前言
ES 的主查询评分模式分为两种,是信息检索领域的重要算法: TF-IDF 算法 和 BM25 算法。
Elasticsearch 从版本 5.0 开始引入了 BM25 算法作为默认的文档评分(relevance scoring)算法。在此之前,Elasticsearch 使用的是 TF-IDF 算法作为默认的文档评分算法。从版本 5.0 起,BM25 算法取代了 TF-IDF,成为了默认的算法,用于计算文档与查询之间的相关性得分。
这个变化主要是为了更好地适应现代信息检索需求,BM25 算法在一些情况下能够提供更准确的文档排序和检索结果。
而 Function Score Query 不夸张的说是 ES 里面终极自定义打分的大招,非常的灵活并且功能强大,常规情况下,我们排序都是基于 _score 的,如果 _score相等的情况下,我们还可以额外增加排序字段,比如按日期,数量,价格等,但在搜索引擎中,排序往往并不像 SQL 那样,从左到右规整的按照多字段排序,在 SQL 里面,排序的主顺序一定是由左边的第一个字段决定的,但在搜索引擎种,却不仅仅是这样的,还可以通过 function score 做到那个字段贡献的分值大,排序顺序就以谁为主,因为这些是真实存在的需求场景,如下:
- 新闻场景:搜索具有某个关键词的文档,同时结合文档的时效性进行综合排序
- 导航场景:搜索某个地点附近的饭店,同时根据距离远近和价格等因素综合排序
- 论坛场景:搜索包含某个关键词的文章,同时根据浏览次数和点赞数进行综合排序
SQL 的排序模型
select * from table order by A, B, C搜索引擎的排序模型
query * from index oder by score max(A, B, C)写入数据
为了用实际例子讲解 function score,我们先写入几条数据
POST test01/doc/_bulk
{ "index" : { "_id" : "1" } }
{"title": "kubernetes", "content": "Development History","vote": 3,"year": 2015}
{ "index" : { "_id" : "2" } }
{"title": "kubernetes", "content": "Competitive Analysis","vote": 5,"year": 2018}
{ "index" : { "_id" : "3" } }
{"title": "kubernetes docker","content": "The connection between virtual and docker technology","vote": 100,"year": 2011}
{ "index" : { "_id" : "4" } }
{"title": "kubernetes network","content": "router vlan tcp","vote": 20,"year": 2009}查询数据
查询关键词:kubernetes
GET test01/_search?search_type=dfs_query_then_fetch
{"query": {"bool": {"should": [{"term": {"title": "kubernetes"}}]}},"explain": false
}返回结果:
"hits" : [{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "2","_score" : 0.12776,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes","content" : "Competitive Analysis","vote" : 5,"year" : 2018}},{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "1","_score" : 0.12776,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes","content" : "Development History","vote" : 3,"year" : 2015}},{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "4","_score" : 0.09954306,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes network","content" : "router vlan tcp","vote" : 20,"year" : 2009}},{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "3","_score" : 0.081535265,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes mesos swarm","content" : "The connection between virtual and docker technology","vote" : 100,"year" : 2011}}]结果看起来是正常的,ok,现在我们要改变需求了,加入了基于点赞量的加权,也就是说匹配关键词并且点赞量高的优先展示,因为点赞量高意味着这些文章质量更高,所以需要优先曝光,这个时候我们就需要用到 function score
Function Score Query介绍
计算原理
使用主查询 的 TF-IDF 或者 BM25 算法得出来的默认评分简称为: query_score
使用 Function Score 查询结合自定义策略得出来的评分简称为:function_score
最终用于排序的评分称为 sort_score
在使用了 自定义的 Fuction Score 之后,我们最终得出来的 sort_score 就是使用 query_score 和 function_score以某种运算形式 (score_mode) 计算出来的,这个策略默认是相乘,也即:
sort_score = query_score * function_score
function_score内的score_mode
score_mode有六种:
| mode | 描述 |
| multiply | 多个函数 score 相乘(默认) |
| sum | 多个函数 score 求和 |
| avg | 多个函数 score 取平均值 |
| first | 使用第一个 filter 函数的 score |
| max | 取多个函数 score 中最大的那个 |
| min | 取多个函数 score 中最大的那个 |
sort_score运算策略
sort_score 是 query_score 和 function_score以某种形式运算而来,支持的运算操作也有六种:
| mode | 描述 |
| multiply | sort_score = query_score * function_score(默认) |
| sum | sort_score = query_score + function_score |
| avg | sort_score = avg ( query_score + function_score ) / 2 |
| replace | sort_score = function_score |
| max | sort_score = max ( query_score + function_score ) |
| min | sort_score = min ( query_score + function_score ) |
默认情况下,修改分数不会更改匹配的文档。要排除不满足特定分数阈值的文档,可以将 min_score 参数设置为所需的分数阈值
fuction score的评分函数
script_score
script_score 支持自定义脚本打分,也就是说可以用类编程语言的脚本来嵌入的打分逻辑,ES 之前用的是 groovy脚本因安全性有问题,现在换成了 Painless 脚本,详细可参考:Painless scripting language | Elasticsearch Guide [8.9] | Elastic
现在我们用 script_score 来完成上面查询场景中的,给点赞量的加权:
GET test01/_search?search_type=dfs_query_then_fetch
{"query": {"function_score": {"query": {"match": { "title": "kubernetes" }},"script_score": {"script": {"params": {"baseScore": 1},"source": "params.baseScore + doc['vote'].value"}},"boost_mode": "replace","score_mode": "multiply"}},"explain": false
}结果如下:
"hits" : [{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "3","_score" : 101.0,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes mesos swarm","content" : "The connection between virtual and docker technology","vote" : 100,"year" : 2011}},{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "4","_score" : 21.0,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes network","content" : "router vlan tcp","vote" : 20,"year" : 2009}},{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "2","_score" : 6.0,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes","content" : "Competitive Analysis","vote" : 5,"year" : 2018}},{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "1","_score" : 4.0,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes","content" : "Development History","vote" : 3,"year" : 2015}}]在这个函数查询中,我们使用了 replace 策略,来直接使用 fuction_score的分数,注意 从 docValue 里面取出来的字段必须是number 类型才可以
weight
直接对查询加权:
例子一:
GET test01/_search?search_type=dfs_query_then_fetch
{"query": {"function_score": {"query": {"match": { "title": "kubernetes" }},"weight": 10}},"explain": false
}
结果:
"hits" : [{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "2","_score" : 1.2775999,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes","content" : "Competitive Analysis","vote" : 5,"year" : 2018}},{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "1","_score" : 1.2775999,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes","content" : "Development History","vote" : 3,"year" : 2015}},{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "4","_score" : 0.9954306,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes network","content" : "router vlan tcp","vote" : 20,"year" : 2009}},{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "3","_score" : 0.8153527,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes mesos swarm","content" : "The connection between virtual and docker technology","vote" : 100,"year" : 2011}}]例子二:
GET test01/_search?search_type=dfs_query_then_fetch
{"query": {"function_score": {"query": {"match_all": {}},"functions": [{"filter": { "match": { "content": "kubernetes" } },"weight": 1},{"filter": { "match": { "title": "mesos" } },"weight": 10},{"filter": { "match": { "content": "tcp" } },"weight": 20}]}},"explain": false
}结果如下:
"hits" : [{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "4","_score" : 20.0,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes network","content" : "router vlan tcp","vote" : 20,"year" : 2009}},{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "3","_score" : 10.0,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes mesos swarm","content" : "The connection between virtual and docker technology","vote" : 100,"year" : 2011}},{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "2","_score" : 1.0,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes","content" : "Competitive Analysis","vote" : 5,"year" : 2018}},{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "1","_score" : 1.0,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes","content" : "Development History","vote" : 3,"year" : 2015}}]这个 filter 很适合竞价排名
random_score
random score 相当于把返回文档的顺序给打乱,比较适合随机召回文档
GET test01/_search?search_type=dfs_query_then_fetch
{"query": {"function_score": {"query": {"match_all": {}},"random_score": {}}},"explain": false
}默认情况下,是每次查询的值都是随机的,但有时候我们想用同一个 id 的保持不变,不同 id 的结果随机,这个时候可以使用 seed 和 field 来控制:
GET test01/_search?search_type=dfs_query_then_fetch
{"query": {"function_score": {"query": {"match_all": {}},"random_score": {"seed": 10,"field": "_seq_no"}}},"explain": false
}这个时候 seed 的值,就可以等同于 id,id 值一样的结果不变
field_value_factor
GET test01/_search?search_type=dfs_query_then_fetch
{"query": {"function_score": {"query": {"match": {"title":"kubernetes"}},"field_value_factor": {"field": "vote","factor": 1.2,"modifier": "sqrt","missing": 1},"boost_mode": "max"}},"explain": false
}等价于script score 脚本 sqrt(1.2 * doc['vote'].value)
其中field 是文档种的字段,missing 是缺失值,factor 是放大的比值默认是 1,modifier 是对结果的再次处理,支持多种函数如:none, log, log1p, log2p, ln, ln1p, ln2p, square, sqrt, or reciprocal
decay functions
衰减函数
- 以某个数值作为中心点,距离多少的范围之外逐渐衰减(缩小分数)
- 以某个日期作为中心点,距离多久的范围之外逐渐衰减(缩小分数)
- 以某个地理位置点作为中心点,方圆多少距离之外逐渐衰减(缩小分数)
一个例子:
"DECAY_FUNCTION": { "FIELD_NAME": { "origin": "11, 12","scale": "2km","offset": "0km","decay": 0.33}
}上例的意思就是在距中心点方圆 2 公里之外,分数减少到三分之一(乘以 decay 的值 0.33)
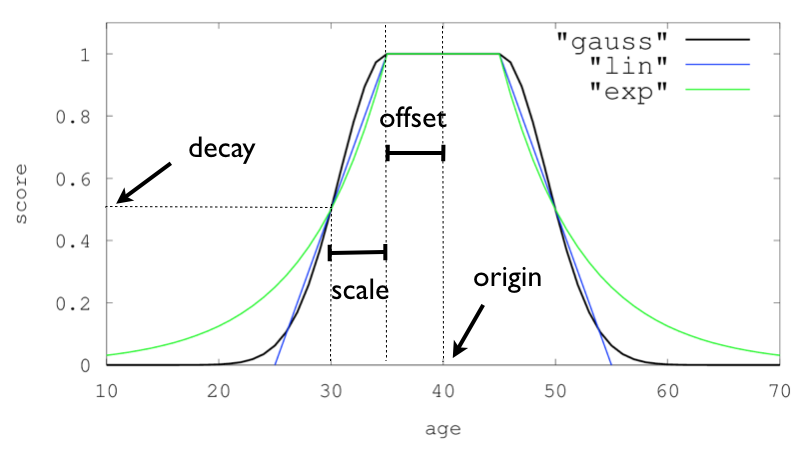
DECAY_FUNCTION 可以是以下任意一种函数:
linear : 线性衰减函数
exp : 指数衰减函数
gauss : 高斯正常衰减函数origin :
用于计算距离的原点。对于数字字段,必须以数字形式给出;对于日期字段,必须以日期形式给出;对于地理字段,必须以地理点形式给出。地理和数字字段是必需的。对于日期字段,默认值为现在。 origin 支持日期数学(例如 now-1h)
scale :
定义计算得分等于衰减参数时距原点 + 偏移量的距离。对于地理字段:可以定义为数字+单位(1km、12m、...)。默认单位是米。对于日期字段:可以定义为数字+单位(“1h”、“10d”、...)。默认单位是毫秒。对于数字字段:任何数字
offset :
如果定义了偏移量,则衰减函数将仅计算距离大于定义的偏移量的文档的衰减函数。默认值为 0
decay :
衰减参数定义如何在给定比例的距离上对文档进行评分。如果未定义衰减,则距离尺度上的文档将评分为 0.5
例如,现在新数据,标题匹配 kubernetes 后,按照优先检索位于 2011-2015 年份进行加权,不再按照点赞量:
GET test01/_search?search_type=dfs_query_then_fetch
{"query": {"function_score": {"query": {"match": {"title":"kubernetes"}},"gauss": {"year": {"origin": "2013", "offset": "2","scale": "2","decay": 0.1 }},"boost_mode": "max"}},"explain": false
}解释一下:
上面使用高斯函数作为衰减,使用的是年份字段:
orgin:代表中心点是 2013 年
offset:2 代表 [2011, 2015] 作为中心圆,也就是 [2011, 2015]位于这之间的文档评分直接为 1
scala: 2 代表 [2009, 2017]之外的评分为 0.1
其他的,如果位于 2009-2011 范围的以及 2015-2017 范围的,就按正常评分就好了
结果如下:
"hits" : [{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "3","_score" : 1.0,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes mesos swarm","content" : "The connection between virtual and docker technology","vote" : 100,"year" : 2011}},{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "1","_score" : 1.0,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes","content" : "Development History","vote" : 3,"year" : 2015}},{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "2","_score" : 0.12776,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes","content" : "Competitive Analysis","vote" : 5,"year" : 2018}},{"_index" : "test01","_type" : "doc","_id" : "4","_score" : 0.1,"_source" : {"title" : "kubernetes network","content" : "router vlan tcp","vote" : 20,"year" : 2009}}]三种衰减的函数的曲线如下:
此外,如果用于计算衰减的字段包含多个值,则默认情况下会选择最接近中心点的值来确定距离。这可以通过设置 multi_value_mode 来更改:
min:距离是最小距离
max:距离是最大距离
avg:距离是平均距离
sum:距离是所有距离的总和
"DECAY_FUNCTION": {"FIELD_NAME": {"origin": ...,"scale": ...},"multi_value_mode": "avg"}function score 的其他参数
max_boost: 最大权重值的范围
boost_mode: 最终 query_score 和 function_score的计算策略
min_score: 最终的结果过滤掉评分低于这个值的