传统上,一般把NLP的研究领域大致分为自然语言理解(NLU)和自然语言生成(NLG)两种。
NLU侧重于如何理解文本,包括文本分类、命名实体识别、指代消歧、句法分析、机器阅读理解等;
NLG则侧重于理解文本后如何生成自然文本,包括自动摘要、机器翻译、问答系统、对话机器人等。
但是以ChatGPT为代表的大模型出来后,这些传统的NLP的细分研究领域基本可以说都失去了独立研究的价值。
为什么呢?因为大模型可以用统一的范式通通将它们搞定,并且效果非常出众。
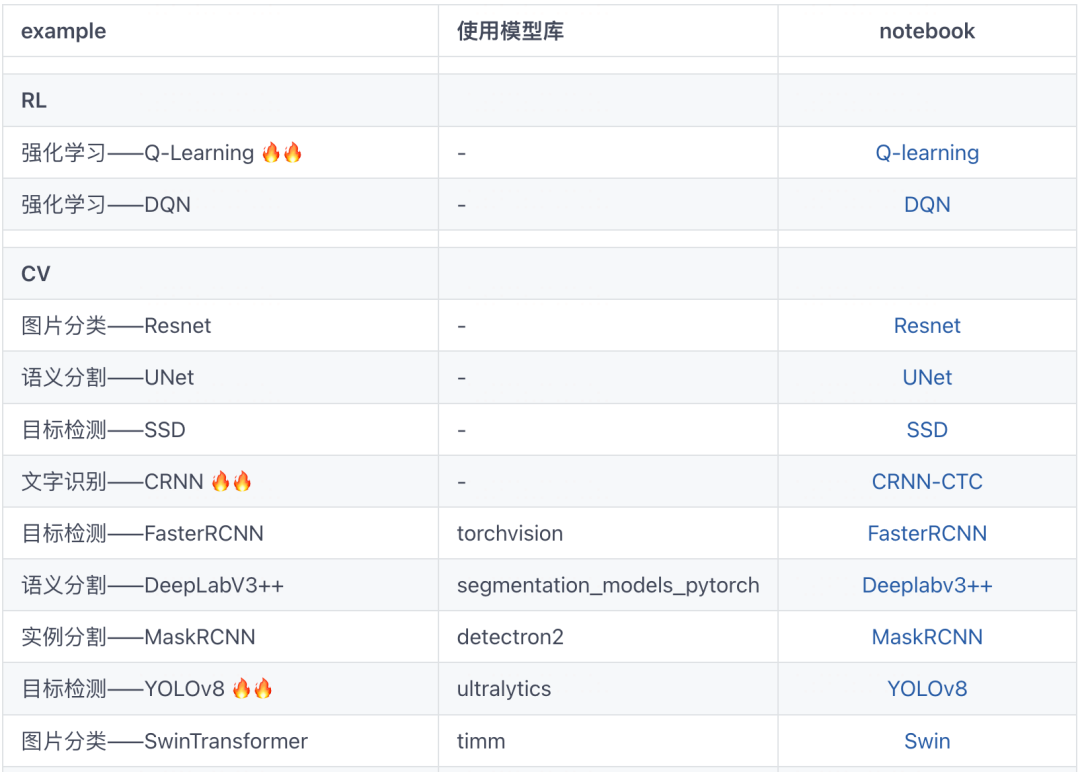
在之前的例子中,我们演示了使用QLoRA算法来对BaiChuan-13B实施微调以处理最简单的文本分类任务。
Baichuan-13B 保姆级微调范例
在外卖评论数据集上,微调后测试集acc由0.8925提升到0.9015约提升了1个百分点。
在本例中,我们使用几乎相同的流程和方法来微调BaiChuan-13B以更好地处理命名实体识别任务。
实验结果显示,在NER任务上经过微调,我们的f1-score取得了不可忽略的提升(0.4313—>0.8768)。
注:跑完本流程需要至少32G的CPU,需要约2个小时的训练时间。
公众号算法美食屋后台回复关键词:torchkeras,获取本文notebook源码和dfner_13k.pkl数据集下载链接~
在我们正式开始之前,请允许我用简短的话给没有NLP基础知识的小伙伴讲解一下什么是命名实体识别。
命名实体识别NER任务是NLP的一个常见基础任务,
它是Named Entity Recognization的简称。
简单地说,就是识别一个句子中的各种 名称实体,诸如:人名,地名,机构 等。
例如对于下面这句话:
小明对小红说:"你听说过安利吗?"其命名实体可以抽取表示如下:
{"人名": ["小明","小红"], "组织": ["安利"]}〇,预训练模型
我们需要从 https://huggingface.co/baichuan-inc/Baichuan-13B-Chat 下载baichuan-13b-chat的模型。
国内可能速度会比较慢,总共有25个G左右,网速不太好的话,大概可能需要两到三个小时。
如果网络不稳定,也可以手动从这个页面一个一个下载全部文件然后放置到 一个文件夹中例如 'baichuan-13b' 以便读取。
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM,AutoConfig, AutoModel, BitsAndBytesConfig
from transformers.generation.utils import GenerationConfig
import torch.nn as nn#使用QLoRA引入的 NF4量化数据类型以节约显存
model_name_or_path ='../baichuan-13b' #远程 'baichuan-inc/Baichuan-13B-Chat'bnb_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_4bit=True,bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.float16,bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True,bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",llm_int8_threshold=6.0,llm_int8_has_fp16_weight=False,)tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path, trust_remote_code=True)model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path,quantization_config=bnb_config,trust_remote_code=True) model.generation_config = GenerationConfig.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)from IPython.display import clear_output
messages = []
messages.append({"role": "user","content": "世界上第二高的山峰是哪座?"})
response = model.chat(tokenizer,messages=messages,stream=True)
for res in response:print(res)clear_output(wait=True)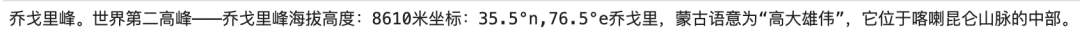
下面我们设计一个7-shot-prompt方法,测试一下BaiChuan13b的实体抽取能力。
prefix = '''命名实体识别:抽取文本中的 人名,地点,组织 这三类命名实体,并按照json格式返回结果。下面是一些范例:小明对小红说:"你听说过安利吗?" -> {"人名": ["小明","小红"], "组织": ["安利"]}
现在,每年有几十万中国人到美国访问,几千名中国留学生到美国就学。 -> {"地点": ["中国", "美国"]}
中国是联合国安理会常任理事国之一。 -> {"地点": ["中国"], "组织": ["联合国"]}请对下述文本进行实体抽取,返回json格式。'''def get_prompt(text):return prefix+text+' -> 'def get_message(prompt,response):return [{"role": "user", "content": f'{prompt} -> '},{"role": "assistant", "content": response}]messages = [{"role": "user", "content": get_prompt("一些摩洛哥球迷已按捺不住,在看台上欢呼雀跃")}]
response = model.chat(tokenizer, messages)
print(response){"地点":["摩洛哥"], "组织":[]}messages = messages+[{"role": "assistant", "content": "{'地点': ['摩洛哥']}"}]
messages.extend(get_message("这次轮到北京国安队,不知会不会再步后尘?","{'组织': ['北京国安队']}"))
messages.extend(get_message("革命党人孙中山在澳门成立同盟会分会","{'人名': ['孙中山'], '地名': ['澳门'], '组织': ['同盟会']}"))
messages.extend(get_message("我曾在安徽芜湖市和上海浦东打工。","{'地点': ['安徽芜湖市', '上海浦东']}"))
display(messages)def predict(text,temperature=0.01):model.generation_config.temperature=temperatureresponse = model.chat(tokenizer, messages = messages+[{'role':'user','content':f'{text} -> '}])return responsepredict('杜甫是李白的粉丝。')"{'人名': ['杜甫', '李白']}"我们拿一个开源的中文NER数据集来测试一下未经微调,仅仅使用7-shot-prompt的预训练模型的效果。
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import pandas as pd df = pd.read_pickle('dfner_13k.pkl')
dfdata,dftest = train_test_split(df,test_size=300,random_state=42)
dftrain,dfval = train_test_split(dfdata,test_size=200,random_state=42)preds = ['' for x in dftest['target']]
for i in tqdm(range(len(preds))):preds[i] = predict(dftest['text'].iloc[i])def toset(s):try:dic = eval(str(s))res = []for k,v in dic.items():for x in v:if x:res.append((k,x))return set(res)except Exception as err:print(err)return set()dftest['pred'] = [toset(x) for x in preds]
dftest['gt'] = [toset(x) for x in dftest['target']]
dftest['tp_cnt'] = [len(pred>) for pred,gt in zip(dftest['pred'],dftest['gt'])]
dftest['pred_cnt'] = [len(x) for x in dftest['pred']]
dftest['gt_cnt'] = [len(x) for x in dftest['gt']]precision = sum(dftest['tp_cnt'])/sum(dftest['pred_cnt'])
print('precision = '+str(precision))recall = sum(dftest['tp_cnt'])/sum(dftest['gt_cnt'])
print('recall = '+str(recall))f1 = 2*precision*recall/(precision+recall)
print('f1_score = '+str(f1))precision = 0.4316109422492401
recall = 0.45151033386327505
f1_score = 0.44133644133644134微调前 f1_score为 0.44.
一,准备数据
我们仿照百川模型的 model._build_chat_input 方法来进行token编码,同时把需要学习的内容添加label.
1,token编码
import torch #将messages编码成 token, 同时返回labels
#注意baichuan-13b通过插入tokenizer.user_token_id和tokenizer.assistant_token_id 来区分用户和机器人会话内容# reference@ model._build_chat_input?
def build_chat_input(messages, model=model,tokenizer=tokenizer, max_new_tokens: int=0):max_new_tokens = max_new_tokens or model.generation_config.max_new_tokensmax_input_tokens = model.config.model_max_length - max_new_tokensmax_input_tokens = max(model.config.model_max_length // 2, max_input_tokens)total_input, round_input, total_label, round_label = [], [], [], []for i, message in enumerate(messages[::-1]):content_tokens = tokenizer.encode(message['content'])if message['role'] == 'user':round_input = [model.generation_config.user_token_id] + content_tokens + round_inputround_label = [-100]+[-100 for _ in content_tokens]+ round_labelif total_input and len(total_input) + len(round_input) > max_input_tokens:breakelse:total_input = round_input + total_inputtotal_label = round_label + total_labelif len(total_input) >= max_input_tokens:breakelse:round_input = []round_label = []elif message['role'] == 'assistant':round_input = [model.generation_config.assistant_token_id] + content_tokens + [model.generation_config.eos_token_id] + round_inputif i==0: #仅对最后一轮的target进行学习round_label = [-100] + content_tokens + [model.generation_config.eos_token_id]+ round_labelelse:round_label = [-100] + [-100 for _ in content_tokens] + [-100]+ round_labelelse:raise ValueError(f"message role not supported yet: {message['role']}")total_input = total_input[-max_input_tokens:] # truncate lefttotal_label = total_label[-max_input_tokens:]total_input.append(model.generation_config.assistant_token_id)total_label.append(-100)return total_input,total_label2,做数据集
from torch.utils.data import Dataset,DataLoader
from copy import deepcopy
class MyDataset(Dataset):def __init__(self,df,messages):self.df = df self.messages = messagesdef __len__(self):return len(self.df)def get_samples(self,index):samples = []d = dict(self.df.iloc[index])samples.append(d)return samplesdef get_messages(self,index):samples = self.get_samples(index)messages = deepcopy(self.messages)for i,d in enumerate(samples):messages.append({'role':'user','content':d['text']+' -> '})messages.append({'role':'assistant','content':str(d['target'])})return messagesdef __getitem__(self,index):messages = self.get_messages(index)input_ids, labels = build_chat_input(messages)return {'input_ids':input_ids,'labels':labels}def show_sample(self,index):samples = self.get_samples(index)print(samples)ds_train = MyDataset(dftrain,messages)
ds_val = MyDataset(dfval,messages)3,创建管道
def data_collator(examples: list):len_ids = [len(example["input_ids"]) for example in examples]longest = max(len_ids) #之后按照batch中最长的input_ids进行paddinginput_ids = []labels_list = []for length, example in sorted(zip(len_ids, examples), key=lambda x: -x[0]):ids = example["input_ids"]labs = example["labels"]ids = ids + [tokenizer.pad_token_id] * (longest - length)labs = labs + [-100] * (longest - length)input_ids.append(torch.LongTensor(ids))labels_list.append(torch.LongTensor(labs))input_ids = torch.stack(input_ids)labels = torch.stack(labels_list)return {"input_ids": input_ids,"labels": labels,}import torch
dl_train = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(ds_train,num_workers=2,batch_size=1,pin_memory=True,shuffle=True,collate_fn = data_collator)dl_val = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(ds_val,num_workers=2,batch_size=1,pin_memory=True,shuffle=False,collate_fn = data_collator)for batch in dl_train:break#试跑一个batch
out = model(**batch)
out.loss#采样300个batch作为一个epoch,便于较快验证
dl_train.size = 300二,定义模型
下面我们将使用QLoRA(实际上用的是量化的AdaLoRA)算法来微调Baichuan-13b模型。
from peft import get_peft_config, get_peft_model, TaskType
model.supports_gradient_checkpointing = True #
model.gradient_checkpointing_enable()
model.enable_input_require_grads()model.config.use_cache = False # silence the warnings. Please re-enable for inference!import bitsandbytes as bnb
def find_all_linear_names(model):"""找出所有全连接层,为所有全连接添加adapter"""cls = bnb.nn.Linear4bitlora_module_names = set()for name, module in model.named_modules():if isinstance(module, cls):names = name.split('.')lora_module_names.add(names[0] if len(names) == 1 else names[-1])if 'lm_head' in lora_module_names: # needed for 16-bitlora_module_names.remove('lm_head')return list(lora_module_names)from peft import prepare_model_for_kbit_training
model = prepare_model_for_kbit_training(model)lora_modules = find_all_linear_names(model)
print(lora_modules)['down_proj', 'gate_proj', 'W_pack', 'o_proj', 'up_proj']from peft import AdaLoraConfig
peft_config = AdaLoraConfig(task_type=TaskType.CAUSAL_LM, inference_mode=False,r=16,lora_alpha=16, lora_dropout=0.05,target_modules= lora_modules
)peft_model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)peft_model.is_parallelizable = True
peft_model.model_parallel = True
peft_model.print_trainable_parameters()trainable params: 41,843,040 || all params: 7,002,181,160 || trainable%: 0.5975715144165165out = peft_model.forward(**batch)
out[0]三,训练模型
from torchkeras import KerasModel
from accelerate import Accelerator class StepRunner:def __init__(self, net, loss_fn, accelerator=None, stage = "train", metrics_dict = None, optimizer = None, lr_scheduler = None):self.net,self.loss_fn,self.metrics_dict,self.stage = net,loss_fn,metrics_dict,stageself.optimizer,self.lr_scheduler = optimizer,lr_schedulerself.accelerator = accelerator if accelerator is not None else Accelerator() if self.stage=='train':self.net.train() else:self.net.eval()def __call__(self, batch):#losswith self.accelerator.autocast():loss = self.net.forward(**batch)[0]#backward()if self.optimizer is not None and self.stage=="train":self.accelerator.backward(loss)if self.accelerator.sync_gradients:self.accelerator.clip_grad_norm_(self.net.parameters(), 1.0)self.optimizer.step()if self.lr_scheduler is not None:self.lr_scheduler.step()self.optimizer.zero_grad()all_loss = self.accelerator.gather(loss).sum()#losses (or plain metrics that can be averaged)step_losses = {self.stage+"_loss":all_loss.item()}#metrics (stateful metrics)step_metrics = {}if self.stage=="train":if self.optimizer is not None:step_metrics['lr'] = self.optimizer.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr']else:step_metrics['lr'] = 0.0return step_losses,step_metricsKerasModel.StepRunner = StepRunner #仅仅保存QLora可训练参数
def save_ckpt(self, ckpt_path='checkpoint', accelerator = None):unwrap_net = accelerator.unwrap_model(self.net)unwrap_net.save_pretrained(ckpt_path)def load_ckpt(self, ckpt_path='checkpoint'):import osself.net.load_state_dict(torch.load(os.path.join(ckpt_path,'adapter_model.bin')),strict =False)self.from_scratch = FalseKerasModel.save_ckpt = save_ckpt
KerasModel.load_ckpt = load_ckptoptimizer = bnb.optim.adamw.AdamW(peft_model.parameters(),lr=6e-05,is_paged=True) #'paged_adamw'
keras_model = KerasModel(peft_model,loss_fn =None,optimizer=optimizer)
ckpt_path = 'baichuan13b_ner'# keras_model.load_ckpt(ckpt_path) #支持加载微调后的权重继续训练(断点续训)
keras_model.fit(train_data = dl_train,val_data = dl_val,epochs=100,patience=10,monitor='val_loss',mode='min',ckpt_path = ckpt_path)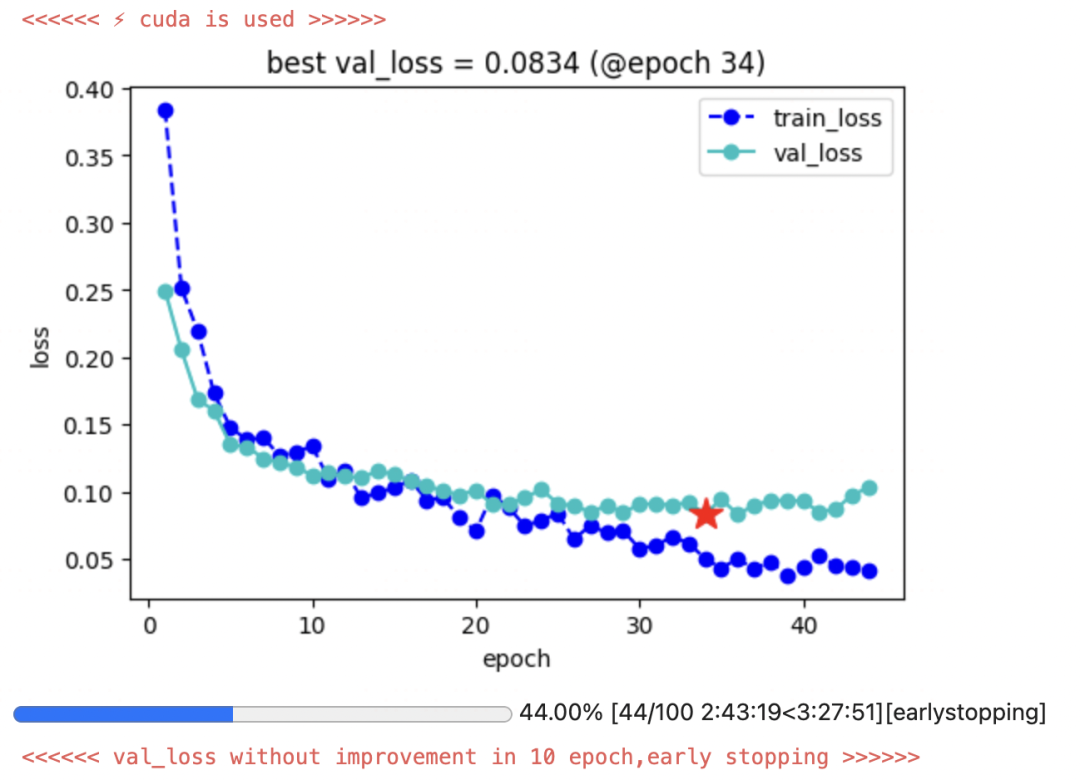
四,保存模型
为减少GPU压力,此处可重启kernel释放显存
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM,AutoConfig, AutoModel, BitsAndBytesConfig
from transformers.generation.utils import GenerationConfig
import torch.nn as nn
model_name_or_path ='../baichuan-13b'
ckpt_path = 'baichuan13b_ner'
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path,trust_remote_code=True
)
model_old = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path,trust_remote_code=True,low_cpu_mem_usage=True,torch_dtype=torch.float16,device_map='auto'
)from peft import PeftModel#可能需要5分钟左右
peft_model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model_old, ckpt_path)
model_new = peft_model.merge_and_unload()from transformers.generation.utils import GenerationConfig
model_new.generation_config = GenerationConfig.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)from IPython.display import clear_output
messages = []
messages.append({"role": "user","content": "世界上第二高的山峰是什么?"})
response = model_new.chat(tokenizer,messages=messages,stream=True)
for res in response:print(res)clear_output(wait=True)乔戈里峰。世界第二高峰———乔戈里峰西方登山者称其为k2峰,海拔高度是8611米,位于喀喇昆仑山脉的中巴边境上.
save_path = 'baichuan-13b-ner'tokenizer.save_pretrained(save_path)
model_new.save_pretrained(save_path)!cp ../baichuan-13b/*.py baichuan-13b-ner五,使用模型
为减少GPU压力,此处可再次重启kernel释放显存。
import torch
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM,AutoConfig, BitsAndBytesConfig
from transformers.generation.utils import GenerationConfig
import torch.nn as nnimport warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')model_name_or_path = 'baichuan-13b-ner'...
...我们测试一下微调后的效果。
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import datasets
from tqdm import tqdm from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import pandas as pd df = pd.read_pickle('dfner_13k.pkl')
dfdata,dftest = train_test_split(df,test_size=300,random_state=42)
dftrain,dfval = train_test_split(dfdata,test_size=200,random_state=42)
...
...
...precision = sum(dftest['tp_cnt'])/sum(dftest['pred_cnt'])
print('precision = '+str(precision))recall = sum(dftest['tp_cnt'])/sum(dftest['gt_cnt'])
print('recall = '+str(recall))f1 = 2*precision*recall/(precision+recall)
print('f1_score = '+str(f1))precision = 0.9139280125195618
recall = 0.8427128427128427
f1_score = 0.876876876876877微调后的f1_score为0.8768,相比微调前的f1_score=0.44,取得了不可忽视的巨大提升。
公众号算法美食屋台回复关键词:torchkeras,获取本文notebook源码和更多有趣范例~