文章目录
- 一,简介
- 二,安装
- 三,三大核心概念Store、Action、Reducer
- 3.1 Store
- 3.2 Reducer
- 3.3 Action
- 四,开始函数式组件中使用
- 4.1,引入store
- 4.1,store.getState()方法
- 4.3,store.dispatch()方法
- 4.4,store.subscribe()方法
- 五,Redux 的三大原则
一,简介
Redux 是 JavaScript 应用的状态容器,提供可预测的状态管理。
它主要的几个方法如下:

重要的有方法 有 dispatch(分发action)、getState(获取state)、subscribe(监听state的变化),下面会介绍到,另外两个可以不用管;
那什么时候使用Redux呢?
当遇到如下问题时,建议开始使用 Redux:
- 你有很多数据随时间而变化
- 你希望状态有一个唯一确定的来源(single source of truth)
- 你发现将所有状态放在顶层组件中管理已不可维护
二,安装
我这里安装的是 "redux": "^4.2.1"版本;
npm install redux --save
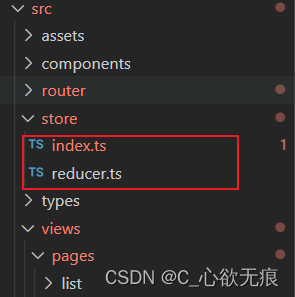
项目的src目录下面新建store文件夹和index.js,reducer.js;如下:
三,三大核心概念Store、Action、Reducer
3.1 Store
Store:存储数据的地方。最好整个应用只有一个 Store。
createStore() :用来生成 Store。接收 Reducer 作为其参数。
index.js
/*** 引入createStore 专门创建最为核心的store对象* 目前createStore已经弃用,所以我们要引用legacy_createStore */iimport { legacy_createStore } from "redux";
import reducer from './reducer.ts'// 创建数据仓库 引入reducer函数进行对数据的处理
const store = legacy_createStore(reducer)export default store
3.2 Reducer
reduce的本质就是一个函数 ,作用是初始化状态和加工状态。
reduce函数里面接收两个参数,第一个参数是state的初始值,第二个参数是一个action对象,对象里的第一个属性是type也就是函数的名称,第二个属性就是传进来的值,用于后续更改state;
reducer.ts
// 约束类型
interface Eula {name: string;age: number;
}
// 定义数据
const defaultState: Eula = {name: "Eula",age: 18
};// reducer 函数 用于更改数据
let reducer = (preState = defaultState, action: { type: string; data: number }) => {// action解构出来let { type, data } = action;// 第一种写法 每个分支使用return进行返回// switch (type) {// case "update_age":// preState.age = data;// return preState;// case "add_age":// preState.age++;// return preState;// case "del_age":// preState.age--;// return preState;// default:// return preState; // 初始化时// }// 第二种写法 break 与最终的return返回结果switch (type) {case "update_age":preState.age = data;break;case "add_age":preState.age++;break;case "del_age":preState.age--;break;default:preState; // 初始化时}return preState; // 此处 一定要使用return进行返回最终改变的值
};export default reducer;
注意: 初次加载 Store 会自动调用一次 Reducer 进行初始化状态,此时 state 是 undefined,action 对象中的 type 为 @@redux/INITxxx。手动调用 store.dispatch() 也会触发 Reducer 的自动执行。
3.3 Action
Action 就是一个普通的 JS 对象,用于描述要更新的数据类型和内容,其中 type 属性是必须的,表示 Action 的名称,其他属性可以自由设置。
redux.tsx
// 引入store
import store from "../../../store/index";
// 更改数据时调用
store.dispatch({ type: "update_age", data: 100 });
store.dispatch():所有数据的变化,必须通过派发(dispatch) Action 来更新。接受一个 Action 对象作为参数,将其发送出去。
四,开始函数式组件中使用
redux.tsx
import React, { useState } from "react";
// 1,引入store
import store from "../../../store/index";// 渲染数据
const myList:[] = [];const Redux: React.FC = () => {let [list, setList] = useState(myList);console.log("store:", store);// 监听数据的变化const unsubscribe = store.subscribe(() => {console.log("订阅数据的变化", store.getState());// 此处用来触发视图的更新setList([]);});// 改变store中的数据const update = () => {store.dispatch({ type: "update_age", data: 100 });};const add = () => {store.dispatch({ type: "add_age" });};const del = () => {store.dispatch({ type: "del_age" });};// 此处才是真正渲染的页面return (<div className="redux"><h3>redux演示</h3><button onClick={update}>更改store的数据+100</button><button onClick={add}>更改store的数据++</button><button onClick={del}>更改store的数据--</button><p>store的num数据:{store.getState().age}</p></div>);
};
export default Redux;效果图:

上面的组件是一个简单的案例演示,定义了三个点击事件,点击第一个按钮state.age+100,点击第二个按钮每次state.age+1,点击第三个按钮age每次减一;下面会详细介绍几个重点内容:
4.1,引入store
先引进来,这个没什么好说的;
import store from "../../../store/index";
4.1,store.getState()方法
getState()方法是redux实例下的方法之一,上面的第一张截图已经通过store实例打印出来了;
getState()的作用是获取当前状态下运行在redux中的state;也就是说获取store中最新的数据;
<p>store的num数据:{store.getState().age}</p>
4.3,store.dispatch()方法
dispatch() 是唯一能够修改 state 数据的行为。通过分发action (其实就是一个对象),配合 dispatch 函数传入的 action 及其 payload 计算得到新的 state,并更新到闭包数据中,这样就实现了 state 的更新;
如下:
reducer.tsx
// 改变store中的数据const update = () => {store.dispatch({ type: "update_age", data: 100 });};const add = () => {store.dispatch({ type: "add_age" });};const del = () => {store.dispatch({ type: "del_age" });};
上面的代码会和下面的 switch case 表达式所判断的type要一 一对应,用于更新state;
reducer.ts
let reducer = (preState = defaultState, action: { type: string; data: number }) => {let { type, data } = action;// 第一种写法 每个分支使用return进行返回// switch (type) {// case "update_age":// preState.age = data;// return preState;// case "add_age":// preState.age++;// return preState;// case "del_age":// preState.age--;// return preState;// default:// return preState; // 初始化时// }// 第二种写法 break 与最终的return返回结果switch (type) {case "update_age":preState.age = data;break;case "add_age":preState.age++;break;case "del_age":preState.age--;break;default:preState; // 初始化时}return preState; // 此处 一定要使用return进行返回最终改变的值
};
上面的两种写法是一样的;对比一下;
4.4,store.subscribe()方法
subscribe函数只要store中的state数据变化了,就会触发subscribe方法,相当注册了一个监听器;监听store中的数据变化;
从 react 层面来说,redux 的 store 是隔离开的,我们需要一个桥梁,使得数据层出现更新的同时更新UI层逻辑,这时 store 中的最后一个方法,subscribe 方法就派上用场了。
注意: setList([]):是为了主动触发react视图更新的方法,否则store中数据改变了,视图却没有重新渲染。
import React, { useState } from "react";
const Redux: React.FC = () => { let [list, setList] = useState(myList);
// 监听数据的变化const unsubscribe = store.subscribe(() => {console.log("订阅数据的变化", store.getState());// 此处用来触发视图的更新setList([]);});
}subscribe也同时返回了一个 unsubscribe 函数。当我们不在希望订阅这个监听器时,调用 unsubscribe(),对应的函数就会从监听器队列中被移除。
unsubscrib() // 不再监听
五,Redux 的三大原则
- 单一数据源:整个应用程序的 State 被存储在一棵 object tree 中,并且这棵 object tree 只存储在一个 Store 中。单一数据源可以让整个应用程序的 State 变得方便维护、修改、追踪。
- State 是只读的:唯一修改 State 的方法就是触发 Action,不要试图在其他地方通过任何的方式来修改State。这样可以保证所有的修改都被集中化处理,并且按照严格的顺序来执行。
- 使用纯函数来执行修改:通过 Reducer 将旧的 State 和 Action 联系在一起,返回一个新的 State。所有的Reducer 都应该是纯函数,不能产生任何的副作用。
End:
[redux中文网]: https://cn.redux.js.org/