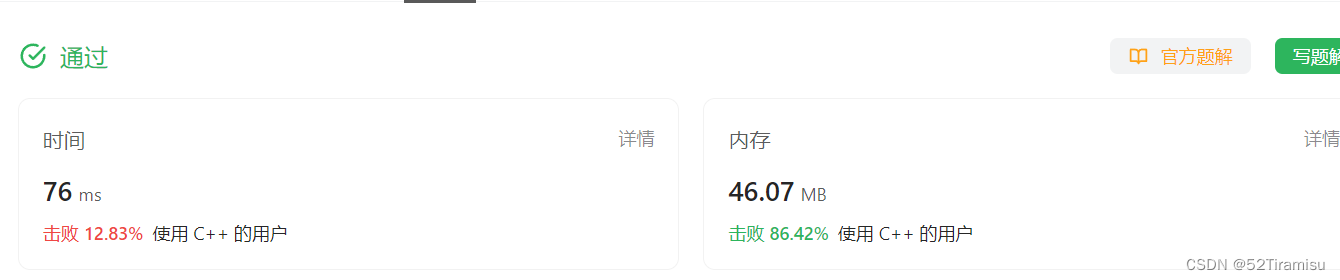
一、括号的匹配
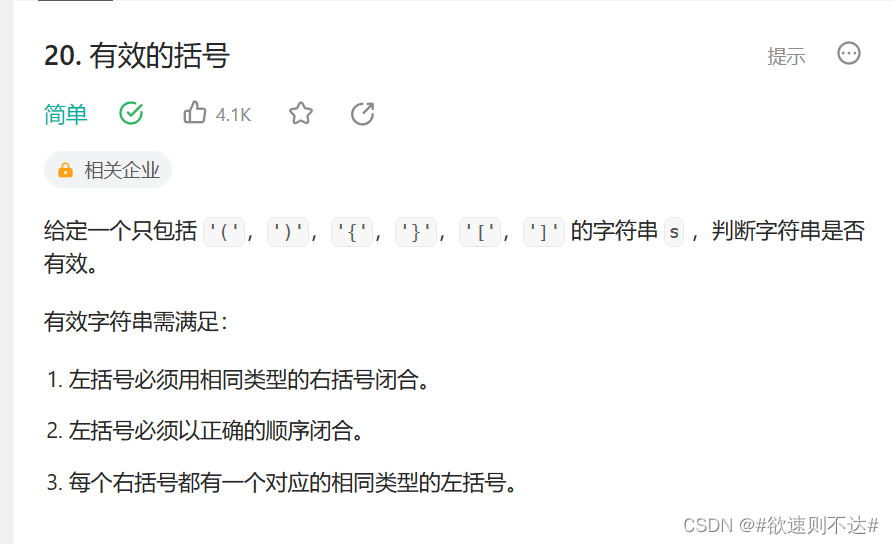
题目介绍:

思路:
- 如果 c 是左括号,则入栈 push;
- 否则通过哈希表判断括号对应关系,若 stack 栈顶出栈括号 stack.pop() 与当前遍历括号 c 不对应,则提前返回 false。
- 栈 stack 为空: 此时 stack.pop() 操作会报错;因此,我们采用一个取巧方法,给 stack 赋初值 ?,并在哈希表 dic 中建立 key: ‘?’,value:’?’ 的对应关系予以配合。此时当 stack 为空且 c 为右括号时,可以正常提前返回 false
字符串 s 以左括号结尾: 此情况下可以正常遍历完整个 s,但 stack 中遗留未出栈的左括号;因此,最后需返回 len(stack) == 1,以判断是否是有效的括号组合
typedef int STDataType;
//动态存储结构
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType *a;int top;int capacity; //容量
}ST;void STInit(ST* ps); //初始化栈
void STDestory(ST* ps); //销毁栈
bool STEmpty(ST* ps); //判断是否为空
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x); //入栈
void STPop(ST* ps); //出栈
STDataType STTop(ST* ps); //取栈顶元素
int STSize(ST* ps); //返回栈元素个数void STInit(ST* ps) //初始化栈
{assert(ps);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = 0;ps->capacity = 0;
}void STDestory(ST* ps) //销毁栈
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = 0;ps->capacity = 0;
}bool STEmpty(ST* ps) //判断是否为空
{assert(ps);return (ps->top == 0);
}void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x) //入栈
{assert(ps);//扩容if (ps->top == ps->capacity){int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;STDataType* tem = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a,sizeof(STDataType)* newcapacity);if (tem == NULL){perror("malloc");exit(-1);}ps->a = tem;ps->capacity = newcapacity;}ps->a[ps->top] = x;ps->top++;
}void STPop(ST* ps) //出栈
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top>0);--ps->top;
}STDataType STTop(ST* ps) //取栈顶元素
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top > 0);return ps->a[ps->top-1];
}int STSize(ST* ps) //返回栈元素个数
{assert(ps);return ps->top ;
}
bool isValid(char * s)
{char topval;ST st;STInit(&st);while(*s){if(*s=='('||*s=='['||*s=='{'){STPush(&st, *s);}else{if(STEmpty(&st)){STDestory(&st);return false;}topval=STTop(&st);STPop(&st);if((*s=='}'&&topval!='{')||(*s==')'&&topval!='(')||(*s==']'&&topval!='[')){STDestory(&st);return false;}}++s;}bool ret=STEmpty(&st);STDestory(&st);return ret;
}二、队列实现栈
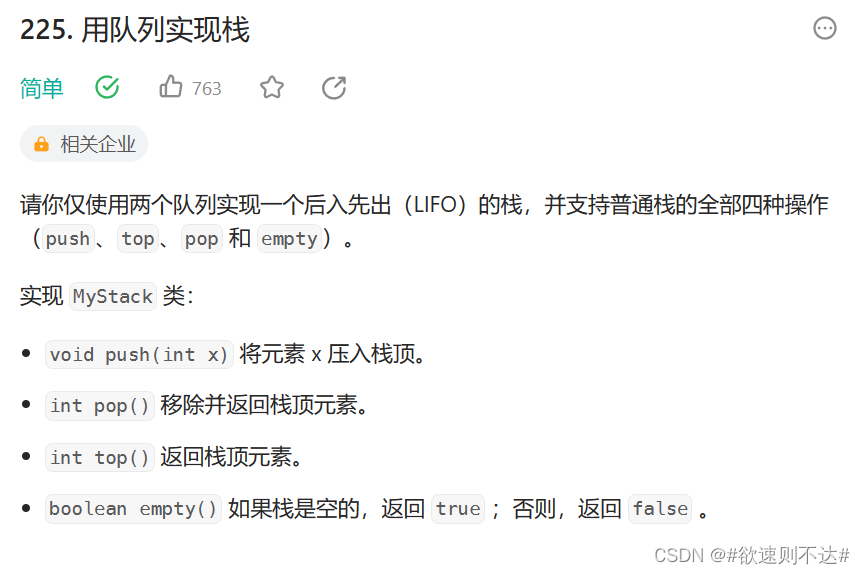
题目介绍:


typedef int QDataType;typedef struct QueueNode
{struct QueueNode* next;QDataType data;
}QNode;typedef struct Queue
{QNode* head; //队头指针QNode* tail; //队尾指针int size; //元素个数
}Que;void QueueInit(Que* pq); //初始化队列
void QueueDestory(Que* pq); //销毁队列
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq); //判断队列是否为空
void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x);//进队列
void QueuePop(Que* pq); //出队列
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq); //取队头元素
QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq); //取队尾元素
int QueueSize(Que* pq); //返回元素个数
void QueueInit(Que* pq) //初始化队列
{assert(pq);pq->head = NULL;pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}void QueueDestory(Que* pq) //销毁队列
{assert(pq);QNode* cur =pq->head;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq) //判断队列是否为空
{assert(pq);return pq -> head == NULL;
}void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x)//进队列
{//尾插assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc");exit(-1);}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;if (pq->tail == NULL){pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;}else{pq->tail->next = newnode;pq->tail = newnode;}pq->size++;}void QueuePop(Que* pq) //出队列
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));if (pq->head->next == NULL){free(pq->head);pq->head = pq->tail=NULL;}else{QNode* next = pq->head->next;free(pq->head);pq->head = next;}pq->size--;
}QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq) //取队头元素
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->head->data;
}QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq) //取队尾元素
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->tail->data;
}int QueueSize(Que* pq) //返回元素个数
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}
typedef struct
{Que q1;Que q2;
} MyStack;MyStack* myStackCreate()
{MyStack*pst=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));QueueInit(&pst->q1);QueueInit(&pst->q2);return pst;
}void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x)
{if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);}else{QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);}
}int myStackPop(MyStack* obj)
{Que*empty=&obj->q1;Que*nonEmpty=&obj->q2;if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){nonEmpty=&obj->q1;empty=&obj->q2;}while(QueueSize(nonEmpty)>1){QueuePush(empty,QueueFront(nonEmpty));QueuePop(nonEmpty);}int top=QueueFront(nonEmpty);QueuePop(nonEmpty);return top;
}int myStackTop(MyStack* obj)
{if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){return QueueBack(&obj->q1);}else{return QueueBack(&obj->q2);}
}bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj)
{return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)&&QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}void myStackFree(MyStack* obj)
{QueueDestory(&obj->q1);QueueDestory(&obj->q2);free(obj);
}/*** Your MyStack struct will be instantiated and called as such:* MyStack* obj = myStackCreate();* myStackPush(obj, x);* int param_2 = myStackPop(obj);* int param_3 = myStackTop(obj);* bool param_4 = myStackEmpty(obj);* myStackFree(obj);
*/三、栈实现队列
题目介绍: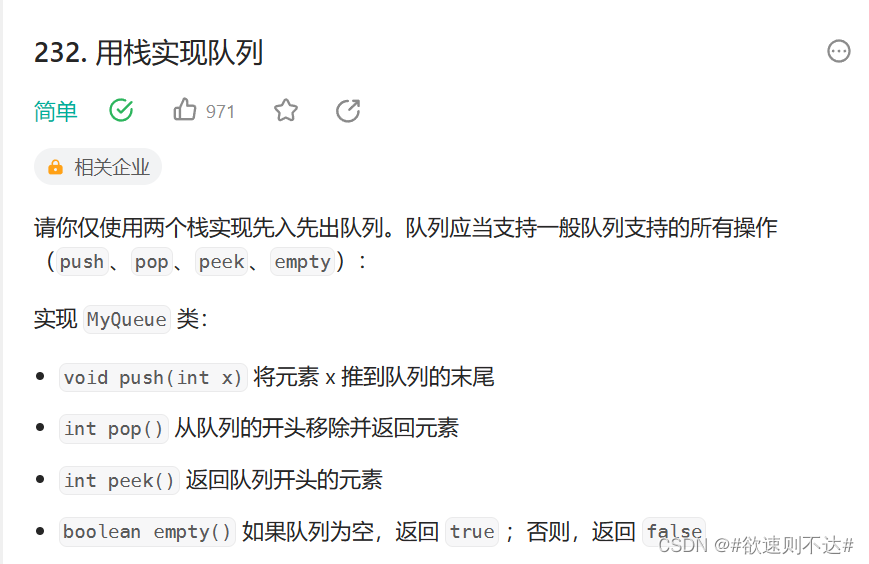
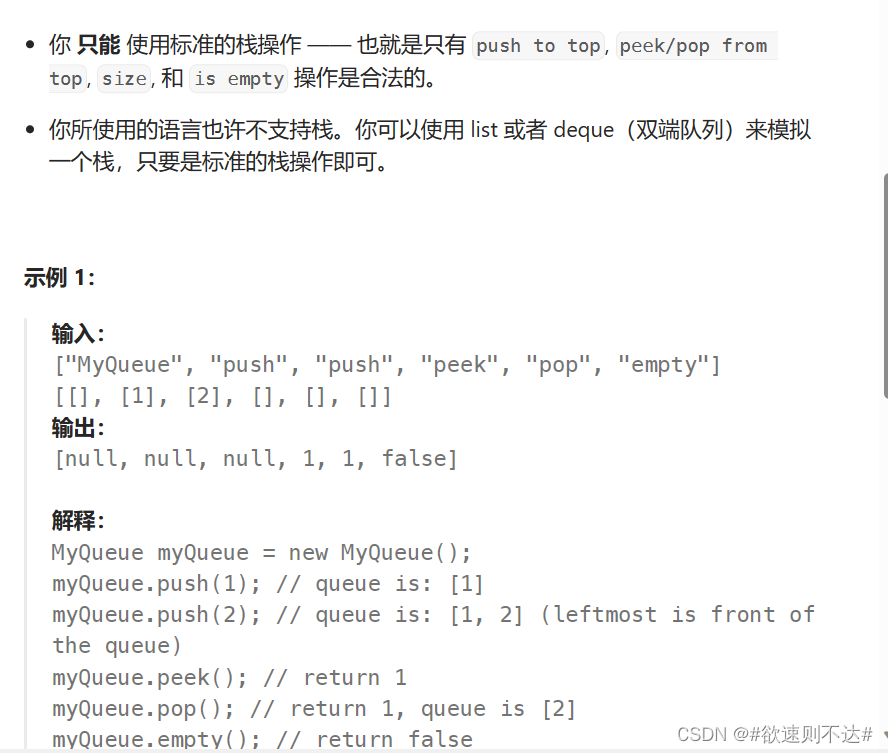
思路:
因为队列先进先出,栈先进后出,所以用两个栈实现队列。栈s1用来入队,栈s2用来出队。
入队:对入队的栈s1直接进行元素入栈。
出队:当出队的栈s2不为空时,s2直接出栈;若s2为空,将s1的元素都导入出队的栈s2里,然后s2进行出栈。、
在入队1、2、3、4后出队,如图所示:s1中的数据都入栈s2(s1,s2中的数据相同,顺序相反,例:s1中的栈底元素1出现在s2中的栈顶),此时s1的top==0(top表示栈中有多少元素,0代表栈中元素都已经出栈),s2的top==3(本来有4个数据,但栈顶元素已经出栈,所以为3).
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType *a;int top;int capacity; //容量
}ST;void STInit(ST* ps); //初始化栈
void STDestory(ST* ps); //销毁栈
bool STEmpty(ST* ps); //判断是否为空
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x); //入栈
void STPop(ST* ps); //出栈
STDataType STTop(ST* ps); //取栈顶元素
int STSize(ST* ps); //返回栈元素个数void STInit(ST* ps) //初始化栈
{assert(ps);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = 0;ps->capacity = 0;
}void STDestory(ST* ps) //销毁栈
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = 0;ps->capacity = 0;
}bool STEmpty(ST* ps) //判断是否为空
{assert(ps);return (ps->top == 0);
}void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x) //入栈
{assert(ps);//扩容if (ps->top == ps->capacity){int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;STDataType* tem = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a,sizeof(STDataType)* newcapacity);if (tem == NULL){perror("malloc");exit(-1);}ps->a = tem;ps->capacity = newcapacity;}ps->a[ps->top] = x;ps->top++;
}void STPop(ST* ps) //出栈
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top>0);--ps->top;
}STDataType STTop(ST* ps) //取栈顶元素
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top > 0);return ps->a[ps->top-1];
}int STSize(ST* ps) //返回栈元素个数
{assert(ps);return ps->top ;
}
typedef struct
{ST pushst;ST popst;
} MyQueue;MyQueue* myQueueCreate()
{MyQueue*obj=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));STInit(&obj->pushst);STInit(&obj->popst);return obj;
}void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x)
{STPush(&obj->pushst,x);
}int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) //取对头数据
{if(STEmpty(&obj->popst)){while(!STEmpty(&obj->pushst)){STPush(&obj->popst,STTop(&obj->pushst));STPop(&obj->pushst);}}return STTop(&obj->popst);
}int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj)
{int front =myQueuePeek(obj);STPop(&obj->popst);return front;
}bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj)
{return STEmpty(&obj->popst)&&STEmpty(&obj->pushst);
}void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj)
{STDestory(&obj->popst);STDestory(&obj->pushst);free(obj);
}/*** Your MyQueue struct will be instantiated and called as such:* MyQueue* obj = myQueueCreate();* myQueuePush(obj, x);* int param_2 = myQueuePop(obj);* int param_3 = myQueuePeek(obj);* bool param_4 = myQueueEmpty(obj);* myQueueFree(obj);
*/四、循环队列
题目介绍:
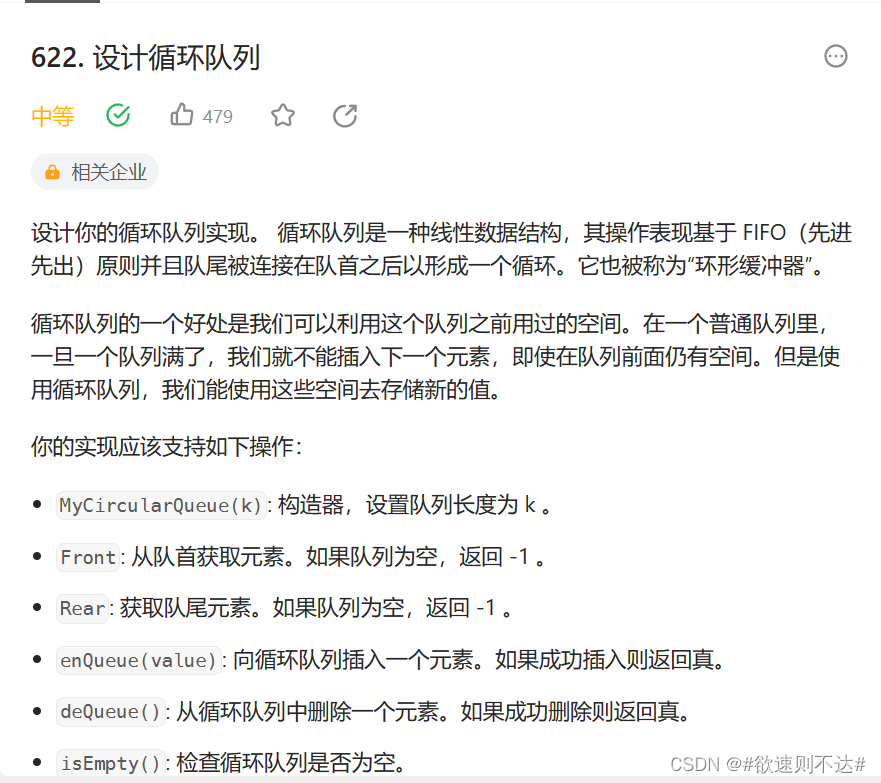

设计一个队列,这个队列的大小是固定的,且队列头尾相连, 然后该队列能够实现题目中的操作。
那么是使用数组实现,还是用链表实现呢?我们接着往下看。
环形队列的几个判断条件
front:指向队列的第一个元素,初始值front=0
rear: 指向队列的最后一个元素的后一个位置(预留一个空间作为约定),初始值rear=0
maxSize: 数组的最大容量
队空:front == rear
队满:(rear+1)%maxSize == front
队列中的有效数据个数:(rear+maxSize-front)% maxSize
其中判断队列满的思想的话,可以看下图,因为是环形的,起初front=rear=0,每当添加元素时,将rear++,但是其实预留了一个长度没有用,比如定义的队列数组长度为5时,但是实际上可以使用的地址就是0,1,2,3,此时rear=4, 4这个空间用来判断队满的条件(rear+1)%maxSize==front
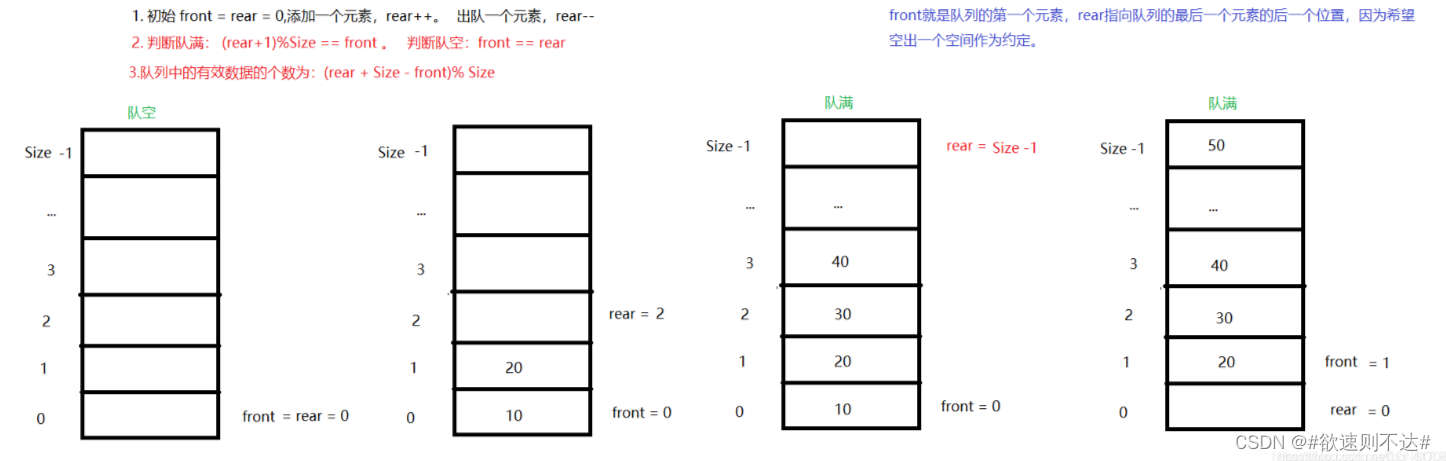
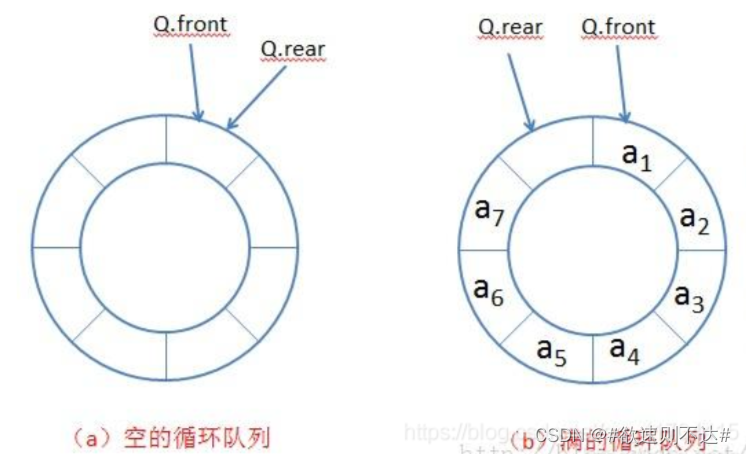
有了上面的铺垫就可以很轻松的写出下面的函数。
typedef struct
{int *a;int front;int rear;int k;
} MyCircularQueue;MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k)
{MyCircularQueue*obj=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));//多开一个空间(浪费掉)为了区分空和满obj->a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));obj->front=obj->rear=0;obj->k=k;return obj;
}bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{return obj->front==obj->rear;
}bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{return (obj->rear+1)%(obj->k+1)==obj->front;
}bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value)
{if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj)){return false;}obj->a[obj->rear]=value;obj->rear++;obj->rear%=(obj->k+1);return true;
}bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return false;}++obj->front;obj->front%=(obj->k+1);return true;
}int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return -1;}return obj->a[obj->front];
}int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return -1;}return obj->a[(obj->rear+(obj->k+1)-1)%(obj->k+1)];
}void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{free(obj->a);free(obj);
}/*** Your MyCircularQueue struct will be instantiated and called as such:* MyCircularQueue* obj = myCircularQueueCreate(k);* bool param_1 = myCircularQueueEnQueue(obj, value);* bool param_2 = myCircularQueueDeQueue(obj);* int param_3 = myCircularQueueFront(obj);* int param_4 = myCircularQueueRear(obj);* bool param_5 = myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj);* bool param_6 = myCircularQueueIsFull(obj);* myCircularQueueFree(obj);
*/