摘要
本文介绍了Java开发中常用的工具类,包括Apache Commons Collections的SetUtils、Google Guava的Sets、Apache Commons Lang的ArrayUtils等,以及它们在集合操作、数组操作、字符串处理、JSON处理等方面的应用。文章还涉及了Optional类、Money工具类、JDK流式函数等,旨在提高Java开发效率和代码质量。

1. static 变量是否可以读区远程配置(不可以读区配置)
在 Java 中,static 变量是属于类的,而不是类的实例。它们在类加载时初始化,并且在类的整个生命周期内存在。因此,static 变量的值在程序运行时是固定的,不会自动从远端配置中读取或更新。
如果你希望从远端配置中动态读取或更新值,通常可以考虑以下几种方法:
- 使用单例模式(Singleton Pattern): 创建一个单例类,用于加载和维护远端配置。这样可以保证在整个应用程序中只存在一个配置实例,并且可以在需要时动态读取或更新配置。
- 通过依赖注入(Dependency Injection): 使用依赖注入框架(如 Spring)来管理配置的加载和更新。这样,你可以将配置注入到需要的类中,并且可以通过配置中心来动态更新配置。
- 使用观察者模式(Observer Pattern): 实现一个观察者模式,使得配置类能够监听远端配置的变化,并在配置发生变化时更新自身的状态。
- 定期刷新配置: 实现一个定时任务(如使用
ScheduledExecutorService),定期从远端配置中心获取最新配置并更新应用程序中的配置。
public class ConfigManager {private static ConfigManager instance;private String remoteConfigValue;private ConfigManager() {// 初始化配置fetchRemoteConfig();startConfigRefreshTask();}public static synchronized ConfigManager getInstance() {if (instance == null) {instance = new ConfigManager();}return instance;}private void fetchRemoteConfig() {// 从远端配置中心获取配置值// remoteConfigValue = ...}private void startConfigRefreshTask() {// 定期刷新配置ScheduledExecutorService scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(this::fetchRemoteConfig, 0, 1, TimeUnit.HOURS);}public String getRemoteConfigValue() {return remoteConfigValue;}
}
在这种实现中,你可以通过 ConfigManager.getInstance().getRemoteConfigValue() 来获取远端配置值。配置会定期刷新,以确保最新值可用。
2. tostring()和JSON.toJSONString()方法
| 方法 | 目的 | 输出 | 格式 | 注意事项 |
|
| 获取对象的字符串表示 | 例如 | 类似 JSON 字符串 | 可能不符合 JSON 格式,特别是当包含 或其他复杂对象时,输出格式不一致。 |
|
| 将对象转换为 JSON 对象 |
| JSON 对象 | 返回 JSON 对象( ),不直接生成字符串。 |
|
| 将对象转换为 JSON 字符串 |
| 格式化的 JSON 字符串 | 正确的 JSON 字符串输出,符合 JSON 格式标准,适合网络传输或存储。 |
- 如果你只是想打印一个对象的字符串表示,
toString()是一种简单快速的方式,但它不会确保格式符合严格的 JSON 标准。 - 如果你需要操作 JSON 格式的对象(如从
List<JSONObject>生成 JSON 字符串), 推荐使用JSON.toJSONString()或JSON.toJSON(),它们提供了更好的格式化和 JSON 规范支持。
JSON.toJSON(childPolicyOutputList) 的输出是一个 JSONObject 类型的对象,不会直接是 JSON 字符串。如果你需要字符串输出,应该使用 JSON.toJSONString()。
3. 是否为null或者空工具类
3.1. 对象判断Objects类判断对象是否为null
在 Java 中,判断对象是否为 null 有几种常见的方式,以下是一些常用的方法:
直接比较判断
if (obj == null) {// obj 为 null
}使用 Objects 类(Java 7 及以上)
import java.util.Objects;if (Objects.isNull(obj)) {// obj 为 null
}if (Objects.nonNull(obj)) {// obj 不为 null
}使用 Optional 类(Java 8 及以上):
import java.util.Optional;Optional<Object> optionalObj = Optional.ofNullable(obj);
if (!optionalObj.isPresent()) {// obj 为 null
}Apache Commons Lang(外部库): 如果项目中使用了 Apache Commons Lang 库,可以使用 ObjectUtils:
import org.apache.commons.lang3.ObjectUtils;if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(obj)) {// obj 为 null 或空
}Guava(外部库): 如果项目中使用了 Guava,可以使用 Preconditions:
import com.google.common.base.Preconditions;Preconditions.checkNotNull(obj, "对象不能为空");3.2. String判断是否为null或者空
StringUtils 提供了丰富的 String 处理工具方法,其中有一个非常常用的方法就是 isEmpty 和 isBlank 来判断字符串是否为空或为 null。
StringUtils.isEmpty(str):判断字符串是否为null或空字符串("")。StringUtils.isBlank(str):判断字符串是否为null或为空字符串,且是否只包含空白字符(如空格、Tab)。
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;public class StringUtilsExample {public static void main(String[] args) {String str1 = null;String str2 = "";String str3 = " "; // 只包含空白字符String str4 = "Hello";System.out.println(StringUtils.isEmpty(str1)); // trueSystem.out.println(StringUtils.isEmpty(str2)); // trueSystem.out.println(StringUtils.isBlank(str3)); // trueSystem.out.println(StringUtils.isBlank(str4)); // false}
}3.3. List判断是否为null或者为空
Collections 是 Java 标准库提供的集合工具类,包含许多静态方法,用于处理集合。isNotEmpty 是用于判断集合(如 List、Set 等)是否非空的常用方法。
Collections.isNotEmpty(collection):判断Collection是否不为null且包含至少一个元素。
注意:Collections.isNotEmpty() 是 Java 8 中引入的方法,实际中,如果你使用的是较早的版本,可以直接用 collection != null && !collection.isEmpty()。
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;public class CollectionsExample {public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list1 = null;List<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>();List<String> list3 = new ArrayList<>();list3.add("item");System.out.println(Collections.isNotEmpty(list1)); // falseSystem.out.println(Collections.isNotEmpty(list2)); // falseSystem.out.println(Collections.isNotEmpty(list3)); // true}
}3.4. Map判断是否为null或者空
MapUtils 是 Apache Commons Collections 提供的一个类,专门用来操作 Map。它提供了 isEmpty 方法来检查 Map 是否为 null 或为空。
MapUtils.isEmpty(map):判断Map是否为null或没有任何元素。
import org.apache.commons.collections4.MapUtils;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;public class MapUtilsExample {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<String, String> map1 = null;Map<String, String> map2 = new HashMap<>();Map<String, String> map3 = new HashMap<>();map3.put("key", "value");System.out.println(MapUtils.isEmpty(map1)); // trueSystem.out.println(MapUtils.isEmpty(map2)); // trueSystem.out.println(MapUtils.isEmpty(map3)); // false}
}4. optional类使用
Java 8 - Optional类深度解析 | Java 全栈知识体系
这是一个可以为null的容器对象。如果值存在则isPresent()方法会返回true,调用get()方法会返回该对象。
public final class Optional<T> {private final T value;private Optional(T value) {this.value = Objects.requireNonNull(value);}public static <T> Optional<T> of(T value) {return new Optional<>(value);}public static <T> Optional<T> ofNullable(T value) {return value == null ? empty() : of(value);}public boolean isPresent() {return value != null;}/*** If a value is present, invoke the specified consumer with the value,* otherwise do nothing.** @param consumer block to be executed if a value is present* @throws NullPointerException if value is present and {@code consumer} is* null*/public void ifPresent(Consumer<? super T> consumer) {if (value != null)consumer.accept(value);}public Optional<T> filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate) {Objects.requireNonNull(predicate);if (!isPresent())return this;elsereturn predicate.test(value) ? this : empty();}public<U> Optional<U> map(Function<? super T, ? extends U> mapper) {Objects.requireNonNull(mapper);if (!isPresent())return empty();else {return Optional.ofNullable(mapper.apply(value));}}public<U> Optional<U> flatMap(Function<? super T, Optional<U>> mapper) {Objects.requireNonNull(mapper);if (!isPresent())return empty();else {return Objects.requireNonNull(mapper.apply(value));}}public <X extends Throwable> T orElseThrow(Supplier<? extends X> exceptionSupplier) throws X {if (value != null) {return value;} else {throw exceptionSupplier.get();}}
}public static <T> T requireNonNull(T obj) {if (obj == null)throw new NullPointerException();return obj;}4.1 Optional类包含的方法
//调用工厂方法创建Optional实例
Optional<String> name = Optional.of("Sanaulla");
//传入参数为null,抛出NullPointerException.
Optional<String> someNull = Optional.of(null);//ofNullable与of方法相似,唯一的区别是可以接受参数为null的情况。示例如下:
//例如,值为'null'
Optional empty = Optional.ofNullable(null);// 如果值存在返回true,否则返回false。
//isPresent方法用来检查Optional实例中是否包含值
if (name.isPresent()) {//在Optional实例内调用get()返回已存在的值System.out.println(name.get());//输出Sanaulla
}// 如果Optional有值则将其返回,否则抛出NoSuchElementException。//执行下面的代码会输出: No value present
try {//在空的Optional实例上调用get(),抛出NoSuchElementExceptionSystem.out.println(empty.get());
} catch (NoSuchElementException ex) {System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}//如果有值,则对其执行调用mapping函数得到返回值。如果返回值不为null,则创建包含mapping返回值的Optional作为map方法返回值,否则返回空Optional。
//map方法执行传入的lambda表达式参数对Optional实例的值进行修改。
//为lambda表达式的返回值创建新的Optional实例作为map方法的返回值。
Optional<String> upperName = name.map((value) -> value.toUpperCase());
System.out.println(upperName.orElse("No value found"));// 如果有值,为其执行mapping函数返回Optional类型返回值,否则返回空Optional。flatMap与map(Funtion)方法类似,区别在于flatMap中的mapper返回值必须是Optional。调用结束时,flatMap不会对结果用Optional封装。flatMap方法与map方法类似,区别在于mapping函数的返回值不同。map方法的mapping函数返回值可以是任何类型T,而flatMap方法的mapping函数必须是Optional。//flatMap与map(Function)非常类似,区别在于传入方法的lambda表达式的返回类型。
//map方法中的lambda表达式返回值可以是任意类型,在map函数返回之前会包装为Optional。
//但flatMap方法中的lambda表达式返回值必须是Optionl实例。
upperName = name.flatMap((value) -> Optional.of(value.toUpperCase()));
System.out.println(upperName.orElse("No value found"));//输出SANAULLAfilter个方法通过传入限定条件对Optional实例的值进行过滤。文档描述如下:
如果有值并且满足断言条件返回包含该值的Optional,否则返回空Optional。读到这里,可能你已经知道如何为filter方法传入一段代码。是的,这里可以传入一个lambda表达式。对于filter函数我们应该传入实现了Predicate接口的lambda表达式。//filter方法检查给定的Option值是否满足某些条件。
//如果满足则返回同一个Option实例,否则返回空Optional。
Optional<String> longName = name.filter((value) -> value.length() > 6);
System.out.println(longName.orElse("The name is less than 6 characters"));//输出Sanaulla//另一个例子是Optional值不满足filter指定的条件。
Optional<String> anotherName = Optional.of("Sana");
Optional<String> shortName = anotherName.filter((value) -> value.length() > 6);
//输出: name长度不足6字符
System.out.println(shortName.orElse("The name is less than 6 characters"));4.2 Optional 优化代码示例
Outer outer = new Outer();
if (outer != null && outer.nested != null && outer.nested.inner != null) {System.out.println(outer.nested.inner.foo);
}// Java 8 的 Optional 类型来摆脱所有这些 null 检查
Optional.of(new Outer()).map(Outer::getNested).map(Nested::getInner).map(Inner::getFoo).ifPresent(System.out::println);
5. 字符工具类
在 Java 中,有许多字符处理的工具类库,这些库提供了丰富的字符串操作方法,简化了日常开发中的字符串操作。以下是一些常用的字符处理工具类及示例:
5.1. Apache Commons Lang (StringUtils)
StringUtils 是 Apache Commons Lang 提供的一个非常强大的字符串处理工具类。
- 常用方法:
-
isEmpty(String str): 判断字符串是否为空或长度为 0。isBlank(String str): 判断字符串是否为空白(空格、空字符串、null)。join(Collection<?> collection, String separator): 将集合元素用指定的分隔符连接成一个字符串。split(String str, String separator): 根据分隔符拆分字符串。reverse(String str): 反转字符串。contains(String str, String searchStr): 判断字符串是否包含子字符串。capitalize(String str): 将字符串的首字母大写。
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;public class StringUtilsExample {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "Hello World";// 判断字符串是否为空或长度为 0System.out.println(StringUtils.isEmpty(str)); // false// 判断字符串是否为空白System.out.println(StringUtils.isBlank(str)); // false// 字符串反转System.out.println(StringUtils.reverse(str)); // "dlroW olleH"// 字符串首字母大写System.out.println(StringUtils.capitalize("hello")); // "Hello"}
}
5.2. Google Guava (Strings)
Google Guava 提供了 Strings 类用于处理字符串。
- 常用方法:
-
nullToEmpty(String string): 将null转换为空字符串。emptyToNull(String string): 将空字符串转换为null。isNullOrEmpty(String string): 检查字符串是否为null或空字符串。padStart(String string, int minLength, char padChar): 用指定字符在字符串左侧填充,达到指定长度。padEnd(String string, int minLength, char padChar): 用指定字符在字符串右侧填充,达到指定长度。repeat(String string, int count): 重复字符串指定次数。
import com.google.common.base.Strings;public class StringsExample {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "Guava";// 检查字符串是否为 null 或空字符串System.out.println(Strings.isNullOrEmpty(str)); // false// 在字符串右侧填充字符System.out.println(Strings.padEnd(str, 10, '!')); // "Guava!!!!!"// 重复字符串System.out.println(Strings.repeat(str, 3)); // "GuavaGuavaGuava"}
}6. 集合类工具类
在 Java 中,当 Map 对象本身为 null 时,就会出现空指针异常。为了防止这种情况,可以采取以下几种方法:
显式初始化 Map 对象:
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
这样可以确保 map 对象不为 null。使用 Collections.emptyMap() 方法:
Map<String, Integer> map = Collections.emptyMap();
这样会创建一个不可变的空 Map 对象,可以避免 map 为 null 的情况。使用 Map.of() 和 Map.ofEntries() 方法(Java 9 及以上版本):
Map<String, Integer> map = Map.of("key1", 1, "key2", 2);
Map<String, Integer> map = Map.ofEntries(Map.entry("key1", 1),Map.entry("key2", 2)
);
这种方式可以直接创建一个不可变的 Map 对象。使用 java.util.Collections.singletonMap() 方法:
Map<String, Integer> map = Collections.singletonMap("key", 1);
这种方式会创建一个只包含一个键值对的不可变 Map 对象。除了初始化 Map 对象,在使用 Map 时也需要注意防止空指针异常。可以使用 Map.get(key) 方法时先进行判空操作:if (map != null && map.containsKey("key")) {int value = map.get("key");// 进行其他操作
}使用 Map.getOrDefault(key, defaultValue) 方法,它会在 key 不存在时返回默认值,从而避免空指针异常。6.1. Map工具类
6.1.1. Apache Commons Collections的MapUtils类
Apache Commons Collections 提供了 MapUtils 工具类,这是一个非常常用的工具类库,包含了各种便捷的 Map 操作方法。
- 常用方法:
-
isEmpty(Map<?,?> map): 检查Map是否为空。getObject(Map<?,?> map, Object key): 从Map中安全地获取值,如果键不存在则返回null。putAll(Map<K,V> map, K[] keys, V[] values): 将数组形式的键和值添加到Map中。invertMap(Map<K,V> map): 反转Map,将键和值的位置交换。
import org.apache.commons.collections4.MapUtils;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;public class MapUtilsExample {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("key1", "value1");map.put("key2", "value2");// 检查是否为空System.out.println("Is map empty? " + MapUtils.isEmpty(map));// 获取对象String value = MapUtils.getObject(map, "key1");System.out.println("Value for key1: " + value);// 反转MapMap<String, String> invertedMap = MapUtils.invertMap(map);System.out.println("Inverted map: " + invertedMap);}
}6.1.2. Google Guava 的Maps类
虽然 Guava 没有一个名为 MapUtils 的工具类,但它提供了很多类似的工具方法,如 Maps 类中包含了一些有用的 Map 操作。
常用方法:
Maps.newHashMap(): 创建一个新的HashMap。Maps.filterKeys(Map<K,V>, Predicate<? super K>): 根据键的条件过滤Map。Maps.filterValues(Map<K,V>, Predicate<? super V>): 根据值的条件过滤Map。
import com.google.common.collect.Maps;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;public class GuavaMapsExample {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<String, Integer> map = Maps.newHashMap();map.put("a", 1);map.put("b", 2);map.put("c", 3);// 过滤值大于 1 的条目Map<String, Integer> filteredMap = Maps.filterValues(map, value -> value > 1);System.out.println("Filtered Map: " + filteredMap);}
}6.2. List的工具类
6.2.1. Apache Commons Collections的ListUtils类
Apache Commons Collections 是一个非常流行的工具库,提供了丰富的集合操作工具,其中 ListUtils 类专门用于处理 List。
- 常用方法:
-
ListUtils.unmodifiableList(List<? extends T> list): 返回一个不可修改的List。ListUtils.subtract(List<T> list1, List<? extends T> list2): 从list1中减去list2的元素。ListUtils.union(List<T> list1, List<? extends T> list2): 返回list1和list2的并集。
import org.apache.commons.collections4.ListUtils;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;public class ListUtilsExample {public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list1 = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c");List<String> list2 = Arrays.asList("b", "c", "d");// 计算并集List<String> union = ListUtils.union(list1, list2);System.out.println("Union: " + union);// 计算差集List<String> subtract = ListUtils.subtract(list1, list2);System.out.println("Subtract: " + subtract);// 创建不可修改的列表List<String> unmodifiableList = ListUtils.unmodifiableList(list1);System.out.println("Unmodifiable List: " + unmodifiableList);}
}6.2.2. Google Guava
Google Guava 提供了大量对 List 的扩展操作,特别是 Lists 类,为常见的 List 操作提供了便捷的方法。
- 常用方法:
-
Lists.newArrayList(): 创建一个新的ArrayList。Lists.partition(List<T> list, int size): 将一个列表分割成指定大小的子列表。Lists.reverse(List<T> list): 反转列表。
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
import java.util.List;public class GuavaListsExample {public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list = Lists.newArrayList("a", "b", "c", "d", "e");// 分割列表List<List<String>> partition = Lists.partition(list, 2);System.out.println("Partitioned Lists: " + partition);// 反转列表List<String> reversed = Lists.reverse(list);System.out.println("Reversed List: " + reversed);}
}6.3. Set工具类
Set<String> remoteExecutors = Collections.emptySet();这行代码的意思是创建了一个空的 Set<String> 对象并将其赋值给变量 remoteExecutors。
Set<String> 表示这是一个字符串集合。Collections.emptySet() 是 Java 集合框架中的一个静态工厂方法,它返回一个不可修改的空集合。将这个空集合赋值给变量 remoteExecutors,意味着在程序执行过程中,remoteExecutors 变量始终代表一个空的字符串集合。
这种做法通常有以下几个目的:
- 初始化一个集合变量为空,以便后续根据需求动态添加元素。
- 表示某些功能在当前情况下不需要任何远程执行器,使用空集合可以简化后续的判断和处理逻辑。
- 作为一种防御性编程手段,确保集合变量不会因为未初始化而出现 NullPointerException 异常。
- 总之,Set<String> remoteExecutors = Collections.emptySet(); 体现了良好的编码习惯,为后续的集合操作奠定了良好的基础。
6.3.1. Apache Commons Collections
Apache Commons Collections 提供了许多有用的工具类来操作 Set,包括 SetUtils 类,它包含了各种 Set 操作的实用方法。
- 常用方法:
-
SetUtils.difference(Set<? extends T> set1, Set<? extends T> set2): 计算两个Set之间的差集。SetUtils.union(Set<? extends T> set1, Set<? extends T> set2): 计算两个Set的并集。SetUtils.intersection(Set<? extends T> set1, Set<? extends T> set2): 计算两个Set的交集。
import org.apache.commons.collections4.SetUtils;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;public class SetUtilsExample {public static void main(String[] args) {Set<String> set1 = new HashSet<>();set1.add("a");set1.add("b");set1.add("c");Set<String> set2 = new HashSet<>();set2.add("b");set2.add("c");set2.add("d");// 计算并集Set<String> union = SetUtils.union(set1, set2);System.out.println("Union: " + union);// 计算差集Set<String> difference = SetUtils.difference(set1, set2);System.out.println("Difference: " + difference);// 计算交集Set<String> intersection = SetUtils.intersection(set1, set2);System.out.println("Intersection: " + intersection);}
}Google Guava6.3.2. Google Guava
Google Guava 提供了 Sets 类,提供了对 Set 的扩展方法,支持集合的各种操作。
- 常用方法:
-
Sets.newHashSet(): 创建一个新的HashSet。Sets.union(Set<T> set1, Set<T> set2): 计算两个Set的并集。Sets.difference(Set<T> set1, Set<T> set2): 计算两个Set之间的差集。Sets.intersection(Set<T> set1, Set<T> set2): 计算两个Set的交集。
import com.google.common.collect.Sets;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;public class GuavaSetsExample {public static void main(String[] args) {Set<String> set1 = new HashSet<>();set1.add("a");set1.add("b");set1.add("c");Set<String> set2 = new HashSet<>();set2.add("b");set2.add("c");set2.add("d");// 计算并集Set<String> union = Sets.union(set1, set2);System.out.println("Union: " + union);// 计算差集Set<String> difference = Sets.difference(set1, set2);System.out.println("Difference: " + difference);// 计算交集Set<String> intersection = Sets.intersection(set1, set2);System.out.println("Intersection: " + intersection);}
}6.4. Array工具类
6.4.1. Apache Commons Lang
Apache Commons Lang 是一个常用的工具库,其中的 ArrayUtils 类提供了大量用于数组操作的方法。
- 常用方法:
-
ArrayUtils.addElement(T[] array, T element): 向数组中添加一个元素。ArrayUtils.removeElement(T[] array, T element): 从数组中移除指定的元素。ArrayUtils.isEmpty(T[] array): 检查数组是否为空。ArrayUtils.subarray(T[] array, int startIndexInclusive, int endIndexExclusive): 获取数组的子数组。
import org.apache.commons.lang3.ArrayUtils;public class ArrayUtilsExample {public static void main(String[] args) {Integer[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};// 添加元素Integer[] newArray = ArrayUtils.addElement(array, 6);System.out.println("Array with added element: " + ArrayUtils.toString(newArray));// 移除元素newArray = ArrayUtils.removeElement(newArray, 3);System.out.println("Array with removed element: " + ArrayUtils.toString(newArray));// 检查是否为空System.out.println("Array is empty: " + ArrayUtils.isEmpty(newArray));// 获取子数组Integer[] subArray = ArrayUtils.subarray(newArray, 1, 4);System.out.println("Subarray: " + ArrayUtils.toString(subArray));}
}6.4.2. Apache Commons Collections
除了 ArrayUtils,Apache Commons Collections 也提供了一些其他数组相关的工具,如 ArrayList 转换和操作。
- 常用方法:
-
CollectionUtils.addAll(Collection<? super T> collection, T... elements): 向集合中添加多个元素。CollectionUtils.subtract(Collection<? super T> c1, Collection<?> c2): 计算集合之间的差集。
import org.apache.commons.collections4.CollectionUtils;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;public class CommonsCollectionsArrayExample {public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c"));CollectionUtils.addAll(list, "d", "e", "f");System.out.println("List after adding elements: " + list);List<String> list2 = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "d");List<String> difference = new ArrayList<>(CollectionUtils.subtract(list, list2));System.out.println("Difference: " + difference);}
}6.4.3. Google Guava
Google Guava 提供了 Ints, Longs, Doubles, 等类用于处理基本数据类型数组的操作。
- 常用方法:
-
Ints.concat(int[]... arrays): 连接多个int数组。Ints.toArray(Collection<Integer> collection): 将Collection转换为int数组。Lists.newArrayList(T... elements): 创建一个新的ArrayList,可以用来创建动态数组。
import com.google.common.primitives.Ints;
import java.util.List;
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;public class GuavaArrayExample {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] array1 = {1, 2, 3};int[] array2 = {4, 5, 6};// 连接数组int[] concatenatedArray = Ints.concat(array1, array2);System.out.println("Concatenated Array: " + Ints.asList(concatenatedArray));// 从集合创建数组List<Integer> list = Lists.newArrayList(7, 8, 9);int[] arrayFromList = Ints.toArray(list);System.out.println("Array from List: " + Ints.asList(arrayFromList));}
}7. json对象工具类
7.1. Jackson
Jackson 是一个非常流行的 JSON 处理库,支持高效的 JSON 解析和生成。它包含了 ObjectMapper, JsonNode 等类用于操作 JSON 数据。
- 常用类和方法:
-
ObjectMapper: JSON 数据和 Java 对象之间的转换。JsonNode: 用于树形结构的 JSON 数据操作。writeValueAsString(Object value): 将 Java 对象转换为 JSON 字符串。readValue(String content, Class<T> valueType): 将 JSON 字符串转换为 Java 对象。
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;public class JacksonExample {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();// 将 Java 对象转换为 JSON 字符串Person person = new Person("John", 30);String jsonString = mapper.writeValueAsString(person);System.out.println("JSON String: " + jsonString);// 将 JSON 字符串转换为 Java 对象Person deserializedPerson = mapper.readValue(jsonString, Person.class);System.out.println("Deserialized Person: " + deserializedPerson);// 使用 JsonNode 进行树形结构操作JsonNode jsonNode = mapper.readTree(jsonString);System.out.println("Name: " + jsonNode.get("name").asText());}static class Person {public String name;public int age;public Person() { }public Person(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{name='" + name + "', age=" + age + "}";}}
}7.2. Gson工具类
Gson 是 Google 提供的一个 JSON 库,用于将 Java 对象与 JSON 数据之间进行转换。
- 常用类和方法:
-
Gson: 主类,用于执行 JSON 转换操作。toJson(Object src): 将 Java 对象转换为 JSON 字符串。fromJson(String json, Class<T> classOfT): 将 JSON 字符串转换为 Java 对象。
import com.google.gson.Gson;public class GsonExample {public static void main(String[] args) {Gson gson = new Gson();// 将 Java 对象转换为 JSON 字符串Person person = new Person("Jane", 25);String jsonString = gson.toJson(person);System.out.println("JSON String: " + jsonString);// 将 JSON 字符串转换为 Java 对象Person deserializedPerson = gson.fromJson(jsonString, Person.class);System.out.println("Deserialized Person: " + deserializedPerson);}static class Person {private String name;private int age;public Person() { }public Person(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{name='" + name + "', age=" + age + "}";}}
}7.3. JSON.simple
JSON.simple 是一个轻量级的 JSON 处理库,提供了基本的 JSON 解析和生成能力。
- 常用类和方法:
-
JSONParser: 用于解析 JSON 数据。JSONObject: 用于创建和操作 JSON 对象。JSONArray: 用于创建和操作 JSON 数组。parse(String json): 解析 JSON 字符串。toJSONString(): 将 JSON 对象或数组转换为字符串。
import org.json.simple.JSONArray;
import org.json.simple.JSONObject;
import org.json.simple.parser.JSONParser;
import org.json.simple.parser.ParseException;public class JSONSimpleExample {public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {JSONParser parser = new JSONParser();// 创建 JSON 对象JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();jsonObject.put("name", "Alice");jsonObject.put("age", 28);// 将 JSON 对象转换为字符串String jsonString = jsonObject.toJSONString();System.out.println("JSON String: " + jsonString);// 解析 JSON 字符串JSONObject parsedObject = (JSONObject) parser.parse(jsonString);System.out.println("Name: " + parsedObject.get("name"));System.out.println("Age: " + parsedObject.get("age"));}
}8. JDK流式函数
8.1. 创建Stream流
从集合创建:
使用集合类的 stream() 或 parallelStream() 方法可以创建对应的流。例如:
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("apple", "banana", "orange");
Stream<String> streamFromList = list.stream();从数组创建:
使用 Arrays.stream() 方法可以从数组中创建流:
String[] array = {"apple", "banana", "orange"};
Stream<String> streamFromArray = Arrays.stream(array);通过Stream的静态方法创建:
Stream 类提供了静态方法 of(),可以传入一系列元素来创建流:
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("apple", "banana", "orange");8.2. Stream API中间操作
filter
用于筛选元素,根据指定的条件保留符合条件的元素。
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Stream<Integer> filteredStream = numbers.stream().filter(x -> x > 2);map
对流中的每个元素应用指定的函数,并将结果映射为一个新的元素。
List<String> words = Arrays.asList("apple", "banana", "orange");
Stream<Integer> wordLengths = words.stream().map(String::length);flatMap
将流中的每个元素都转换为一个流,然后将这些流连接起来成为一个流。
List<List<Integer>> numbers = Arrays.asList(Arrays.asList(1, 2),Arrays.asList(3, 4),Arrays.asList(5, 6)
);Stream<Integer> flatStream = numbers.stream().flatMap(List::stream);distinct
去除流中的重复元素。
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5);
Stream<Integer> distinctNumbers = numbers.stream().distinct();sorted
对流中的元素进行排序。
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6);
Stream<Integer> sortedNumbers = numbers.stream().sorted();peek
对流中的每个元素执行操作,主要用于调试和观察流中的元素。
List<String> words = Arrays.asList("apple", "banana", "orange");
Stream<String> peekStream = words.stream().peek(System.out::println);limit 和 skip
limit 用于截断流,保留指定数量的元素,而 skip 则用于跳过指定数量的元素。
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Stream<Integer> limitedStream = numbers.stream().limit(3);
Stream<Integer> skippedStream = numbers.stream().skip(2);8.3. Stream API终端操作
forEach
对流中的每个元素执行指定的操作。
List<String> words = Arrays.asList("apple", "banana", "orange");
words.stream().forEach(System.out::println);toArray
将流中的元素转换为数组。
List<String> words = Arrays.asList("apple", "banana", "orange");
String[] wordArray = words.stream().toArray(String[]::new);reduce
对流中的元素进行归约操作,可以用于求和、求最大值、最小值等。
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Optional<Integer> sum = numbers.stream().reduce(Integer::sum);collect
将流中的元素收集到一个集合中,例如 List、Set 或 Map。
List<String> words = Arrays.asList("apple", "banana", "orange");
List<String> collectedWords = words.stream().collect(Collectors.toList());count
返回流中的元素数量。
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
long count = numbers.stream().count();anyMatch、allMatch 和 noneMatch
用于检查流中是否存在满足指定条件的元素。
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
boolean anyGreaterThanThree = numbers.stream().anyMatch(x -> x > 3);
boolean allGreaterThanTwo = numbers.stream().allMatch(x -> x > 2);
boolean noneGreaterThanFive = numbers.stream().noneMatch(x -> x > 5);findAny 和 findFirst
返回流中的任意一个元素或者第一个元素。
List<String> words = Arrays.asList("apple", "banana", "orange");
Optional<String> anyWord = words.stream().findAny();
Optional<String> firstWord = words.stream().findFirst();min 和 max
返回流中的最小值或最大值。
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6);
Optional<Integer> minNumber = numbers.stream().min(Integer::compare);
Optional<Integer> maxNumber = numbers.stream().max(Integer::compare); public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();personList.add(new Person("张三", 16000, 20, "男", "北京"));personList.add(new Person("李四", 8500, 21, "男", "南京"));personList.add(new Person("王五", 7300, 20, "女", "合肥"));personList.add(new Person("赵六", 8000, 22, "男", "合肥"));personList.add(new Person("孙七", 15860, 25, "女", "上海"));// 按工资升序排序(自然排序)List<String> newList = personList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getSalary)).map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());// 按工资倒序排序List<String> newList2 = personList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getSalary).reversed()).map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());// 先按工资再按年龄升序排序List<String> newList3 = personList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getSalary).thenComparing(Person::getAge)).map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());// 先按工资再按年龄自定义排序(降序)List<String> newList4 = personList.stream().sorted((p1, p2) -> {if (p1.getSalary().equals(p2.getSalary())) {return p2.getAge() - p1.getAge();} else {return p2.getSalary() - p1.getSalary();}}).map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println("按工资升序排序:" + newList);System.out.println("按工资降序排序:" + newList2);System.out.println("先按工资再按年龄升序排序:" + newList3);System.out.println("先按工资再按年龄自定义降序排序:" + newList4);} public static void main(String[] args) {String[] arr1 = {"a", "b", "c", "d"};String[] arr2 = {"d", "e", "f", "g"};Stream<String> stream1 = Stream.of(arr1);Stream<String> stream2 = Stream.of(arr2);// concat:合并两个流 distinct:去重List<String> newList = Stream.concat(stream1, stream2).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());// limit:限制从流中获得前n个数据List<Integer> collect = Stream.iterate(1, x -> x + 2).limit(10).collect(Collectors.toList());// skip:跳过前n个数据List<Integer> collect2 = Stream.iterate(1, x -> x + 2).skip(1).limit(5).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println("流合并:" + newList);System.out.println("limit:" + collect);System.out.println("skip:" + collect2);} public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();personList.add(new Person("张三", 6000, 20, "男", "北京"));personList.add(new Person("李四", 6500, 21, "男", "南京"));personList.add(new Person("王五", 7300, 20, "女", "合肥"));personList.add(new Person("赵六", 8000, 22, "男", "合肥"));personList.add(new Person("孙七", 9860, 25, "女", "上海"));// 每个员工减去起征点后的薪资之和(这里个税的算法并不正确,但没想到更好的例子)Integer sum = personList.stream().map(Person::getSalary).reduce(0, (i, j) -> (i + j - 5000));System.out.println("员工扣税薪资总和:" + sum);// stream的reduceOptional<Integer> sum2 = personList.stream().map(Person::getSalary).reduce(Integer::sum);System.out.println("员工薪资总和:" + sum2.get());} public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();personList.add(new Person("张三", 1000, 20, "男", "北京"));personList.add(new Person("李四", 2000, 21, "男", "南京"));personList.add(new Person("王五", 3000, 20, "女", "合肥"));personList.add(new Person("赵六", 4000, 22, "男", "合肥"));personList.add(new Person("孙七", 5000, 25, "女", "上海"));String persons = personList.stream().map(p -> p.getName() + "-" + p.getSex() + "-" + p.getSalary()).collect(Collectors.joining(","));System.out.println("所有员工信息:" + persons);} public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();personList.add(new Person("张三", 1000, 20, "男", "北京"));personList.add(new Person("李四", 2000, 21, "男", "南京"));personList.add(new Person("王五", 3000, 20, "女", "合肥"));personList.add(new Person("赵六", 4000, 22, "男", "合肥"));personList.add(new Person("孙七", 5000, 25, "女", "上海"));// 按薪资高于3000分组Map<Boolean, List<Person>> salaryGroup = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(p -> p.getSalary() > 3000));List<Person> group1 = salaryGroup.get(true);List<Person> group2 = salaryGroup.get(false);for (Person person : group1) {System.out.println("薪资高于3000元组:" + person);}for (Person person : group2) {System.out.println("薪资低于3000元组:" + person);}// 按性别分组Map<String, List<Person>> sexGroup = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getSex));List<Person> group3 = sexGroup.get("男");List<Person> group4 = sexGroup.get("女");for (Person person : group3) {System.out.println("男子组:" + person);}for (Person person : group4) {System.out.println("女子组:" + person);}// 将员工先按性别分组,再按地区分组Map<String, Map<String, List<Person>>> group = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getSex, Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getArea)));Map<String, List<Person>> manGroup = group.get("男");Map<String, List<Person>> womenGroup = group.get("女");List<Person> group5 = manGroup.get("合肥");List<Person> group6 = womenGroup.get("上海");System.out.println("地区在合肥的男子组:" + group5);System.out.println("地区在上海的女子组:" + group6);} public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();personList.add(new Person("张三", 1000, 20, "男", "北京"));personList.add(new Person("李四", 2000, 21, "男", "南京"));personList.add(new Person("王五", 3000, 20, "女", "合肥"));personList.add(new Person("赵六", 4000, 22, "男", "四川"));personList.add(new Person("孙七", 5000, 25, "女", "上海"));// 统计员工人数、平均工资、工资总额、最高工资// 员工总人数long count = personList.stream().count();// 平均工资Double average = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Person::getSalary));// 最高工资Optional<Integer> max = personList.stream().map(Person::getSalary).max(Integer::compare);// 工资之和int sum = personList.stream().mapToInt(Person::getSalary).sum();// 一次性统计所有信息DoubleSummaryStatistics collect = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingDouble(Person::getSalary));System.out.println("员工总人数:" + count);System.out.println("员工平均工资:" + average);System.out.println("员工工资总和:" + sum);System.out.println("员工工资所有统计:" + collect);}public static void main(String[] args) {List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 3, 4, 8, 6, 2, 20, 13);List<Integer> list1 = list.stream().filter(a -> a % 2 == 0).collect(Collectors.toList());Set<Integer> list2 = list.stream().filter(a -> a % 2 == 0).collect(Collectors.toSet());System.out.println("被2整除的list集合" + list1);System.out.println("被2整除的set集合" + list2);List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();personList.add(new Person("张三", 1000, 20, "男", "北京"));personList.add(new Person("李四", 2000, 21, "男", "南京"));personList.add(new Person("王五", 3000, 20, "女", "合肥"));personList.add(new Person("赵六", 4000, 22, "男", "四川"));personList.add(new Person("孙七", 5000, 25, "女", "上海"));// 工资大于3000元的员工Map<String, Integer> map = personList.stream().filter(person -> person.getSalary() > 3000).collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getName, person -> person.getSalary()));System.out.println("工资大于3000元的员工:" + map);}public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();personList.add(new Person("张三", 1000, 20, "男", "北京"));personList.add(new Person("李四", 2000, 21, "男", "南京"));personList.add(new Person("王五", 3000, 20, "女", "合肥"));personList.add(new Person("赵六", 4000, 22, "男", "四川"));personList.add(new Person("孙七", 5000, 25, "女", "上海"));// 求所有员工的工资之和、最高工资// 求工资之和方法1:Optional<Integer> sumSalary = personList.stream().map(Person::getSalary).reduce(Integer::sum);// 求工资之和方法2:Integer sumSalary2 = personList.stream().reduce(0, (sum, p) -> sum += p.getSalary(), Integer::sum);// 求最高工资方法1:Integer maxSalary = personList.stream().reduce(0, (max, p) -> max > p.getSalary() ? max : p.getSalary(), Integer::max);// 求最高工资方法2:Integer maxSalary2 = personList.stream().reduce(0, (max, p) -> max > p.getSalary() ? max : p.getSalary(), (max1, max2) -> max1 > max2 ? max1 : max2);// 求最高工资方法3:Integer maxSalary3 = personList.stream().map(Person::getSalary).reduce(Integer::max).get();System.out.println("工资之和,方法1:" + sumSalary);System.out.println("工资之和,方法2:" + sumSalary2);System.out.println("最高工资,方法1:" + maxSalary);System.out.println("最高工资,方法2:" + maxSalary2);System.out.println("最高工资,方法3:" + maxSalary3);} public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();personList.add(new Person("张三", 1000, 20, "男", "北京"));personList.add(new Person("李四", 2000, 21, "男", "南京"));personList.add(new Person("王五", 3000, 20, "女", "合肥"));personList.add(new Person("赵六", 4000, 22, "男", "四川"));personList.add(new Person("孙七", 5000, 25, "女", "上海"));// 将员工工作全部增加10000元// 1、方式一:不改变原来员工集合List<Person> personListNew = personList.stream().map(person -> {Person personNew = new Person(person.getName(), 0, 0, null, null);personNew.setSalary(person.getSalary() + 10000);return personNew;}).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println("一次改动前:" + personList.get(0).getName() + ">>>" + personList.get(0).getSalary());System.out.println("一次改动后:" + personListNew.get(0).getName() + ">>>" + personListNew.get(0).getSalary());// 2、方式二:改变原来员工集合的方式List<Person> personListNew2 = personList.stream().map(person -> {person.setSalary(person.getSalary() + 10000);return person;}).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println("二次改动前:" + personList.get(0).getName() + ">>>" + personListNew.get(0).getSalary());System.out.println("二次改动后:" + personListNew2.get(0).getName() + ">>>" + personListNew.get(0).getSalary());// 将两个字符数组合并成一个新的字符数组List<String> list = Arrays.asList("Hello", "World");Stream<String> map = list.stream().map(s -> s.split("")).flatMap(Arrays::stream);map.forEach(System.out::print);System.out.println();// 给定两个数字列表 获取所有的数对List<Integer> numbers1 = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3);List<Integer> numbers2 = Arrays.asList(3, 4);// flatMap升维度List<int[]> pairs = numbers1.stream().flatMap(x -> numbers2.stream().map(y -> new int[] { x, y })).collect(Collectors.toList());for (int[] pair : pairs) {System.out.print(Arrays.toString(pair));}}9. Money工具类
https://gitee.com/yinmosc/gateway/blob/master/src/main/java/com/demo/gateway/common/Money.java
JAVA有制定金额处理规范JSR 354 (Java Specification Request 354),对应的实现包是Java Money APl (javax.money),它提供了一套用于处理货币和货币计算的API。不过我们通常选择实现自己的Money类,主要是方便,可以自由定制,比如小数舍入问题。
一个Money类通常包括以下几个主要方面:
- 通过参数生成一个Money类。
- 加减乘除处理。
- 比较处理。
- 获取金额(元)和获取最小单位金额(元或分)。
注意除法有除不尽舍入的问题,需要根据业务来指定舍入的模式,建议默认提供四舍五入,但是保留指定模式的能力。具体可以参考: java.math.RoundingMode。
加和减,需要先判断币种,只有币种相同才能做加减。返回元和分单位的数字, 所有内部应用全部使用getAmount(),不允许使用getCent()。保证内部应用大家的语义保持一致。只有请求外部渠道时,如果渠道要求使用币种最小单位,才使用getCent()。
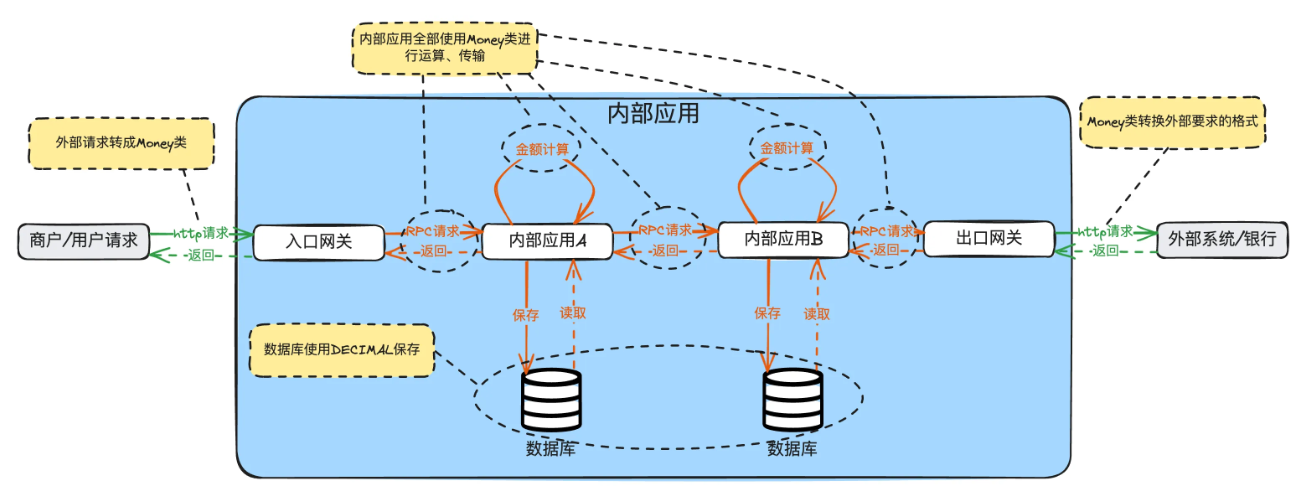
- 制定适用于公司业务的Money类来统一处理金额。
- 在入口网关接收到请求后,就转换为Money类。
- 所有内部应用的金额处理,强制全部使用Money类运算、传输,禁止自己手动加减乘除、单位换算(比如元到分)。
- 数据库使用DECIMAL类型保存,保存单位为元。
- 在出口网关外发时,再根据外部接口文档要求,转换成使用指定的单位。有些是元,有些是分(最小货币单位)
10. 项目中使用断言工具类统一错误
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//package cn.tongdun.tiangong.preserver.common.utils;import cn.tongdun.fast2jack.JSON;
import cn.tongdun.fast2jack.JSONArray;
import cn.tongdun.fast2jack.JSONObject;
import cn.tongdun.tiangong.preserver.common.i18n.BusExceptionMessageEnum;
import cn.tongdun.tianzhou.common.base.BusException;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Objects;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;public class AssertUtil {public AssertUtil() {}public static void isNotNull(Object input, String fieldName) {if (input instanceof String) {if (input == null || input.toString().matches("\\s*")) {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_NOTNULL.getMessage(new Object[]{fieldName}));}} else if (input == null) {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_NOTNULL.getMessage(new Object[]{fieldName}));}}public static void isNumber(String input, String fieldName) {try {Double.valueOf(input);} catch (Exception var3) {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_NUMBERIC.getMessage(new Object[]{fieldName}));}}public static void isInteger(String input, String fieldName) {try {Integer.valueOf(input);} catch (Exception var3) {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_INTEGER.getMessage(new Object[]{fieldName}));}}public static void greaterThan(Number num1, Number num2, String fieldName1, String fieldName2) {if (num1 != null && num2 != null) {if (num1.doubleValue() <= num2.doubleValue()) {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_GT.getMessage(new Object[]{fieldName1, fieldName2}));}} else {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_GT.getMessage(new Object[]{fieldName1, fieldName2}));}}public static void greaterThanOrEqual(Number num1, Number num2, String fieldName1, String fieldName2) {if (num1 != null && num2 != null) {if (num1.doubleValue() < num2.doubleValue()) {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_GTE.getMessage(new Object[]{fieldName1, fieldName2}));}} else {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_GTE.getMessage(new Object[]{fieldName1, fieldName2}));}}public static void greaterThanOrEqual(Date date1, Date date2, String fieldName1, String fieldName2) {if (date1 != null && date2 != null) {if (date1.getTime() < date2.getTime()) {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_GTE.getMessage(new Object[]{fieldName1, fieldName2}));}} else {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_GTE.getMessage(new Object[]{fieldName1, fieldName2}));}}public static void equals(Object str1, Object str2, String err) {if (str1 != null && str2 != null) {if (!str1.equals(str2)) {throw new BusException(err);}} else {throw new BusException(err);}}public static void overMaxLength(String input, String field, int maxLen) {if (input != null) {if (input.length() > maxLen) {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_FIELD_LIMIT.getMessage(new Object[]{field, maxLen}));}}}public static void isNotNull(Object input) {if (input instanceof String) {if (input == null || input.toString().matches("\\s*")) {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_VALUE_NOTNULL.getMessage());}} else if (input == null) {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_VALUE_NOTNULL.getMessage());}}public static void stringLength(String str, Integer length, String fieldName) {if (null != str && str.length() > length) {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_FIELD_LIMIT.getMessage(new Object[]{fieldName, length}));}}public static void notTrue(boolean result, String message) {if (result) {if (!isBlank(message)) {throw new BusException(message);} else {throw new BusException("");}}}public static void notFalse(boolean result, String message) {notTrue(!result, message);}private static boolean isBlank(CharSequence cs) {int strLen;if (cs != null && (strLen = cs.length()) != 0) {for(int i = 0; i < strLen; ++i) {if (!Character.isWhitespace(cs.charAt(i))) {return false;}}return true;} else {return true;}}public static void notNull(Object param, String message) {notTrue(param == null, message);}public static void notBlank(String param, String message) {notTrue(isBlank(param), message);}public static void checkJsonObject(String text, String field) {if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(text)) {JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(text);if (Objects.isNull(jsonObject)) {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_JSON_ILLEGAL.getMessage(new Object[]{field}));}} else {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_JSON_ILLEGAL.getMessage(new Object[]{field}));}}public static void checkJsonArray(String text, String field) {if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(text)) {try {JSONArray jsonArray = JSONArray.parseArray(text);if (Objects.isNull(jsonArray)) {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_JSON_ILLEGAL.getMessage(new Object[]{field}));}} catch (Exception var3) {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_JSON_ILLEGAL.getMessage(new Object[]{field}));}} else {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_JSON_ILLEGAL.getMessage(new Object[]{field}));}}public static void checkJson(String text, String field) {try {checkJsonObject(text, field);} catch (Exception var5) {try {checkJsonArray(text, field);} catch (Exception var4) {throw new BusException(BusExceptionMessageEnum.PRESERVER_INVALID_JSON_ILLEGAL.getMessage(new Object[]{field}));}}}
}