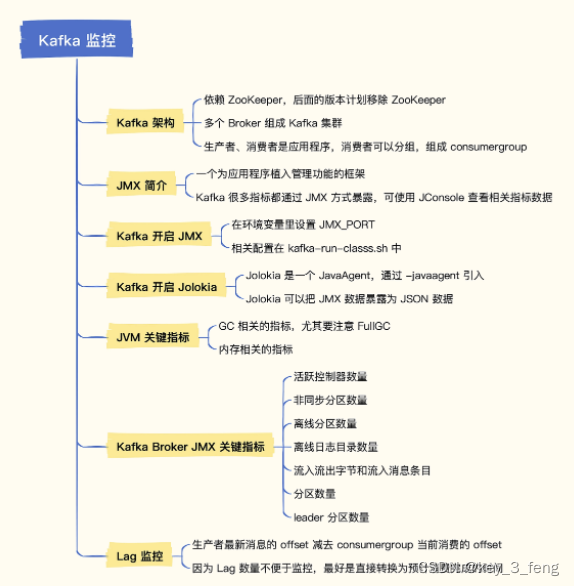
1、kubectl 概述
kubectl是一种命令行工具,用于管理Kubernetes集群和与其相关的资源。通过kubectl,您可以查看和管理Pod、Deployment、Service、Volume、ConfigMap等资源,也可以创建、删除和更新它们。
kubectl还提供了许多其他功能,例如:
- 查看集群状态、节点列表和事件日志。
- 在Pod中执行命令或启动交互式终端。
- 管理Secret和ConfigMap。
- 部署应用程序、扩展和缩小应用程序副本数量。
- 在多个Kubernetes集群之间切换。
kubectl是Kubernetes的核心组件之一,可帮助管理员和开发人员管理和操作Kubernetes集群。
2、kubectl 命令的语法
使用以下语法从终端窗口运行 kubectl 命令:
kubectl [command] [TYPE] [NAME] [flags]
(1)comand:指定要对资源执行的操作,例如 create、get、describe 和 delete
(2)TYPE:指定资源类型,资源类型是大小写敏感的,开发者能够以单数、复数和缩略的形式。
例如,以下命令输出相同的结果

(3)NAME:指定资源的名称,名称也大小写敏感的。如果省略名称,则会显示所有资源的详细信息
在对多个资源执行操作时,你可以按类型和名称指定每个资源,或指定一个或多个文件
例如
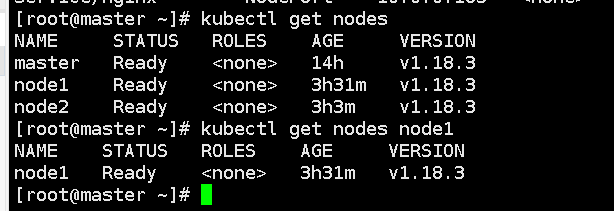
kubectl get nodes
kubectl get nodes node1
(4)flags:指定可选的参数。例如,可用-s 或者–server 参数指定 Kubernetes API server 的地址和端口。
3、kubectl help 获取更多信息
如果你需要帮助,可在终端窗口中运行 kubectl help
具体的语法使用方式可以通过 kubectl 命令的内置帮助文档来查看,例如:
kubectl --help
kubectl [command] --help
kubectl [command] [TYPE] --help
kubectl [command] [TYPE] [NAME] --help
kubectl --help
[root@master ~]# kubectl --help
kubectl controls the Kubernetes cluster manager.Find more information at: https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/kubectl/overview/Basic Commands (Beginner):create Create a resource from a file or from stdin.expose 使用 replication controller, service, deployment 或者 pod 并暴露它作为一个 新的 Kubernetes
Servicerun 在集群中运行一个指定的镜像set 为 objects 设置一个指定的特征Basic Commands (Intermediate):explain 查看资源的文档get 显示一个或更多 resourcesedit 在服务器上编辑一个资源delete Delete resources by filenames, stdin, resources and names, or by resources and label selectorDeploy Commands:rollout Manage the rollout of a resourcescale Set a new size for a Deployment, ReplicaSet or Replication Controllerautoscale 自动调整一个 Deployment, ReplicaSet, 或者 ReplicationController 的副本数量Cluster Management Commands:certificate 修改 certificate 资源.cluster-info 显示集群信息top Display Resource (CPU/Memory/Storage) usage.cordon 标记 node 为 unschedulableuncordon 标记 node 为 schedulabledrain Drain node in preparation for maintenancetaint 更新一个或者多个 node 上的 taintsTroubleshooting and Debugging Commands:describe 显示一个指定 resource 或者 group 的 resources 详情logs 输出容器在 pod 中的日志attach Attach 到一个运行中的 containerexec 在一个 container 中执行一个命令port-forward Forward one or more local ports to a podproxy 运行一个 proxy 到 Kubernetes API servercp 复制 files 和 directories 到 containers 和从容器中复制 files 和 directories.auth Inspect authorizationAdvanced Commands:diff Diff live version against would-be applied versionapply 通过文件名或标准输入流(stdin)对资源进行配置patch 使用 strategic merge patch 更新一个资源的 field(s)replace 通过 filename 或者 stdin替换一个资源wait Experimental: Wait for a specific condition on one or many resources.convert 在不同的 API versions 转换配置文件kustomize Build a kustomization target from a directory or a remote url.Settings Commands:label 更新在这个资源上的 labelsannotate 更新一个资源的注解completion Output shell completion code for the specified shell (bash or zsh)Other Commands:alpha Commands for features in alphaapi-resources Print the supported API resources on the serverapi-versions Print the supported API versions on the server, in the form of "group/version"config 修改 kubeconfig 文件plugin Provides utilities for interacting with plugins.version 输出 client 和 server 的版本信息Usage:kubectl [flags] [options]Use "kubectl <command> --help" for more information about a given command.
Use "kubectl options" for a list of global command-line options (applies to all commands).
kubectl get --help
[root@master ~]# kubectl get --help
Display one or many resourcesPrints a table of the most important information about the specified resources. You can filter the list using a label
selector and the --selector flag. If the desired resource type is namespaced you will only see results in your current
namespace unless you pass --all-namespaces.Uninitialized objects are not shown unless --include-uninitialized is passed.By specifying the output as 'template' and providing a Go template as the value of the --template flag, you can filter
the attributes of the fetched resources.Use "kubectl api-resources" for a complete list of supported resources.Examples:# List all pods in ps output format.kubectl get pods# List all pods in ps output format with more information (such as node name).kubectl get pods -o wide# List a single replication controller with specified NAME in ps output format.kubectl get replicationcontroller web# List deployments in JSON output format, in the "v1" version of the "apps" API group:kubectl get deployments.v1.apps -o json# List a single pod in JSON output format.kubectl get -o json pod web-pod-13je7# List a pod identified by type and name specified in "pod.yaml" in JSON output format.kubectl get -f pod.yaml -o json# List resources from a directory with kustomization.yaml - e.g. dir/kustomization.yaml.kubectl get -k dir/# Return only the phase value of the specified pod.kubectl get -o template pod/web-pod-13je7 --template={{.status.phase}}# List resource information in custom columns.kubectl get pod test-pod -o custom-columns=CONTAINER:.spec.containers[0].name,IMAGE:.spec.containers[0].image# List all replication controllers and services together in ps output format.kubectl get rc,services# List one or more resources by their type and names.kubectl get rc/web service/frontend pods/web-pod-13je7Options:-A, --all-namespaces=false: If present, list the requested object(s) across all namespaces. Namespace in current
context is ignored even if specified with --namespace.--allow-missing-template-keys=true: If true, ignore any errors in templates when a field or map key is missing in
the template. Only applies to golang and jsonpath output formats.--chunk-size=500: Return large lists in chunks rather than all at once. Pass 0 to disable. This flag is beta and
may change in the future.--field-selector='': Selector (field query) to filter on, supports '=', '==', and '!='.(e.g. --field-selector
key1=value1,key2=value2). The server only supports a limited number of field queries per type.-f, --filename=[]: Filename, directory, or URL to files identifying the resource to get from a server.--ignore-not-found=false: If the requested object does not exist the command will return exit code 0.-k, --kustomize='': Process the kustomization directory. This flag can't be used together with -f or -R.-L, --label-columns=[]: Accepts a comma separated list of labels that are going to be presented as columns. Names are
case-sensitive. You can also use multiple flag options like -L label1 -L label2...--no-headers=false: When using the default or custom-column output format, don't print headers (default print
headers).-o, --output='': Output format. One of:
json|yaml|wide|name|custom-columns=...|custom-columns-file=...|go-template=...|go-template-file=...|jsonpath=...|jsonpath-file=...
See custom columns [http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/kubectl-overview/#custom-columns], golang template
[http://golang.org/pkg/text/template/#pkg-overview] and jsonpath template
[http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/jsonpath].--output-watch-events=false: Output watch event objects when --watch or --watch-only is used. Existing objects are
output as initial ADDED events.--raw='': Raw URI to request from the server. Uses the transport specified by the kubeconfig file.-R, --recursive=false: Process the directory used in -f, --filename recursively. Useful when you want to manage
related manifests organized within the same directory.-l, --selector='': Selector (label query) to filter on, supports '=', '==', and '!='.(e.g. -l key1=value1,key2=value2)--server-print=true: If true, have the server return the appropriate table output. Supports extension APIs and
CRDs.--show-kind=false: If present, list the resource type for the requested object(s).--show-labels=false: When printing, show all labels as the last column (default hide labels column)--sort-by='': If non-empty, sort list types using this field specification. The field specification is expressed
as a JSONPath expression (e.g. '{.metadata.name}'). The field in the API resource specified by this JSONPath expression
must be an integer or a string.--template='': Template string or path to template file to use when -o=go-template, -o=go-template-file. The
template format is golang templates [http://golang.org/pkg/text/template/#pkg-overview].-w, --watch=false: After listing/getting the requested object, watch for changes. Uninitialized objects are excluded
if no object name is provided.--watch-only=false: Watch for changes to the requested object(s), without listing/getting first.Usage:kubectl get
[(-o|--output=)json|yaml|wide|custom-columns=...|custom-columns-file=...|go-template=...|go-template-file=...|jsonpath=...|jsonpath-file=...]
(TYPE[.VERSION][.GROUP] [NAME | -l label] | TYPE[.VERSION][.GROUP]/NAME ...) [flags] [options]Use "kubectl options" for a list of global command-line options (applies to all commands).
4、kubectl 子命令使用分类
(1)基础命令
create
通过文件名或标准输入创建资源
kubectl create -f FILENAME [flags]
例如:
通过Kubernetes资源清单文件nginx.yaml创建一个NGINX应用程序。
kubectl create -f nginx.yaml
expose
将副本控制器、服务或 Pod 作为新的 Kubernetes 服务暴露。
kubectl expose (-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME | TYPE/NAME) [--port=port] [--protocol=TCP|UDP] [--target-port=number-or-name] [--name=name] [--external-ip=external-ip-of-service] [--type=type] [flags]
例如
创建nginx镜像后,我们就需要将端口暴露出去,让其它外界能够访问
对外暴露端口
kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80 --type=NodePort
run
在集群中运行一个特定的镜像
kubectl run NAME --image=image [--env="key=value"] [--port=port] [--dry-run=server | client | none] [--overrides=inline-json] [flags]
例如:
创建一个名为 nginx 的 Deployment,并暴露 80 端口。
kubectl run nginx --image=nginx --port=80
set
配置应用资源。
kubectl set SUBCOMMAND [options]
比如kubectl set image:用于更新 Deployment、ReplicaSet、DaemonSet 等资源中的镜像,
将nginx容器的镜像版本设置为1.8的nginx镜像。
kubectl set image deployment/myapp nginx=nginx:1.8
get
列出一个或多个资源。
kubectl get (-f FILENAME | TYPE [NAME | /NAME | -l label]) [--watch] [--sort-by=FIELD] [[-o | --output]=OUTPUT_FORMAT] [flags]
比如
列出集群中所有的Pod并显示它们的状态。
列出所有的Service并显示它们的状态
kubectl get pod,svc
explain
获取多种资源的文档。例如 Pod、Node、Service 等。
kubectl explain [--recursive=false] [flags]
比如:
查看Pod这个资源的详细说明,包括其定义的字段、含义以及使用方法等。
kubectl explain pod
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1RESOURCE: pod <Object>DESCRIPTION:Pod is a top-level object that can represent a containerized application.The name for a pod must be unique within the namespace. Pod definitions arealways required to include a spec section, which specifies at least onecontainer to run in the pod.FIELDS:apiVersion <string>APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an object.Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal value, andmay reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/api-conventions.md#resourceskind <string>Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this object represents.Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/api-conventions.md#types-kindsmetadata <Object>Standard object's metadata. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/api-conventions.md#metadataspec <Object>Specification of the desired behavior of the pod. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/api-conventions.md#spec-and-statusstatus <Object>Most recently observed status of the pod. This data may not be up to date. Populated by the system. Read-only. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status
edit
使用默认编辑器编辑和更新服务器上一个或多个资源的定义。
kubectl edit (-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME | TYPE/NAME) [flags]
比如:编辑名为my-deployment的Deployment对象
kubectl edit deployment/my-deployment
执行以上命令后,会自动打开Deployment的配置文件,并进入编辑模式。
delete
基于文件、标准输入或通过指定标签选择器、名称、资源选择器或资源本身,删除资源。
kubectl delete (-f FILENAME | TYPE [NAME | /NAME | -l label | --all]) [flags]
比如:从Kubernetes集群中删除名为“nginx”的deployment以及相关的pod和副本集。
kubectl delete deployment nginx
(2)部署和集群管理命令
部署命令
rollout
管理资源的上线。有效的资源类型包括:Deployment、 DaemonSet 和 StatefulSet。
kubectl rollout SUBCOMMAND [options]
例如 回滚 Deployment 到前一个版本
kubectl rollout undo deployment/my-deployment
scale
扩容或缩容pod数量,有效的资源类型包括:Deployment、 ReplicaSet 、RC和 Job。
kubectl scale (-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME | TYPE/NAME) --replicas=COUNT [--resource-version=version] [--current-replicas=count] [flags]
例如 扩容 Deployment 中的 Pod副本
kubectl scale deployment my-deployment --replicas=3
autoscale
自动扩缩容pod数量
kubectl autoscale (-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME | TYPE/NAME) [--min=MINPODS] --max=MAXPODS [--cpu-percent=CPU] [flags]
例如:根据CPU使用率自动扩容或缩容Pod。 当Pod的CPU使用率达到50%时,HPA会自动增加Pod的数量,最小数量为1个,最大数量为10个。
kubectl autoscale deployment my-deployment --cpu-percent=50 --min=1 --max=10
集群管理命令
certificate
用于管理 Kubernetes 中的证书
kubectl certificate SUBCOMMAND [options]
例如用于批准证书签名请求:
kubectl certificate approve csr-name
cluster-info
显示有关集群中主服务器和服务的端口信息。
kubectl cluster-info [flags]
例如查看Kubernetes节点的信息
kubectl cluster-info nodes
top
显示资源(CPU、内存、存储)的使用情况。
kubectl top [flags] [options]
例如获取当前命名空间下的所有Pod的CPU和内存使用情况:
kubectl top pods
cordon
标记节点不可调度
kubectl cordon NODE [options]
例如将其中一个节点 node1 标记为不可调度(即不允许在该节点上创建新的 pod)
kubectl cordon node1
让 Kubernetes 知道该节点不可用,并阻止 Kubernetes 在该节点上调度新的 pod。但是,已经运行在该节点上的 pod 不会被迁移,除非您使用 kubectl drain 命令将它们删除或迁移到其他节点。
uncordon
标记节点可调度
kubectl uncordon NODE [options]
例如将不可调度的节点node1标记为可调度
kubectl uncordon node1
drain
腾空节点以准备维护。将节点从集群中删除,通常在节点升级、维护或故障处理期间使用。在将节点删除之前,它会将节点上的所有Pod迁移到其他节点上。
kubectl drain NODE [options]
举例将节点“node1”从集群中删除,并将该节点上的所有Pod迁移到其他可用节点。
kubectl drain node1 --ignore-daemonsets
–ignore-daemonsets选项将忽略守护进程集,以便它们可以在节点上正常运行,而不会迁移到其他节点。如果您不使用此选项,则守护进程集中的Pod也将被迁移。
taint
用于标记节点(污点),以便Pod可以选择性地调度到节点上。在Kubernetes集群中,节点可以被标记为“不可调度”。
kubectl taint NODE NAME KEY_1=VAL_1:TAINT_EFFECT_1 ... KEY_N=VAL_N:TAINT_EFFECT_N [options]
例如
在名为“node1”的节点上设置两个污点,一个是“app=nginx:NoSchedule”
kubectl taint nodes node1 app=nginx:NoSchedule
“app=nginx”是污点的key和value,NoSchedule是taint effect
标记的效果effect可以是下列任意一个:
- NoSchedule:表示不允许调度新的Pod到这个节点上。
- PreferNoSchedule:表示不建议将Pod调度到这个节点上,但不是禁止的。
- NoExecute:表示如果已经存在Pod在节点上运行,当标记应用于节点时,这些Pod将被驱逐出节点。
(3)故障和调试命令
describe
显示一个或多个资源的详细状态,默认情况下包括未初始化的资源。
kubectl describe (-f FILENAME | TYPE [NAME_PREFIX | /NAME | -l label]) [flags]
举例

logs
打印 Pod 中容器的日志。
kubectl logs POD [-c CONTAINER] [--follow] [flags]
举例

attach
将当前终端附加到运行中的容器中,以便与容器进行交互。
kubectl attach POD -c CONTAINER [-i] [-t] [flags]
例如连接到名为“my-pod”的Pod中的容器
kubectl attach my-pod -c container-name
exec
在Kubernetes Pod中执行命令或进入容器的交互式终端。
kubectl exec POD [-c CONTAINER] [-i] [-t] [flags] [-- COMMAND [args...]]
例如要进入名为my-pod的Pod的交互式终端,可以使用以下命令:
kubectl exec -it my-pod – /bin/bash
在进入Pod的交互式终端后,可以执行任何命令,就像在本地终端中一样。
attach与exec命令的区别:
kubectl exec命令会启动一个新的进程并与容器进行交互,而kubectl attach命令会连接到容器的主进程,使终端成为容器的标准输入/输出/错误流。
port-forward
将本地端口与 Kubernetes 集群中服务的端口进行映射,使得我们可以直接访问 Kubernetes 中的服务。
kubectl port-forward POD [LOCAL_PORT:]REMOTE_PORT [...[LOCAL_PORT_N:]REMOTE_PORT_N] [flags]
例如将 Kubernetes 集群中名为 my-service 的服务的 80 端口映射到本地的 8080 端口。
kubectl port-forward svc/my-service 8080:80
这样就可以在本地使用 http://localhost:8080 访问 Kubernetes 集群中的服务。
proxy
将本地端口与 Kubernetes API Server 上的端口相关联。
kubectl proxy [--port=PORT] [--www=static-dir] [--www-prefix=prefix] [--api-prefix=prefix] [flags]
例如将本地的 8080 端口映射到 Kubernetes API Server 上的 8001 端口。在 Kubernetes 集群中,默认情况下 Kubernetes API Server 监听在 8001 端口上
kubectl proxy --port=8080
cp
从容器复制文件、目录或将文件、目录复制到容器。
kubectl cp [options]
例如 将本地文件复制到 Pod 中
kubectl cp /path/to/local/file pod-name:/path/to/remote/destination
pod-name是目标 Pod 的名称
/path/to/local/file是本地文件的路径
/path/to/remote/destination是要存储文件的远程目录的路径
auth
管理Kubernetes集群中的认证和授权相关配置,包括用户、角色和角色绑定等。
kubectl auth [flags] [options]
例如检查您是否有在默认命名空间创建Pod的权限
kubectl auth can-i create pods
(4)其他命令
高级命令
apply
通过文件名或标准输入对资源应用配置
kubectl apply -f FILENAME [flags]
例如:
patch
对已有的 Kubernetes 资源进行部分修改。可以使用该命令修改某个资源的某个属性值,或添加/删除某个标签或注释等。
kubectl patch (-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME | TYPE/NAME) --patch PATCH [flags]
例如将某个 Deployment 的 replicas 数量改为 3:
kubectl patch deployment my-deployment -p ‘{“spec”:{“replicas”: 3}}’
replace
通过完全覆盖(即替换)方式更新Kubernetes对象的特定字段
kubectl replace -f FILENAME
例如我们有一个Deployment对象,其名称为my-deployment,并且我们想要将其镜像更改为nginx:1.16:
kubectl replace deployment my-deployment --image=nginx:1.16
convert
将一个API对象的配置从一种API版本转换为另一种API版本。
kubectl convert -f FILENAME [options]
例如将Deployment API对象的配置文件从v1beta1版本转换为v1版本:
kubectl convert -f deployment.yaml --output-version=v1
设置命令
label
添加或更新一个或多个资源的标签。
kubectl label (-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME | TYPE/NAME) KEY_1=VAL_1 ... KEY_N=VAL_N [--overwrite] [--all] [--resource-version=version] [flags]
例如为一个Pod添加label:
kubectl label pod nginx-app app=web
为名为"nginx-app" 的Pod添加一个标签 “app=web”。
annotate
添加或更新一个或多个资源的注解。
kubectl annotate (-f FILENAME | TYPE NAME | TYPE/NAME) KEY_1=VAL_1 ... KEY_N=VAL_N [--overwrite] [--all] [--resource-version=version] [flags]
例如将pod名为my-pod的注释添加到key=value的标签,其中key是“key” , value是“value” 。
kubectl annotate pod my-pod key=value
其他命令
api-versions
列出可用的 API 版本。
kubectl api-versions [flags]
例如
kubectl api-versions
admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
apiregistration.k8s.io/v1
apps/v1
authentication.k8s.io/v1
authorization.k8s.io/v1
autoscaling/v1
batch/v1
certificates.k8s.io/v1
coordination.k8s.io/v1
events.k8s.io/v1
extensions/v1beta1
networking.k8s.io/v1
node.k8s.io/v1
policy/v1beta1
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
storage.k8s.io/v1
v1
config
修改 kubeconfig 文件。有关详细信息,请参阅各个子命令。
kubectl config SUBCOMMAND [flags]
例如设置一个新的上下文
kubectl config set-context my-context --cluster=my-cluster --user=my-user
plugin
提供用于与插件交互的实用程序。
kubectl plugin [flags] [options]
例如安装一个插件
kubectl plugin install
version
显示运行在客户端和服务器上的 Kubernetes 版本。
kubectl version [--client] [flags]
例如
kubectl version
该命令会返回客户端和服务器的版本信息。客户端版本指安装在本地的kubectl命令行工具版本;服务器版本指运行在Kubernetes集群中的Kubernetes组件版本,包括kube-apiserver、kube-controller-manager、kube-scheduler、kubelet等。