写在前面:本文所收录真题解答都是本人自己所写,由于本人水平所限,部分题解可能存在错误,如存在错误,望各位指出。
更新:CSDN不会再更新,移步Pykt的博客
2021年真题
第一题
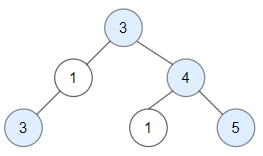
题目描述:给定一颗二叉树,树的每个节点的值为一个正整数。如果从根节点到节点 N 的路径上不存在比节点 N 的值大的节点,那么节点 N 被认为是树上的关键节点。求树上所有的关键节点的个数。请写出程序,并解释解题思路。
例子:

输入:
3, 1, 4, 3, null, 1, 5
输出:4(图中蓝色节点是关键节点)
解题思路:由题意可知,输入数据是以完全二叉树形式进行输入的,于是我们将输入数据变为一个数组,且当结点为null时在数组中的值为-1。并且易知以 data 为完全二叉树的存储结构的时候,二叉树的父节点的计算公式为parent = (child - 1) /2 ( data 默认0号位也存储了正常数据),于是对于每个结点,只需要正常遍历其所有的父节点就可以知道其是否为关键结点。
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>using namespace std;vector<int> data;
int count = 0;bool charIsDigit(char a){return a <= '9' and a >= '0';
}int charToInt(char a){return a - '0';
}int getParentIndex(int childIndex){return (childIndex - 1) / 2;
}void judgeKeyNode(int index){int pivot = data[index];int flag = true;while (index != 0){index = getParentIndex(index);if (data[index] > pivot){flag = false;break;}}if (flag){count++;}
}int main(){string input;getline(cin, input);int nodeValue = 0;bool remain = false; // 前面是否还有连续的值for (int i=0; i<input.length(); i++){char tmp = input[i];if (charIsDigit(tmp)){nodeValue = nodeValue * 10 + charToInt(tmp);}else{if (nodeValue != 0){data.push_back(nodeValue);nodeValue = 0;}else if(tmp == 'n'){data.push_back(-1);}}}data.push_back(nodeValue);// 构建树for (int i=0; i<data.size(); i++){if (data[i] != -1){judgeKeyNode(i);}}cout << count << endl;return 0;
}
第二题
题目描述:训练场上有一个台阶,总共有 n 级。一个运动员可以跳 1 级,也可以跳 2 级。求运动员有多少种跳法。请写出程序,并解释解题思路。
解题思路:这题是一个明显的动态规划的题目。设 d p [ i ] dp[i] dp[i]为当台阶数为 i i i时的跳法种树,其状态转移方程为:
d p [ i ] = d p [ i − 1 ] + d p [ i − 2 ] , i ≥ 2 dp[i]=dp[i-1]+dp[i-2]\,,i\ge 2 dp[i]=dp[i−1]+dp[i−2],i≥2
其边界条件为:dp[0]=1, dp[1]=1
示例代码:
#include <cstdio>int main(){int n;scanf("%d", &n);int dp[n+1];// 初始化dpdp[0] = 1;dp[1] = 1;for (int i=2; i<=n; i++){dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2];}printf("%d\n", dp[n]);
}
后续改进与说明:这里与LeetCode里面的爬楼梯的题目本质是一样的,可以用滚动数组对空间复杂度进行优化。
第三题
题目描述:给定一个非负整数序列 x 1 , x 2 , ⋯ , x n x_1, x_2, \cdots, x_n x1,x2,⋯,xn,可以给每一个整数取负数或者取原值,求有多少种取法使得这些整数的和等于期望值 E E E。请写出程序,并解释解题思路。
例子输入:
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3
例子输出:
5
样例解释:5 种取法分别为:
-1+1+1+1+1 = 3
1-1+1+1+1 = 3
1+1-1+1+1 = 3
1+1+1-1+1 = 3
1+1+1+1-1 = 3
解题思路:设 d p [ i ] [ v ] dp[i][v] dp[i][v]是指前 i i i个数期望为 v v v时,最多有多少种取法。
状态转移方程为:
d p [ i ] [ v ] = d p [ i − 1 ] [ v − d a t a [ i − 1 ] ] + d p [ i − 1 ] [ v + d a t a [ i + 1 ] ] dp[i][v]=dp[i-1][v-data[i-1]]+dp[i-1][v+data[i+1]] dp[i][v]=dp[i−1][v−data[i−1]]+dp[i−1][v+data[i+1]]
此处的data为存储原来数据的数组,索引从0开始,这里状态转移方程有限制,限制如下: -sum <= data[i-1] + v <= sum 且 -sum <= v - data[i-1] <= sum ,其中 sum 为输入序列的和。其边界条件为:
d p [ i ] [ j ] = 0 , 0 ≤ i ≤ d a t a . s i z e ( ) , − s u m ≤ j ≤ s u m d p [ 0 ] [ 0 ] = 1 dp[i][j]=0 \, ,0 \le i \le data.size() \,, -sum \le j \le sum \\ dp[0][0]=1 dp[i][j]=0,0≤i≤data.size(),−sum≤j≤sumdp[0][0]=1
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <map>using namespace std;vector<int> data;
int expect = 0; // 期望值
int result = 0; // 有多少种取法bool charIsDigit(char a) {return a <= '9' and a >= '0';
}int charToInt(char a) {return a - '0';
}int main() {string input;getline(cin, input);int nodeValue = 0;for (int i = 0; i < input.length(); i++) {char tmp = input[i];if (charIsDigit(tmp)) {nodeValue = nodeValue * 10 + charToInt(tmp);} else {if (nodeValue != 0) {data.push_back(nodeValue);nodeValue = 0;}}}// 最后一个值为期望值expect = nodeValue;int sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < data.size(); i++) {sum += data[i];}vector<map<int, int>> dp(data.size() + 1);// 初始化for (int j = 0; j <= data.size(); j++) {for (int i = -sum; i <= sum; i++) {if (i == 0 and j==0) {dp[j][i] = 1;} else {dp[j][i] = 0;}}}// DP的主过程for (int i = 1; i<=data.size(); i++){for (int v=-sum; v<=sum; v++){int tmp1 = 0, tmp2 = 0, currentNum = data[i-1];if (-sum <= v - currentNum and v-currentNum <= sum){tmp1 = dp[i-1][v - currentNum];}if (-sum <= currentNum + v and currentNum + v <= sum){tmp2 = dp[i-1][v+currentNum];}dp[i][v] = tmp1 + tmp2;}}cout << dp[data.size()][expect] << endl;return 0;
}
历年真题(2011-2020)专题总结
历年真题收录了本人当时准备机试的时候重点做的一些真题,有些真题或觉得做起来太繁琐,或觉得做起来太无聊,就没有去做。
动态规划
动态规划可以说是复旦历年机试中的重中之重了,基本上都有出现,且难度一般都集中在这里。
2011 最长公共子序列
问题描述:输入3个子串, 输出这3个子串的最大公共子串
输入:
abcd acb abc
输出:
ab
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>using namespace std;/*** 明显的LCS问题* 设dp[i][j][k]是指字符串1第i个字符串2第j个字符串3第k个字符之前的最长公共子序列* 状态方程:* dp[i][j][k] = dp[i-1][j-1][k-1] + str1[i]; if str1[i] == str2[j] == str3[k]* dp[i][j][k] = max{dp[i-1][j][k], dp[i][j-1][k], dp[i][j][k-1]}* 边界条件:* dp[][][] = 0;*/int main(){string str1, str2, str3, tmp, ans;cin >> str1 >> str2 >> str3;string dp[str1.length() + 1][str2.length() + 1][str3.length() + 1];for (int i=1; i<=str1.length(); i++){for (int j=1; j<=str2.length(); j++){for (int k=1; k<str3.length(); k++){if (str1[i-1] == str2[j-1] and str1[i-1] == str3[k-1]){ // 相等tmp = dp[i-1][j-1][k-1];tmp.push_back(str1[i-1]);dp[i][j][k] = tmp;}else{ // 不想等int len1 = dp[i-1][j][k].length(), len2 = dp[i][j-1][k].length(), len3 = dp[i][j][k-1].length();if (len1 > len2 and len1 > len3){dp[i][j][k] = dp[i-1][j][k];} else if(len2 > len1 and len2 > len3){dp[i][j][k] = dp[i][j-1][k];} else{dp[i][j][k] = dp[i][j][k-1];}}}}}// 输出结果for (int i=1; i<=str1.length(); i++){for (int j=1; j<=str2.length(); j++){for (int k=1; k<=str3.length(); k++){if (dp[i][j][k].length() > ans.length()){ans = dp[i][j][k];}}}}cout << ans << endl;
}
2014 字符串的编辑距离
这个题犯的错误在于把这个当做了LCS的问题进行处理,当做LCS问题处理时没办法解决
abc和acd的情况,因为这个时候会输出1而非输出2。
题目描述:
把两个字符串变成相同的三个基本操作定义如下:
1.修改一个字符(如把a变成b)
2.增加一个字符(如abed 变成abedd)
3.删除一个字符(如jackbllog 变成jackblog)
针对于jackbllog到jackblog只需要删除一个或增加一个l 就可以把两个字符串变为相同。
把这种操作需要的最小次数定义为两个字符串的编辑距离L。
编写程序计算指定文件中字符串的距离。输入两个长度不超过512字节的ASCII字符串,在屏幕上输出字符串的编辑距离。
输入:
Hello world!
Hello word!
输出:
1
#include <iostream>
#include <string>using namespace std;/*** 设dp[i][j]是指当字符串1第i个位置和字符串2第j个位置的最小编辑距离* 状态转移方程为: dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] if str1[i] == str2[j]* dp[i][j] = min{dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]} + 1; else* 边界条件为:* dp[i][0] = i* dp[0][j] = j*/int main(){string input1, input2;getline(cin, input1);getline(cin, input2);int length1 = input1.length(), length2 = input2.length();int dp[length1][length2];// 处理dp边界for (int i=0; i<=length1; i++){dp[i][0] = i;}for (int j=0; j<=length2; j++){dp[0][j] = j;}// dp过程for (int i=1; i<=length1; i++){for (int j=1; j<=length2; j++){if (input2[j-1] == input1[i-1]){dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1];}else{if (dp[i-1][j] < dp[i][j-1]){dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + 1;}else{dp[i][j] = dp[i][j-1] + 1;}}}}cout << dp[length1][length2] << endl;return 0;
}
2016 求最大连续公共字串长度
题目描述:给定两个字符串,求最大公共字串的长度,长度小于1000
输入:
1111hello2222
1133hello444
输出:
5
#include <iostream>
#include <string>using namespace std;/**** 是一道很明显DP的问题* 设dp[i][j]是字符串1第i个位置与字符串2第j个位置之前的最大连续字符串的长度* 状态转移方程: if (input[i] == input[j]) dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1]* else dp[i][j] = 0;* 边界条件: 0*/int main(){string input1, input2;getline(cin, input1);getline(cin, input2);int length1 = input1.length(), length2 = input2.length(), ans;int dp[length1 + 1][length2 + 1];// 初始化for (int i=0; i<=length1; i++){for (int j=0; j<=length2; j++){dp[i][j] = 0;}}// DPfor (int i=1; i<=length1; i++){for (int j=1; j<=length2; j++){if (input1[i-1] == input2[j-1]){dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1;}}}// 找最大值for (int i=0; i<=length1; i++){for (int j=0; j<=length2; j++){if (dp[i][j] > ans){ans = dp[i][j];}}}cout << ans << endl;
}
2019 最大连续子序列
OJ题目链接
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>using namespace std;vector<int> data, dp;// 最大连续子序列 复旦2019年真题/*** 这里很明显是一个动态规划的题* 设dp[i]是以第i个结尾的序列的最大值* 1. 状态转移方程* dp[i] = { dp[i-1] + data[i], dp[i-1] + data[i] >= 0* 0 , dp[i-1] + data[i] < 0* 2. 边界条件* dp[0] = 0;*/int main(){int n, tmp, max=0;scanf("%d", &n);for (int i=0; i<n; i++){scanf("%d", &tmp);data.push_back(tmp);}// 初始化for (int i=0; i<=n; i++){dp.push_back(0);}for (int i=1; i<=n; i++){int pivot = dp[i-1] + data[i-1];if (pivot >= 0){dp[i] = pivot;}else{dp[i] = 0;}}for (int i=0; i<=n; i++){if (dp[i] > max){max = dp[i];}}printf("%d\n", max);return 0;
}
2020 序列
题目描述:给定⼀个⻓为 n n n的序列 A,其中序列中的元素都是0~9之间的整数,对于⼀个⻓度同样为 n n n整数序列B,定义其权值为 ∣ A i − B i ∣ ( 1 ≤ i ≤ n ) |A_i-B_i| (1\le i\le n) ∣Ai−Bi∣(1≤i≤n) 之和加上 ( B j − B j + 1 ) 2 ( 1 ≤ j < n ) (B_j-B_{j+1})^2 (1\le j<n) (Bj−Bj+1)2(1≤j<n)之和。求所有⻓为 n n n的整数序列中,权值最⼩的序列的权值是多少。
输⼊格式:第⼀⾏⼀个整数 n ( 1 ≤ n ≤ 1 0 5 ) n (1\le n\le 10^5) n(1≤n≤105),表⽰序列A的⻓度。 第⼆⾏ n n n个整数 a 1 , a 2 , … , a n ( 0 ≤ a i ≤ 9 , 1 ≤ i ≤ n ) a_1, a_2, …, a_n (0\le a_i\le 9, 1\le i\le n) a1,a2,…,an(0≤ai≤9,1≤i≤n),表⽰序列A中的元素。
输出格式:仅⼀⾏⼀个整数,表⽰答案。
样例输⼊:
6
1 4 2 8 5 7
样例输出:
11
解释:
A 数组是 [1 4 2 8 5 7]
B 数组可以是 [3 4 4 5 5 6]。
权值为 ∣ A i − B i ∣ ( 1 ≤ i ≤ n ) |A_i - B_i| (1 \le i \le n) ∣Ai−Bi∣(1≤i≤n)之和加上 ( B j − B j + 1 ) 2 ( 1 ≤ j < n ) (B_j - B_{j+1})^2 (1 \le j <n) (Bj−Bj+1)2(1≤j<n)之和。
权值第⼀部分 ∣ A i − B i ∣ ( 1 ≤ i ≤ n ) |A_i - B_i| (1 \le i \le n) ∣Ai−Bi∣(1≤i≤n)之和为:
∣ 1 − 3 ∣ + ∣ 4 − 4 ∣ + ∣ 2 − 4 ∣ + ∣ 8 − 5 ∣ + ∣ 5 − 5 ∣ + ∣ 7 − 6 ∣ = 2 + 0 + 2 + 3 + 0 + 1 = 8 |1 - 3| + |4 - 4| + |2 - 4| + |8 - 5| + |5 - 5| + |7 - 6| = 2 + 0 + 2 + 3 + 0 + 1 = 8 ∣1−3∣+∣4−4∣+∣2−4∣+∣8−5∣+∣5−5∣+∣7−6∣=2+0+2+3+0+1=8
权值第⼆部分 ( B j − B j + 1 ) 2 ( 1 ≤ j < n ) (B_j - B_{j+1})^2 (1\le j <n) (Bj−Bj+1)2(1≤j<n)之和为:
( 3 − 4 ) 2 + ( 4 − 4 ) 2 + ( 4 − 5 ) 2 + ( 5 − 5 ) 2 + ( 5 − 6 ) 2 = 1 + 0 + 1 + 0 + 1 = 3 (3 - 4)^2 + (4 - 4)^2 + (4 - 5)^2 + (5 - 5)^2 + (5 - 6)^2 = 1 + 0 + 1 + 0 + 1 = 3 (3−4)2+(4−4)2+(4−5)2+(5−5)2+(5−6)2=1+0+1+0+1=3
所以总权值为 8 + 3 = 11。
示例代码:
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <climits>using namespace std;int calculateAWeight(int a_value, int b_value){return abs(a_value - b_value);
}int calculateBWeight(int b_value_i, int b_value_i2){return (b_value_i - b_value_i2) * (b_value_i - b_value_i2);
}int main(){int n;scanf("%d", &n);int dataA[n], dp[n][10], ans = INT_MAX;for (int i=0; i<n; i++){scanf("%d", &dataA[i]);}// 初始化for (int i=0; i<=9; i++){dp[0][i] = calculateAWeight(dataA[0], i);}// DP Mainfor (int i=1; i<n; i++){for (int j=0; j<10; j++){int minWeight = INT_MAX;int weightA = calculateAWeight(dataA[i], j);for (int k=0; k<10; k++){int weightB = calculateBWeight(k, j);int total = dp[i-1][k] + weightB;if (total < minWeight){minWeight = total;}}dp[i][j] = weightA + minWeight;}}for (int i=0; i<=9; i++){if (dp[n-1][i] < ans){ans = dp[n-1][i];}}printf("%d\n", ans);return 0;
}
递归
搞清楚递归只要搞清两点:
- 结束条件
- 把问题规模缩小
2014 Hanoi塔
其实如果单纯求移动次数,可以简单知道: f ( n ) = 2 f ( n − 1 ) + 1 f(n)=2f(n-1)+1 f(n)=2f(n−1)+1,从而根据这个式子去书写代码。
其实也可以根据这个得到通项公式: f ( n ) = 2 f ( n − 1 ) + 1 → f ( n ) + 1 = 2 ( f ( n − 1 ) + 1 ) f(n)=2f(n-1)+1 \rightarrow f(n) + 1=2(f(n-1)+1) f(n)=2f(n−1)+1→f(n)+1=2(f(n−1)+1)由等比数列的性质可得: f ( n ) = 2 n − 1 f(n)=2^n-1 f(n)=2n−1
问题描述
Hanoi塔问题是印度的一个古老的传说。开天辟地的神勃拉玛在一个庙里留下了三根金刚石的棒,第一根上面套着64个圆的金片,最大的一个在底下,其余一个比一个小,依次叠上去,庙里的众僧不倦地把它们一个个地从这根棒搬到另一根棒上,规定可利用中间的一根棒作为帮助,但每次只能搬一个,而且大的不能放在小的上面。
请编写程序,把A柱上的n个金片,搬动到C柱(中间可以使用B柱),使得搬动的次数最少。输入金片的个数n(1<=n<=64),输出总搬动次数,以及最后100次搬动。如果搬动次数小于等于100 则全部输出;每个搬动占一行,加上是这第几次搬动的数字和”:”,格式见示例。
输入:
2
输出:
3
1:A->B
2:A->C
3:B->C
#include <cstdio>int current = 0, total = 1;void print(char from, char to);void hanoi(char from, char to, char helper, int n){if (n==1){current++;print(from, to);}else{hanoi(from, helper, to, n-1);// single movecurrent ++;print(from , to);// reversehanoi(helper, to, from, n-1);}
}void print(char from, char to){if (total - current < 100){ // 倒序100以内才进行打印printf("%d:%c->%c\n", current, from, to);}
}int main(){int n;scanf("%d", &n);// 根据通项公式计算总的移动次数for (int i=0; i<n; i++){total *= 2;}total -= 1;hanoi('A', 'C', 'B', n);return 0;
}
栈与队列
2016 后缀序列求值
后缀表达式的运算符在操作数后面,在后缀表达式中已考虑了运算符的优先级。
题目描述:
给定一个后缀序列,要求求值,只有加减
输入:
123++4-
输出:
2
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>using namespace std;stack<int> numbers;int charToInt(char target){return target - '0';
}bool charIsNumber(char target){if (target >= '0' and target <= '9'){return true;}else{return false;}
}int main(){int ans = 0, first, second;char tmp;string input;getline(cin, input);for (int i=0; i<input.length(); i++){tmp = input[i];if (charIsNumber(tmp)){ // 为数字的话numbers.push(charToInt(tmp));}else{second = numbers.top();numbers.pop();first = numbers.top();numbers.pop();if (tmp == '+'){ans = first + second;}else{ans = first - second;}numbers.push(ans);}}cout << ans << endl;return 0;
}
树与二叉树
2016 字符串的哈夫曼编码的最短长度
有个问题,这里如果只输入完全一样的字符串,结果是0,其实不满足题意,但是Huffman编码确实没有这么特殊的例子。
题目描述:给定一个字符串(长度不超过100),求哈夫曼编码的最短长度。
输入1:
abbcccdddd
输出1:
19
输入2:
we will we will r u
输出2:
50
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <map>using namespace std;typedef struct Node{char data;int weight;bool leaf;struct Node *left;struct Node *right;Node(char _data, int _weight, bool isLeaf, struct Node * _left = nullptr, struct Node * _right = nullptr){data = _data;weight = _weight;leaf = isLeaf;left = _left;right = _right;}
}*tree, Node;struct cmp{bool operator () (tree n1, tree n2){return n1->weight > n2->weight;}
};priority_queue<tree, vector<tree>, cmp> q;
map<char, int> charCount;
map<char, int> charLength;void calculateHuffmanCodeLength(tree root, int length=0){if (root != nullptr){if (root->leaf){charLength[root->data] = length;}else{length++;calculateHuffmanCodeLength(root->left, length);calculateHuffmanCodeLength(root->right, length);}}
}int main(){string input;tree first, second, head;int sum=0;getline(cin, input);for (int i=0; i<input.length(); i++){char tmp = input[i];if (charCount.find(tmp) != charCount.end()){ // 找到了charCount[tmp] += 1;}else{charCount[tmp] = 1;}}// 构建初始的优先队列for (auto it=charCount.begin(); it!=charCount.end(); it++){q.push(new Node(it->first, it->second, true));}// 构建Huffman Treewhile (q.size() != 1){first = q.top();q.pop();second = q.top();q.pop();// 构建一个新的节点,然后放进去q.push(new Node(' ', first->weight + second->weight, false, first, second));}head = q.top();calculateHuffmanCodeLength(head);for (auto it=charCount.begin(); it!=charCount.end(); it++){sum += it->second * charLength[it->first];}cout << sum << endl;return 0;
}
2019 有向树形态
OJ题目链接
注意范围,这里要使用long long而不能使用int,要不然超了。
#include <cstdio>// 2019年真题 有向树形态int main(){int n;scanf("%d", &n);long long data[n+1];data[0] = 1;data[1] = 1;for (int i=2; i<=n; i++){long long sum = 0, left;for (int j=0; j<= i-1; j++){left = i - j - 1;if (left==j){sum += data[j]*data[j];}else{sum += data[j]*data[left];}data[i] = sum;}}printf("%lld\n", data[n]);return 0;
}
2020 二叉搜索树
题目描述:
给定⼀个 1~n 的排列 P,即⻓度为 n,且 1~n 中所有数字都恰好出现⼀次的序列。现在按顺序将排列中的元素⼀⼀插⼊到初始为空的⼆叉搜索树中(左⼩右⼤),问最后每个节点的⽗亲节点的元素是什么。特别地,根节点的⽗亲节点元素视为 0。
输入格式:
第⼀⾏⼀个整数 n ( 1 ≤ n ≤ 1 0 5 ) n (1\le n \le 10^5) n(1≤n≤105),表⽰排列 P 中的元素个数。
第⼆⾏ n 个整数 p 1 , p 2 , . . . , p n ( 1 ≤ p i ≤ n , 1 ≤ i ≤ n ) p1, p2, ..., pn (1\le pi\le n, 1\le i\le n) p1,p2,...,pn(1≤pi≤n,1≤i≤n),表⽰给定的排列。
输出格式:
⼀⾏ n 个整数,其中第 i 个整数 ai 表⽰元素 i 对应节点的⽗亲节点的元素。特别地,根节点的⽗亲节点元素视为 0。
样例输入:
5
2 3 5 1 4
样例输出:
2 0 2 5 3
样例解释:
最后建出来的⼆叉搜索树如下:

1 的⽗亲为 2,2 为根结点,所以⽗亲为 0,3 的⽗亲为 2,4 的⽗亲为 5,5 的⽗亲为 3。
解答:想到的一种方法是复杂度比较高的方法,在n比较大的时候会有段错误。
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>using namespace std;typedef struct Node{int data;struct Node * left;struct Node * right;Node(int _data){data = _data;left = nullptr;right = nullptr;}
}*tree, Node;vector<int> result;
tree root = nullptr;void insert(tree &head, int target){if (head == nullptr){head = new Node(target);}else{if (target < head->data){insert(head->left, target);}else{insert(head->right, target);}}
}void inorderTraverse(tree head, int parentData){if (head != nullptr){inorderTraverse(head->left, head->data);result.push_back(parentData);inorderTraverse(head->right, head->data);}
}int main(){int n, tmp;scanf("%d", &n);for (int i=0; i<n; i++){scanf("%d", &tmp);insert(root, tmp);}inorderTraverse(root, 0);for (int i=0; i<result.size(); i++){printf("%d", result[i]);if (i != result.size() - 1){printf(" ");}else{printf("\n");}}return 0;
}
某大佬解法:
数据规模1e5,显然需要至少 n log n n\log{n} nlogn的算法,而二叉排序树最差情况为 n 2 n^2 n2,因此不能考虑建树
分析二叉排序树的特点:
- 新加入的结点大于树中的所有结点,则该结点的父亲结点为值小于自己且最接近自身的结点
- 新加入的结点小于树中的所有结点,则该结点的父亲结点为值大于自己且最接近自身的结点
- 更一般的,树中的结点既有比新加入的结点大的也有比新加入的结点小的。
此时新节点的父亲结点也一定是最接近自身的大于自己或者小于自己的结点,设大于自己的结点为m,小于自己的结点为n,判断是新结点的父亲结点是m和n哪个结点的依据是:如果大于的结点m先于小于的结点n插入,由于n<m,根据插入排序的规律,n可能在m的左子树上,或者是m的父亲结点,但是由于m先于n插入,n不可能是m的父亲结点,所有n在m的左子树上;同理小于的结点n先于大于的结点m插入,m在n的右子树上由于新结点的大小介于m和n之间,所有新结点的父亲结点,必定为后插入的结点。
此时问题转化为寻找,之前插入的元素中,大小最接近新结点的两个大小值,并判断这两个值的插入顺序。普通的查找在最坏情况下复杂度为n,插入n次复杂度为 n 2 n^2 n2,因此问题转化为$ log n \log{n} logn的查找:有二分查找和平衡二叉树查找,二分查找需要连续存储且排序,尽管排序 n log n n\log{n} nlogn,但每插入一个都要排序一次,连续存储的呢情况复杂度不会低于 n 2 n^2 n2,因此只能平衡二叉树查找,STL的set和map都是红黑树结构属于平衡二叉树,又因为需要保存结点的插入序号和结点本身的值,采用map结构。
简单模拟
2015 长方形中的正方形
OJ题目链接
#include <cstdio>int sum = 0;void cutRectangle(int height, int width){if(height > width){cutRectangle(width, height - width);}else if(width > height){cutRectangle(height, width - height);}sum++;
}int main(){int width, height;scanf("%d%d", &height, &width);cutRectangle(height, width);printf("%d\n", sum);return 0;
}
2015 a与b得到c
Oh题目链接
#include <cstdio>int main(){int a, b, c;bool flag = false;scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);if (a * b == c){flag = true;}if (a + b == c){flag = true;}if (a - b == c){flag = true;}if (b - a == c){flag = true;}if (double(b) / double (a) == double (c)){flag = true;}if (double(a) / double (b) == double (c)){flag = true;}if (flag){printf("YES\n");}else{printf("NO\n");}return 0;
}
2018 求众数
OJ题目链接
这个题虽然使用下面的解题方法复杂度也就是 O ( n log n ) O(n\log{n}) O(nlogn),复杂度可以接受,但也可以使用map进行处理的,处理过程感觉只会更加简单。
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#define MAX 100000// 2018年真题
int data[MAX];bool cmp(int a, int b){return a < b;
}int main(){int n;int max=0, max_count=0, current=0, current_count=0;scanf("%d", &n);for (int i=0; i<n; i++){scanf("%d", &data[i]);}// 排序std::sort(data, data+n, cmp);// 统计for (int i=0; i<n; i++){if (data[i] == current){current_count++;}else{// 统计之前的频率if (current_count > max_count){max = current;max_count = current_count;}current = data[i];current_count = 1;}}// 对最后一个元素进行统计if (current_count > max_count){max = current;max_count = current_count;}// 输出结果printf("%d\n", max);return 0;
}
2018 解一元一次方程
OJ题目链接
感觉这种写法有几个问题:
- 没有考虑乘除法
- 没有考虑小数的情况
#include <iostream>
#include <string>using namespace std;// 复旦2018年真题,求解一元一次方程组/*** 1. 有无穷个解,x的系数为0, 剩余等式成立* 2. 无解,x的系数为0, 剩余等式不成立* 3. 有唯一解,x的系数不为0*/bool charIsNumber(char target){if (target >= '0' and target <= '9'){return true;}return false;
}int charToInt(char target){return target - '0';
}int main(){int tmp = 0, last = 0;// 分别表示数字和未知数int coefficient=0, number=0;// 分别表示当前的数是否为正数,1为正数,-1为复试,后面那个reverse为1表示不用反过来,如果为-1表示需要反过来int positive=1, reverse=1;string input;getline(cin, input);// 遍历for (int i=0; i<input.length(); i++){if (charIsNumber(input[i])){tmp = charToInt(input[i]);if (last == 0){ // 之前没有值last = tmp;}else{ // 之前有值last = last * 10 + tmp;}}else if(input[i] == 'x'){if (last == 0){last = 1;}coefficient += last * positive * reverse;last = 0;}else if(input[i] == '+'){number += last * positive * reverse;positive = 1;last = 0;}else if(input[i] == '-'){number += last * positive * reverse;positive = -1;last = 0;}else if(input[i] == '='){number += last * positive * reverse;last = 0;reverse = -1;positive = 1;}}// 如果最后还有值number += last * positive * reverse;if (coefficient == 0 and number == 0){cout << "infinite solutions" << endl;}else if(coefficient == 0 and number != 0){cout << "no solution" << endl;}else{cout << "x=" << -number/coefficient << endl;}return 0;
}
2018 骨牌
OJ题目链接
之前有个测试点没有通过:n=10000的时候,因为表示范围超出了int的范围,所以造成了错误,因此在求dp的过程中就要先去取余数。
#include <cstdio>// 2018年复旦真题 骨牌 非常明显是一个dp的问题/*** DP问题两个关键的地方* 1. 边界* dp[1] = 1 dp[2] = 2* 2. 状态转移方程* dp[n] = dp[n-1] + dp[n-2]*/int main(){int n;scanf("%d", &n);int dp[n+2];dp[0] = 0;dp[1] = 1;for (int i=2; i<=n+1; i++){dp[i] = (dp[i-1] + dp[i-2])% 999983;}printf("%d\n", dp[n+1]);return 0;
}
2018 集合交并
OJ题目链接
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>using namespace std;
// 2018年复旦真题 集合交并vector<int > outer, inner, tmp_vec;bool inVector(int target, vector<int> data){for (int i=0; i<data.size(); i++){if (target == data[i]){return true;}}return false;
}int main(){int first, second, tmp;scanf("%d%d", &first, &second);while (first-- >0){scanf("%d", &tmp);if (!inVector(tmp, outer)){outer.push_back(tmp);}}while (second-- >0){scanf("%d", &tmp);if (!inVector(tmp, tmp_vec)){tmp_vec.push_back(tmp);}}for (int i=0; i<tmp_vec.size(); i++){if (inVector(tmp_vec[i], outer)){inner.push_back(tmp_vec[i]);}else{outer.push_back(tmp_vec[i]);}}printf("%d %d\n", inner.size(), outer.size());return 0;
}
2018 约数求和
OJ题目链接
常规方法枚举是会超时的,这样子减少重复运算才能够满足时间复杂度。
#include <cstdio>int main(){int n; long long sum=0;scanf("%d", &n);for (int i=1; i<=n; i++){sum += i*(n/i);}printf("%lld\n", sum);
}
2018 求交点
OJ题目链接
#include <cstdio>// 2018年真题 求两直线 交点int main() {double x0, x1, x2, x3, y0, y1, y2, y3;scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", &x0, &y0, &x1, &y1, &x2, &y2, &x3, &y3);double k1 = (y1 - y0) / (x1 - x0);double b1 = y1 - x1 * k1;double k2 = (y3 - y2) / (x3 - x2);double b2 = y3 - x3 * k2;if (k1 == k2) {printf("Parallel or coincident\n");return 0;}double ansx = (b1 - b2) / (k2 - k1);double ansy = k1 * ansx + b1;printf("%.2f %.2f\n", ansx, ansy);return 0;
}
2019 相隔天数
OJ题目链接
这里还要注意判断闰年的方式。
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;//month[2][0]平年, month[2][1]闰年
int month[13][2] = {{0,0}, {31, 31}, {28,29}, {31,31}, {30,30}, {31, 31}, {30,30},{31, 31}, {31, 31}, {30,30}, {31, 31},{30,30},{31, 31}} ;bool isLeapYear(int year){if(year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0)){return true;}return false;
}int main(){int time1, time2 = 20190205;scanf("%d", &time1);if(time1 > time2){swap(time1, time2);}int y1, m1, d1, y2, m2, d2;y1 = time1 / 10000, m1 = time1 % 10000 / 100, d1 = time1 % 100;y2 = time2 / 10000, m2 = time2 % 10000 / 100, d2 = time2 % 100;int num = 0;while(y1 < y2 || m1 < m2 || d1 < d2){d1++;num++;if(d1 == month[m1][isLeapYear(y1)] + 1){m1++;d1 = 1;}if(m1 == 13){y1++;m1 = 1;}}cout << num << endl;return 0;
}
2020 斗牛
题目描述:
给定五个0~9 范围内的整数 a 1 , a 2 , a 3 , a 4 , a 5 a_1, a_2, a_3, a_4, a_5 a1,a2,a3,a4,a5。如果能从五个整数中选出三个并且这三个整数的和为10 的倍数(包括 0),那么这五个整数的权值即为剩下两个没被选出来的整数的和对10取余的结果,显然如果有多个三元组满⾜和是10的倍数,剩下两个数之和对10取余的结果都是相同的;如果 选不出这样三个整数,则这五个整数的权值为 -1。 现在给定 T组数据,每组数据包含五个 0~9 范围内的整数,分别求这T组数据中五个整数的权值。
输⼊格式:
第⼀⾏⼀个整数 T ( 1 < = T < = 1000 ) T (1<=T<=1000) T(1<=T<=1000),表⽰数据组数。
接下来 T ⾏,每⾏ 5 个 0~9 的整数,表⽰⼀组数据。
输出格式:
输出T⾏,每⾏⼀个整数,表⽰每组数据中五个整数的权值。
样例输⼊:
4
1 0 0 1 0
1 0 0 8 6
3 4 5 6 7
4 5 6 7 8
样例输出:
2
-1
-1
0
解释:
在第⼀组(1 0 0 1 0)中,三元组 0 0 0 的和为 0,是 10 的倍数,剩余的 1 1 之和为 2,对 10 取余为 2。
在第⼆组中,不存在任何⼀个三元祖只和为 10 的倍数。
在第四组中,三元组 5 7 8 的和为 20,是 10 的倍数,剩余的 4 6 只和为 10,对 10取余为 0。
在第五组中,三元组 0 3 7 和三元组 0 4 6 的和都是 10,是 10 的倍数,但是根据简单的数论可知,如 果存在多个三元组满⾜情况,那么剩余数字的结果之和对 10 取余是相等的,在本例中和为 10,对 10 取余为 0。
#include <cstdio>int calculate(int* data){for (int i=0; i<5; i++){for(int j=i+1; j<5; j++){// 看看剩下三张牌是否能为10的倍数int total = 0;for (int k=0; k<5; k++){if (k != i and k != j){total += data[k];}}if (total % 10 == 0){return (data[i] + data[j]) % 10;}}}return -1;
}int main(){int n, data[5];scanf("%d", &n);int result[n], index=0;while (n-- > 0){for (int i=0; i<5; i++){scanf("%d", &data[i]);}result[index++] = calculate(data);}for (int i=0; i<index; i++){printf("%d\n", result[i]);}return 0;
}
2020 打地鼠
题目描述:
给定 n 个整数 a 1 , a 2 , . . . , a n a_1, a_2, ..., a_n a1,a2,...,an和⼀个d,你需要选出若⼲个整数,使得将这些整数从⼩到⼤排好序之后,任意两个相邻的数之差都不⼩于给定的 d,问最多能选多少个数出来。
输⼊格式:
第⼀⾏两个整数 n , d ( 1 < = n < = 1 0 5 , 0 < = d < = 1 0 9 ) n,d (1<=n<=10^5, 0<=d<=10^9) n,d(1<=n<=105,0<=d<=109),分别表⽰整数个数和相邻整数差的下界。
第⼆⾏n个整数 a 1 , a 2 , . . . , a n ( 1 < = a i < = 1 0 9 , 1 < = i < = n ) a_1, a_2, ..., a_n (1<=a_i<=10^9, 1<=i<=n) a1,a2,...,an(1<=ai<=109,1<=i<=n),表⽰给定的 n 个整数。
输出格式:
仅⼀⾏⼀个整数,表⽰答案。
样例输⼊:
6 2
1 4 2 8 5 7
样例输出:
3
解释:
注意,选出的数在排序后,相邻两数之差不⼩于给定值。 ⽐如,对于给定值 2,[1 4 7] 是⼀个满⾜条件的选择⽅案,但是[1 4 5] 却不是,因为 5 - 4 = 1 < 2。 在本样例中,[1 4 7],[1 4 8],[1 5 7],[1 5 8],[2 4 7],[2 4 8] 都是满⾜要求的选择⽅案,但是⽆论如何都没有办法得到⼀个选出 4 个数且满⾜条件的⽅案,所以本样例的答案为 3。
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>int main(){int n, d, ans=1;scanf("%d%d", &n, &d);int data[n];for (int i=0; i<n; i++){scanf("%d", &data[i]);}// 排序std::sort(data, data+n); // 默认升序// Main Partint cmpBase = data[0];for (int i=1; i<n; i++){if (data[i] - cmpBase >= d){ans += 1;cmpBase = data[i];}}printf("%d\n", ans);return 0;
}
2020 排队打饭
题目描述:
下课了,有 n 位同学陆续赶到⻝堂进⾏排队打饭,其中第 i 位同学的到达时间为 ai,打饭耗时为 ti, 等待时间上限为 bi,即如果其在第 ai+bi 秒的时刻仍然没有轮到他开始打饭,那么他将离开打饭队列,另寻吃饭的地⽅。问每位同学的开始打饭时间,或者指出其提前离开了队伍(如果这样则输出 -1)。
输入格式:
第⼀⾏⼀个整数 n ( 1 ≤ n ≤ 1 0 5 ) n (1\le n\le10^5) n(1≤n≤105),表⽰来打饭的同学数量。
接下来 n ⾏,每⾏三个整数 a i , t i , b i ( 1 ≤ a i , t i , b i ≤ 1 0 9 , 1 ≤ i ≤ n ) ai,ti,bi (1\le ai,ti,bi\le 10^9, 1\le i\le n) ai,ti,bi(1≤ai,ti,bi≤109,1≤i≤n),分别表⽰每位同学的到达时间、打饭耗时、等待时间上限。 保证 a1<a2<…<an
输出格式:
⼀⾏ n 个整数,表⽰每位同学的开始打饭时间或者 -1(如果该同学提前离开了队伍)。
样例输入:
4
1 3 3
2 2 2
3 9 1
4 3 2
样例输出:
1 4 -1 6
解释:
第⼀个同学在 1 时刻到达队列,需要 3 个单位时间才能打好饭(也就是说如果在 1 时刻开始打饭,那么将在 1 + 3 = 4 时刻打好饭离开),最⻓等待时间为 3 个单位时间(也就说如果在到达队列之后的 3 单位时间后还没开始给他打饭,他就忍耐不了离开了)。
在本样例中,
1 时刻:第⼀个同学在 1 时刻到达队列,同时开始了打饭操作(对应输出的第⼀个值为 1)。
2 时刻:在 2 时刻,第⼆个同学加⼊了队列,给第⼆个同学打饭需要 2 个单位时间,但是如果在等待 了 2 个单位时间没给第⼆个同学打饭的话,第⼆个同学将离开。
3 时刻:在 3 时刻,第三个同学加⼊了队列,给第三个同学打饭需要 9 个单位时间,但是如果在等待 了 1 个单位时间没给第三个同学打饭的话,第三个同学将离开,换句话说,如果在 3 (到达时刻) + 1 (可等待时间⻓度)= 4 时刻还没给第三个同学打饭,那么第三个同学将离开。
4 时刻:第⼀个同学在时刻 4 打完饭离开,同时队列⾥的第⼆个同学开始打饭(对应输出的第⼆个值 为 4),此时第三个同学没有达到饭,所以第三个同学就在时刻 4 离开了队伍(对应输出的第三个值 为 -1)。同时,在时刻 4,第四个同学也加⼊了队列,第四个同学最⻓等待到 4(到达时刻)+ 2 (可等待时间⻓度)= 6 时刻。
5 时刻:5 时刻还在给第⼆个同学打饭,第四个同学还在队列⾥⾯排队。
6 时刻:6 时刻,第⼆个同学打饭完成,同时第四个同学开始打饭(对应输出的第四个值为 6)。
根据上⾯描述的过程,输出为 1 4 -1 6。
#include <cstdio>int main(){int n, arriveTime, dafanTime, waitTime, lastFinishTime=0;scanf("%d", &n);int result[n];for (int i=0; i<n; i++){scanf("%d%d%d", &arriveTime, &dafanTime, &waitTime);if (lastFinishTime > arriveTime + waitTime){ // 到了忍受上限,离开result[i] = -1;}else{result[i] = arriveTime > lastFinishTime ? arriveTime : lastFinishTime;lastFinishTime = result[i] + dafanTime;}}// 输出结果for (int i=0; i<n; i++){printf("%d", result[i]);if (i != n-1){printf(" ");}else{printf("\n");}}return 0;
}