寻找图中是否存在路径
原题
有一个具有 n 个顶点的 双向 图,其中每个顶点标记从 0 到 n - 1(包含 0 和 n - 1)。图中的边用一个二维整数数组 edges 表示,其中 edges[i] = [ui, vi] 表示顶点 ui 和顶点 vi 之间的双向边。 每个顶点对由 最多一条 边连接,并且没有顶点存在与自身相连的边。
请你确定是否存在从顶点 source 开始,到顶点 destination 结束的 有效路径。
给你数组 edges 和整数 n、source 和 destination,如果从 source 到 destination 存在 有效路径 ,则返回 true,否则返回 false 。
示例 1:(图片转存自LeetCode)

输入:n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0]], source = 0, destination = 2
输出:true
解释:存在由顶点 0 到顶点 2 的路径:
- 0 → 1 → 2
- 0 → 2
示例 2:
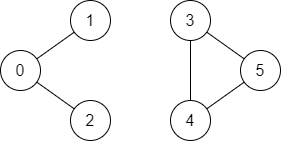
输入:n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[3,5],[5,4],[4,3]], source = 0, destination = 5
输出:false
解释:不存在由顶点 0 到顶点 5 的路径.
提示:
1 <= n <= 2 * 1050 <= edges.length <= 2 * 105edges[i].length == 20 <= ui, vi <= n - 1ui != vi0 <= source, destination <= n - 1- 不存在重复边
- 不存在指向顶点自身的边
class Solution {public boolean validPath(int n, int[][] edges, int source, int destination) {}
}解题思路
- 将图的边列表(二维整数数组
edges)转化为图的邻接表形式,以便快速访问每个节点的相邻节点信息。由于节点编号从0到n-1连续,故采用数组而非 HashMap 进行存储。 - 使用[[深度优先搜索]]递归地进行图的遍历。在遍历过程中,需要避免重复访问已经访问过的节点,因此使用一个
visited数组来记录哪些节点已经被访问过。 - 终止条件:
- 如果在遍历过程中找到了
destination,则可以立即返回true,表示路径存在。 - 如果遍历了所有可能的路径都没有找到
destination,则返回false,表示路径不存在。
- 如果在遍历过程中找到了
代码示例
class Solution {public boolean validPath(int n, int[][] edges, int source, int destination) {// 如果起点和终点是同一个点,直接返回 trueif (source == destination) return true;// 构建邻接表,用数组表示图List<Integer>[] graph = new ArrayList[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();}// 填充邻接表for (int[] edge : edges) {int fromNode = edge[0];int toNode = edge[1];graph[fromNode].add(toNode);graph[toNode].add(fromNode);}// 创建访问标记数组boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];// 使用 DFS 检查是否存在从 source 到 destination 的路径return dfs(graph, visited, source, destination);}private boolean dfs(List<Integer>[] graph, boolean[] visited, int node, int destination) {// 如果当前节点是目标节点,返回 trueif (node == destination) return true;// 标记当前节点为已访问visited[node] = true;// 遍历所有相邻节点for (int neighbor : graph[node]) {// 如果相邻节点没有访问过,进行递归 DFSif (!visited[neighbor]) {if (dfs(graph, visited, neighbor, destination)) {// 找到能到达终点的路径就返回 truereturn true;}}}// 所有路径都不能到达终点,返回 falsereturn false;}
}优化思路
这是一个经典的并查集问题。通过并查集的数据结构,可以高效地判断两个节点是否连通。每次将两个节点的根节点连接在一起,最终只需检查 source 和 destination 是否有相同的根节点即可。
优化后代码
class Solution {private int[] parent;private int[] rank; // 树的高度数组public boolean validPath(int n, int[][] edges, int source, int destination) {parent = new int[n];rank = new int[n];// 初始化并查集:每个节点的父节点为自己,rank 初始化为 1for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {parent[i] = i;rank[i] = 1;}// 遍历所有边,将两个节点连接(即在并查集中合并)for (int[] edge : edges) {union(edge[0], edge[1]);}// 检查起始节点和目标节点是否在同一集合中return find(source) == find(destination);}// 查找某个节点的根节点,同时进行路径压缩private int find(int x) {if (parent[x] != x) { // 如果当前节点不是它自己的父节点,则继续向上查找parent[x] = find(parent[x]);}return parent[x];}// 合并两个集合,使用 rank 优化合并private void union(int x, int y) {int rootX = find(x);int rootY = find(y);if (rootX != rootY) {// 比较两个集合的 rank,rank 小的合并到大的上if (rank[rootX] > rank[rootY]) {parent[rootY] = rootX; // 将 y 的根节点挂到 x 的根节点上} else if (rank[rootX] < rank[rootY]) {parent[rootX] = rootY; // 将 x 的根节点挂到 y 的根节点上} else {parent[rootY] = rootX; // 如果 rank 相同,随意合并,但要增加新根的 rankrank[rootX]++;}}}
}









![[WMCTF2020]Make PHP Great Again 2.01](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/9bef470f85ef4304906764a6c22b256f.png)