to its gradient representation and then employ it as a regularization term to constrain noise in the model output. These designs improve the interpretability and representation capability of the model. Extensive experiments on multiple low-light image enhancement datasets demonstrate the superiority of our proposed paradigm over state-of-the-art methods. Code is available at https://github.com/zheng980629/CUE.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了深度神经网络在增强低光照图像方面取得的显著进展,通过提高亮度和消除噪声来改善图像质量。然而,大多数现有方法在构建端到端映射网络时是启发式的,忽视了图像增强任务的固有先验,并且缺乏透明度和可解释性。虽然一些展开解决方案已经被提出来缓解这些问题,但它们依赖于提供模糊和隐含先验的近端算子网络。在这项工作中,作者提出了一种低光照图像增强的范式,探索了定制可学习先验的潜力,以提高深度展开范式的透明性。受到掩蔽自动编码器(MAE)强大的特征表示能力的启发,作者定制了基于MAE的照明和噪声先验,并从两个角度重新开发了它们:1)结构流:从正常光照图像训练MAE到其照明属性,然后将其嵌入到展开架构的近端算子设计中;2)优化流:从正常光照图像训练MAE到其梯度表示,并将其作为正则化项来约束模型输出中的噪声。这些设计改善了模型的可解释性和表示能力。在多个低光照图像增强数据集上进行的大量实验表明,作者提出的范式优于现有方法。源代码可在https://github.com/zheng980629/CUE 上找到。
Paper22 Sat2Density: Faithful Density Learning from Satellite-Ground Image Pairs
摘要原文: This paper aims to develop an accurate 3D geometry representation of satellite images using satellite-ground image pairs. Our focus is on the challenging problem of 3D-aware ground-views synthesis from a satellite image. We draw inspiration from the density field representation used in volumetric neural rendering and propose a new approach, called Sat2Density. Our method utilizes the properties of ground-view panoramas for the sky and non-sky regions to learn faithful density fields of 3D scenes in a geometric perspective. Unlike other methods that require extra depth information during training, our Sat2Density can automatically learn accurate and faithful 3D geometry via density representation without depth supervision. This advancement significantly improves the ground-view panorama synthesis task. Additionally, our study provides a new geometric perspective to understand the relationship between satellite and ground-view images in 3D space.
中文总结: 这篇论文旨在利用卫星-地面图像对开发出一种准确的卫星图像的3D几何表示方法。我们关注的是从卫星图像中合成具有3D感知的地面视图的挑战性问题。我们从体积神经渲染中使用的密度场表示中获得灵感,并提出了一种新方法,称为Sat2Density。我们的方法利用地面视角全景图的性质,针对天空和非天空区域学习3D场景的忠实密度场的几何透视。与其他方法在训练过程中需要额外的深度信息不同,我们的Sat2Density可以通过密度表示自动学习准确和忠实的3D几何,无需深度监督。这一进步显著改善了地面视角全景合成任务。此外,我们的研究提供了一种新的几何透视,以理解卫星图像和地面视图图像在3D空间中的关系。
Paper23 Mesh2Tex: Generating Mesh Textures from Image Queries
摘要原文: Remarkable advances have been achieved recently in learning neural representations that characterize object geometry, while generating textured objects suitable for downstream applications and 3D rendering remains at an early stage. In particular, reconstructing textured geometry from images of real objects is a significant challenge - reconstructed geometry is often inexact, making realistic texturing a significant challenge. We present Mesh2Tex, which learns a realistic object texture manifold from uncorrelated collections of 3D object geometry and photorealistic RGB images, by leveraging a hybrid mesh-neural-field texture representation. Our texture representation enables compact encoding of high-resolution textures as a neural field in the barycentric coordinate system of the mesh faces. The learned texture manifold enables effective navigation to generate an object texture for a given 3D object geometry that matches to an input RGB image, which maintains robustness even under challenging real-world scenarios where the mesh geometry approximates an inexact match to the underlying geometry in the RGB image. Mesh2Tex can effectively generate realistic object textures for an object mesh to match real images observations towards digitization of real environments, significantly improving over previous state of the art.
中文总结: 最近在学习神经表示方面取得了显著进展,这些表示表征了物体的几何结构,但生成适用于下游应用和3D渲染的纹理对象仍处于早期阶段。特别是,从真实物体的图像重建带纹理的几何结构是一个重大挑战 - 重建的几何结构通常不精确,使得逼真的纹理成为一个重大挑战。我们提出了Mesh2Tex,它从不相关的3D物体几何和逼真的RGB图像集合中学习了一个逼真的物体纹理流形,利用了混合的网格-神经场纹理表示。我们的纹理表示能够将高分辨率纹理紧凑地编码为网格面的重心坐标系中的神经场。学习到的纹理流形使得能够有效地导航,为给定的3D物体几何生成一个与输入的RGB图像匹配的物体纹理,即使在挑战性的真实世界场景下,其中网格几何近似于RGB图像中的基础几何的不精确匹配。Mesh2Tex能够有效地为物体网格生成逼真的物体纹理,以匹配真实图像观察结果,从而显著改善了先前的技术水平。
Paper24 RSFNet: A White-Box Image Retouching Approach using Region-Specific Color Filters
摘要原文: Abstract not available
中文总结: 抱歉,无法提供对具体文本内容的概述,因为您没有提供具体的文本。如果您能提供具体的文本内容,我可以帮您进行概述。
Paper25 Better May Not Be Fairer: A Study on Subgroup Discrepancy in Image Classification
摘要原文: In this paper, we provide 20,000 non-trivial human annotations on popular datasets as a first step to bridge gap to studying how natural semantic spurious features affect image classification, as prior works often study datasets mixing low-level features due to limitations in accessing realistic datasets. We investigate how natural background colors play a role as spurious features by annotating the test sets of CIFAR10 and CIFAR100 into subgroups based on the background color of each image. We name our datasets CIFAR10-B and CIFAR100-B and integrate them with CIFAR-Cs. We find that overall human-level accuracy does not guarantee consistent subgroup performances, and the phenomenon remains even on models pre-trained on ImageNet or after data augmentation (DA). To alleviate this issue, we propose FlowAug, a semantic DA that leverages decoupled semantic representations captured by a pre-trained generative flow. Experimental results show that FlowAug achieves more consistent subgroup results than other types of DA methods on CIFAR10/100 and on CIFAR10/100-C. Additionally, it shows better generalization performance. Furthermore, we propose a generic metric, MacroStd, for studying model robustness to spurious correlations, where we take a macro average on the weighted standard deviations across different classes. We show MacroStd being more predictive of better performances; per our metric, FlowAug demonstrates improvements on subgroup discrepancy. Although this metric is proposed to study our curated datasets, it applies to all datasets that have subgroups or subclasses. Lastly, we also show superior out-of-distribution results on CIFAR10.1.
中文总结: 在这篇论文中,我们提供了2万个非平凡的人类注释,作为研究自然语义虚假特征如何影响图像分类的第一步,以弥合研究数据集中存在低级特征混合的差距,这是因为以往的研究往往研究混合了低级特征的数据集,这是由于无法获取现实数据集的限制。我们通过对CIFAR10和CIFAR100的测试集进行注释,根据每个图像的背景颜色将其分成子组,命名为CIFAR10-B和CIFAR100-B,并将它们与CIFAR-Cs集成。我们发现,整体的人类级别准确率并不能保证一致的子组表现,这种现象甚至在在ImageNet上预训练的模型或数据增强(DA)之后仍然存在。为了缓解这个问题,我们提出了FlowAug,这是一种语义DA,利用了由预训练生成流捕获的分离的语义表示。实验结果表明,FlowAug在CIFAR10/100和CIFAR10/100-C上实现了比其他类型的DA方法更一致的子组结果,并展现了更好的泛化性能。此外,我们提出了一个用于研究模型对虚假相关性的稳健性的通用度量标准MacroStd,其中我们对不同类别的加权标准差进行宏平均。我们展示MacroStd更有利于预测更好的性能;根据我们的度量标准,FlowAug在子组差异方面表现出改进。尽管这个度量标准是为了研究我们策划的数据集而提出的,但它适用于所有具有子组或子类的数据集。最后,我们还展示了在CIFAR10.1上的优越的超出分布结果。
Paper26 Foreground and Text-lines Aware Document Image Rectification
摘要原文: This paper aims at the distorted document image rectification problem, the objective to eliminate the geometric distortion in the document images and realize document intelligence. Improving the readability of distorted documents is crucial to effectively extract information from deformed images. According to our observations, the foreground and text-line of the original warped image can represent the deformation tendency. However, previous distorted image rectification methods pay little attention to the readability of the warped paper. In this paper, we focus on the foreground and text-line regions of distorted paper and proposes a global and local fusion method to improve the rectification effect of distorted images and enhance the readability of document images. We introduce cross attention to capture the features of the foreground and text-lines in the warped document and effectively fuse them. The proposed method is evaluated quantitatively and qualitatively on the public DocUNet benchmark and DIR300 Dataset, which achieve state-of-the-art performances. Experimental analysis shows the proposed method can well perform overall geometric rectification of distorted images and effectively improve document readability (using the metrics of Character Error Rate and Edit Distance). The code is available at https://github.com/xiaomore/Document-Image-Dewarping.
中文总结: 本文旨在解决文档图像失真矫正问题,目标是消除文档图像中的几何失真,实现文档智能化。改善失真文档的可读性对于有效提取变形图像中的信息至关重要。根据我们的观察,原始扭曲图像的前景和文本行可以代表变形趋势。然而,先前的失真图像矫正方法很少关注扭曲纸张的可读性。本文专注于扭曲纸张的前景和文本行区域,并提出了一种全局和局部融合方法,以改善扭曲图像的矫正效果并增强文档图像的可读性。我们引入交叉注意力来捕捉扭曲文档中前景和文本行的特征,并有效地融合它们。所提出的方法在公开的DocUNet基准和DIR300数据集上进行了定量和定性评估,取得了最先进的性能。实验分析表明,所提出的方法可以很好地执行失真图像的整体几何矫正,并有效地提高文档的可读性(使用字符错误率和编辑距离等指标)。代码可在https://github.com/xiaomore/Document-Image-Dewarping找到。
Paper27 Learning Image Harmonization in the Linear Color Space
摘要原文: Harmonizing cut-and-paste images into perceptually realistic ones is challenging, as it requires a full understanding of the discrepancies between the background of the target image and the inserted object. Existing methods mainly adjust the appearances of the inserted object via pixel-level manipulations. They are not effective in correcting color discrepancy caused by different scene illuminations and the image formation processes. We note that image colors are essentially camera ISP projection of the scene radiance. If we can trace the image colors back to the radiance field, we may be able to model the scene illumination and harmonize the discrepancy better. In this paper, we propose a novel neural approach to harmonize the image colors in a camera-independent color space, in which color values are proportional to the scene radiance. To this end, we propose a novel image unprocessing module to estimate an intermediate high dynamic range version of the object to be inserted. We then propose a novel color harmonization module that harmonizes the colors of the inserted object by querying the estimated scene radiance and re-rendering the harmonized object in the output color space. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了将剪贴和粘贴的图像融合成感知真实图像的挑战性问题。现有方法主要通过像素级的操作调整插入对象的外观,但这些方法并不有效地解决由不同场景照明和图像形成过程引起的颜色差异。作者指出图像颜色本质上是相机ISP对场景辐射的投影。如果能将图像颜色追溯到辐射场,就有可能更好地建模场景照明并协调颜色差异。作者提出了一种新颖的神经网络方法,以在独立于相机的颜色空间中协调图像颜色,其中颜色值与场景辐射成比例。为此,作者提出了一个新颖的图像反处理模块,用于估计待插入对象的中间高动态范围版本。然后,作者提出了一个新颖的颜色协调模块,通过查询估计的场景辐射并在输出颜色空间中重新渲染协调后的对象来协调插入对象的颜色。大量实验证明,作者的方法优于现有的最先进方法。
Paper28 Physics-Driven Turbulence Image Restoration with Stochastic Refinement
摘要原文: Image distortion by atmospheric turbulence is a stochastic degradation, which is a critical problem in long-range optical imaging systems. A number of research has been conducted during the past decades, including model-based and emerging deep-learning solutions with the help of synthetic data. Although fast and physics-grounded simulation tools have been introduced to help the deep-learning models adapt to real-world turbulence conditions recently, the training of such models only relies on the synthetic data and ground truth pairs. This paper proposes the Physics-integrated Restoration Network (PiRN) to bring the physics-based simulator directly into the training process to help the network to disentangle the stochasticity from the degradation and the underlying image. Furthermore, to overcome the “average effect” introduced by deterministic models and the domain gap between the synthetic and real-world degradation, we further introduce PiRN with Stochastic Refinement (PiRN-SR) to boost its perceptual quality. Overall, our PiRN and PiRN-SR improve the generalization to real-world unknown turbulence conditions and provide a state-of-the-art restoration in both pixel-wise accuracy and perceptual quality.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了大气湍流对图像的失真问题,这是长距离光学成像系统中的一个关键问题。过去几十年进行了大量研究,包括基于模型和新兴的深度学习解决方案,利用合成数据。尽管最近引入了快速且基于物理的模拟工具来帮助深度学习模型适应真实世界的湍流条件,但这些模型的训练仅依赖于合成数据和地面实况对。本文提出了物理集成恢复网络(PiRN),将基于物理的模拟器直接引入训练过程,帮助网络将随机性与退化和底层图像分离开来。此外,为了克服确定性模型引入的“平均效应”和合成与真实世界退化之间的领域差距,我们进一步引入了带有随机细化的PiRN(PiRN-SR)来提高其感知质量。总的来说,我们的PiRN和PiRN-SR提高了对真实世界未知湍流条件的泛化能力,并在像素精度和感知质量方面提供了最先进的恢复效果。
Paper29 Grounded Image Text Matching with Mismatched Relation Reasoning
摘要原文: This paper introduces Grounded Image Text Matching with Mismatched Relation (GITM-MR), a novel visual-linguistic joint task that evaluates the relation understanding capabilities of transformer-based pre-trained models. GITM-MR requires a model to first determine if an expression describes an image, then localize referred objects or ground the mismatched parts of the text. We provide a benchmark for evaluating vision-language (VL) models on this task, with a focus on the challenging settings of limited training data and out-of-distribution sentence lengths. Our evaluation demonstrates that pre-trained VL models often lack data efficiency and length generalization ability. To address this, we propose the Relation-sensitive Correspondence Reasoning Network (RCRN), which incorporates relation-aware reasoning via bi-directional message propagation guided by language structure. Our RCRN can be interpreted as a modular program and delivers strong performance in terms of both length generalization and data efficiency. The code and data are available on https://github.com/SHTUPLUS/GITM-MR.
中文总结: 本文介绍了一种名为Grounded Image Text Matching with Mismatched Relation (GITM-MR)的新颖视觉-语言联合任务,评估了基于Transformer预训练模型的关系理解能力。GITM-MR要求模型首先确定一个表达是否描述了一幅图像,然后定位所指对象或将文本中不匹配的部分与图像关联。我们提供了一个用于评估视觉-语言(VL)模型在这一任务上的基准,重点关注训练数据有限和超出分布的句子长度这两个具有挑战性的设置。我们的评估表明,预训练的VL模型通常缺乏数据效率和长度泛化能力。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了Relation-sensitive Correspondence Reasoning Network (RCRN),通过双向消息传递引导的关系感知推理,融入了关系感知的推理。我们的RCRN可以被解释为一个模块化程序,并在长度泛化和数据效率方面表现出色。代码和数据可在https://github.com/SHTUPLUS/GITM-MR 上获得。
Paper30 Class Prior-Free Positive-Unlabeled Learning with Taylor Variational Loss for Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Imagery
摘要原文: Positive-unlabeled learning (PU learning) in hyperspectral remote sensing imagery (HSI) is aimed at learning a binary classifier from positive and unlabeled data, which has broad prospects in various earth vision applications. However, when PU learning meets limited labeled HSI, the unlabeled data may dominate the optimization process, which makes the neural networks overfit the unlabeled data. In this paper, a Taylor variational loss is proposed for HSI PU learning, which reduces the weight of the gradient of the unlabeled data by Taylor series expansion to enable the network to find a balance between overfitting and underfitting. In addition, the self-calibrated optimization strategy is designed to stabilize the training process. Experiments on 7 benchmark datasets (21 tasks in total) validate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Code is at: https://github.com/Hengwei-Zhao96/T-HOneCls.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了在高光谱遥感图像中的正样本-未标记学习(PU学习)旨在从正样本和未标记数据中学习二元分类器,该方法在各种地球视觉应用中具有广阔的前景。然而,当PU学习遇到有限标记的HSI时,未标记数据可能主导优化过程,导致神经网络过度拟合未标记数据。本文提出了一种Taylor变分损失用于HSI PU学习,通过Taylor级数展开减少未标记数据梯度的权重,使网络在过度拟合和欠拟合之间找到平衡。此外,设计了自校准优化策略以稳定训练过程。在7个基准数据集(总共21个任务)上的实验证实了所提方法的有效性。源代码链接为:https://github.com/Hengwei-Zhao96/T-HOneCls。
Paper31 DRAW: Defending Camera-shooted RAW Against Image Manipulation
摘要原文: RAW files are the initial measurement of scene radiance widely used in most cameras, and the ubiquitously-used RGB images are converted from RAW data through Image Signal Processing (ISP) pipelines. Nowadays, digital images are risky of being nefariously manipulated. Inspired by the fact that innate immunity is the first line of body defense, we propose DRAW, a novel scheme of defending images against manipulation by protecting their sources, i.e., camera-shooted RAWs. Specifically, we design a lightweight Multi-frequency Partial Fusion Network (MPF-Net) friendly to devices with limited computing resources by frequency learning and partial feature fusion. It introduces invisible watermarks as protective signal into the RAW data. The protection capability can not only be transferred into the rendered RGB images regardless of the applied ISP pipeline, but also is resilient to post-processing operations such as blurring or compression. Once the image is manipulated, we can accurately identify the forged areas with a localization network. Extensive experiments on several famous RAW datasets, e.g., RAISE, FiveK and SIDD, indicate the effectiveness of our method. We hope that this technique can be used in future cameras as an option for image protection, which could effectively restrict image manipulation at the source.
中文总结: 这段话主要内容是介绍了RAW文件作为大多数相机中广泛使用的场景辐射的初始测量,以及通过图像信号处理(ISP)管道将RAW数据转换为普遍使用的RGB图像。现在,数字图像面临着被恶意篡改的风险。受到先天免疫是身体防御的第一道防线的启发,提出了一种名为DRAW的新颖方案,通过保护其源,即相机拍摄的RAW文件,来防御图像被篡改。具体地,设计了一种轻量级的多频部分融合网络(MPF-Net),通过频率学习和部分特征融合,对具有有限计算资源的设备友好。它将隐形水印作为保护信号引入RAW数据中。保护能力不仅可以转移到渲染的RGB图像中,而且对于诸如模糊或压缩等后处理操作也具有韧性。一旦图像被篡改,我们可以通过定位网络准确识别伪造区域。对几个著名的RAW数据集,如RAISE、FiveK和SIDD进行了大量实验,表明了我们方法的有效性。希望这种技术能够作为图像保护的选项应用于未来的相机中,从而有效地限制图像篡改源头。
Paper32 Learning Global-aware Kernel for Image Harmonization
摘要原文: Image harmonization aims to solve the visual inconsistency problem in composited images by adaptively adjusting the foreground pixels with the background as references. Existing methods employ local color transformation or region matching between foreground and background, which neglects powerful proximity prior and independently distinguishes fore-/back-ground as a whole part for harmonization. As a result, they still show a limited performance across varied foreground objects and scenes. To address this issue, we propose a novel Global-aware Kernel Network (GKNet) to harmonize local regions with comprehensive consideration of long-distance background references.
Specifically, GKNet includes two parts, i.e., harmony kernel prediction and harmony kernel modulation branches. The former includes a Long-distance Reference Extractor (LRE) to obtain long-distance context and Kernel Prediction Blocks (KPB) to predict multi-level harmony kernels by fusing global information with local features. To achieve this goal, a novel Selective Correlation Fusion (SCF) module is proposed to better select relevant long-distance background references for local harmonization. The latter employs the predicted kernels to harmonize foreground regions with both local and global awareness. Abundant experiments demonstrate the superiority of our method for image harmonization over state-of-the-art methods, e.g., achieving 39.53dB PSNR that surpasses the best counterpart by +0.78dB; decreasing fMSE by 11.5% and MSE by 6.7% compared with the SoTA method.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了图像和谐化的问题,旨在通过自适应地调整前景像素与背景作为参考来解决合成图像中的视觉不一致问题。现有方法采用局部颜色转换或前景与背景之间的区域匹配,这忽略了强大的接近性先验,并独立地将前景和背景作为整体部分区分开来进行和谐化。因此,它们在各种前景对象和场景中仍然表现出有限的性能。为了解决这个问题,提出了一种新颖的全局感知核网络(GKNet)来和谐化具有全面考虑长距离背景参考的局部区域。
具体而言,GKNet包括两部分,即和谐核预测和和谐核调制分支。前者包括一个长距离参考提取器(LRE)来获取长距离上下文和核预测块(KPB)通过融合全局信息与局部特征来预测多级和谐核。为了实现这一目标,提出了一种新颖的选择性相关融合(SCF)模块,以更好地选择相关的长距离背景参考进行局部和谐化。后者利用预测的核来使前景区域具有局部和全局意识的和谐化。大量实验证明了我们的方法在图像和谐化方面优于最先进的方法,例如实现了39.53dB的PSNR,超过最佳对手+0.78dB;与最先进的方法相比,fMSE减少了11.5%,MSE减少了6.7%。
Paper33 Boosting Whole Slide Image Classification from the Perspectives of Distribution, Correlation and Magnification
摘要原文: Bag-based multiple instance learning (MIL) methods have become the mainstream for Whole Slide Image (WSI) classification. However, there are still three important issues that have not been fully addressed: (1) positive bags with a low positive instance ratio are prone to the influence of a large number of negative instances; (2) the correlation between local and global features of pathology images has not been fully modeled; and (3) there is a lack of effective information interaction between different magnifications. In this paper, we propose MILBooster, a powerful dual-scale multi-stage MIL framework to address these issues from the perspectives of distribution, correlation, and magnification. Specifically, to address issue (1), we propose a plug-and-play bag filter that effectively increases the positive instance ratio of positive bags. For issue (2), we propose a novel window-based Transformer architecture called PiceBlock to model the correlation between local and global features of pathology images. For issue (3), we propose a dual-branch architecture to process different magnifications and design an information interaction module called Scale Mixer for efficient information interaction between them. We conducted extensive experiments on four clinical WSI classification tasks using three datasets. MILBooster achieved new state-of-the-art performance on all these tasks. Codes will be available.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了基于袋子的多实例学习(MIL)方法已成为全幻灯片图像(WSI)分类的主流,但仍存在三个重要问题尚未得到充分解决:(1)具有低正实例比率的正袋易受大量负实例影响;(2)病理图像的局部和全局特征之间的相关性尚未完全建模;以及(3)不同放大倍数之间缺乏有效信息交互。本文提出了MILBooster,一个强大的双尺度多阶段MIL框架,从分布、相关性和放大的角度解决这些问题。具体来说,为了解决问题(1),提出了一种可插拔的袋子过滤器,有效增加了正袋的正实例比率。对于问题(2),提出了一种名为PiceBlock的新型基于窗口的Transformer架构,用于建模病理图像的局部和全局特征之间的相关性。对于问题(3),提出了双分支架构来处理不同的放大倍数,并设计了一个名为Scale Mixer的信息交互模块,用于它们之间的有效信息交互。在三个数据集上进行了广泛的实验,使用四个临床WSI分类任务。MILBooster在所有这些任务上均取得了新的最先进性能。代码将可用。
Paper34 Prototypical Mixing and Retrieval-Based Refinement for Label Noise-Resistant Image Retrieval
摘要原文: Label noise is pervasive in real-world applications, which influences the optimization of neural network models. This paper investigates a realistic but understudied problem of image retrieval under label noise, which could lead to severe overfitting or memorization of noisy samples during optimization. Moreover, identifying noisy samples correctly is still a challenging problem for retrieval models. In this paper, we propose a novel approach called Prototypical Mixing and Retrieval-based Refinement (TITAN) for label noise-resistant image retrieval, which corrects label noise and mitigates the effects of the memorization simultaneously. Specifically, we first characterize numerous prototypes with Gaussian distributions in the hidden space, which would direct the Mixing procedure in providing synthesized samples. These samples are fed into a similarity learning framework with varying emphasis based on the prototypical structure to learn semantics with reduced overfitting. In addition, we retrieve comparable samples for each prototype from simple to complex, which refine noisy samples in an accurate and class-balanced manner. Comprehensive experiments on five benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of our proposed TITAN compared with various competing baselines.
中文总结: 这篇论文研究了标签噪声对神经网络模型优化的影响,探讨了在标签噪声下进行图像检索的现实但不太研究的问题,这可能会在优化过程中导致严重的过拟合或记忆噪声样本。此外,正确识别噪声样本仍然是检索模型的一个具有挑战性的问题。在这篇论文中,我们提出了一种名为Prototypical Mixing and Retrieval-based Refinement (TITAN)的新方法,用于抗标签噪声的图像检索,该方法同时纠正标签噪声并减轻记忆效应。具体地,我们首先在隐藏空间中用高斯分布表征了许多原型,这将指导混合过程提供合成样本。这些样本被输入到一个基于相似性学习框架中,根据原型结构的不同重点学习语义以减少过拟合。此外,我们从简单到复杂为每个原型检索可比较的样本,以准确且类别平衡的方式完善噪声样本。对五个基准数据集的全面实验表明,我们提出的TITAN相对于各种竞争基线具有更高的优越性。
Paper35 Neglected Free Lunch - Learning Image Classifiers Using Annotation Byproducts
摘要原文: Supervised learning of image classifiers distills human knowledge into a parametric model through pairs of images and corresponding labels (X,Y). We argue that this simple and widely used representation of human knowledge neglects rich auxiliary information from the annotation procedure, such as the time-series of mouse traces and clicks left after image selection. Our insight is that such annotation byproducts Z provide approximate human attention that weakly guides the model to focus on the foreground cues, reducing spurious correlations and discouraging shortcut learning. To verify this, we create ImageNet-AB and COCO-AB. They are ImageNet and COCO training sets enriched with sample-wise annotation byproducts, collected by replicating the respective original annotation tasks. We refer to the new paradigm of training models with annotation byproducts as learning using annotation byproducts (LUAB). We show that a simple multitask loss for regressing Z together with Y already improves the generalisability and robustness of the learned models. Compared to the original supervised learning, LUAB does not require extra annotation costs. ImageNet-AB and COCO-AB are at https://github.com/naver-ai/NeglectedFreeLunch.
中文总结: 这段话的主要内容是:监督学习图像分类器将人类知识通过图像和相应标签(X,Y)的配对转化为参数模型。作者认为这种简单且广泛使用的人类知识表示方式忽略了来自注释过程的丰富辅助信息,例如在图像选择后留下的鼠标轨迹和点击的时间序列。作者认为这些注释副产品Z提供了近似人类注意力,弱化了模型对前景线索的关注,减少了伪相关性并避免了捷径学习。为了验证这一观点,作者创建了ImageNet-AB和COCO-AB,它们是ImageNet和COCO训练集,其中包含了通过复制原始注释任务收集的样本级注释副产品。作者将使用注释副产品进行模型训练的新范式称为学习注释副产品(LUAB)。作者展示了通过使用简单的多任务损失来回归Z和Y,已经可以提高学习模型的泛化能力和鲁棒性。与原始监督学习相比,LUAB不需要额外的注释成本。可以在https://github.com/naver-ai/NeglectedFreeLunch找到ImageNet-AB和COCO-AB。
歇一会儿
Paper1 OxfordTVG-HIC: Can Machine Make Humorous Captions from Images?
摘要原文: Abstract not available
中文总结: 抱歉,由于没有提供摘要,我无法为您总结主要内容。您是否需要我对原文进行翻译或提供其他帮助?
Paper2 DiffuMask: Synthesizing Images with Pixel-level Annotations for Semantic Segmentation Using Diffusion Models
摘要原文: Collecting and annotating images with pixel-wise labels is time-consuming and laborious. In contrast, synthetic data can be freely available using a generative model (e.g., DALL-E, Stable Diffusion). In this paper, we show that it is possible to automatically obtain accurate semantic masks of synthetic images generated by the pre-trained Stable Diffusion, which uses only text-image pairs during training. Our approach, called DiffuMask, exploits the potential of the cross-attention map between text and image, which is natural and seamless to extend the text-driven
image synthesis to semantic mask generation. DiffuMask uses text-guided cross-attention information to localize class/word-specific regions, which are combined with practical techniques to create a novel high-resolution and class-discriminative pixel-wise mask. The methods help to reduce data collection and annotation costs obviously. Experiments demonstrate that the existing segmentation methods trained on synthetic data of DiffuMask can achieve a
competitive performance over the counterpart of real data (VOC 2012, Cityscapes). For some classes (e.g., bird), DiffuMask presents promising performance, close to the state-of-the-art result of real data (within 3% mIoU gap). Moreover, in the open-vocabulary segmentation (zero-shot) setting,
DiffuMask achieves a new SOTA result on Unseen class of VOC 2012.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了使用像素级标注收集和注释图像是耗时且费力的,而相比之下,可以利用生成模型(如DALL-E、Stable Diffusion)免费获得合成数据。作者展示了他们可以自动获取由预训练的Stable Diffusion生成的合成图像的准确语义掩模的可能性,该模型在训练过程中仅使用文本-图像对。他们提出的方法名为DiffuMask,利用文本和图像之间的交叉注意力图的潜力,将文本驱动的图像合成扩展到语义掩模生成,以定位类/词特定区域,并结合实用技术创建新颖的高分辨率和类别区分的像素级掩模。这些方法显著降低了数据收集和注释成本。实验表明,使用DiffuMask合成数据训练的现有分割方法在VOC 2012、Cityscapes等真实数据的对应方法上可以取得竞争性表现。对于一些类别(如鸟类),DiffuMask表现出有希望的性能,接近真实数据的最新结果(mIoU差距在3%以内)。此外,在开放词汇分割(零样本)设置中,DiffuMask在VOC 2012的未见类别上取得了新的最优结果。
Paper3 I Can’t Believe There’s No Images! Learning Visual Tasks Using only Language Supervision
摘要原文: Many high-level skills that are required for computer vision tasks, such as parsing questions, comparing and contrasting semantics, and writing descriptions, are also required in other domains such as natural language processing. In this paper, we ask whether it is possible to learn those skills from text data and then transfer them to vision tasks without ever training on visual training data. Key to our approach is exploiting the joint embedding space of contrastively trained vision and language encoders. In practice, there can be systematic differences between embedding spaces for different modalities in contrastive models, and we analyze how these differences affect our approach and study strategies to mitigate this concern. We produce models using only text training data on four representative tasks: image captioning, visual entailment, visual question answering and visual news captioning, and evaluate them on standard benchmarks using images. We find these models perform close to models trained on images, while surpassing prior work for captioning and visual entailment in this text-only setting by over 9 points, and outperforming all prior work on visual news by over 30 points. We also showcase a variety of stylistic image captioning models that are trained using no image data and no human-curated language data, but instead using readily-available text data from books, the web, or language models.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了在计算机视觉任务中所需的许多高级技能,如解析问题、比较和对比语义以及撰写描述,在自然语言处理等其他领域也同样需要。作者探讨了是否可能从文本数据中学习这些技能,然后将其转移到视觉任务中,而无需在视觉训练数据上进行训练。他们的方法的关键在于利用对比训练的视觉和语言编码器的联合嵌入空间。实际上,在对比模型中,不同模态的嵌入空间之间可能存在系统性差异,作者分析了这些差异如何影响他们的方法,并研究了缓解这一问题的策略。他们使用仅文本训练数据在四个代表性任务上生成模型:图像字幕、视觉蕴涵、视觉问答和视觉新闻字幕,并在标准基准测试中使用图像对其进行评估。他们发现这些模型在仅使用文本训练数据的情况下表现接近于在图像上训练的模型,同时在此仅文本设置下的字幕和视觉蕴涵方面超过之前的工作超过9个点,并在视觉新闻方面超过所有先前的工作超过30个点。他们还展示了一系列风格的图像字幕模型,这些模型是使用无图像数据和无人工策划的语言数据进行训练的,而是使用来自书籍、网络或语言模型的现成文本数据。
Paper4 LoGoPrompt: Synthetic Text Images Can Be Good Visual Prompts for Vision-Language Models
摘要原文: Prompt engineering is a powerful tool used to enhance the performance of pre-trained models on downstream tasks. For example, providing the prompt “Let’s think step by step” improved GPT-3’s reasoning accuracy to 63% on MutiArith while prompting “a photo of” filled with a class name enables CLIP to achieve 80% zero-shot accuracy on ImageNet. While previous research has explored prompt learning for the visual modality, analyzing what constitutes a good visual prompt specifically for image recognition is limited. In addition, existing visual prompt tuning methods’ generalization ability is worse than text-only prompting tuning. This paper explores our key insight: synthetic text images are good visual prompts for vision-language models! To achieve that, we propose our LoGoPrompt, which reformulates the classification objective to the visual prompt selection and addresses the chicken-and-egg challenge of first adding synthetic text images as class-wise visual prompts or predicting the class first. Without any trainable visual prompt parameters, experimental results on 16 datasets demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in few-shot learning, base-to-new generalization, and domain generalization. The code will be publicly available upon publication.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了Prompt engineering在增强预训练模型在下游任务中性能的重要性。举例说明了如何通过提供特定提示来改善模型的性能,如在MutiArith任务中使用"Let’s think step by step"提示可以将GPT-3的推理准确率提高到63%,而在ImageNet上使用"a photo of"提示填充类名可以使CLIP实现80%的零样本准确率。同时指出先前的研究虽然探索了视觉模态的提示学习,但对于图像识别而言,什么构成一个好的视觉提示的分析是有限的。作者提出了他们的关键见解:合成文本图像是视觉-语言模型的良好视觉提示!他们提出了LoGoPrompt方法,通过将分类目标重新制定为视觉提示选择,并解决了首先将合成文本图像添加为类别视觉提示还是首先预测类别的困难问题。实验结果表明,LoGoPrompt方法在16个数据集上一致优于现有方法,包括在少样本学习、基于新数据的泛化和领域泛化方面。文章发布后将公开代码。
Paper5 MPI-Flow: Learning Realistic Optical Flow with Multiplane Images
摘要原文: The accuracy of learning-based optical flow estimation models heavily relies on the realism of the training datasets. Current approaches for generating such datasets either employ synthetic data or generate images with limited realism. However, the domain gap of these data with real-world scenes constrains the generalization of the trained model to real-world applications. To address this issue, we investigate generating realistic optical flow datasets from real-world images. Firstly, to generate highly realistic new images, we construct a layered depth representation, known as multiplane images (MPI), from single-view images. This allows us to generate novel view images that are highly realistic. To generate optical flow maps that correspond accurately to the new image, we calculate the optical flows of each plane using the camera matrix and plane depths. We then project these layered optical flows into the output optical flow map with volume rendering. Secondly, to ensure the realism of motion, we present an independent object motion module that can separate the camera and dynamic object motion in MPI. This module addresses the deficiency in MPI-based single-view methods, where optical flow is generated only by camera motion and does not account for any object movement. We additionally devise a depth-aware inpainting module to merge new images with dynamic objects and address unnatural motion occlusions. We show the superior performance of our method through extensive experiments on real-world datasets. Moreover, our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in both unsupervised and supervised training of learning-based models. The code will be made publicly available at: https://github.com/Sharpiless/MPI-Flow.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了学习型光流估计模型的准确性与训练数据集的逼真程度密切相关。目前生成这些数据集的方法要么使用合成数据,要么生成逼真程度有限的图像。然而,这些数据与真实世界场景之间的领域差距限制了训练模型在真实应用中的泛化能力。为了解决这个问题,作者研究了从真实世界图像生成逼真光流数据集的方法。首先,为了生成高度逼真的新图像,他们构建了一个分层深度表示,称为多平面图像(MPI),从单视图图像中。这使他们能够生成高度逼真的新视图图像。为了生成与新图像准确对应的光流图,他们使用相机矩阵和平面深度计算每个平面的光流。然后,他们将这些分层光流投影到输出光流图中进行体素渲染。其次,为了确保运动的逼真性,他们提出了一个独立的对象运动模块,可以将相机运动和动态对象运动在MPI中分离开来。这个模块解决了基于MPI的单视图方法中的不足,其中光流仅由相机运动生成,而不考虑任何物体运动。此外,他们设计了一个深度感知修补模块,将新图像与动态对象合并,并解决不自然的运动遮挡问题。作者通过对真实世界数据集进行大量实验展示了他们方法的优越性能。此外,他们的方法在学习型模型的无监督和监督训练中均取得了最先进的性能。该代码将公开发布在: https://github.com/Sharpiless/MPI-Flow。
Paper6 Doppelgangers: Learning to Disambiguate Images of Similar Structures
摘要原文: We consider the visual disambiguation task of determining whether a pair of visually similar images depict the same or distinct 3D surfaces (e.g., the same or opposite sides of a symmetric building). Illusory image matches, where two images observe distinct but visually similar 3D surfaces, can be challenging for humans to differentiate, and can also lead 3D reconstruction algorithms to produce erroneous results. We propose a learning-based approach to visual disambiguation, formulating it as a binary classification task on image pairs. To that end, we introduce a new dataset for this problem, Doppelgangers, which includes image pairs of similar structures with ground truth labels. We also design a network architecture that takes the spatial distribution of local keypoints and matches as input, allowing for better reasoning about both local and global cues. Our evaluation shows that our method can distinguish illusory matches in difficult cases, and can be integrated into SfM pipelines to produce correct, disambiguated 3D reconstructions. See our project page for our code, datasets, and more results: http://doppelgangers-3d.github.io/.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了视觉消歧任务,即确定一对视觉上相似的图像是否描绘了相同或不同的3D表面(例如,对称建筑的同一侧或相反侧)。作者指出,对于人类来说,虚假的图像匹配很难区分,这可能导致3D重建算法产生错误的结果。作者提出了一种基于学习的视觉消歧方法,将其构建为对图像对的二元分类任务。为此,作者引入了一个新的数据集Doppelgangers,其中包含了具有地面真实标签的相似结构的图像对。作者还设计了一个网络架构,将局部关键点和匹配的空间分布作为输入,从而更好地推理局部和全局线索。评估结果显示,作者的方法可以在困难情况下区分虚假匹配,并可以集成到SfM流程中,产生正确的、消歧的3D重建结果。详情请参阅项目页面获取代码、数据集和更多结果:http://doppelgangers-3d.github.io/。
Paper7 Generating Realistic Images from In-the-wild Sounds
摘要原文: Representing wild sounds as images is an important but challenging task due to the lack of paired datasets between sound and image data and the significant differences in the characteristics of these two modalities. Previous studies have focused on generating images from sound in limited categories or music. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to generate images from wild sounds. First, we convert sound into text using audio captioning. Second, we propose audio attention and sentence attention to represent the rich characteristics of sound and visualize the sound. Lastly, we propose a direct sound optimization with CLIPscore and AudioCLIP and generate images with a diffusion-based model. In experiments, it shows that our model is able to generate high quality images from wild sounds and outperforms baselines in both quantitative and qualitative evaluations on wild audio datasets.
中文总结: 这段话主要讲述了将野生声音表示为图像是一项重要但具有挑战性的任务,因为声音和图像数据之间缺乏配对数据集,并且这两种模态的特征存在显著差异。先前的研究主要集中在有限类别或音乐中从声音生成图像。本文提出了一种新颖的方法来从野生声音生成图像。首先,我们使用音频字幕将声音转换为文本。其次,我们提出了音频注意力和句子注意力来表示声音的丰富特征并可视化声音。最后,我们提出了基于CLIPscore和AudioCLIP的直接声音优化,并使用扩散模型生成图像。实验证明,我们的模型能够从野生声音生成高质量的图像,并在野生音频数据集上的定量和定性评估中优于基线模型。
Paper8 BlindHarmony: “Blind” Harmonization for MR Images via Flow Model
摘要原文: In MRI, images of the same contrast (e.g., T1) from the same subject can exhibit noticeable differences when acquired using different hardware, sequences, or scan parameters. These differences in images create a domain gap that needs to be bridged by a step called image harmonization, to process the images successfully using conventional or deep learning-based image analysis (e.g., segmentation). Several methods, including deep learning-based approaches, have been proposed to achieve image harmonization. However, they often require datasets from multiple domains for deep learning training and may still be unsuccessful when applied to images from unseen domains. To address this limitation, we propose a novel concept called ‘Blind Harmonization’, which utilizes only target domain data for training but still has the capability to harmonize images from unseen domains. For the implementation of blind harmonization, we developed BlindHarmony using an unconditional flow model trained on target domain data. The harmonized image is optimized to have a correlation with the input source domain image while ensuring that the latent vector of the flow model is close to the center of the Gaussian distribution. BlindHarmony was evaluated on both simulated and real datasets and compared to conventional methods. BlindHarmony demonstrated noticeable performance on both datasets, highlighting its potential for future use in clinical settings. The source code is available at: https://github.com/SNU-LIST/BlindHarmony
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了在MRI中,同一主题的同一对比度(例如T1)的图像在使用不同的硬件、序列或扫描参数进行采集时可能会出现明显的差异。这些图像之间的差异造成了一个需要通过图像协调步骤来弥合的领域差距,以便成功地使用传统或基于深度学习的图像分析(例如分割)处理这些图像。已经提出了几种方法,包括基于深度学习的方法,用于实现图像协调。然而,它们通常需要来自多个领域的数据集进行深度学习训练,并且在应用于未知领域的图像时可能仍然不成功。为了解决这一限制,作者提出了一个名为“盲协调”的新概念,该概念仅利用目标领域数据进行训练,但仍具有协调来自未知领域的图像的能力。为了实现盲协调,作者使用在目标领域数据上训练的无条件流模型开发了BlindHarmony。经过优化,协调后的图像与输入源领域图像具有相关性,同时确保流模型的潜在向量接近高斯分布的中心。BlindHarmony在模拟和真实数据集上进行了评估,并与传统方法进行了比较。BlindHarmony在两个数据集上表现出明显的性能,突显了其在未来临床设置中的潜力。源代码可在以下链接找到:https://github.com/SNU-LIST/BlindHarmony。
Paper9 Navigating to Objects Specified by Images
摘要原文: Images are a convenient way to specify which particular object instance an embodied agent should navigate to. Solving this task requires semantic visual reasoning and exploration of unknown environments. We present a system that can perform this task in both simulation and the real world. Our modular method solves sub-tasks of exploration, goal instance re-identification, goal localization, and local navigation. We re-identify the goal instance in egocentric vision using feature-matching and localize the goal instance by projecting matched features to a map. Each sub-task is solved using off-the-shelf components requiring zero fine-tuning. On the HM3D InstanceImageNav benchmark, this system outperforms a baseline end-to-end RL policy 7x and outperforms a state-of-the-art ImageNav model 2.3x (56% vs. 25% success). We deploy this system to a mobile robot platform and demonstrate effective performance in the real world, achieving an 88% success rate across a home and an office environment.
中文总结: 这段话主要介绍了一种系统,可以在仿真环境和现实世界中执行特定目标导航任务。该系统通过语义视觉推理和对未知环境的探索来解决任务,包括探索、目标实例重新识别、目标定位和本地导航等子任务。通过使用特征匹配在自我中心视野中重新识别目标实例,并通过将匹配的特征投影到地图上来定位目标实例。每个子任务都使用现成组件解决,无需进行微调。在HM3D InstanceImageNav基准测试中,该系统比基准端到端RL策略提高了7倍,比最先进的ImageNav模型提高了2.3倍(成功率为56%对25%)。我们将该系统部署到移动机器人平台,并在现实世界中展示了有效性能,在家庭和办公环境中实现了88%的成功率。
Paper10 Adaptive Illumination Mapping for Shadow Detection in Raw Images
摘要原文: Shadow detection methods rely on multi-scale contrast, especially global contrast, information to locate shadows correctly. However, we observe that the camera image signal processor (ISP) tends to preserve more local contrast information by sacrificing global contrast information during the raw-to-sRGB conversion process. This often causes existing methods to fail in scenes with high global contrast but low local contrast in shadow regions. In this paper, we propose a novel method to detect shadows from raw images. Our key idea is that instead of performing a many-to-one mapping like the ISP process, we can learn a many-to-many mapping from the high dynamic range raw images to the sRGB images of different illumination, which is able to preserve multi-scale contrast for accurate shadow detection. To this end, we first construct a new shadow dataset with 7000 raw images and shadow masks. We then propose a novel network, which includes a novel adaptive illumination mapping (AIM) module to project the input raw images into sRGB images of different intensity ranges and a shadow detection module to leverage the preserved multi-scale contrast information to detect shadows. To learn the shadow-aware adaptive illumination mapping process, we propose a novel feedback mechanism to guide the AIM during training. Experiments show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art shadow detectors. Code and dataset are available at https://github.com/jiayusun/SARA.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了阴影检测方法依赖于多尺度对比度,特别是全局对比度信息来正确定位阴影。然而,研究人员观察到相机图像信号处理器(ISP)在从原始到sRGB转换过程中往往会通过牺牲全局对比度信息来保留更多的局部对比度信息。这通常会导致现有方法在具有高全局对比度但阴影区域局部对比度较低的场景中失败。在这篇论文中,提出了一种从原始图像中检测阴影的新方法。关键思想是,我们可以学习从高动态范围原始图像到不同照明条件下的sRGB图像的多对多映射,以保留多尺度对比度以实现准确的阴影检测,而不是像ISP过程那样执行多对一映射。为了实现这一目标,首先构建了一个包含7000个原始图像和阴影蒙版的新阴影数据集。然后提出了一个新的网络,其中包括一个新的自适应照明映射(AIM)模块,用于将输入的原始图像投影到不同强度范围的sRGB图像,以及一个阴影检测模块,利用保留的多尺度对比度信息来检测阴影。为了学习阴影感知的自适应照明映射过程,提出了一种新的反馈机制来指导AIM在训练过程中的学习。实验证明,该方法优于现有阴影检测器。代码和数据集可在https://github.com/jiayusun/SARA获得。
Paper11 Translating Images to Road Network: A Non-Autoregressive Sequence-to-Sequence Approach
摘要原文: The extraction of road network is essential for the generation of high-definition maps since it enables the precise localization of road landmarks and their interconnections. However, generating road network poses a significant challenge due to the conflicting underlying combination of Euclidean (e.g., road landmarks location) and non-Euclidean (e.g., road topological connectivity) structures. Existing methods struggle to merge the two types of data domains effectively, but few of them address it properly. Instead, our work establishes a unified representation of both types of data domain by projecting both Euclidean and non-Euclidean data into an integer series called RoadNet Sequence. Further than modeling an auto-regressive sequence-to-sequence Transformer model to understand RoadNet Sequence, we decouple the dependency of RoadNet Sequence into a mixture of auto-regressive and non-autoregressive dependency. Building on this, our proposed non-autoregressive sequence-to-sequence approach leverages non-autoregressive dependencies while fixing the gap towards auto-regressive dependencies, resulting in success on both efficiency and accuracy. Extensive experiments on nuScenes dataset demonstrate the superiority of RoadNet Sequence representation and the non-autoregressive approach compared to existing state-of-the-art alternatives.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了道路网络的提取对于生成高清地图的重要性,因为它可以实现道路地标的精确定位和它们之间的连接。然而,由于欧几里得(例如,道路地标位置)和非欧几里得(例如,道路拓扑连接)结构之间存在冲突的组合,生成道路网络面临重大挑战。现有方法很难有效地合并这两种数据域,但很少有方法能够妥善解决这个问题。相反,作者的工作建立了一个统一的表示,将欧几里得和非欧几里得数据投影到一个称为RoadNet Sequence的整数序列中。进一步,作者建立了一个自回归序列到序列Transformer模型来理解RoadNet Sequence,将RoadNet Sequence的依赖关系解耦为自回归和非自回归依赖的混合。基于此,作者提出的非自回归序列到序列方法利用非自回归依赖关系,同时修复了自回归依赖关系的差距,从而在效率和准确性方面取得成功。对nuScenes数据集进行的大量实验表明,与现有的最先进方法相比,RoadNet Sequence表示和非自回归方法具有优势。
Paper12 CHORUS : Learning Canonicalized 3D Human-Object Spatial Relations from Unbounded Synthesized Images
摘要原文: We present a method for teaching machines to understand and model the underlying spatial common sense of diverse human-object interactions in 3D in a self-supervised way. This is a challenging task, as there exist specific manifolds of the interactions that can be considered human-like and natural, but the human pose and the geometry of objects can vary even for similar interactions. Such diversity makes the annotating task of 3D interactions difficult and hard to scale, which limits the potential to reason about that in a supervised way. One way of learning the 3D spatial relationship between humans and objects during interaction is by showing multiple 2D images captured from different viewpoints when humans interact with the same type of objects. The core idea of our method is to leverage a generative model that produces high-quality 2D images from an arbitrary text prompt input as an “unbounded” data generator with effective controllability and view diversity. Despite its imperfection of the image quality over real images, we demonstrate that the synthesized images are sufficient to learn the 3D human-object spatial relations. We present multiple strategies to leverage the synthesized images, including (1) the first method to leverage a generative image model for 3D human-object spatial relation learning; (2) a framework to reason about the 3D spatial relations from inconsistent 2D cues in a self-supervised manner via 3D occupancy reasoning with pose canonicalization; (3) semantic clustering to disambiguate different types of interactions with the same object types; and (4) a novel metric to assess the quality of 3D spatial learning of interaction. Project Page: https://jellyheadandrew.github.io/projects/chorus
中文总结: 这段话主要介绍了一种方法,用于以自监督的方式教会机器理解和建模3D中多样化的人-物互动的基础空间常识。这是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为存在可以被视为类似人类和自然的特定互动流形,但即使是相似的互动,人类姿势和物体的几何形状也可能不同。这种多样性使得标注3D互动任务困难且难以扩展,从而限制了以监督方式推理的潜力。学习人类与物体在互动过程中的3D空间关系的一种方法是展示多个从不同视角捕获的2D图像,当人类与相同类型的物体互动时。我们方法的核心思想是利用生成模型,从任意文本提示输入产生高质量的2D图像作为“无限”的数据生成器,具有有效的可控性和视角多样性。尽管合成图像的质量不及真实图像,我们证明合成图像足以学习3D人-物空间关系。我们提出了多种策略来利用合成图像,包括:(1)利用生成图像模型进行3D人-物空间关系学习的第一种方法;(2)通过3D占用推理与姿势规范化的自监督方式推理不一致的2D线索中的3D空间关系的框架;(3)语义聚类以消除相同对象类型的不同互动类型的歧义;以及(4)一种评估互动的3D空间学习质量的新型度量标准。项目页面:https://jellyheadandrew.github.io/projects/chorus
Paper13 RecRecNet: Rectangling Rectified Wide-Angle Images by Thin-Plate Spline Model and DoF-based Curriculum Learning
摘要原文: The wide-angle lens shows appealing applications in VR technologies, but it introduces severe radial distortion into its captured image. To recover the realistic scene, previous works devote to rectifying the content of the wide-angle image. However, such a rectification solution inevitably distorts the image boundary, which changes related geometric distributions and misleads the current vision perception models. In this work, we explore constructing a win-win representation on both content and boundary by contributing a new learning model, i.e., Rectangling Rectification Network (RecRecNet). In particular, we propose a thin-plate spline (TPS) module to formulate the non-linear and non-rigid transformation for rectangling images. By learning the control points on the rectified image, our model can flexibly warp the source structure to the target domain and achieves an end-to-end unsupervised deformation. To relieve the complexity of structure approximation, we then inspire our RecRecNet to learn the gradual deformation rules with a DoF (Degree of Freedom)-based curriculum learning. By increasing the DoF in each curriculum stage, namely, from similarity transformation (4-DoF) to homography transformation (8-DoF), the network is capable of investigating more detailed deformations, offering fast convergence on the final rectangling task. Experiments show the superiority of our solution over the compared methods on both quantitative and qualitative evaluations. The code and dataset will be made available.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了广角镜头在虚拟现实技术中的吸引人应用,但是它会在拍摄的图像中引入严重的径向畸变。为了恢复真实的场景,先前的研究致力于矫正广角图像的内容。然而,这种矫正方案不可避免地会扭曲图像边界,从而改变相关的几何分布并误导当前的视觉感知模型。在这项工作中,我们探索了通过提出一种新的学习模型,即Rectangling Rectification Network (RecRecNet),在内容和边界上构建一个双赢的表示。具体来说,我们提出了一个薄板样条(TPS)模块,用于制定用于矫正图像的非线性和非刚性变换。通过学习矫正图像上的控制点,我们的模型可以灵活地将源结构扭曲到目标领域,并实现端到端的无监督变形。为了减轻结构近似的复杂性,我们启发我们的RecRecNet通过基于DoF(自由度)的课程学习学习渐进变形规则。通过在每个课程阶段增加DoF,即从相似变换(4-DoF)到单应性变换(8-DoF),网络能够研究更详细的变形,为最终的矫正任务提供快速收敛。实验证明我们的解决方案在定量和定性评估上优于比较方法。代码和数据集将会提供。
Paper14 Versatile Diffusion: Text, Images and Variations All in One Diffusion Model
摘要原文: Recent advances in diffusion models have set an impressive milestone in many generation tasks, and trending works such as DALL-E2, Imagen, and Stable Diffusion have attracted great interest. Despite the rapid landscape changes, recent new approaches focus on extensions and performance rather than capacity, thus requiring separate models for separate tasks. In this work, we expand the existing single-flow diffusion pipeline into a multi-task multimodal network, dubbed Versatile Diffusion (VD), that handles multiple flows of text-to-image, image-to-text, and variations in one unified model. The pipeline design of VD instantiates a unified multi-flow diffusion framework, consisting of sharable and swappable layer modules that enable the crossmodal generality beyond images and text. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that VD successfully achieves the following: a) VD outperforms the baseline approaches and handles all its base tasks with competitive quality; b) VD enables novel extensions such as disentanglement of style and semantics, dual- and multi-context blending, etc.; c) The success of our multi-flow multimodal framework over images and text may inspire further diffusion-based universal AI research. Our code and models are open-sourced at https://github.com/SHI-Labs/Versatile-Diffusion.
中文总结: 最近在扩散模型方面取得的进展在许多生成任务中设立了令人印象深刻的里程碑,像DALL-E2、Imagen和Stable Diffusion等热门作品引起了极大关注。尽管景观变化迅速,最近的新方法侧重于扩展和性能而非容量,因此需要为不同任务单独设计模型。在这项工作中,我们将现有的单流扩散管道扩展为一个多任务多模网络,命名为Versatile Diffusion(VD),可处理文本到图像、图像到文本和变体的多个流,并统一到一个模型中。VD的管道设计实例化了一个统一的多流扩散框架,由可共享和可交换的层模块组成,能够实现超越图像和文本的跨模态普适性。通过大量实验,我们证明了VD成功实现了以下目标:a)VD优于基线方法,并以竞争性质量处理其所有基本任务;b)VD实现了新的扩展,如风格和语义的解耦、双重和多重上下文混合等;c)我们的多流多模框架在图像和文本上的成功可能会激发进一步基于扩散的通用人工智能研究。我们的代码和模型已在https://github.com/SHI-Labs/Versatile-Diffusion 开源。
Paper15 LoCUS: Learning Multiscale 3D-consistent Features from Posed Images
摘要原文: An important challenge for autonomous agents such as robots is to maintain a spatially and temporally consistent model of the world. It must be maintained through occlusions, previously-unseen views, and long time horizons (e.g., loop closure and re-identification). It is still an open question how to train such a versatile neural representation without supervision.
We start from the idea that the training objective can be framed as a patch retrieval problem: given an image patch in one view of a scene, we would like to retrieve (with high precision and recall) all patches in other views that map to the same real-world location. One drawback is that this objective does not promote reusability of features: by being unique to a scene (achieving perfect precision/recall), a representation will not be useful in the context of other scenes. We find that it is possible to balance retrieval and reusability by constructing the retrieval set carefully, leaving out patches that map to far-away locations. Similarly, we can easily regulate the scale of the learned features (e.g., points, objects, or rooms) by adjusting the spatial tolerance for considering a retrieval to be positive. We optimize for (smooth) Average Precision (AP), in a single unified ranking-based objective. This objective also doubles as a criterion for choosing landmarks or keypoints, as patches with high AP.
We show results creating sparse, multi-scale, semantic spatial maps composed of highly identifiable landmarks, with applications in landmark retrieval, localization, semantic segmentation and instance segmentation.
中文总结: 这段话主要讨论了自主代理(如机器人)面临的重要挑战,即如何在空间和时间上保持对世界的一致性模型。为了实现这一目标,需要处理遮挡、之前未见过的视角以及长时间跨度(例如循环闭合和重新识别)等问题。目前尚不清楚如何在没有监督的情况下训练这样一种多功能的神经表示。作者提出了将训练目标构建为一个补丁检索问题的想法:给定一个场景中某个视角的图像补丁,希望能够检索出所有映射到同一实际位置的其他视角的补丁。作者通过精心构建检索集合来平衡检索和可重用性,从而优化平均精度(AP)作为一个单一统一的基于排名的目标。最终,作者展示了创建稀疏的、多尺度的、语义空间地图的结果,其中包含高度可识别的地标,可应用于地标检索、定位、语义分割和实例分割等领域。
Paper16 Vanishing Point Estimation in Uncalibrated Images with Prior Gravity Direction
摘要原文: We tackle the problem of estimating a Manhattan frame, i.e. three orthogonal vanishing points, and the unknown focal length of the camera, leveraging a prior vertical direction. The direction can come from an Inertial Measurement Unit that is a standard component of recent consumer devices, e.g., smartphones. We provide an exhaustive analysis of minimal line configurations and derive two new 2-line solvers, one of which does not suffer from singularities affecting existing solvers. Additionally, we design a new non-minimal method, running on an arbitrary number of lines, to boost the performance in local optimization. Combining all solvers in a hybrid robust estimator, our method achieves increased accuracy even with a rough prior. Experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate the superior accuracy of our method compared to the state of the art, while having comparable runtimes. We further demonstrate the applicability of our solvers for relative rotation estimation. The code is available at https://github.com/cvg/VP-Estimation-with-Prior-Gravity.
中文总结: 本文主要讨论了估计曼哈顿坐标系的问题,即三个正交消失点和相机未知焦距的估计,利用先验垂直方向。该方向可以来自最近消费设备的标准组件,例如智能手机上的惯性测量单元。文章对最小线配置进行了详尽的分析,并推导出两种新的2线解算器,其中一种不会受到现有解算器所受的奇异性影响。此外,设计了一种新的非最小方法,可在任意数量的线上运行,以提高局部优化性能。将所有解算器结合在一个混合鲁棒估计器中,我们的方法即使具有粗糙先验也能实现更高的准确性。对合成和真实数据集的实验表明,与现有技术相比,我们的方法具有更高的准确性,同时具有可比较的运行时间。我们进一步展示了我们的解算器在相对旋转估计中的适用性。源代码可在https://github.com/cvg/VP-Estimation-with-Prior-Gravity 找到。
Paper17 Simulating Fluids in Real-World Still Images
摘要原文: In this work, we tackle the problem of real-world fluid animation from a still image. The key of our system is a surface-based layered representation, where the scene is decoupled into a surface fluid layer and an impervious background layer with corresponding transparencies to characterize the composition of the two layers. The animated video can be produced by warping only the surface fluid layer according to the estimation of fluid motions and recombining it with the background. In addition, we introduce surface-only fluid simulation, a 2.5D fluid calculation, as a replacement for motion estimation.
Specifically, we leverage triangular mesh based on a monocular depth estimator to represent fluid surface layer and simulate the motion with the inspiration of classic physics theory of hybrid Lagrangian-Eulerian method, along with a learnable network so as to adapt to complex real-world image textures.Extensive experiments not only indicate our method’s competitive performance for common fluid scenes but also better robustness and reasonability under complex transparent fluid scenarios. Moreover, as proposed surface-based layer representation and surface-only fluid simulation naturally disentangle the scene, interactive editing such as adding objects and texture replacing could be easily achieved with realistic results.
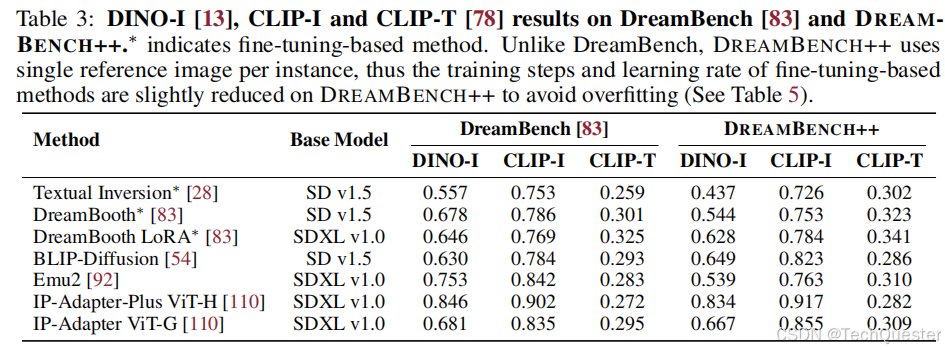



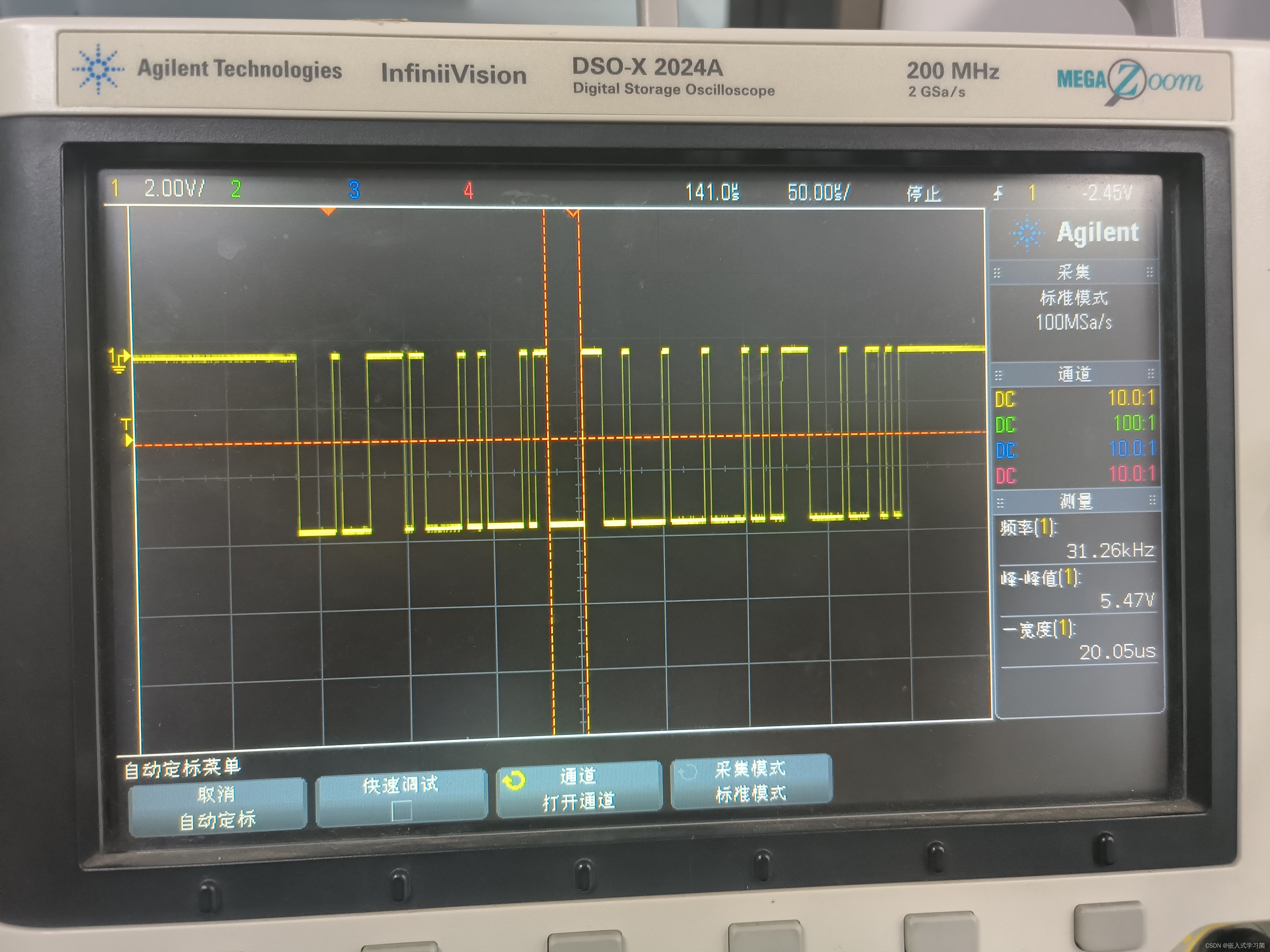


![[开源软件] 支持链接汇总](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/35ae3fb6261f492c922962d642e62666.png)