趋势(一)利用python绘制折线图
折线图( Line Chart)简介
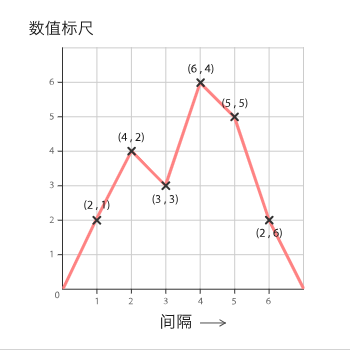
折线图用于在连续间隔或时间跨度上显示定量数值,最常用来显示趋势和关系(与其他折线组合起来)。折线图既能直观地显示数量随时间的变化趋势,也能展示两个变量的关系。
快速绘制
-
基于matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np# 自定义数据 values = np.cumsum(np.random.randn(1000,1))# 绘制折线图 plt.plot(values) plt.show()
-
基于seaborn
import seaborn as sns import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np# 自定义数据 values = np.cumsum(np.random.randn(1000,1))# 绘制折线图 sns.lineplot(x=np.array(range(1, 1001)), y=values.ravel()) # 使用 ravel() 将 values 转化为一维 plt.show()
-
基于plotly
import plotly.graph_objects as go import numpy as np# 自定义数据 values = np.cumsum(np.random.randn(1000,1))# 绘制折线图 fig = go.Figure(data=go.Scatter(x=list(range(1, 1001)), y=values.ravel(), mode='lines')) fig.show()
-
基于pandas
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import pandas as pd# 自定义数据 values = np.cumsum(np.random.randn(1000,1)) df = pd.DataFrame(values, columns=['Values'])# 绘制折线图 df.plot() plt.show()
定制多样化的折线图
自定义折线图一般是结合使用场景对相关参数进行修改,并辅以其他的绘图知识。参数信息可以通过官网进行查看,其他的绘图知识则更多来源于实战经验,大家不妨将接下来的绘图作为一种学习经验,以便于日后总结。
通过matplotlib绘制多样化的折线图
matplotlib主要利用plot绘制折线图,可以通过matplotlib.pyplot.plot了解更多用法
-
修改参数
import matplotlib as mpl import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import pandas as pdplt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签# 自定义数据 df=pd.DataFrame({'x_values': range(1,11), 'y_values': np.random.randn(10) })# 初始化布局 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,3))# 自定义颜色 plt.subplot(1, 3, 1) plt.plot( 'x_values', 'y_values', data=df, color='skyblue') plt.title('自定义颜色')# 自定义透明度 plt.subplot(1, 3, 2) plt.plot( 'x_values', 'y_values', data=df, color='skyblue', alpha=0.3) plt.title('自定义透明度')# 自定义线条 plt.subplot(1, 3, 3) plt.plot( 'x_values', 'y_values', data=df, linestyle='dashed', linewidth=5) plt.title('自定义线条')plt.show()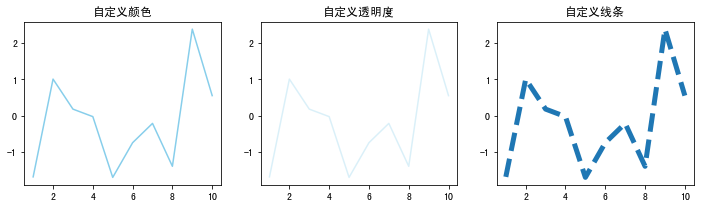
-
带注释的折线图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import pandas as pdplt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签# 自定义数据 dates = []for date in range(1970,2023):dates.append(str(date))sample_size = 2023-1970 variable = np.random.normal(100,15,sample_size,)df = pd.DataFrame({'date': dates,'value': variable})# 初始化布局 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))# 1-基本折线图 plt.subplot(2, 1, 1) plt.plot(df['date'], df['value'])# 轴标签 plt.xlabel('X-axis') plt.ylabel('Y-axis') plt.title('基本折线图')# 刻度 plt.xticks(rotation=45)# 2-带注释的折线图 plt.subplot(2, 1, 2) plt.plot(df['date'], df['value'])# 轴标签 plt.xlabel('X-axis') plt.ylabel('Y-axis') plt.title('带注释的折线图')# 刻度 plt.xticks(rotation=45)# 添加文本注释 plt.text(df['date'].iloc[38], # x位置df['value'].iloc[1], # y位置'What a nice chart!', # 文本注释fontsize=13,color='red')# 找到最大值索引 highest_index = df['value'].idxmax()# 最高值标记 plt.scatter(df['date'].iloc[highest_index],df['value'].iloc[highest_index],color='blue',marker='o', # 标记特殊的店s=100,)# 计算均值 median_value = df['value'].median()# 添加均值线 plt.axhline(y=median_value, color='green', linestyle='--', label='Reference Line (Median)')fig.tight_layout() # 自动调整间距 plt.show()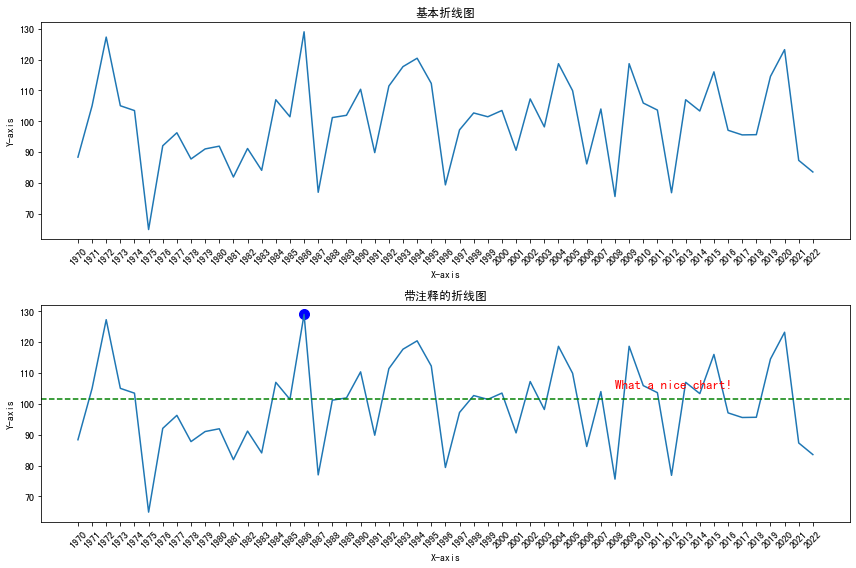
-
对数变换的折线图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.ticker import MultipleLocator import numpy as np import pandas as pdplt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签# 自定义数据 x = np.linspace(1, 10, 100) y = np.exp(x) df = pd.DataFrame({'x': x, 'y': y})# 初始化布局 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,4))# 1-基本折线图 plt.subplot(1, 2, 1) plt.plot(df['x'], df['y'])# 轴标签 plt.xlabel('X-axis') plt.ylabel('Y-axis') plt.title('基本折线图')# 添加网格线 plt.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.6)# 2-对数转化折线图 plt.subplot(1, 2, 2) plt.plot(df['x'], df['y'])# y轴对数化 plt.yscale('log')# 轴标签 plt.xlabel('X-axis') plt.ylabel('Y-axis') plt.title('对数化的折线图')# 对数刻度的网格 y_major_locator = MultipleLocator(3000) plt.gca().yaxis.set_major_locator(y_major_locator)# 添加网格线 plt.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.6)plt.show()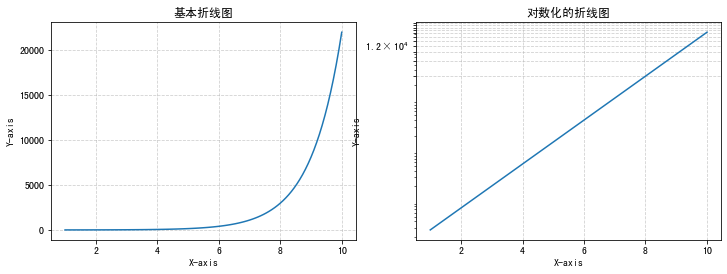
-
双轴折线图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from datetime import datetime, timedelta from matplotlib import colorsplt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签rng = np.random.default_rng(1234)date = [datetime(2019, 1, 1) + timedelta(i) for i in range(100)] temperature = np.arange(100) ** 2.5 / 10000 + rng.uniform(size=100) price = np.arange(120, 20, -1) ** 1.5 / 10 + rng.uniform(size=100)# 设置多子图 fig, axarr = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(12, 8))# 1-基础的双轴折线图 ax1 = axarr[0, 0] ax2 = ax1.twinx() ax1.plot(date, temperature) ax2.plot(date, price) ax1.set_title('基础的双轴折线图')# 2-自定义颜色双轴 COLOR_TEMPERATURE = "#69b3a2" COLOR_PRICE = "#3399e6"ax1 = axarr[0, 1] ax2 = ax1.twinx() ax1.plot(date, temperature, color=COLOR_TEMPERATURE, lw=3) ax2.plot(date, price, color=COLOR_PRICE, lw=4)ax1.set_xlabel("Date") ax1.set_ylabel("Temperature (Celsius °)", color=COLOR_TEMPERATURE, fontsize=14) ax1.tick_params(axis="y", labelcolor=COLOR_TEMPERATURE) ax2.set_ylabel("Price ($)", color=COLOR_PRICE, fontsize=14) ax2.tick_params(axis="y", labelcolor=COLOR_PRICE) ax1.set_title('自定义颜色双轴')# 3-折线与条形图组合 ax1 = axarr[1, 0] ax2 = ax1.twinx() ax1.bar(date, temperature, color=COLOR_TEMPERATURE, edgecolor="black", alpha=0.4, width=1.0) ax2.plot(date, price, color=COLOR_PRICE, lw=4)ax1.set_xlabel("Date") ax1.set_ylabel("Temperature (Celsius °)", color=COLOR_TEMPERATURE, fontsize=14) ax1.tick_params(axis="y", labelcolor=COLOR_TEMPERATURE)ax2.set_ylabel("Price ($)", color=COLOR_PRICE, fontsize=14) ax2.tick_params(axis="y", labelcolor=COLOR_PRICE)fig.autofmt_xdate() ax1.set_title("折线与条形图组合")# 4-自定义组合图样式 color = list(colors.to_rgba(COLOR_TEMPERATURE)) color[3] = 0.4ax1 = axarr[1, 1] ax2 = ax1.twinx() ax1.bar(date, temperature, color=color, edgecolor="black", width=1.0) ax2.plot(date, price, color=COLOR_PRICE, lw=4)ax1.set_xlabel("Date") ax1.set_ylabel("Temperature (Celsius °)", color=COLOR_TEMPERATURE, fontsize=14) ax1.tick_params(axis="y", labelcolor=COLOR_TEMPERATURE)ax2.set_ylabel("Price ($)", color=COLOR_PRICE, fontsize=14) ax2.tick_params(axis="y", labelcolor=COLOR_PRICE)fig.autofmt_xdate() ax1.set_title("自定义组合图样式")fig.tight_layout() # 自动调整间距 plt.show()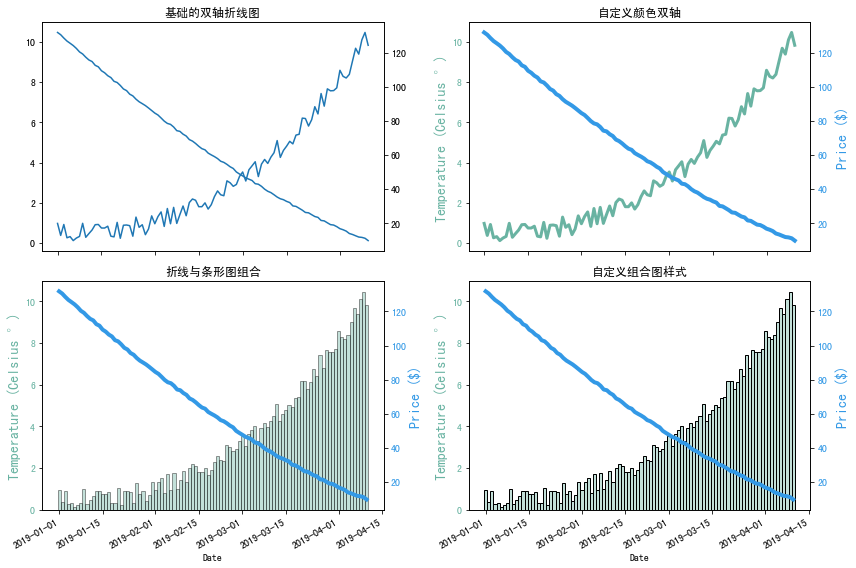
-
多个折线图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from datetime import datetime, timedelta from matplotlib import colors import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspecplt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签# 创建 2x3 的大布局 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(18, 8)) gs = gridspec.GridSpec(2, 3, figure=fig) # 获得每个子图的位置 ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 0]) ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 1]) ax3 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 2]) # ax4 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1, 0]) # ax5 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1, 1]) ax6 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1, 2])# 1-基础的多折线图 df=pd.DataFrame({'x_values': range(1,11), 'y1_values': np.random.randn(10), 'y2_values': np.random.randn(10)+range(1,11), 'y3_values': np.random.randn(10)+range(11,21) })ax1.plot( 'x_values', 'y1_values', data=df, marker='o', markerfacecolor='blue', markersize=12, color='skyblue', linewidth=4) ax1.plot( 'x_values', 'y2_values', data=df, marker='', color='olive', linewidth=2) ax1.plot( 'x_values', 'y3_values', data=df, marker='', color='olive', linewidth=2, linestyle='dashed', label="toto") ax1.legend() ax1.set_title('基础的多折线图')# 2-高亮显示一组 df=pd.DataFrame({'x': range(1,11), 'y1': np.random.randn(10), 'y2': np.random.randn(10)+range(1,11), 'y3': np.random.randn(10)+range(11,21), 'y4': np.random.randn(10)+range(6,16), 'y5': np.random.randn(10)+range(4,14)+(0,0,0,0,0,0,0,-3,-8,-6), 'y6': np.random.randn(10)+range(2,12), 'y7': np.random.randn(10)+range(5,15), 'y8': np.random.randn(10)+range(4,14) })for column in df.drop('x', axis=1):ax2.plot(df['x'], df[column], marker='', color='grey', linewidth=1, alpha=0.4) ax2.plot(df['x'], df['y5'], marker='', color='orange', linewidth=4, alpha=0.7) # 高亮y5 ax2.set_xlim(0,12) # 增加注释 num=0 for i in df.values[9][1:]:num+=1name=list(df)[num]if name != 'y5':ax2.text(10.2, i, name, horizontalalignment='left', size='small', color='grey')else:ax2.text(10.2, i, 'Mr Orange', horizontalalignment='left', size='small', color='orange') # 高亮组的文本注释 ax2.set_title("高亮显示一组")# 3-多折线模式(Spaghetti Plot) df=pd.DataFrame({'x': range(1,11), 'y1': np.random.randn(10), 'y2': np.random.randn(10)+range(1,11), 'y3': np.random.randn(10)+range(11,21), 'y4': np.random.randn(10)+range(6,16), 'y5': np.random.randn(10)+range(4,14)+(0,0,0,0,0,0,0,-3,-8,-6), 'y6': np.random.randn(10)+range(2,12), 'y7': np.random.randn(10)+range(5,15), 'y8': np.random.randn(10)+range(4,14), 'y9': np.random.randn(10)+range(4,14), 'y10': np.random.randn(10)+range(2,12) })palette = plt.get_cmap('Set1') num=0 for column in df.drop('x', axis=1):num+=1ax3.plot(df['x'], df[column], marker='', color=palette(num), linewidth=1, alpha=0.9, label=column)ax3.legend(loc=2, ncol=2) ax3.set_title("多折线模式(Spaghetti Plot)")# 4-多折线小图 df=pd.DataFrame({'x': range(1,11), 'y1': np.random.randn(10), 'y2': np.random.randn(10)+range(1,11), 'y3': np.random.randn(10)+range(11,21), 'y4': np.random.randn(10)+range(6,16), 'y5': np.random.randn(10)+range(4,14)+(0,0,0,0,0,0,0,-3,-8,-6), 'y6': np.random.randn(10)+range(2,12), 'y7': np.random.randn(10)+range(5,15), 'y8': np.random.randn(10)+range(4,14), 'y9': np.random.randn(10)+range(4,14) }) # 在第一行第一列的位置创建3*3的子布局 ax4 = gridspec.GridSpecFromSubplotSpec(3, 3, subplot_spec=gs[1, 0]) # 在 3x3 的小布局中添加子图 axes = [] for i in range(3):for j in range(3):ax = fig.add_subplot(ax4[i, j])axes.append(ax) # 将子图句柄添加到列表中 num = 0 for column in df.drop('x', axis=1):num += 1ax = axes[num - 1]ax.plot(df['x'], df[column], marker='', color=palette(num), linewidth=1.9, alpha=0.9, label=column)ax.set_xlim(0,10)ax.set_ylim(-2,22)# 如果当前子图不在最左边,就不显示y轴的刻度标签if num not in [1,4,7] :ax.tick_params(labelleft=False)# 如果当前子图不在最下边,就不显示x轴的刻度标签if num not in [7,8,9] :ax.tick_params(labelbottom=False)ax.annotate(column, xy=(0, 1), xycoords='axes fraction', fontsize=12, fontweight=0, color=palette(num),xytext=(5, -5), textcoords='offset points', ha='left', va='top')axes[1].set_title('多折线小图') # 通过设置3*3图的第二个子图的标题替代2*3图中的第4个图的子标题# 5-多折线小图细节处理 df=pd.DataFrame({'x': range(1,11), 'y1': np.random.randn(10), 'y2': np.random.randn(10)+range(1,11), 'y3': np.random.randn(10)+range(11,21), 'y4': np.random.randn(10)+range(6,16), 'y5': np.random.randn(10)+range(4,14)+(0,0,0,0,0,0,0,-3,-8,-6), 'y6': np.random.randn(10)+range(2,12), 'y7': np.random.randn(10)+range(5,15), 'y8': np.random.randn(10)+range(4,14), 'y9': np.random.randn(10)+range(4,14) }) # 在第一行第一列的位置创建3*3的子布局 ax5 = gridspec.GridSpecFromSubplotSpec(3, 3, subplot_spec=gs[1, 1]) # 在 3x3 的小布局中添加子图 axes = [] for i in range(3):for j in range(3):ax = fig.add_subplot(ax5[i, j])axes.append(ax) # 将子图句柄添加到列表中 num=0 for column in df.drop('x', axis=1):num+=1ax = axes[num - 1]for v in df.drop('x', axis=1):ax.plot(df['x'], df[v], marker='', color='grey', linewidth=0.6, alpha=0.3)ax.plot(df['x'], df[column], marker='', color=palette(num), linewidth=2.4, alpha=0.9, label=column)ax.set_xlim(0,10)ax.set_ylim(-2,22)# 如果当前子图不在最左边,就不显示y轴的刻度标签if num not in [1,4,7] :ax.tick_params(labelleft=False)# 如果当前子图不在最下边,就不显示x轴的刻度标签if num not in [7,8,9] :ax.tick_params(labelbottom=False)ax.annotate(column, xy=(0, 1), xycoords='axes fraction', fontsize=12, fontweight=0, color=palette(num),xytext=(5, -5), textcoords='offset points', ha='left', va='top')axes[1].set_title('多折线小图细节处理') # 通过设置3*3图的第二个子图的标题替代2*3图中的第5个图的子标题# 6-带区域填充的多折线图 time = np.arange(12) income = np.array([5, 9, 6, 6, 10, 7, 6, 4, 4, 5, 6, 4]) expenses = np.array([6, 6, 8, 3, 6, 9, 7, 8, 6, 6, 4, 8])ax6.plot(time, income, color="green") ax6.plot(time, expenses, color="red")# 当income > expenses填充绿色 ax6.fill_between(time, income, expenses, where=(income > expenses), interpolate=True, color="green", alpha=0.25, label="Positive" )# 当income <= expenses填充红色 ax6.fill_between(time, income, expenses, where=(income <= expenses), interpolate=True, color="red", alpha=0.25,label="Negative" )ax6.set_title('带区域填充的多折线图') ax6.legend()plt.tight_layout() # 自动调整间距 plt.show()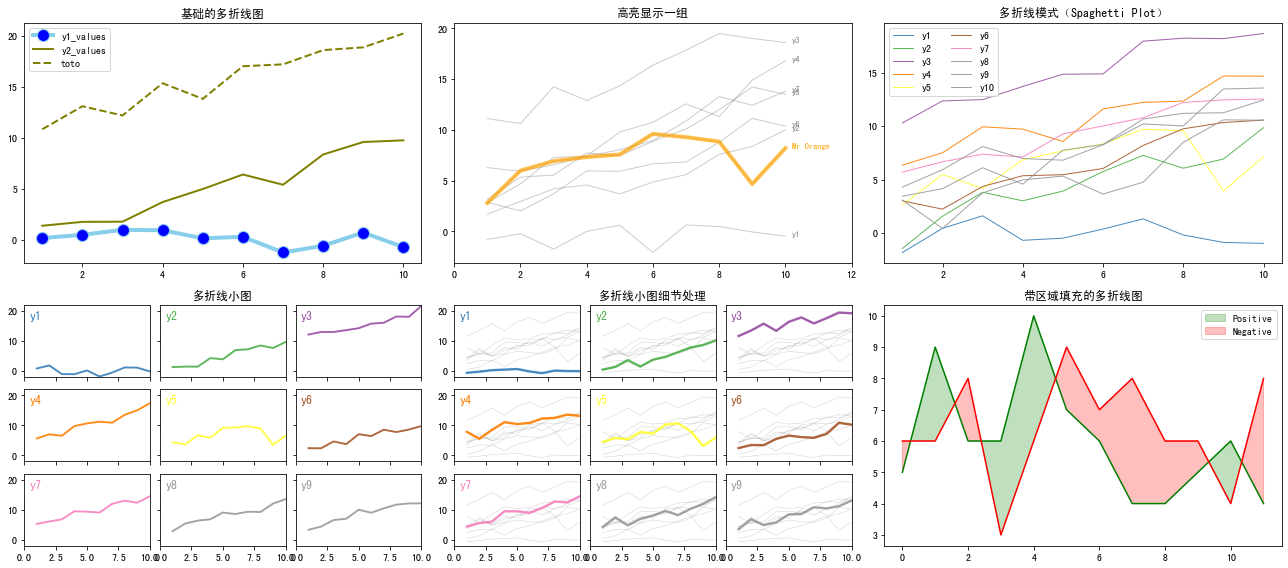
-
绘制时间序列图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import pandas as pd import matplotlib.dates as mdates# 导入数据 data = pd.read_csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/holtzy/data_to_viz/master/Example_dataset/3_TwoNumOrdered.csv", delim_whitespace=True )# 日期格式 data["date"] = pd.to_datetime(data["date"])date = data["date"] value = data["value"]# 绘制时间序列图 fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))# 设置6个月间隔为一刻度 half_year_locator = mdates.MonthLocator(interval=6) # 半年刻度 monthly_locator = mdates.MonthLocator() # 每月子刻度 year_month_formatter = mdates.DateFormatter("%Y-%m") # 格式化日期yyyy-MMax.xaxis.set_major_locator(half_year_locator) ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(monthly_locator) ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(year_month_formatter)ax.plot(date, value)fig.autofmt_xdate() # 自动旋转轴标签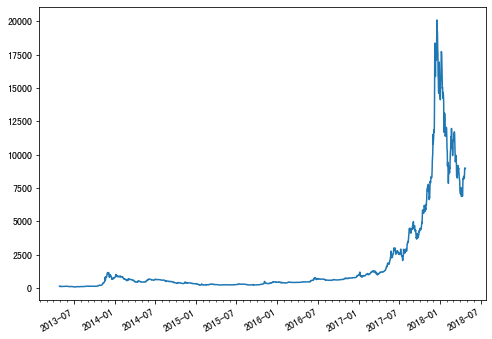
通过plotly绘制多样化的折线图
import plotly.graph_objects as go
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd# 自定义数据dates = []
start = 1990
end = 2022
for date in range(start,end):dates.append(str(date))# 生成随机序列,并计算累计和来生成随机漫步1、2、3
random_steps = np.random.choice([-1, 1], size=end-start, p=[0.5, 0.5])
random_walk1 = np.cumsum(random_steps)random_steps = np.random.choice([-1, 1], size=end-start, p=[0.5, 0.5])
random_walk2 = np.cumsum(random_steps)random_steps = np.random.choice([-1, 1], size=end-start, p=[0.5, 0.5])
random_walk3 = np.cumsum(random_steps)# 具有三个随机漫步的数据
df = pd.DataFrame({'date': dates,'value1': random_walk1,'value2': random_walk2,'value3': random_walk3,})fig = go.Figure()# 自定义变量1
fig.add_trace(go.Scatter(x=df['date'],y=df['value1'],mode='lines+markers', # 点线连接样式name='Line1',marker=dict(symbol='square', size=10, color='red'), line=dict(color='blue', width=5)
))# 自定义变量2
fig.add_trace(go.Scatter(x=df['date'], y=df['value2'], mode='lines+markers', name='Line2', marker=dict(symbol='circle', size=7, color='purple'), line=dict(color='orange', width=8)
))# 自定义变量3
fig.add_trace(go.Scatter(x=df['date'], y=df['value3'], mode='lines+markers', name='Line3',marker=dict(symbol='diamond', size=15, color='yellow'), line=dict(color='green', width=4)
))# 自定义布局
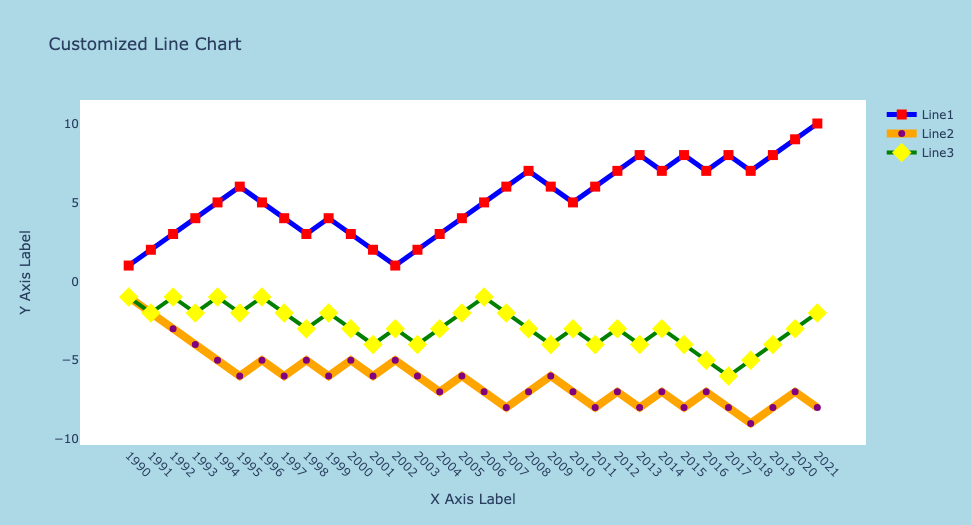
fig.update_layout(title='Customized Line Chart',xaxis_title='X Axis Label', yaxis_title='Y Axis Label',xaxis_tickangle=45, showlegend=True, plot_bgcolor='white', paper_bgcolor='lightblue',
)
通过pandas绘制多样化的折线图
-
修改参数
import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 导入数据 url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/holtzy/The-Python-Graph-Gallery/master/static/data/gapminderData.csv' df = pd.read_csv(url) df_france = df[df['country']=='France']# 绘制折线图 ax = df_france.plot(x='year',y='lifeExp',grid=True,linestyle='--',alpha=0.5,color='purple',linewidth=2.0, marker='d', markersize=8, markerfacecolor='orange', label='France')# 标题 ax.set_title('Evolution of \nthe life expectancy in France',weight='bold') # 轴标签 ax.set_ylabel('Life Expectancy') ax.set_xlabel('Time (in year)')plt.show()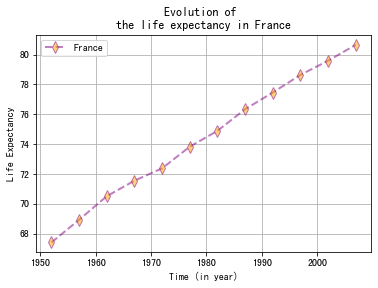
-
多变量折线图
import pandas as pd import random, numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 自定义数据 num_time_points = 100 time_values = np.arange(num_time_points)temperature = np.random.uniform(200, 400, num_time_points) pressure = np.random.uniform(500, 700, num_time_points) humidity = np.random.uniform(800, 1000, num_time_points) data = {'Time': time_values,'Temperature': temperature,'Pressure': pressure,'Humidity': humidity } df = pd.DataFrame(data)# 绘制多变量折线图 df.plot(x='Time',kind='line', grid=True, ) plt.legend(loc='upper right',bbox_to_anchor=(1.35, 1), ) plt.show()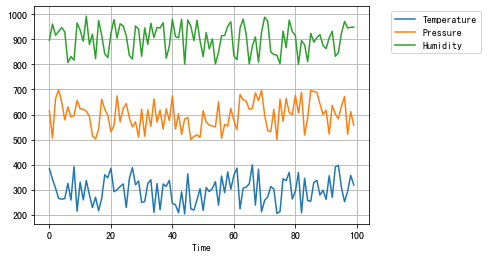
-
分组折线图
import pandas as pd import random, numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 自定义数据 num_data_points_per_country = 20# 设置多个国家的温度 france_temperatures = np.random.uniform(10, 20, num_data_points_per_country) germany_temperatures = np.random.uniform(0, 10, num_data_points_per_country) italy_temperatures = np.random.uniform(25, 30, num_data_points_per_country) # 对应的国家数据 countries = ['France', 'Germany', 'Italy'] country_labels = np.repeat(countries, num_data_points_per_country)# 时间数据 time_values = np.tile(np.arange(num_data_points_per_country), len(countries))data = {'Country': country_labels,'Temperature': np.concatenate([france_temperatures, germany_temperatures, italy_temperatures]),'Time': time_values }df = pd.DataFrame(data)# 绘制折线图 for name, group in df.groupby('Country'):plt.plot(group['Time'], group['Temperature'], label=name)# 设置图表的标题和坐标轴标签,并显示图例 plt.title('Temperature Trend over Time by Country') plt.xlabel('Time') plt.ylabel('Temperature') plt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.05, 1), loc='upper left')# 显示图表 plt.show()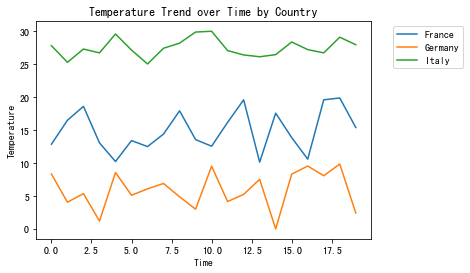
总结
以上通过matplotlib、seaborn、plotly和pandas快速绘制折线图。并通过修改参数或者辅以其他绘图知识自定义各种各样的折线图来适应相关使用场景。
共勉~