堆
堆(Heap)是一种特殊的数据结构。它是一棵完全二叉树(完全二叉树是指除了最后一层外,每一层上的节点数都是满的,并且最后一层的节点都集中在左边),结放在数组(切片)中,通常分为最大堆(Max Heap)和最小堆(Min Heap)两种类型。
- 最大堆:在最大堆中,对于每个非叶子节点,它的值都大于或等于其左右子节点的值。也就是说,根节点的值是整个堆中的最大值。例如,对于节点
i,如果它有左子节点2i + 1和右子节点2i+2(这里假设节点编号从 0 开始),那么heap[i]>=heap[2i + 1]且heap[i]>=heap[2i+2]。 - 最小堆:与最大堆相反,在最小堆中,对于每个非叶子节点,它的值都小于或等于其左右子节点的值。根节点的值是整个堆中的最小值。即对于节点
i,heap[i]<=heap[2i + 1]且heap[i]<=heap[2i+2]。
堆的实现
1、使用container/heap包
heap源码中定义了一个Interface 的接口,此接口一共包含五个方法,我们定义一个实现此接口的类就实现了一个二叉堆
package mainimport ("container/heap""fmt"
)type MaxHeap []intfunc (m MaxHeap) Len() int {return len(m)
}func (m MaxHeap) Less(i, j int) bool {//建立大根堆,使用>return m[i] > m[j]
}func (m *MaxHeap) Swap(i, j int) {(*m)[i], (*m)[j] = (*m)[j], (*m)[i]
}func (m *MaxHeap) Push(x any) {*m = append(*m, x.(int))
}func (m *MaxHeap) Pop() any {//拿到堆顶元素res := (*m)[len(*m)-1]//删除堆顶元素*m = (*m)[:len(*m)-1]return res
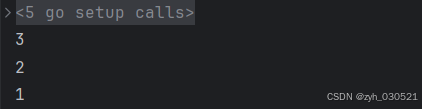
}func main() {h := make(MaxHeap, 0)//结构体实现了接口中的全部方法后,结构体也就是这个接口类型了,因此我们可以传入hheap.Init(&h)heap.Push(&h, 2)heap.Push(&h, 1)heap.Push(&h, 3)fmt.Println(heap.Pop(&h))fmt.Println(heap.Pop(&h))fmt.Println(heap.Pop(&h))}
下面我们一起去看看源码:
// Copyright 2009 The Go Authors. All rights reserved.
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style
// license that can be found in the LICENSE file.// Package heap provides heap operations for any type that implements
// heap.Interface. A heap is a tree with the property that each node is the
// minimum-valued node in its subtree.
//
// The minimum element in the tree is the root, at index 0.
//
// A heap is a common way to implement a priority queue. To build a priority
// queue, implement the Heap interface with the (negative) priority as the
// ordering for the Less method, so Push adds items while Pop removes the
// highest-priority item from the queue. The Examples include such an
// implementation; the file example_pq_test.go has the complete source.
package heapimport "sort"// The Interface type describes the requirements
// for a type using the routines in this package.
// Any type that implements it may be used as a
// min-heap with the following invariants (established after
// [Init] has been called or if the data is empty or sorted):
//
// !h.Less(j, i) for 0 <= i < h.Len() and 2*i+1 <= j <= 2*i+2 and j < h.Len()
//
// Note that [Push] and [Pop] in this interface are for package heap's
// implementation to call. To add and remove things from the heap,
// use [heap.Push] and [heap.Pop].堆的接口,定义实现该接口内部的全部方法后,我们定义的类就实现了堆
下面是sort.Interface的实现,内部有三个方法,分别是Len()、Less()、Swap()
通过Less()方法,以此确定建立的是大根堆,还是小根堆// An implementation of Interface can be sorted by the routines in this package.
// The methods refer to elements of the underlying collection by integer index.
type Interface interface {// Len is the number of elements in the collection.Len() int// Less reports whether the element with index i// must sort before the element with index j.//// If both Less(i, j) and Less(j, i) are false,// then the elements at index i and j are considered equal.// Sort may place equal elements in any order in the final result,// while Stable preserves the original input order of equal elements.//// Less must describe a transitive ordering:// - if both Less(i, j) and Less(j, k) are true, then Less(i, k) must be true as well.// - if both Less(i, j) and Less(j, k) are false, then Less(i, k) must be false as well.//// Note that floating-point comparison (the < operator on float32 or float64 values)// is not a transitive ordering when not-a-number (NaN) values are involved.// See Float64Slice.Less for a correct implementation for floating-point values.Less(i, j int) bool// Swap swaps the elements with indexes i and j.Swap(i, j int)
}^
|
|
|
重点type Interface interface {sort.InterfacePush(x any) // add x as element Len()Pop() any // remove and return element Len() - 1.
}|
|
|
——init方法,将实现接口的类init进行建堆// Init establishes the heap invariants required by the other routines in this package.
// Init is idempotent with respect to the heap invariants
// and may be called whenever the heap invariants may have been invalidated.
// The complexity is O(n) where n = h.Len().
func Init(h Interface) {// heapifyn := h.Len()for i := n/2 - 1; i >= 0; i-- {down(h, i, n)}
}Push插入元素// Push pushes the element x onto the heap.
// The complexity is O(log n) where n = h.Len().
func Push(h Interface, x any) {h.Push(x)up(h, h.Len()-1)
}Pop弹出元素// Pop removes and returns the minimum element (according to Less) from the heap.
// The complexity is O(log n) where n = h.Len().
// Pop is equivalent to [Remove](h, 0).
func Pop(h Interface) any {n := h.Len() - 1h.Swap(0, n)down(h, 0, n)return h.Pop()
}Remove移除元素// Remove removes and returns the element at index i from the heap.
// The complexity is O(log n) where n = h.Len().
func Remove(h Interface, i int) any {n := h.Len() - 1if n != i {h.Swap(i, n)if !down(h, i, n) {up(h, i)}}return h.Pop()
}Fix重新调整堆// Fix re-establishes the heap ordering after the element at index i has changed its value.
// Changing the value of the element at index i and then calling Fix is equivalent to,
// but less expensive than, calling [Remove](h, i) followed by a Push of the new value.
// The complexity is O(log n) where n = h.Len().
func Fix(h Interface, i int) {if !down(h, i, h.Len()) {up(h, i)}
}堆调整的两个重要方法,up和down,具体我没看,我们可以自己写出更简单更好理解的heapInsert和heapifyfunc up(h Interface, j int) {for {i := (j - 1) / 2 // parentif i == j || !h.Less(j, i) {break}h.Swap(i, j)j = i}
}func down(h Interface, i0, n int) bool {i := i0for {j1 := 2*i + 1if j1 >= n || j1 < 0 { // j1 < 0 after int overflowbreak}j := j1 // left childif j2 := j1 + 1; j2 < n && h.Less(j2, j1) {j = j2 // = 2*i + 2 // right child}if !h.Less(j, i) {break}h.Swap(i, j)i = j}return i > i0
}
2、自己实现堆
自己实现堆,最重要的就是heapInsert和heapify方法,通过这两个方法,以此保证正确实现堆结构。
heapInsert方法:新来的一个元素,新来的元素若大于他的父节点元素,则上升,确定其应该在堆中的正确位置,实现大根堆
for循环虽然只有一个判断,却包含了另一层判断,当index到达0位置后,循环也会停止
func heapInsert(arr []int, index int) {for arr[index] > arr[(index-1)/2] {arr[index], arr[(index-1)/2] = arr[(index-1)/2], arr[index]index = (index - 1) / 2}
}heapify方法,节点位置为最大值,实现大根堆
func heapify(arr []int, index int, heapsize int) {//左孩子的位置left := index*2 + 1for left < heapsize {//largest的含义为:节点和子节点中的最大值largest := left //一开始放在左孩子上//如果存在右孩子,并且右孩子的值比左孩子大,以此选出左右孩子中的较大节点if left+1 < heapsize && arr[left] < arr[left+1] {//在largest放在右孩子的位置largest = left + 1}//判断largest和index节点位置谁大if arr[index] > arr[largest] {//若节点大于largest,则largest来到index位置largest = index}//index位置为最大,则退出循环,不需要向下进行if largest == index {break}//交换节点位置arr[largest], arr[index] = arr[index], arr[largest]//index来到largest位置,继续下次循环index = largest//left继续来到左孩子的位置left = index * 2 + 1}
}建堆
// 建堆
func buildHeap(arr []int) {//从上至下建堆//for i := 0; i < len(arr); i++ {// heapInsert(arr, i)//}//从下至上建堆for i := len(arr) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {heapify(arr, i, len(arr))}}堆排序
能够自己实现堆之后,实现堆排序就十分简单了。
若我们实现了大根堆,那么每次堆顶元素就是最大值,那么只需要堆顶与最后一个元素进行交换,交换后,堆的大小减1,然后在将交换后位于第一位的元素使用heapify让其下降,这样循环进行,最后堆的大小减到0,那么就实现了排序。
func heapSort(arr []int) {heapSize := len(arr)heapSize--arr[0], arr[heapSize] = arr[heapSize], arr[0]for heapSize > 0 {heapify(arr, 0, heapSize)heapSize--arr[0], arr[heapSize] = arr[heapSize], arr[0]}
}Leetcode堆相关题目
(累了,下次再写)
1、215. 数组中的第K个最大元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
求数组中第K大的元素,有很简单的方法,将数组进行排序,返回第k个数,即为第k大的数。
题目要求时间复杂度为O(N),可以使用桶排序,这道题目给了数据范围,确实可以用。
题解里还有改进的快速排序,也能达到O(N)的时间复杂度。
但我们主要还是使用堆来完成。
//题解标准答案
func findKthLargest(nums []int, k int) int {//建立大根堆buildHeap(nums)heapSize := len(nums)for i := len(nums) - 1; i >= len(nums)-k+1; i-- {nums[0], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[0]heapSize--heapify(nums, 0, heapSize)}return nums[0]
}//我觉得不好理解,就自己写了i从0——K,但是需要加判断,要不会出现nums[-1]的报错
func findKthLargest(nums []int, K int) int {buildHeap(nums)heapSize := len(nums)nums[0], nums[heapSize-1] = nums[heapSize-1], nums[0]for i:= 0; i < K; i++ {heapSize--heapify(nums,0,heapSize)if heapSize-1 >= 0{nums[0], nums[heapSize-1] = nums[heapSize-1], nums[0]} else {return nums[heapSize]}}return nums[heapSize]
}func heapify(arr []int, index int, heapsize int) {//左孩子的位置left := index*2 + 1for left < heapsize {//largest的含义为:节点和子节点中的最大值largest := left //一开始放在左孩子上//如果存在右孩子,并且右孩子的值比左孩子大,以此选出左右孩子中的较大节点if left+1 < heapsize && arr[left] < arr[left+1] {//在largest放在右孩子的位置largest = left + 1}//判断largest和index节点位置谁大if arr[index] > arr[largest] {//若节点大于largest,则largest来到index位置largest = index}//index位置为最大,则退出循环,不需要向下进行if largest == index {break}//交换节点位置arr[largest], arr[index] = arr[index], arr[largest]//index来到largest位置,继续下次循环index = largest//left继续来到左孩子的位置left = index*2 + 1}
}func buildHeap(arr []int) {//从上至下建堆//for i := 0; i < len(arr); i++ {// heapInsert(arr, i)//}//从下至上建堆for i := len(arr) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {heapify(arr, i, len(arr))}}2、502. IPO - 力扣(LeetCode)
3、373. 查找和最小的 K 对数字 - 力扣(LeetCode)
TODO
4、295. 数据流的中位数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
TODO