机器人搬运货物
实验目的
(1)理解分支限界法的求解过程。
(2)分析分支限界法的时间复杂度,比较分支限界法算法与其他算法的时间效率差异。
(3)学会如何利用分支限界法求解具体问题,了解动分支限界法的应用范围及在实际应用中的局限性。
实验任务
(1)完成实验8.3(机器人搬运货物问题)的各项要求。
(2)用C++语言实现该算法并进行测试。
(3)撰写实验报告,实验报告内容包括实验目的、实验任务、实验环境、实验步骤、实验结果和实验总结等部分。
实验步骤及结果
实验预习
给出采用分支限界法求解该问题时的目标函数,约束条件以及限界函数

给出采用分支限界法求解样例输入时的解空间树
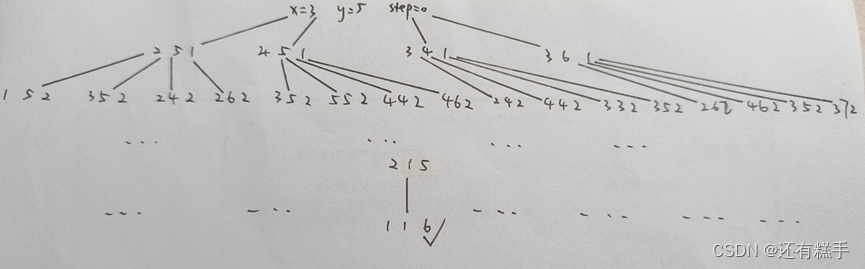
分析采用分支限界法求解样例输入时的求解过程,堆结点的定义,堆结点的值以及堆中元素的变化过程
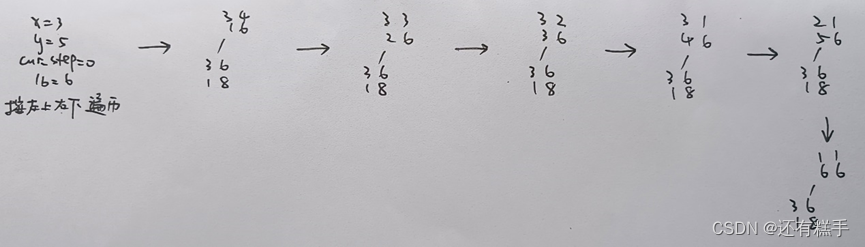
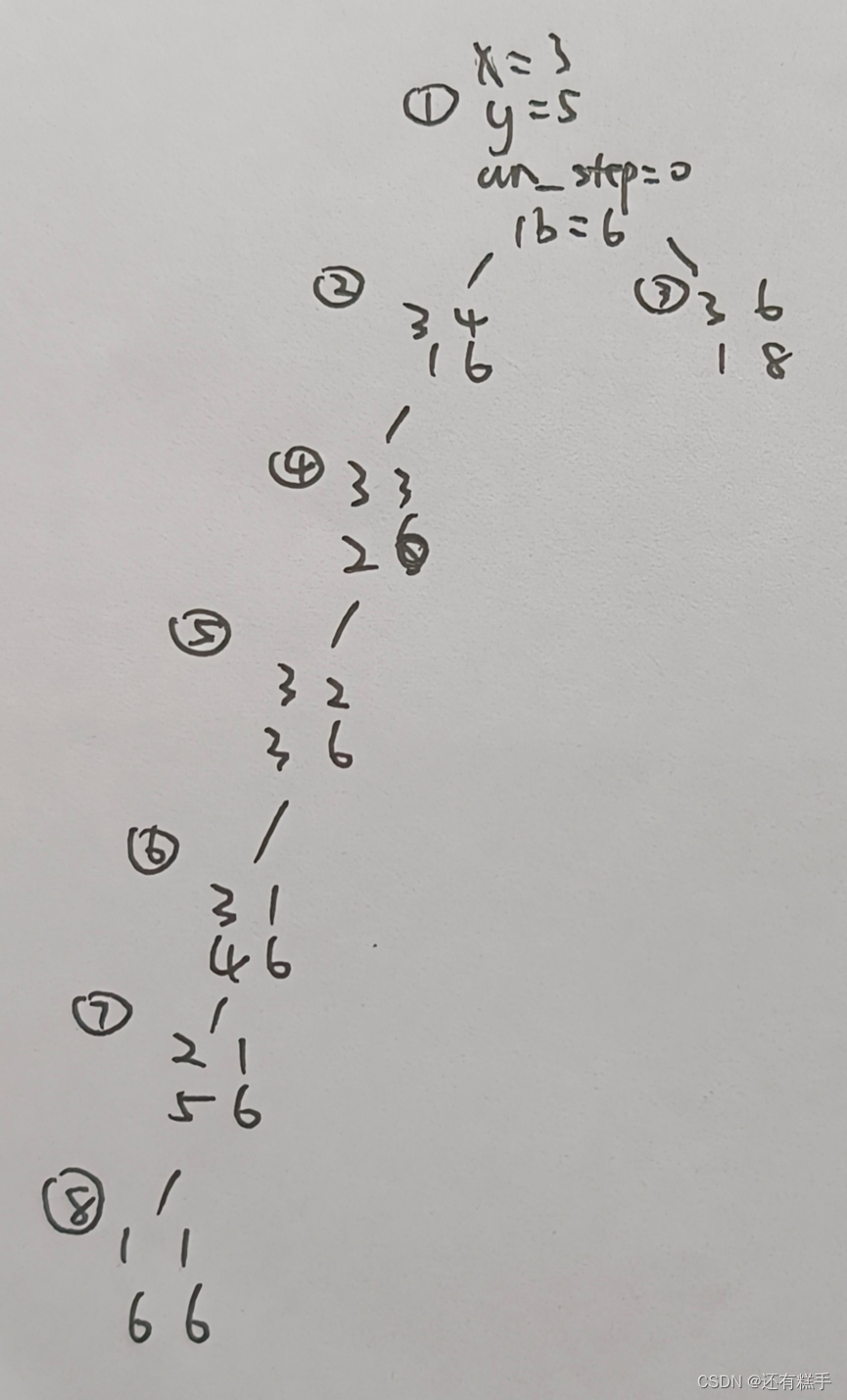
画出采用分支限界法求解样例输入时的搜索空间树
用C/C++语言编写程序求解上述问题
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct b_node
{int x;int y;int step;int lb;int r_x;int r_y;
};struct r_node
{int x;int y;int step;int lb;
};
struct r_cmp
{bool operator()(r_node n1, r_node n2){return n1.lb > n2.lb;}
};
struct b_cmp
{bool operator()(b_node n1, b_node n2){return n1.lb > n2.lb;}
};
int n, m, begin_x, begin_y, end_x, end_y, r_begin_x, r_begin_y;
char arr[100][100];
int MIN = 100000;
bool b_used[100][100] = {false};
bool r_used[100][100] = {false};
int row[] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
int column[] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
int pre_r[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int pre_c[] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
void r_get_lb(r_node &n, int x, int y){n.lb = n.step + abs(n.x - x) + abs(n.y - y);
}
bool r_is_valid(int x, int y, int b_x, int b_y){if(x < 0 || x > n-1 || y < 0 || y > m-1 || arr[x][y] == '#' || r_used[x][y] == true || (x == b_x && y == b_y)){return false;}return true;
}
void r_recover(){for(int i = 0;i < 100;++i){for(int j = 0;j < 100;++j){r_used[i][j] = false;}}
}
bool r_is_come(int cur_x, int cur_y, int orientation_x, int orientation_y, int b_x, int b_y){r_node begin;begin.x = cur_x;begin.y = cur_y;r_used[cur_x][cur_y] = true;begin.step = 0;r_get_lb(begin, orientation_x, orientation_y);priority_queue<r_node, vector<r_node>, r_cmp> q;q.push(begin);while (!q.empty()){r_node temp = q.top();q.pop();if(temp.x == orientation_x && temp.y == orientation_y){r_recover();return true;}for(int i = 0;i < 4;++i){int x = temp.x + row[i];int y = temp.y + column[i];int step = temp.step + 1;if(r_is_valid(x, y, b_x, b_y)){r_node tmp;tmp.x = x;tmp.y = y;tmp.step = step;r_get_lb(tmp, orientation_x, orientation_y);r_used[x][y] = true;q.push(tmp);}}}r_recover();return false;
}
void b_get_lb(b_node &n, int x, int y){n.lb = n.step + abs(n.x - x) + abs(n.y - y);
}
bool b_is_valid(int x, int y){if(x < 0 || x > n-1 || y < 0 || y > m-1 || arr[x][y] == '#' || b_used[x][y] == true){return false;}return true;
}
void bound(){b_node start;start.x = begin_x;start.y = begin_y;start.r_x = r_begin_x;start.r_y = r_begin_y;start.step = 0;b_get_lb(start, end_x, end_y);priority_queue<b_node, vector<b_node>, b_cmp> q;q.push(start);while (!q.empty()){b_node temp = q.top();q.pop();if(temp.x == end_x && temp.y == end_y){MIN = temp.step;break;}for(int i = 0;i < 4;++i){int b_o_x = temp.x + row[i];int b_o_y = temp.y + column[i];int r_o_x = temp.x + pre_r[i];int r_o_y = temp.y + pre_c[i];int step = temp.step + 1;if(b_is_valid(b_o_x, b_o_y) && r_is_valid(r_o_x, r_o_y, temp.x, temp.y) && r_is_come(temp.r_x, temp.r_y, r_o_x, r_o_y, temp.x, temp.y)){b_node tmp;tmp.x = b_o_x;tmp.y = b_o_y;tmp.r_x = temp.x;tmp.r_y = temp.y;tmp.step = step;b_get_lb(tmp, end_x, end_y);b_used[b_o_x][b_o_y] = true;q.push(tmp);}}}
}
int main(void){cin>>n>>m;for(int i = 0;i < n;++i){for(int j = 0;j < m;++j){cin>>arr[i][j];if(arr[i][j] == 'B'){begin_x = i;begin_y = j;b_used[i][j] = true;}else if(arr[i][j] == 'T'){end_x = i;end_y = j;}else if(arr[i][j] == 'S'){r_begin_x = i;r_begin_y = j;}}}bound();cout<<MIN<<endl;system("pause");return 0;
}
上机实验
调试步骤(5)的程序,验证样例输入时程序执行过程中堆的变化过程是否与步骤(3)的分析结果一致
程序运行截图
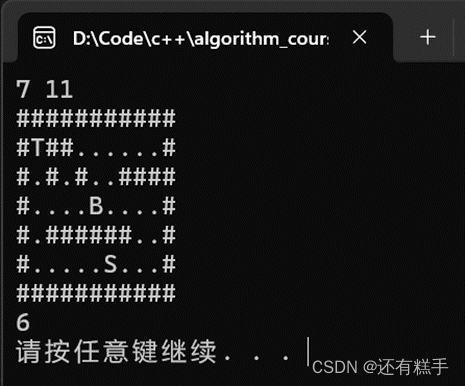
节点截图
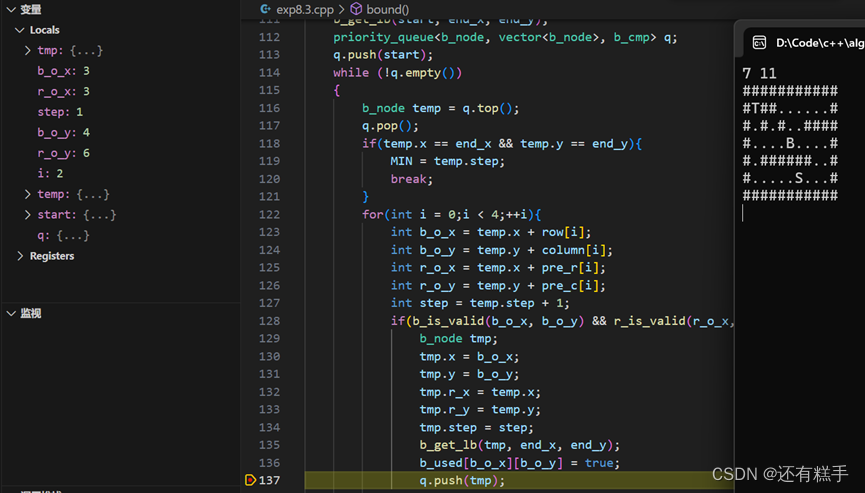
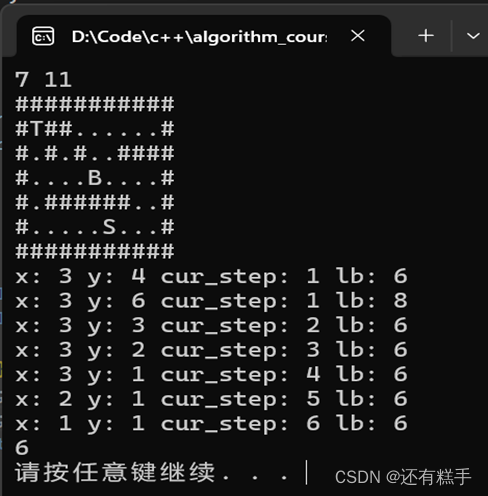
除起始节点外第一个节点变量截图,后面通过程序给出除起始节点外每个节点变量。
设计新的测试用例,对程序进行进一步验证
输入:
6 6
######
#..T.#
#..B.#
##.#S#
#....#
######
手工计算结果:
3
程序运行截图

实验总结
通过此次实验,理解分支限界法的求解过程。学会如何利用分支限界法求解具体问题。同时加深了对于手动求解堆以及堆的变化过程的熟练度和理解,并且对于搜索空间树的画法过程更加清楚明白。