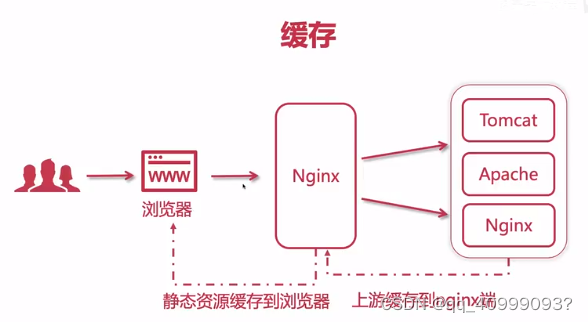
1.简介

2.SpringCache 整合
简化缓存开发
1.导入依赖
<!-- spring cache --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId></dependency>
2.redis 作为缓存场景
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId></dependency>3. 配置类
1.自动配置
自动配置了哪些
CacheAutoConfiguration 自动导入 RedisCacheConfiguration
自动配好了缓存管理器 RedisCacheManager
2.手动需要得yaml配置
spring:
#缓存cache:type: redis3.测试 使用缓存

1.开启缓存
1.使用redis作为缓存
spring:
#缓存cache:type: redis@EnableCaching //放在主启动类上2.使用注解就可以完成缓存
//每一个需要缓存的数据我们都来指定要放到哪个名字的缓存 [缓存的分区(按照业务类型分区)]@Cacheable({"category"}) //代表这个数据是可以缓存的 当前方法的结果需要缓存,如果缓存中有,方法不用调用。//如果缓存中没有,调用方法,将方法结果放入缓存@Overridepublic List<CategoryEntity> getLevel1Category() {System.out.println("调用了数据库getLevel1Category");List<CategoryEntity> parentCid = this.list(new QueryWrapper<CategoryEntity>().eq("parent_cid", 0));return parentCid;}
//默认行为//1.如果缓存中有,方法不用调用//2.key默认自动生成 : 缓存的名字::SimpleKey [](自主生产的key的值)//3.缓存的value的值 默认使用JDK序列化机制 将序列化后的数据存入Redis//4.默认ttl时间 -1;
//自定义//1. 指定生成的缓存使用的key key 属性指定,接受一个SPEL 表达式 ${} #{}//2. 指定缓存的过期时间 yml 配置文件中修改ttl//3. 将数据存入JSON标准格式 
public String mycategorykey="我自定义的key";@Override
// @Cacheable(value = {"category"}, key = "'level1Category'")
// @Cacheable(value = {"category"}, key = "#root.method.name")//root是当前上下文的意思 method 是方法 可以有参数 各种东西@Cacheable(value = {"category"}, key = "#root.target.mycategorykey")//root 可以拿到当前对象 当前方法 当前参数public List<CategoryEntity> getLevel1Category() {System.out.println("调用了数据库getLevel1Category");List<CategoryEntity> parentCid = this.list(new QueryWrapper<CategoryEntity>().eq("parent_cid", 0));return parentCid;}
2.自定义缓存设置
保存的数据为json格式
1.讲一下 缓存redis配置类的 原理
CacheAutoConfiguration->RedisCacheConfiguration->自动配置了缓存管理器 RedisCacheManager->初始化所有的缓存->每个缓存觉得使用什么配置->如果RedisCacheConfiguration有在 容器中自己 配置,就要用自己的配置,否则就用默认的配置
所以,我们只需要给容器中放入一个RedisCacheConfiguration即可
就会应用到当前缓存管理器的所有缓存中

2.配置类
package com.jmj.gulimall.product.config;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheProperties;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class MyCacheConfig {/*** 给了默认配置文件就不生效了* 因为 条件判断了 if config !=null 就返回* 也不需要加@EnableConfigurationProperties(CacheProperties.class)* 因为默认自动装配类已经加入这个* @return*/@Beanpublic RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties) {RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();/*** public RedisCacheConfiguration entryTtl(Duration ttl) { 是new新对象 得要覆盖上* return new RedisCacheConfiguration(ttl, cacheNullValues, usePrefix, keyPrefix, keySerializationPair,* valueSerializationPair, conversionService);* }*/config = config.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()));config = config.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()));CacheProperties.Redis redisProperties = cacheProperties.getRedis();if (redisProperties.getTimeToLive() != null) {config = config.entryTtl(redisProperties.getTimeToLive());}if (redisProperties.getKeyPrefix() != null) {config = config.prefixKeysWith(redisProperties.getKeyPrefix());}if (!redisProperties.isCacheNullValues()) {config = config.disableCachingNullValues();}if (!redisProperties.isUseKeyPrefix()) {config = config.disableKeyPrefix();}return config;}}
#配置数据源
spring:
#缓存cache:redis:time-to-live: 36000000 #单位 ms 先设定一个小时过期时间use-key-prefix: false #不使用,原来的前缀就没有了 key是什么 就是什么key-prefix: CACHE_ #所有Key都设置一个前缀来区分 如果指定了 前缀就用指定的,没有就用默认的 name::[]cache-null-values: true #是否缓存入空值 可以解决缓存穿透type: redis3.实现
//每一个需要缓存的数据我们都来指定要放到哪个名字的缓存 [缓存的分区(按照业务类型分区)]//代表这个数据是可以缓存的 当前方法的结果需要缓存,如果缓存中有,方法不用调用。//如果缓存中没有,调用方法,将方法结果放入缓存//默认行为//1.如果缓存中有,方法不用调用//2.key默认自动生成 : 缓存的名字::SimpleKey [](自主生产的key的值)//3.缓存的value的值 默认使用JDK序列化机制 将序列化后的数据存入Redis//4.默认ttl时间 -1;//自定义//1. 指定生成的缓存使用的key key 属性指定,接受一个SPEL 表达式 #{}//2. 指定缓存的过期时间 yml 配置文件中修改ttl//3. 将数据存入JSON标准格式public String mycategorykey="我自定义的key";@Override
// @Cacheable(value = {"category"}, key = "'level1Category'")
// @Cacheable(value = {"category"}, key = "#root.method.name")//root是当前上下文的意思 method 是方法 可以有参数 各种东西@Cacheable(value = {"category"}, key = "#root.target.mycategorykey")//root 可以拿到当前对象 当前方法 当前参数public List<CategoryEntity> getLevel1Category() {System.out.println("调用了数据库getLevel1Category");//线程不安全,需要加分布式锁和读写锁List<CategoryEntity> parentCid = this.list(new QueryWrapper<CategoryEntity>().eq("parent_cid", 0));return parentCid;}1.删除缓存
/*** 级联更新所有关联数据* @param category* @throws Exception*/@CacheEvict(value = "category", key = "'category::tree'")//删除缓存@Override@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)public void updateDetails(List<CategoryEntity> category) throws Exception {category.stream().filter(c -> StringUtils.isNotBlank(c.getName())).forEach(c -> {List<CategoryBrandRelationEntity> updateList = categoryBrandRelationService.list(new QueryWrapper<CategoryBrandRelationEntity>().eq("catelog_id", c.getCatId())).stream().peek(r -> r.setCatelogName(c.getName())).collect(Collectors.toList());categoryBrandRelationService.updateBatchById(updateList);});this.updateBatchById(category);}2.存入
@Override@Cacheable(value = {"category"}, key = "'category::tree'")public List<CategoryEntity> listWithTree() {//1.查出所有分类System.out.println("三级分类查询数据库");List<CategoryEntity> all = this.list();//2.组装成父子的属性结构List<CategoryEntity> level1Menus = all.stream().filter(c -> c.getParentCid().equals(0L)).map(categoryEntity -> categoryEntity.setChildren(getChildrenCategory(all, categoryEntity.getCatId())))//大于放后面 升序.sorted(Comparator.comparing(CategoryEntity::getSort)).collect(Collectors.toList());return level1Menus;}3.要操作多个
// @CacheEvict(value = "category", key = "'category::tree'")//删除缓存//如果多操作的话@Caching(evict = {@CacheEvict(value = "category", key = "'category::tree'"),@CacheEvict(value = "category", key = "#root.target.mycategorykey")})@Override@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)public void updateDetails(List<CategoryEntity> category) throws Exception {category.stream().filter(c -> StringUtils.isNotBlank(c.getName())).forEach(c -> {List<CategoryBrandRelationEntity> updateList = categoryBrandRelationService.list(new QueryWrapper<CategoryBrandRelationEntity>().eq("catelog_id", c.getCatId())).stream().peek(r -> r.setCatelogName(c.getName())).collect(Collectors.toList());categoryBrandRelationService.updateBatchById(updateList);});this.updateBatchById(category);}4.删除这个分区下所有数据 (失效模式)
存储同一类型的数据,都可以指定一个分区
@CacheEvict(value = "category", allEntries = true)// 设定了 use-key-prefix: false 这个如果没有这个分类,将全部缓存删除use-key-prefix必须要为true 和 key-prefix: 不设置 这个才有用
5.双写模式
@CachePut//双写模式
3.SpringCache的不足

基本都能解决,唯独缓存击穿特别一点
这样就是加了个本地锁,本地也就是放一个过来
@Override@Cacheable(value = {"category"}, key = "'tree'",sync = true)public List<CategoryEntity> listWithTree() {//1.查出所有分类System.out.println("三级分类查询数据库");List<CategoryEntity> all = this.list();//2.组装成父子的属性结构List<CategoryEntity> level1Menus = all.stream().filter(c -> c.getParentCid().equals(0L)).map(categoryEntity -> categoryEntity.setChildren(getChildrenCategory(all, categoryEntity.getCatId())))//大于放后面 升序.sorted(Comparator.comparing(CategoryEntity::getSort)).collect(Collectors.toList());return level1Menus;}只有cacheable 查询注解的时候 才能够加锁
虽然加的是本地锁,但是一台服务器只能一个访问,也是够用了
4.总结
常规数据(读多写少,即时性,一致性要求不高的数据 ):完全可以使用springcache(写模式:只有数据有过期时间 就完全足够了 这样可以保证数据的最终一致性)
特殊数据 (特殊设计)例如 canal 感知数据库去更新 缓存