1、成员变量和成员函数
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <string>//成员变量和成员函数分开存储class Person {int m_A;//非静态成员变量 属于类的对象上的static int m_B;//静态成员变量 不属于类的对象上void func() {} //非静态成员函数 不属于类的对象上static void func2(){}//静态成员函数 不属于类的对象上 }; int Person::m_B=0;void test01() {Person p;//空对象占用内存空间为:1//c++编译器会给每个空对象也分配一个字节空间,是为了区分空对象占内存的位置//每个空对象也应该有一个独一无二的内存地址cout << "size of p = " << sizeof(p) << endl; }void test02() {Person p;cout << "size of p = " << sizeof(p) << endl; }int main() {//test01();test02();system("pause");return 0; }
2、this指针的用途
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <string>class Person { public:Person(int age) {//this指针指向 被调用的成员函数 所属的对象this->age = age;}Person& PersonAddAge(Person &p) {this->age += p.age;//this指向p2的指针,而*this指向的就是p2这个对象本体return *this;}int age;};//1、解决名称冲突 void test01() {Person p1(18);cout << "p1的年龄为:" << p1.age << endl;} //2、返回对象本身用*this void test02() {Person p1(10);Person p2(10);/*p2.PersonAddAge(p1);cout << "p2的年龄为:" << p2.age << endl;*///链式编程思想p2.PersonAddAge(p1).PersonAddAge(p1).PersonAddAge(p1);cout << "p2的年龄为:" << p2.age << endl; }int main() {//test01();test02();system("pause");return 0; }
3、空指针访问成员函数
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <string>class Person { public:void showClassNmae() {cout << "this is Person class" << endl;}//报错原因是因为传入的指针是为NULLvoid showPersonAge() {if (this == NULL) {return;}cout << "age = " << m_Age << endl;}int m_Age; };void test01() {Person* p = NULL;p->showClassNmae();//p->showPersonAge();报错 }int main() {test01();system("pause");return 0; }
4、const修饰成员函数
常函数:
- 成员函数后加const后我们称为这个函数为常函数
- 常函数内不可以修改成员属性
- 成员属性声明时加关键字mutable后,在常函数中依然可以修改
常对象:
- 声明对象前加const称该对象为常对象
- 常对象只能调用常函数
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <string>//常函数 class Person { public://this指针的本质 是指针常量 指针的指向是不可以修改的//const Person * const this;//在成员函数后面加const,修饰的是this指向,让指针指向的值也不可以修改void showPerson() const{this->m_B=100;//this->m_A = 100;//this指针是不可以修改指针的指向的//this = NULL;} void func() {}int m_A;mutable int m_B;//特色变量,即使在常函数中,也可以修饰这个值 };void test01() {Person p;p.showPerson(); }//常对象 void test02() {const Person p;//在对象前加const,变为常对象//p.m_A = 100;p.m_B = 100;//m_Bs是特殊值,在常对象下也可以修改//常对象只能调用常函数p.showPerson();//p.func();//常对象 不可以调用普通成员函数,因为普通成员函数可以修改属性 }int main() {test01();test02();system("pause");return 0; }
对象模型和this指针(个人学习笔记黑马学习)
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.rhkb.cn/news/124636.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系长河编程网进行投诉反馈email:809451989@qq.com,一经查实,立即删除!相关文章
博客程序系统其它功能扩充
一、注册功能
1、约定前后端接口 2、后端代码编写
WebServlet("/register")
public class RegisterServlet extends HttpServlet {Overrideprotected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {//设置…
《向量数据库指南》——提高向量数据库Milvus Cloud 2.3的运行效率
简介:向量数据库彻底改变了我们处理复杂数据结构的方式: 向量数据库彻底改变了我们处理复杂数据结构的方式,为高维矢量提供了高效的存储和检索。作为向量数据库专家和《向量数据库指南》的作者,我很高兴能与大家分享向量数据库运行效率方面的最新进展。在本文中,我们将探讨…
ARM编程模型-常用指令集
一、ARM指令集
ARM是RISC架构,所有的指令长度都是32位,并且大多数指令都在一个单周期内执行。主要特点:指令是条件执行的,内存访问使用Load/store架构。 二、Thumb 指令集
Thumb是一个16位的指令集,是ARM指令集的功能…
PandaGPT部署演示
PandaGPT 是一种通用的指令跟踪模型,可以看到和听到。实验表明,PandaGPT 可以执行复杂的任务,例如生成详细的图像描述、编写受视频启发的故事以及回答有关音频的问题。更有趣的是,PandaGPT 可以同时接受多模态输入并自然地组合它们…
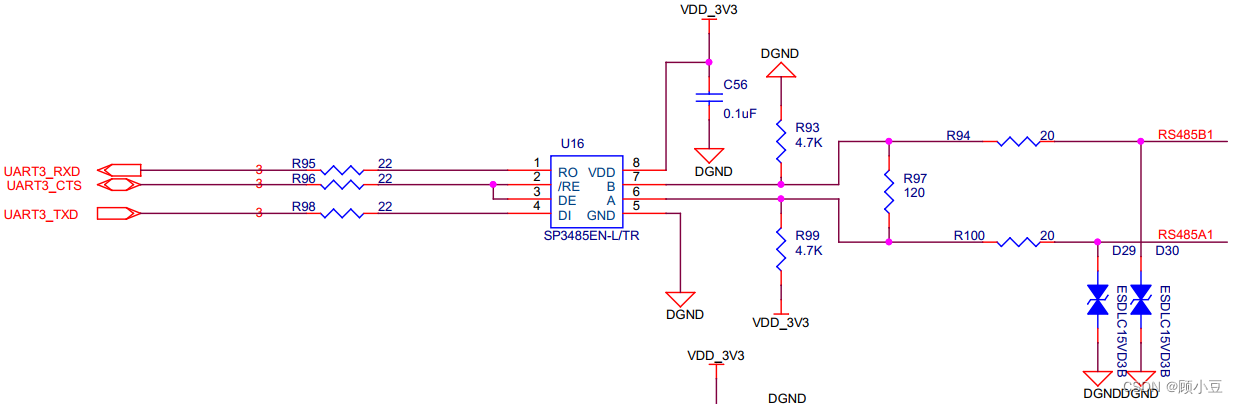
嵌入式linux(imx6ull)下RS485接口配置
接口原理图如下: 由原理图可知收发需要收UART_CTS引脚控制,高电平时接收,低电平时发送。通过查看Documentation/devicetree/bindings/serial/fsl-imx-uart.yaml和Documentation/devicetree/bindings/serial/rs485.yaml两个说明文档,修改设备树…
Nginx__高级进阶篇之LNMP动态网站环境部署
动态网站和LNMP(LinuxNginxMySQLPHP)都是用于建立和运行 web 应用程序的技术。
动态网站是通过服务器端脚本语言(如 PHP、Python、Ruby等)动态生成网页内容的网站。通过这种方式,动态网站可以根据用户的不同请求生成不…
分类算法系列⑤:决策树
目录
1、认识决策树
2、决策树的概念
3、决策树分类原理
基本原理
数学公式
4、信息熵的作用
5、决策树的划分依据之一:信息增益
5.1、定义与公式
5.2、⭐手动计算案例
5.3、log值逼近
6、决策树的三种算法实现
7、API
8、⭐两个代码案例
8.1、决策树…
SpringCloud(34):Nacos服务发现
1 从单体架构到微服务
1.1单体架构
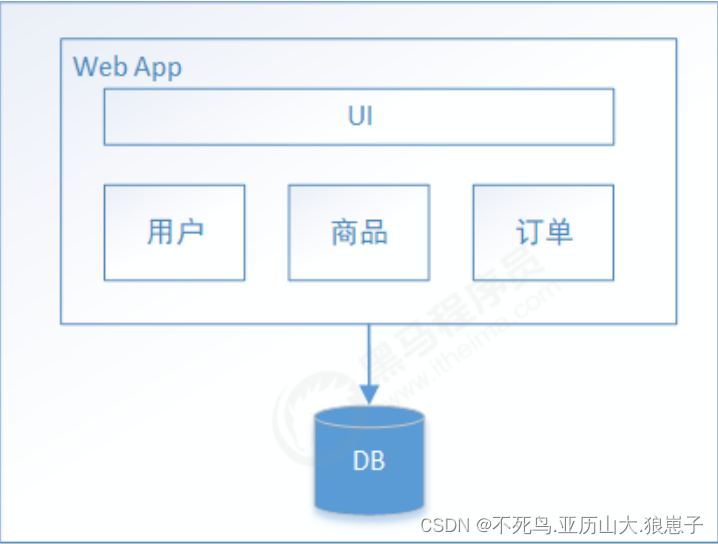
Web应用程序发展的早期,大部分web工程师将所有的功能模块打包到一起并放在一个web容器中运行,所有功能模块使用同一个数据库,同时,它还提供API或者UI访问的web模块等。 尽管也是模块化逻辑,但是最终它还是会打包并部署为单体式应用,这…
C++:类和对象(二)
本文主要介绍:构造函数、析构函数、拷贝构造函数、赋值运算符重载、const成员函数、取地址及const取地址操作符重载。
目录
一、类的六个默认成员函数
二、构造函数
1.概念
2.特性
三、析构函数
1.概念
2.特性
四、拷贝构造函数
1.概念
2.特征
五、赋值…
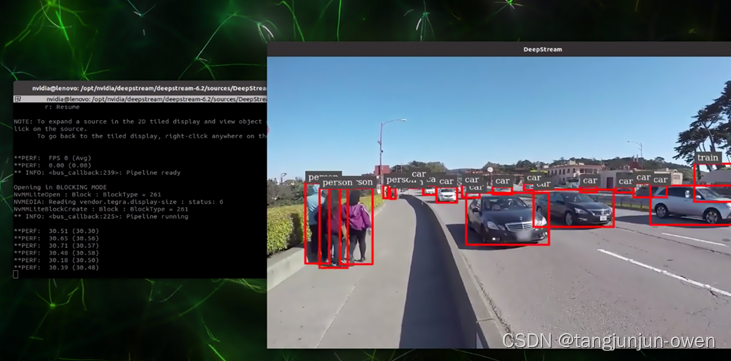
deepstream6.2部署yolov5详细教程与代码解读
文章目录 引言一.环境安装1、yolov5环境安装2、deepstream环境安装 二、源码文件说明三.wts与cfg生成1、获得wts与cfg2、修改wts 四.libnvdsinfer_custom_impl_Yolo.so库生成五.修改配置文件六.运行demo 引言
DeepStream 是使用开源 GStreamer 框架构建的优化图形架构…
Element Plus table formatter函数返回html内容
查看 Element Plus table formatter 支持返回 类型为string 和 VNode对象;
若依全局直接用h函数,无需引用 下面普通基本用法:在Element Plus中,你可以使用自定义的formatter函数来返回VNode对象,从而实现更灵活的自定…
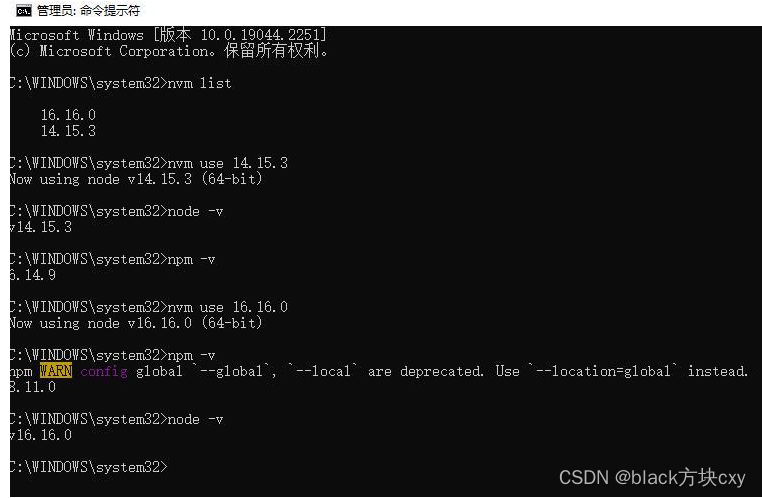
nvm管理(切换)node版本,方便vue2,vue3+ts开发
使用nvm切换node版本 1. 完全删除之前的node及npm(清理干净Node: 应用程序,缓存的文件,环境变量 ) 2. 使用管理员身份安装nvm,下载如下 3. 安装完nvm之后找到nvm下载路径对应的文件 4. 使用管理员身份打开cmdÿ…
人工智能和大数据:跨境电商如何实现定制化营销?
在跨境电商竞争激烈的市场中,如何精准地满足消费者的需求并提供个性化的购物体验成为了商家们面临的重要挑战。幸运的是,人工智能和大数据技术的崛起为跨境电商带来了新的机遇,使得定制化营销成为可能。本文将探讨人工智能和大数据在跨境电商…
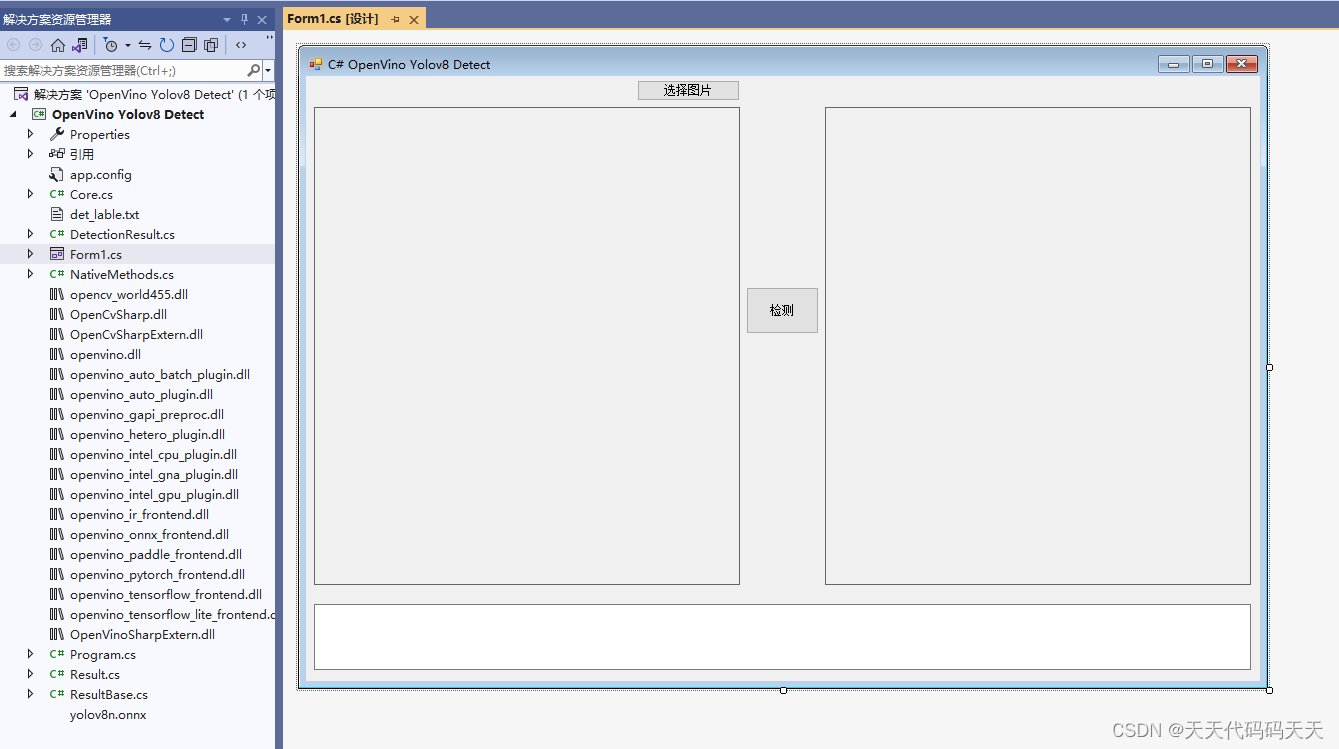
C# OpenVino Yolov8 Detect 目标检测
效果
项目 代码
using OpenCvSharp;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using static System.Net.Mime.MediaT…
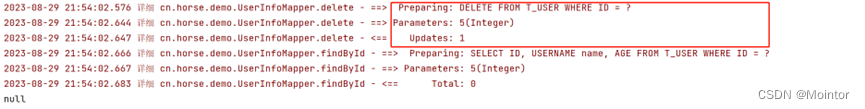
Mybatis 插入、修改、删除
前面几篇我们介绍了使用Mybatis查询数据,并且也了解了如何在Mybatis中使用JDK的日志系统打印日志;本篇我们继续介绍如何使用Mybatis完成数据的插入、修改和删除。
如果您对查询数据和Mybatis集成JDK日志系统不太了解,建议您先进行了解后再阅…
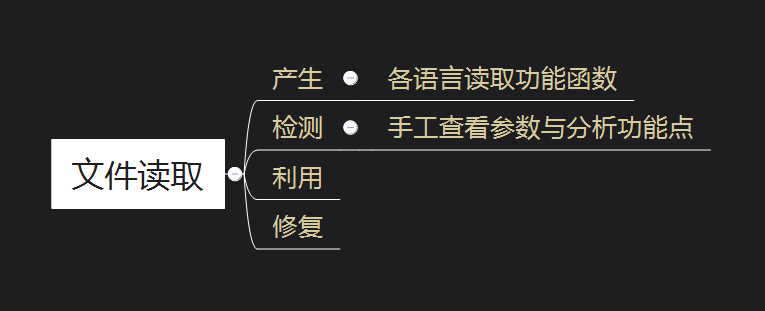
《Web安全基础》04. 文件操作安全
web 1:文件操作安全2:文件上传漏洞2.1:简介2.2:防护与绕过2.3:WAF 绕过2.3.1:数据溢出2.3.2:符号变异2.3.3:数据截断2.3.4:重复数据 3:文件包含漏洞4…
Pyecharts数据可视化(一)
目录 1.Pyecharts简介
2.Pyecharts的常用方法
3.Pyecharts绘制柱状图
3.1 绘制并列柱状图
3.2 绘制水平直方图 1.Pyecharts简介
Pyecharts是一个用于创建交互式图表的Python库。它基于Echarts,一个强大的JavaScript图表库,Pyecharts允许Python开发者…
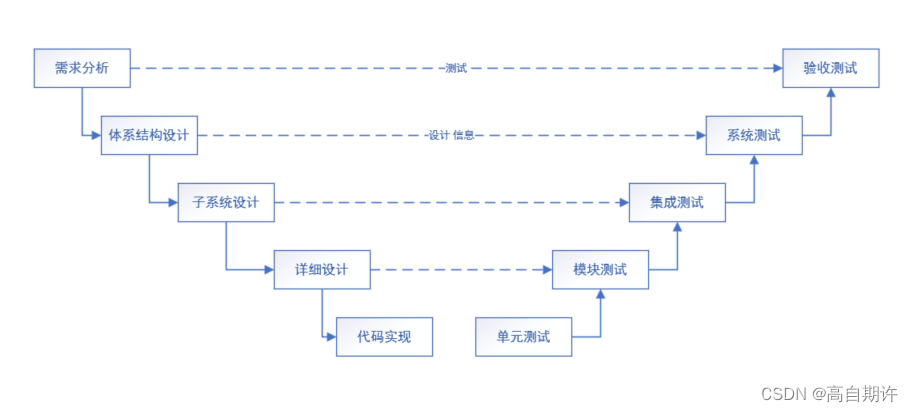
二、模型驱动测试设计
如果能够提升抽象层级,测试设计师会更加有效和有效率。 完全改正软件是不可能到达的,其原因是可以以形式化的方式来表述的而且是富有哲理的。聪明的软件工程师不再追求软件的完全正确,而是试着评判软件的行为来决定其是否为可接受的。**包括可…
人工智能的优势:使用 GPT 和扩散模型生成图像
推荐:使用 NSDT场景编辑器快速搭建3D应用场景 世界被人工智能 (AI) 所吸引,尤其是自然语言处理 (NLP) 和生成 AI 的最新进展,这是有充分理由的。这些突破性技术有可能提高各种任务的日常生产力。…