目录
1.LinkedList的介绍
LinkedList的结构
2.LinkedList的模拟实现
2.1创建双链表
2.2头插法
2.3尾插法
2.4任意位置插入
2.5查找关键字
2.6链表长度
2.7遍历链表
2.8删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
2.9删除所有值为key的节点
2.10清空链表
2.11完整代码
3.LinkedList的使用
3.1LinkedList的构造
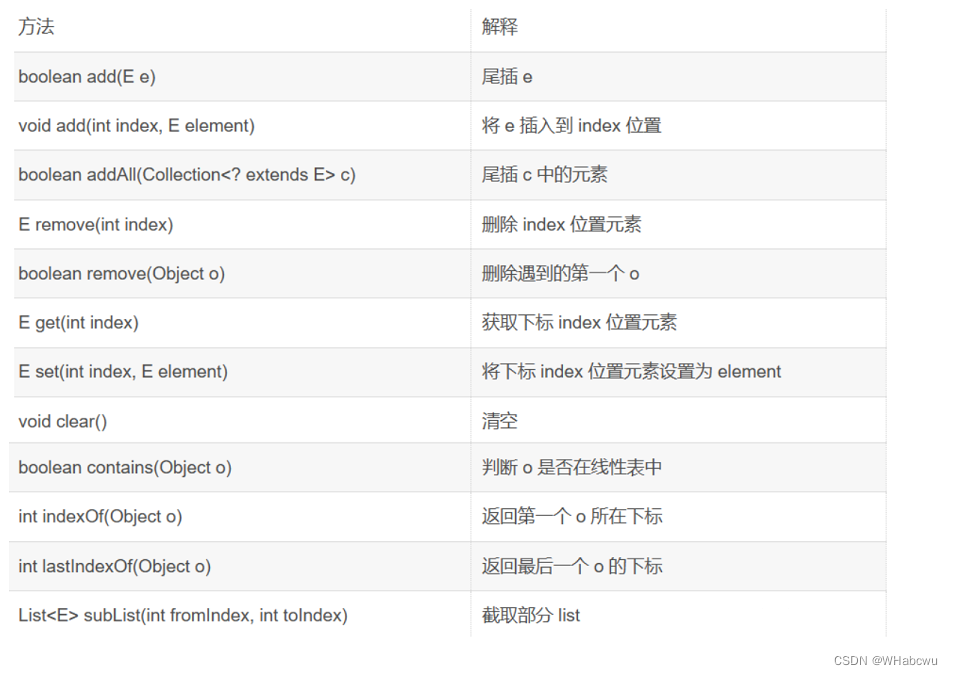
3.2LinkedList的其他常用方法介绍
3.3LinkedList的遍历
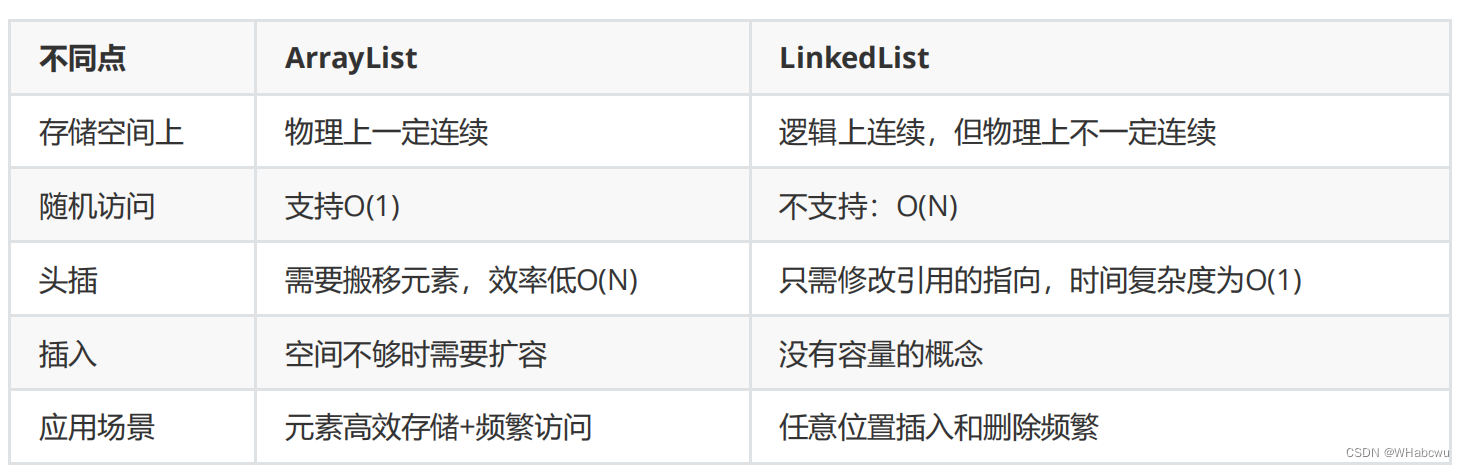
3.4ArrayList和LinkedList的区别
1.LinkedList的介绍
LinkedList的底层是双向链表结构,元素存储在单独的节点中,通过引用将节点连接起来了。
如果对双向链表或链表不太清晰,可以先看看本博主写的有关链表的文章。
链表的顶级理解_WHabcwu的博客-CSDN博客
在集合框架中,LinkedList也实现了List接口,具体如下:
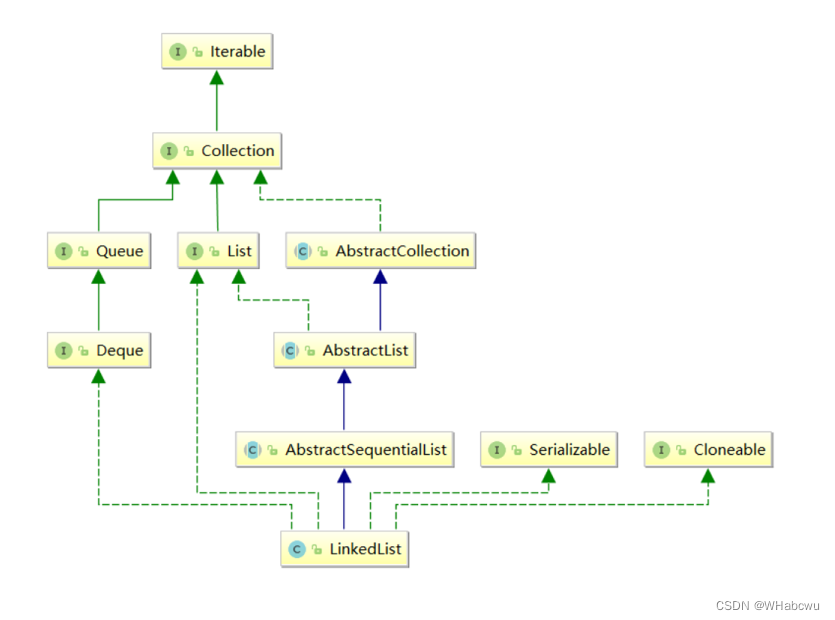
注意:
1. LinkedList 实现了 List 接口2. LinkedList 的底层使用了双向链表3. LinkedList 没有实现 RandomAccess 接口,因此 LinkedList 不支持随机访问4. LinkedList 的任意位置插入和删除元素时效率比较高,时间复杂度为 O(1)5. LinkedList 比较适合任意位置插入的场景
LinkedList的结构


- 前驱节点:用于存储前一节点的位置,用prev表示
- 后继节点:用于储存下一节点的位置,用next表示
- 所需要储存的数据,用val表示
- 头节点:用head表示
- 尾节点:用last表示
2.LinkedList的模拟实现
无非是增删查改,在某位置的插入与删除,对数据内容进行管理和操作。
具体实现内容:
(1)创建双链表
(2)头插法
(3)尾插法
(4)任意位置插入
(5)查找关键字
(6)链表长度
(7)遍历链表
(8)删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
(9)删除所有值为key的节点
(10)清空链表
2.1创建双链表
public class MyLinkedList {static class ListNode {public int val;public ListNode prev;//前驱public ListNode next;//后继public ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}}public ListNode head;//头节点public ListNode last;//尾节点
}
2.2头插法
(1)首先判断头节点是否为null若为null,则该节点就是头节点,也是尾节点.
(2)头节点不为null,将原先head的前驱节点指向新增节点位置,新增节点后驱节点指向head节点的位置。
(3)head指向新增节点位置。
//插法 O(1)public void addFirst(int data){ListNode node = new ListNode(data);if(head == null) {head = node;last = node;}else {node.next = head;head.prev = node;head = node;}}
2.3尾插法
与头插法大同小异
//尾插法 O(1)public void addLast(int data){ListNode node = new ListNode(data);if(head == null) {head = node;last = node;}else {last.next = node;node.prev = last;last = node;}}2.4任意位置插入
需要插入的位置必须为合法,如果不合法,我们会抛出一个异常进行提醒
public class ListIndexOutOfException extends RuntimeException{public ListIndexOutOfException() {}public ListIndexOutOfException(String message) {super(message);}
}
任意位置插入,我们可以分为种情况,插在开头,插在结尾,插在中间

//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标public void addIndex(int index,int data){if(index < 0 || index > size()) {throw new ListIndexOutOfException("违规数据");}if(index == 0) {addFirst(data);return;}if(index == size()) {addLast(data);return;}ListNode cur = findIndex(index);//ListNode node = new ListNode(data);cur.prev.next = node;node.next = cur;node.prev = cur.prev;cur.prev = node;}2.5查找关键字
直接遍历查找即可
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中public boolean contains(int key){ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {if(cur.val == key) {return true;}cur = cur.next;}return false;}
2.6链表长度
用一个len变量进行记录,遍历链表
public int size(){int len = 0;ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {len++;cur = cur.next;}return len;}
2.7遍历链表
public void display(){ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {System.out.print(cur.val+" ");cur = cur.next;}System.out.println();}
2.8删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
(1)一个节点都没有
(2)删除数据在第一个
(3)没有你要删除的数据
(4)有你要删除的数据且不是第一个(5)删除数据最后一个
找到就return;
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点public void remove(int key){ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {//开始删除了if(cur.val == key) {//1. 删除的是头节点if(cur == head) {head = head.next;//只有一个节点if(head != null) {head.prev = null;}}else {//中间 尾巴cur.prev.next = cur.next;//不是尾巴节点if(cur.next != null) {cur.next.prev = cur.prev;}else {//是尾巴节点last = last.prev;}}return;}cur = cur.next;}}2.9删除所有值为key的节点
与删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点几乎是一模一样的;
我们只需要遍历完就好,只需要return删掉就好。
//删除所有值为key的节点public void removeAllKey(int key){ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {//开始删除了if(cur.val == key) {//1. 删除的是头节点if(cur == head) {head = head.next;//只有一个节点if(head != null) {head.prev = null;}}else {//中间 尾巴cur.prev.next = cur.next;//不是尾巴节点if(cur.next != null) {cur.next.prev = cur.prev;}else {//是尾巴节点last = last.prev;}}}cur = cur.next;}}2.10清空链表
只需要遍历整个链表,将每个节点的前驱与后继节点都置为null就好
public void clear(){ListNode cur = head;while(cur != null) {cur.prev = null;cur = cur.next;cur.prev.next = null;}head = null;last = null;}2.11完整代码
public class MyLinkedList {static class ListNode {public int val;public ListNode prev;//前驱public ListNode next;//后继public ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}}public ListNode head;//头节点public ListNode last;//尾节点//头插法 O(1)public void addFirst(int data){ListNode node = new ListNode(data);if(head == null) {head = node;last = node;}else {node.next = head;head.prev = node;head = node;}}//尾插法 O(1)public void addLast(int data){ListNode node = new ListNode(data);if(head == null) {head = node;last = node;}else {last.next = node;node.prev = last;last = node;}}//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标public void addIndex(int index,int data){if(index < 0 || index > size()) {throw new ListIndexOutOfException("违规数据");}if(index == 0) {addFirst(data);return;}if(index == size()) {addLast(data);return;}ListNode cur = findIndex(index);//ListNode node = new ListNode(data);cur.prev.next = node;node.next = cur;node.prev = cur.prev;cur.prev = node;}private ListNode findIndex(int index) {ListNode cur = head;while (index != 0) {cur = cur.next;index--;}return cur;}//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中public boolean contains(int key){ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {if(cur.val == key) {return true;}cur = cur.next;}return false;}//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点public void remove(int key){ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {//开始删除了if(cur.val == key) {//1. 删除的是头节点if(cur == head) {head = head.next;//只有一个节点if(head != null) {head.prev = null;}}else {//中间 尾巴cur.prev.next = cur.next;//不是尾巴节点if(cur.next != null) {cur.next.prev = cur.prev;}else {//是尾巴节点last = last.prev;}}return;}cur = cur.next;}}//删除所有值为key的节点public void removeAllKey(int key){ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {//开始删除了if(cur.val == key) {//1. 删除的是头节点if(cur == head) {head = head.next;//只有一个节点if(head != null) {head.prev = null;}}else {//中间 尾巴cur.prev.next = cur.next;//不是尾巴节点if(cur.next != null) {cur.next.prev = cur.prev;}else {//是尾巴节点last = last.prev;}}}cur = cur.next;}}public int size(){int len = 0;ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {len++;cur = cur.next;}return len;}public void display(){ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {System.out.print(cur.val+" ");cur = cur.next;}System.out.println();}public void clear(){ListNode cur = head;while(cur != null) {cur.prev = null;cur = cur.next;cur.prev.next = null;}head = null;last = null;}
}
3.LinkedList的使用
3.1LinkedList的构造

3.2LinkedList的其他常用方法介绍
3.3LinkedList的遍历
public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();linkedList.add(1);linkedList.add(2);linkedList.add(3);linkedList.add(4);linkedList.add(5);// foreach遍历for (int e:list) {System.out.print(e + " ");}System.out.println();System.out.println("=====================");// 使用迭代器遍历---正向遍历Iterator<Integer> iterator1 = linkedList.iterator();while(iterator1.hasNext()){System.out.println(iterator1.next());}System.out.println("=====================");// 使用反向迭代器---反向遍历ListIterator<Integer> iterator2 = linkedList.listIterator(linkedList.size());while (iterator2.hasPrevious()){System.out.println(iterator2.previous());}}3.4ArrayList和LinkedList的区别
以上为我个人的小分享,如有问题,欢迎讨论!!!
都看到这了,不如关注一下,给个免费的赞 ![]()







![【洛谷】P1873 [COCI2011-2012#5] EKO / 砍树](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d4b4df2f8b7d43ec839d8100ae4704ff.png)