文章目录
- 前言
- 一、list
- 二、list类的初始化和尾插
- 三、list的迭代器的基本实现
- 四、list的完整实现
- 五、测试
- 六、整个list类
- 总结
前言
C++模拟实现list:list、list类的初始化和尾插、list的迭代器的基本实现、list的完整实现、测试、整个list类等的介绍
一、list
list本质上是一个双向带头循环链表。
实现list类,需要节点类(clase list_node)、迭代器(class __list_iterator);
节点类(clase list_node): 定义每个节点的结构;
迭代器(class __list_iterator): 使用节点的指针封装出一个类,可以使用运算符重载的形式更好的访问链表;
二、list类的初始化和尾插
namespace hhb
{// 节点template <class T>struct list_node{list_node(const T& val = T()): _next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr), _val(val){}list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;T _val;};// 链表template<class T> class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:list(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}void push_back(const T& x){Node* newNode = new Node(x);Node* tail = _head->_prev;newNode->_next = _head;newNode->_prev = tail;tail->_next = newNode;_head->_prev = newNode;}private:Node* _head;};
}
三、list的迭代器的基本实现
- 使用链表节点的指针封装出一个类,是list链表的访问可以向vector一样使用++等操作访问
- vector和list的使用,虽然在形式上一样,但是他们的底层是不一样的
- (*)vector迭代器是对指针的解引用
- (*)list迭代器是调用operator(解引用操作符)函数重载,本质是不一样的
对于const迭代器,是operator(*)和 operator(->)的运算符重载函数的返回值不一样,因此需要增加两个模板参数
- 即: (T& 和 T*)
// 迭代器
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator
{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;
public:__list_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_val;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_val;}self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const self& it) const{return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const self& it) const{return _node == it._node;}Node* _node;
};
- operator->运算符重载编译器会进行优化, 如下:
struct A
{
public:A(int a1 = 0, int a2 = 0): _a1(a1), _a2(a2){}int _a1;int _a2;
};
void test_list02()
{hhb::list<A> lt;lt.push_back(A(1, 1));lt.push_back(A(2, 2));lt.push_back(A(3, 3));lt.push_back(A(4, 4));lt.push_back(A(5, 5));hhb::list<A>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){//cout << (*it)._a1 << " " << (*it)._a2 << " " << endl;cout << it->_a1 << " " << it->_a2 << " " << endl;// 此处编译器进行了优化, it->返回的是T* 也就是 A*, 如果要访问A的成员// 按道理来讲,应该是 (it->)->_a1 / (it->)->_a2 来进行访问++it;}cout << endl;}
四、list的完整实现
- list需要有size()的接口,所以需要对链表节点个数进行计数,增加一个成员变量_size.
- 实现insert()和erase()接口后,push_back()和push_front()、pop_back()和pop_front()接口都可以复用接口。
- clear()只清除(不包含哨兵位的头节点)数据,不销毁链表
- 析构函数调用clear()后,释放_head节点(哨兵位的头节点)
- 拷贝构造函数在拷贝之前,一定要先自己初始化(创建哨兵位的头节点)
- 赋值(=)运算符重载使用现代写法,拷贝构造加交换函数加自动调用析构函数。
// 链表template<class T> class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _head->_next;}iterator end(){return _head;}const_iterator begin() const{return _head->_next;}const_iterator end() const{return _head;}void emptyInit(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}list(){emptyInit();}list(const list<T>& lt){emptyInit();for (auto e : lt){push_back(e);}}void swap(list<T>& lt){std::swap(_head, lt._head);std::swap(_size, lt._size);}list<T> operator=(list<T> lt){swap(lt);return *this;}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;_size = 0;}void push_back(const T& x){//Node* newNode = new Node(x);//Node* tail = _head->_prev;//newNode->_next = _head;//newNode->_prev = tail;//tail->_next = newNode;//_head->_prev = newNode;insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pos_front(){erase(begin());}iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* newNode = new Node(x);Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;newNode->_next = cur;newNode->_prev = prev;cur->_prev = newNode;prev->_next = newNode;++_size;return newNode;}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;cur = nullptr;--_size;return next;}//size_t size()//{// int sz = 0;// iterator it = begin();// while (it != end())// {// sz++;// ++it;// }// // return sz;//}size_t size(){return _size;}void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}_size = 0;}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};
}
五、测试
- 测试push_back, pop_back可以顺便测试insert, erase函数, 所以不单独测试insert和erase函数
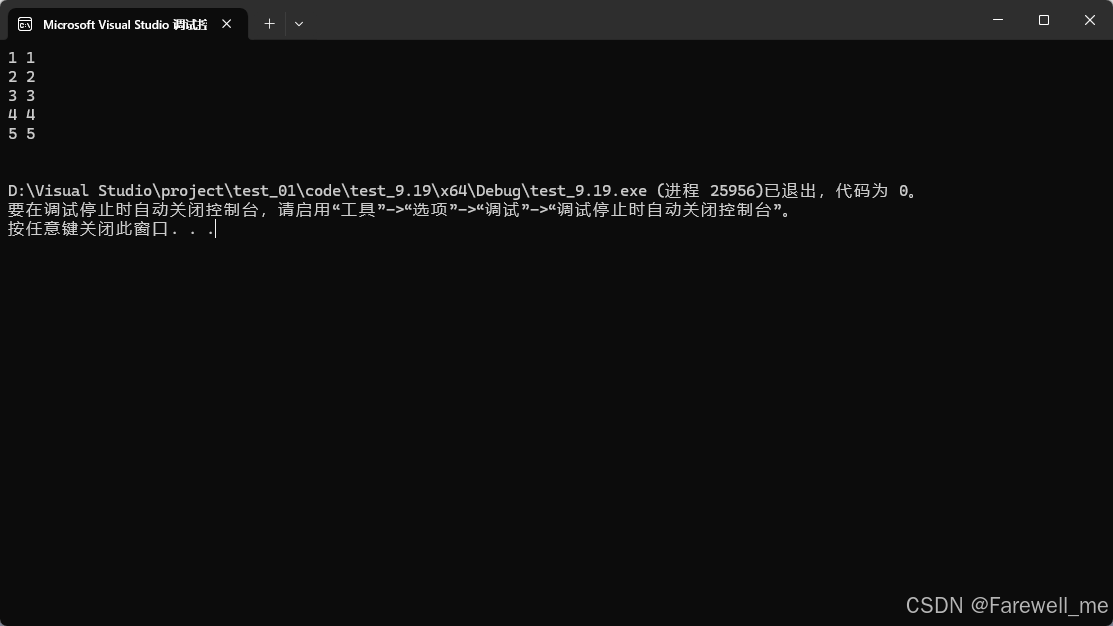
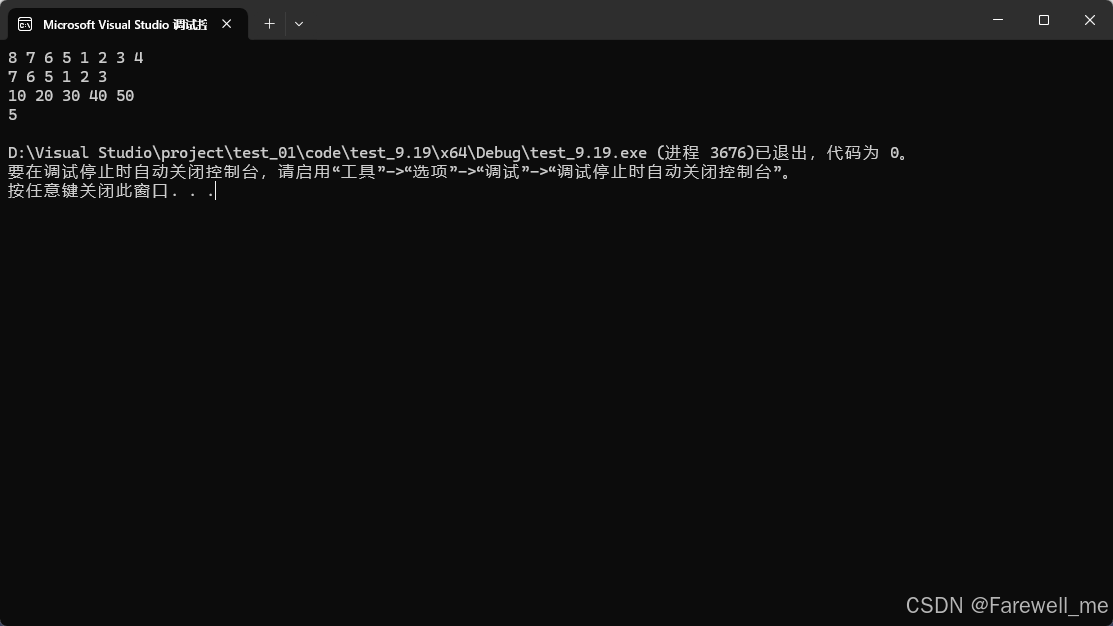
void test_list03()
{hhb::list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);lt.push_front(5);lt.push_front(6);lt.push_front(7);lt.push_front(8);for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;lt.pop_back();lt.pos_front();for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;lt.clear();lt.push_back(10);lt.push_back(20);lt.push_back(30);lt.push_back(40);lt.push_back(50);for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;cout << lt.size() << endl;}
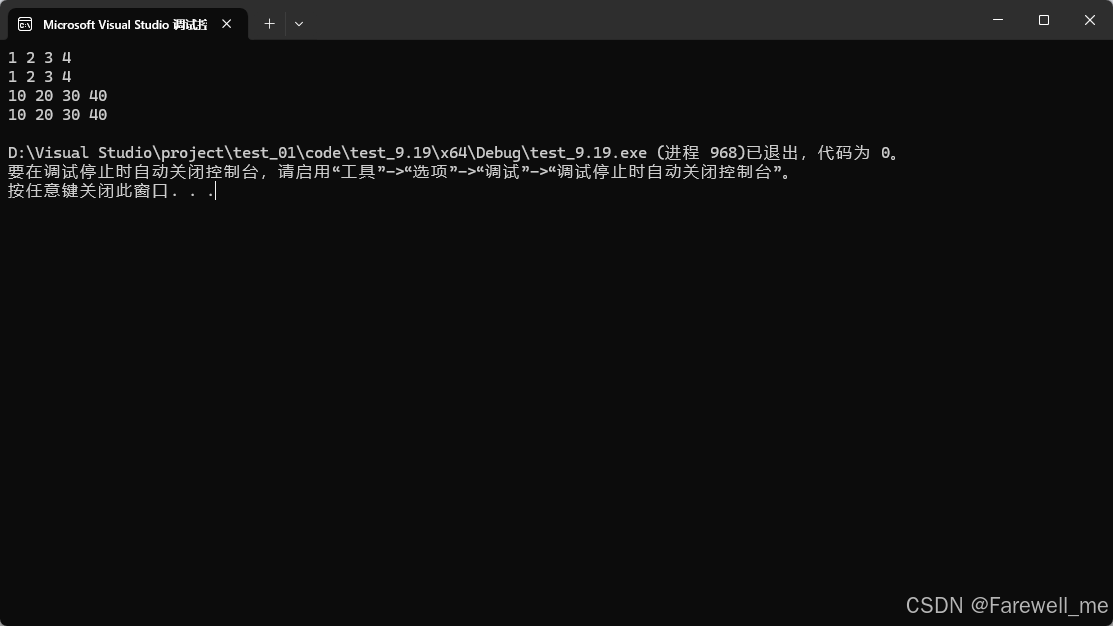
- 测试拷贝构造和赋值运算符重载
void test_list04()
{hhb::list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;hhb::list<int> lt1(lt);for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;hhb::list<int> lt2;lt2.push_back(10);lt2.push_back(20);lt2.push_back(30);lt2.push_back(40);lt1 = lt2;for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;for (auto e : lt2){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}
六、整个list类
// list.h
#pragma once#include <assert.h>
namespace hhb
{// 节点template <class T>struct list_node{list_node(const T& val = T()): _next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr), _val(val){}list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;T _val;};// 迭代器template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct __list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;public:__list_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_val;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_val;}self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const self& it) const{return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const self& it) const{return _node == it._node;}Node* _node;};// 链表template<class T> class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _head->_next;}iterator end(){return _head;}const_iterator begin() const{return _head->_next;}const_iterator end() const{return _head;}void emptyInit(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}list(){emptyInit();}list(const list<T>& lt){emptyInit();for (auto e : lt){push_back(e);}}void swap(list<T>& lt){std::swap(_head, lt._head);std::swap(_size, lt._size);}list<T> operator=(list<T> lt){swap(lt);return *this;}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;_size = 0;}void push_back(const T& x){//Node* newNode = new Node(x);//Node* tail = _head->_prev;//newNode->_next = _head;//newNode->_prev = tail;//tail->_next = newNode;//_head->_prev = newNode;insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pos_front(){erase(begin());}iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* newNode = new Node(x);Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;newNode->_next = cur;newNode->_prev = prev;cur->_prev = newNode;prev->_next = newNode;++_size;return newNode;}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;cur = nullptr;--_size;return next;}//size_t size()//{// int sz = 0;// iterator it = begin();// while (it != end())// {// sz++;// ++it;// }// // return sz;//}size_t size(){return _size;}void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}_size = 0;}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};
}
- 整个测试
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
#include "list.h"void print1(const hhb::list<int>& lt)
{hhb::list<int>::const_iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;
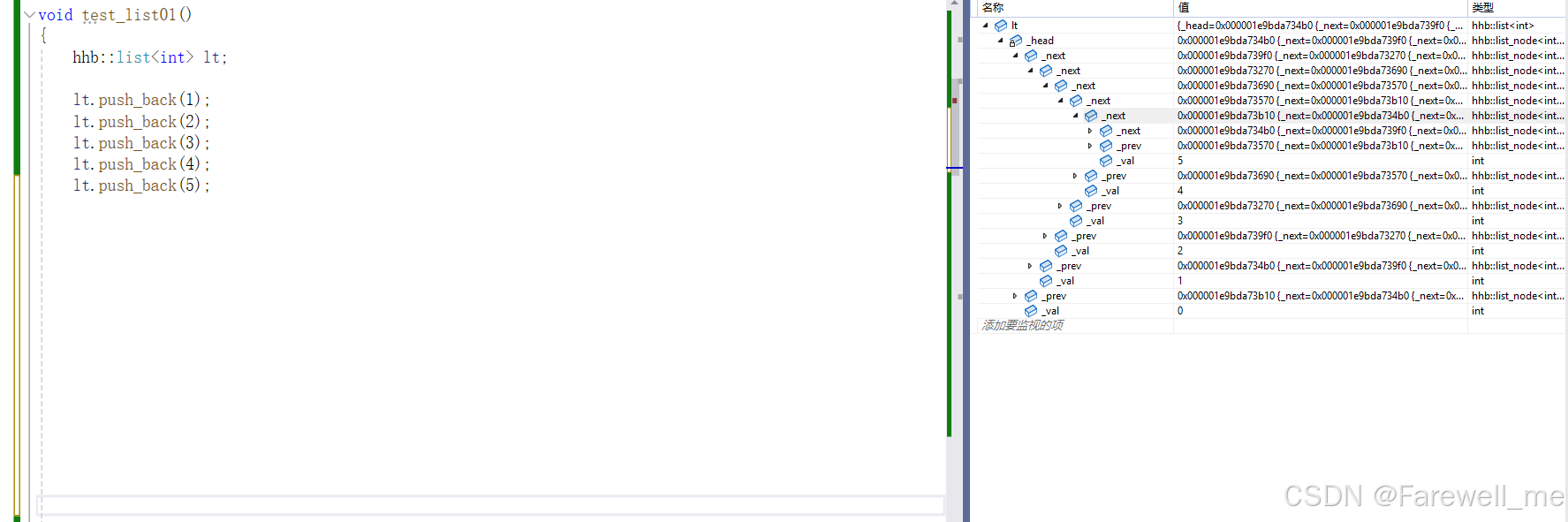
}void test_list01()
{hhb::list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);lt.push_back(5);hhb::list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;print1(lt);
}struct A
{
public:A(int a1 = 0, int a2 = 0): _a1(a1), _a2(a2){}int _a1;int _a2;
};void test_list02()
{hhb::list<A> lt;lt.push_back(A(1, 1));lt.push_back(A(2, 2));lt.push_back(A(3, 3));lt.push_back(A(4, 4));lt.push_back(A(5, 5));hhb::list<A>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){//cout << (*it)._a1 << " " << (*it)._a2 << " " << endl;cout << it->_a1 << " " << it->_a2 << " " << endl;// 此处编译器进行了优化, it->返回的是T* 也就是 A*, 如果要访问A的成员// 按道理来讲,应该是 (it->)->_a1 / (it->)->_a2 来进行访问++it;}cout << endl;}void test_list03()
{hhb::list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);lt.push_front(5);lt.push_front(6);lt.push_front(7);lt.push_front(8);for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;lt.pop_back();lt.pos_front();for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;lt.clear();lt.push_back(10);lt.push_back(20);lt.push_back(30);lt.push_back(40);lt.push_back(50);for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;cout << lt.size() << endl;}void test_list04()
{hhb::list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;hhb::list<int> lt1(lt);for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;hhb::list<int> lt2;lt2.push_back(10);lt2.push_back(20);lt2.push_back(30);lt2.push_back(40);lt1 = lt2;for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;for (auto e : lt2){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}int main()
{//test_list01();test_list02();//test_list03();//test_list04();return 0;
}
总结
C++模拟实现list:list、list类的初始化和尾插、list的迭代器的基本实现、list的完整实现、测试、整个list类等的介绍
![[Linux]从零开始的Minecraft服务器搭建教程](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/0d45750fd73443c399b59437d3ac8f4d.png)















![[uni-app]小兔鲜-02项目首页](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/76ac29ad7495165212f0eb20b78e3949.png)
