一 前言
对于一个类别特征,如果这个特征的取值非常多,则称它为高基数(high-cardinality)类别特征。在深度学习场景中,对于类别特征我们一般采用Embedding的方式,通过预训练或直接训练的方式将类别特征值编码成向量。在经典机器学习场景中,对于有序类别特征,我们可以使用LabelEncoder进行编码处理,对于低基数无序类别特征(在lightgbm中,默认取值个数小于等于4的类别特征),可以采用OneHotEncoder的方式进行编码,但是对于高基数无序类别特征,若直接采用OneHotEncoder的方式编码,在目前效果比较好的GBDT、Xgboost、lightgbm等树模型中,会出现特征稀疏性的问题,造成维度灾难, 若先对类别取值进行聚类分组,然后再进行OneHot编码,虽然可以降低特征的维度,但是聚类分组过程需要借助较强的业务经验知识。本文介绍一种针对高基数无序类别特征非常有效的预处理方法:平均数编码(Mean Encoding)。在很多数据挖掘类竞赛中,有许多人使用这种方法取得了非常优异的成绩。
二 原理
平均数编码,有些地方也称之为目标编码(Target Encoding),是一种基于目标变量统计(Target Statistics)的有监督编码方式。该方法基于贝叶斯思想,用先验概率和后验概率的加权平均值作为类别特征值的编码值,适用于分类和回归场景。平均数编码的公式如下所示:
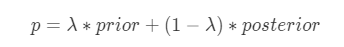
其中:
1. prior为先验概率,在分类场景中表示样本属于某一个_y__i_的概率
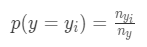
其中_n__y__i_表示y =_y__i_时的样本数量,_n__y_表示y的总数量;在回归场景下,先验概率为目标变量均值:

2. posterior为后验概率,在分类场景中表示类别特征为k时样本属于某一个_y__i_的概率
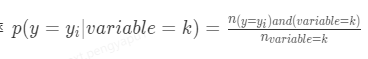
在回归场景下表示 类别特征为k时对应目标变量的均值。
3. _λ_为权重函数,本文中的权重函数公式相较于原论文做了变换,是一个单调递减函数,函数公式:
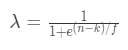
其中 输入是特征类别在训练集中出现的次数n,权重函数有两个参数:
① k:最小阈值,当n = k时,λ= 0.5,先验概率和后验概率的权重相同;当n < k时,λ> 0.5, 先验概率所占的权重更大。
② f:平滑因子,控制权重函数在拐点处的斜率,f越大,曲线坡度越缓。下面是k=1时,不同f对于权重函数的影响:
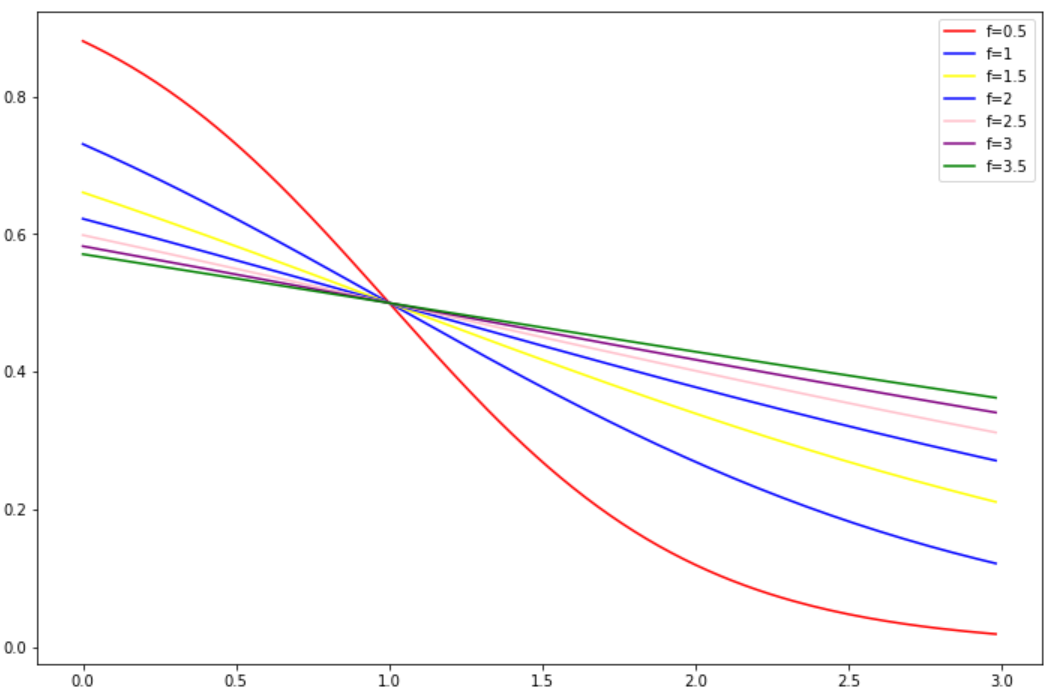
由图可知,f越大,权重函数S型曲线越缓,正则效应越强。
对于分类问题,在计算后验概率时,目标变量有C个类别,就有C个后验概率,且满足

一个 _y__i_ 的概率值必然和其他 _y__i_ 的概率值线性相关,因此为了避免多重共线性问题,采用平均数编码后数据集将增加C-1列特征。对于回归问题,采用平均数编码后数据集将增加1列特征。
三 实践
平均数编码不仅可以对单个类别特征编码,也可以对具有层次结构的类别特征进行编码。比如地区特征,国家包含了省,省包含了市,市包含了街区,对于街区特征,每个街区特征对应的样本数量很少,以至于每个街区特征的编码值接近于先验概率。平均数编码通过加入不同层次的先验概率信息解决该问题。下面将以分类问题对这两个场景进行展开:
1. 单个类别特征编码:

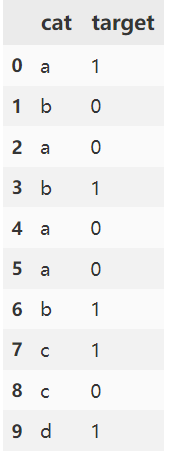
在具体实践时可以借助category_encoders包,代码如下:
import pandas as pd
from category_encoders import TargetEncoderdf = pd.DataFrame({'cat': ['a', 'b', 'a', 'b', 'a', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'c', 'd'], 'target': [1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1]})
te = TargetEncoder(cols=["cat"], min_samples_leaf=2, smoothing=1)
df["cat_encode"] = te.transform(df)["cat"]
print(df)
# 结果如下:cat target cat_encode
0 a 1 0.279801
1 b 0 0.621843
2 a 0 0.279801
3 b 1 0.621843
4 a 0 0.279801
5 a 0 0.279801
6 b 1 0.621843
7 c 1 0.500000
8 c 0 0.500000
9 d 1 0.6344712. 层次结构类别特征编码:
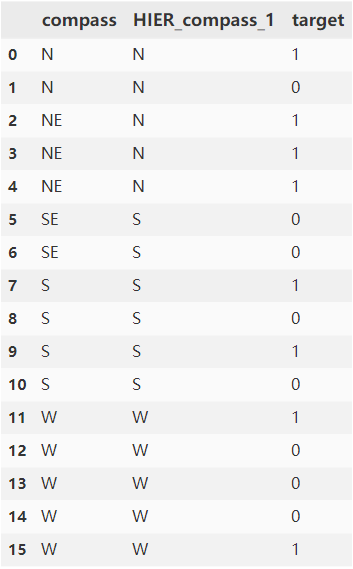
对以下数据集,方位类别特征具有{‘N’: (‘N’, ‘NE’), ‘S’: (‘S’, ‘SE’), ‘W’: ‘W’}层级关系,以compass中类别NE为例计算_y__i_=1,k = 2 f = 2时编码值,计算公式如下:
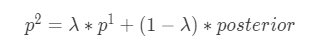
其中_p_1为HIER_compass_1中类别N的编码值,计算可以参考单个类别特征编码: 0.74527,posterior=3/3=1,λ= 0.37754 ,则类别NE的编码值:0.37754 * 0.74527 + (1 - 0.37754)* 1 = 0.90383。
代码如下:
from category_encoders import TargetEncoder
from category_encoders.datasets import load_compassX, y = load_compass()
# 层次参数hierarchy可以为字典或者dataframe
# 字典形式
hierarchical_map = {'compass': {'N': ('N', 'NE'), 'S': ('S', 'SE'), 'W': 'W'}}
te = TargetEncoder(verbose=2, hierarchy=hierarchical_map, cols=['compass'], smoothing=2, min_samples_leaf=2)
# dataframe形式,HIER_cols的层级顺序由顶向下
HIER_cols = ['HIER_compass_1']
te = TargetEncoder(verbose=2, hierarchy=X[HIER_cols], cols=['compass'], smoothing=2, min_samples_leaf=2)
te.fit(X.loc[:,['compass']], y)
X["compass_encode"] = te.transform(X.loc[:,['compass']])
X["label"] = y
print(X)# 结果如下,compass_encode列为结果列:index compass HIER_compass_1 compass_encode label
0 1 N N 0.622636 1
1 2 N N 0.622636 0
2 3 NE N 0.903830 1
3 4 NE N 0.903830 1
4 5 NE N 0.903830 1
5 6 SE S 0.176600 0
6 7 SE S 0.176600 0
7 8 S S 0.460520 1
8 9 S S 0.460520 0
9 10 S S 0.460520 1
10 11 S S 0.460520 0
11 12 W W 0.403328 1
12 13 W W 0.403328 0
13 14 W W 0.403328 0
14 15 W W 0.403328 0
15 16 W W 0.403328 1注意事项:
采用平均数编码,容易引起过拟合,可以采用以下方法防止过拟合:
- 增大正则项f
- k折交叉验证
以下为自行实现的基于k折交叉验证版本的平均数编码,可以应用于二分类、多分类、回归场景中对单一类别特征或具有层次结构类别特征进行编码,该版本中用prior对unknown类别和缺失值编码。
from itertools import product
from category_encoders import TargetEncoder
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold, KFoldclass MeanEncoder:def __init__(self, categorical_features, n_splits=5, target_type='classification', min_samples_leaf=2, smoothing=1, hierarchy=None, verbose=0, shuffle=False, random_state=None):"""Parameters----------categorical_features: list of strthe name of the categorical columns to encode.n_splits: intthe number of splits used in mean encoding.target_type: str,'regression' or 'classification'.min_samples_leaf: intFor regularization the weighted average between category mean and global mean is taken. The weight isan S-shaped curve between 0 and 1 with the number of samples for a category on the x-axis.The curve reaches 0.5 at min_samples_leaf. (parameter k in the original paper)smoothing: floatsmoothing effect to balance categorical average vs prior. Higher value means stronger regularization.The value must be strictly bigger than 0. Higher values mean a flatter S-curve (see min_samples_leaf).hierarchy: dict or dataframeA dictionary or a dataframe to define the hierarchy for mapping.If a dictionary, this contains a dict of columns to map into hierarchies. Dictionary key(s) should be the column name from Xwhich requires mapping. For multiple hierarchical maps, this should be a dictionary of dictionaries.If dataframe: a dataframe defining columns to be used for the hierarchies. Column names must take the form:HIER_colA_1, ... HIER_colA_N, HIER_colB_1, ... HIER_colB_M, ...where [colA, colB, ...] are given columns in cols list. 1:N and 1:M define the hierarchy for each column where 1 is the highest hierarchy (top of the tree). A single column or multiple can be used, as relevant.verbose: intinteger indicating verbosity of the output. 0 for none.shuffle : bool, default=Falserandom_state : int or RandomState instance, default=NoneWhen `shuffle` is True, `random_state` affects the ordering of theindices, which controls the randomness of each fold for each class.Otherwise, leave `random_state` as `None`.Pass an int for reproducible output across multiple function calls."""self.categorical_features = categorical_featuresself.n_splits = n_splitsself.learned_stats = {}self.min_samples_leaf = min_samples_leafself.smoothing = smoothingself.hierarchy = hierarchyself.verbose = verboseself.shuffle = shuffleself.random_state = random_stateif target_type == 'classification':self.target_type = target_typeself.target_values = []else:self.target_type = 'regression'self.target_values = Nonedef mean_encode_subroutine(self, X_train, y_train, X_test, variable, target):X_train = X_train[[variable]].copy()X_test = X_test[[variable]].copy()if target is not None:nf_name = '{}_pred_{}'.format(variable, target)X_train['pred_temp'] = (y_train == target).astype(int) # classificationelse:nf_name = '{}_pred'.format(variable)X_train['pred_temp'] = y_train # regressionprior = X_train['pred_temp'].mean()te = TargetEncoder(verbose=self.verbose, hierarchy=self.hierarchy, cols=[variable], smoothing=self.smoothing, min_samples_leaf=self.min_samples_leaf)te.fit(X_train[[variable]], X_train['pred_temp'])tmp_l = te.ordinal_encoder.mapping[0]["mapping"].reset_index()tmp_l.rename(columns={"index":variable, 0:"encode"}, inplace=True)tmp_l.dropna(inplace=True)tmp_r = te.mapping[variable].reset_index()if self.hierarchy is None:tmp_r.rename(columns={variable: "encode", 0:nf_name}, inplace=True)else:tmp_r.rename(columns={"index": "encode", 0:nf_name}, inplace=True)col_avg_y = pd.merge(tmp_l, tmp_r, how="left",on=["encode"])col_avg_y.drop(columns=["encode"], inplace=True)col_avg_y.set_index(variable, inplace=True)nf_train = X_train.join(col_avg_y, on=variable)[nf_name].valuesnf_test = X_test.join(col_avg_y, on=variable).fillna(prior, inplace=False)[nf_name].valuesreturn nf_train, nf_test, prior, col_avg_ydef fit(self, X, y):""":param X: pandas DataFrame, n_samples * n_features:param y: pandas Series or numpy array, n_samples:return X_new: the transformed pandas DataFrame containing mean-encoded categorical features"""X_new = X.copy()if self.target_type == 'classification':skf = StratifiedKFold(self.n_splits, shuffle=self.shuffle, random_state=self.random_state)else:skf = KFold(self.n_splits, shuffle=self.shuffle, random_state=self.random_state)if self.target_type == 'classification':self.target_values = sorted(set(y))self.learned_stats = {'{}_pred_{}'.format(variable, target): [] for variable, target inproduct(self.categorical_features, self.target_values)}for variable, target in product(self.categorical_features, self.target_values):nf_name = '{}_pred_{}'.format(variable, target)X_new.loc[:, nf_name] = np.nanfor large_ind, small_ind in skf.split(y, y):nf_large, nf_small, prior, col_avg_y = self.mean_encode_subroutine(X_new.iloc[large_ind], y.iloc[large_ind], X_new.iloc[small_ind], variable, target)X_new.iloc[small_ind, -1] = nf_smallself.learned_stats[nf_name].append((prior, col_avg_y))else:self.learned_stats = {'{}_pred'.format(variable): [] for variable in self.categorical_features}for variable in self.categorical_features:nf_name = '{}_pred'.format(variable)X_new.loc[:, nf_name] = np.nanfor large_ind, small_ind in skf.split(y, y):nf_large, nf_small, prior, col_avg_y = self.mean_encode_subroutine(X_new.iloc[large_ind], y.iloc[large_ind], X_new.iloc[small_ind], variable, None)X_new.iloc[small_ind, -1] = nf_smallself.learned_stats[nf_name].append((prior, col_avg_y))return X_newdef transform(self, X):""":param X: pandas DataFrame, n_samples * n_features:return X_new: the transformed pandas DataFrame containing mean-encoded categorical features"""X_new = X.copy()if self.target_type == 'classification':for variable, target in product(self.categorical_features, self.target_values):nf_name = '{}_pred_{}'.format(variable, target)X_new[nf_name] = 0for prior, col_avg_y in self.learned_stats[nf_name]:X_new[nf_name] += X_new[[variable]].join(col_avg_y, on=variable).fillna(prior, inplace=False)[nf_name]X_new[nf_name] /= self.n_splitselse:for variable in self.categorical_features:nf_name = '{}_pred'.format(variable)X_new[nf_name] = 0for prior, col_avg_y in self.learned_stats[nf_name]:X_new[nf_name] += X_new[[variable]].join(col_avg_y, on=variable).fillna(prior, inplace=False)[nf_name]X_new[nf_name] /= self.n_splitsreturn X_new四 总结
本文介绍了一种对高基数类别特征非常有效的编码方式:平均数编码。详细的讲述了该种编码方式的原理,在实际工程应用中有效避免过拟合的方法,并且提供了一个直接上手的代码版本。
作者:京东保险 赵风龙
来源:京东云开发者社区 转载请注明来源