前言
- 在vs2019下使用C++与Python进行混合编程,在根源上讲,Python 本身就是一个C库,那么这里使用其中最简单的一种方法是把Python的C API来嵌入C++项目中,来实现混合编程。
- 当前的环境是,win10,IDE是vs2019,python版本是3.9,python的环境是使用Anacond安装的。
一、环境配置
1. 安装Python
首先要安装好Python的库,Python可以直接从官网下载,或者直接在conda里面进行安装。
2.添加环境变量
安装完成之后,添加两个系统环境变量,分别是:PYTHONHOME和PYTHONPATH。
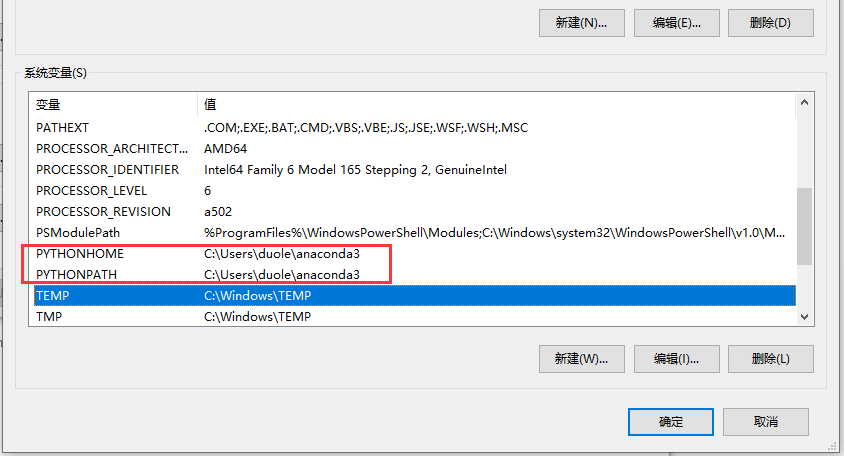
如果不添加这两个系统环境变量会报以下的错误:
Python path configuration:PYTHONHOME = (not set)PYTHONPATH = (not set)program name = 'python'isolated = 0environment = 1user site = 1import site = 1sys._base_executable = 'C:\\code\\cpp\\PDFToDoc\\x64\\Release\\PDFToDoc.exe'sys.base_prefix = 'C:\\Users\\duole\\anaconda3'sys.base_exec_prefix = 'C:\\Users\\duole\\anaconda3'sys.platlibdir = 'lib'sys.executable = 'C:\\code\\cpp\\PDFToDoc\\x64\\Release\\PDFToDoc.exe'sys.prefix = 'C:\\Users\\duole\\anaconda3'sys.exec_prefix = 'C:\\Users\\duole\\anaconda3'sys.path = ['C:\\Users\\duole\\anaconda3\\python39.zip','.\\DLLs','.\\lib','C:\\code\\cpp\\PDFToDoc\\x64\\Release',]
Fatal Python error: init_fs_encoding: failed to get the Python codec of the filesystem encoding
Python runtime state: core initialized
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'encodings'Current thread 0x000042d4 (most recent call first):
<no Python frame>
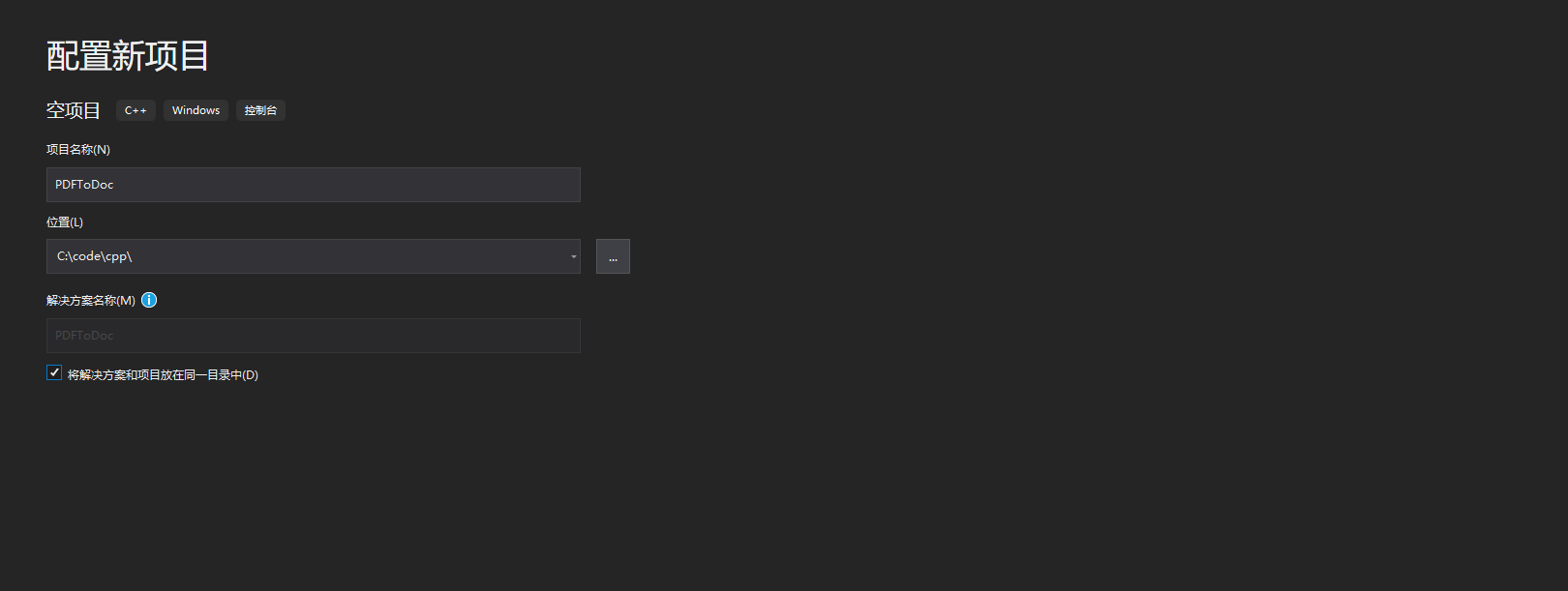
3. 创建项目
打开vs2019,创建一个空的新C++项目:
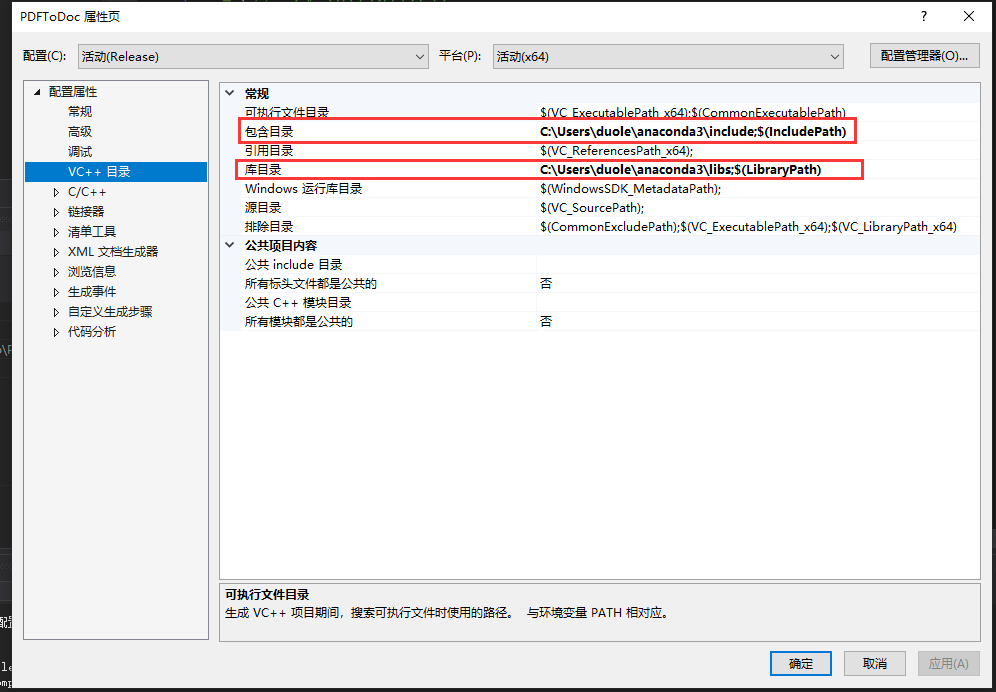
创建完成后打开项目属于配置包含目录与库目录:
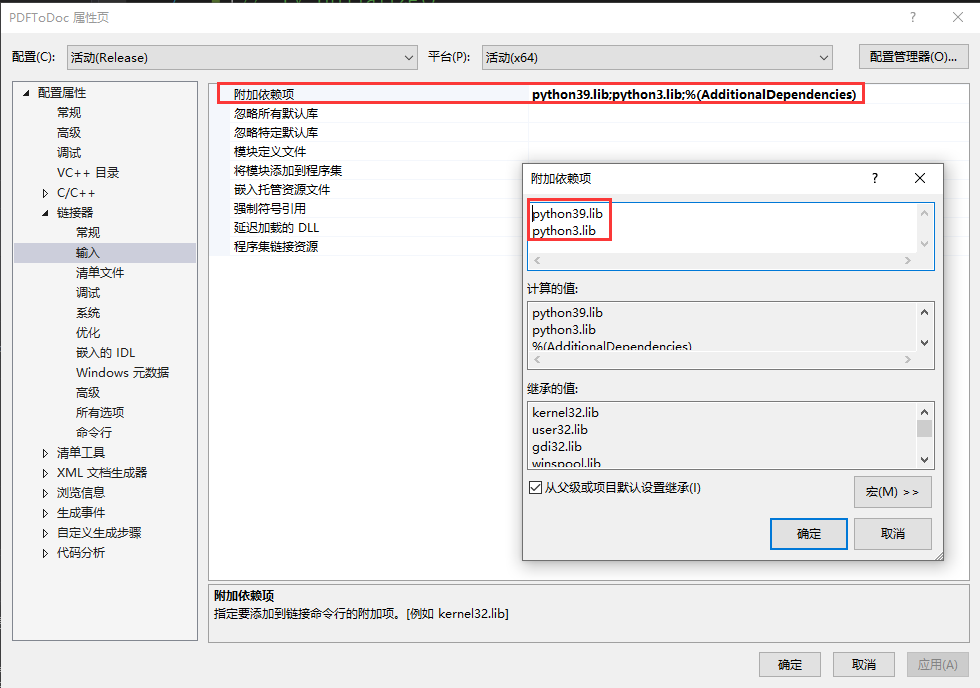
在附加依赖项目里把python的lib库名添加到里面:
4.添加代码
在项目里面新添一个main.cpp
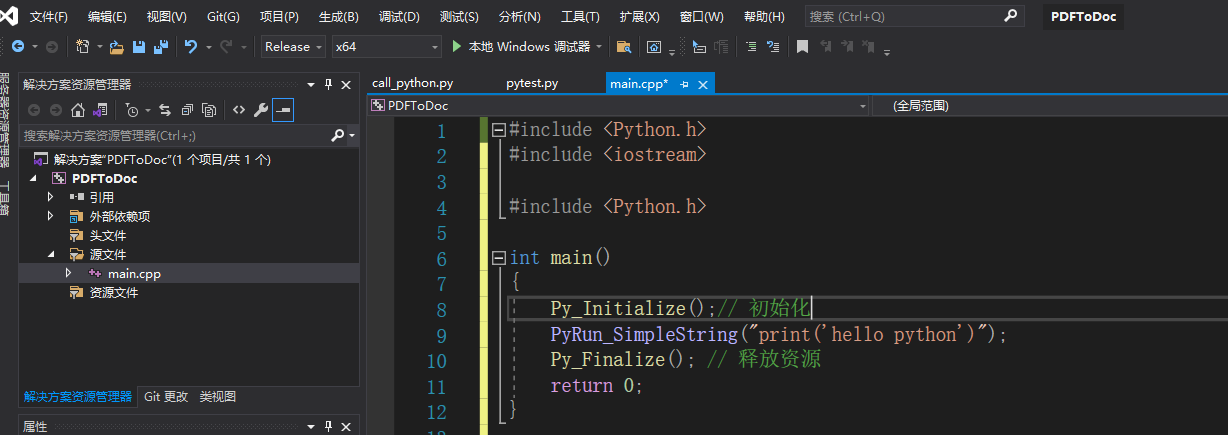
main.cpp里面的代码:
#include <Python.h>int main()
{Py_Initialize(); // 初始化python解释器PyRun_SimpleString("print('hello python')");Py_Finalize(); // 释放资源return 0;
}
然后运行项目
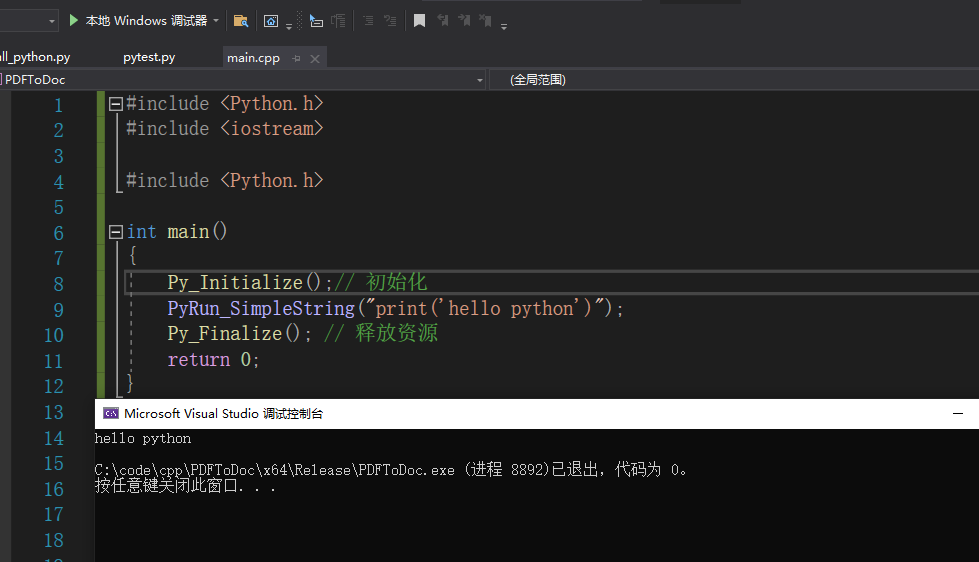
这样配置就算法成功了。
二、Python C API 调用
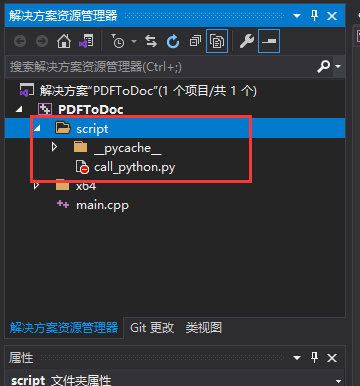
为了方便项目测试,在项目根目录下添加一个script目录,在script目录里面创建一个call_python.py的文件。
2.1 调用Python代码无参函数
C++调用python无参函数流程:
- 初始化python接口(Py_Initialize)
- 导入依赖库 (PyRun_SimpleString)
- 初始化python系统文件路径(PyRun_SimpleString)
- 调用python文件名(PyImport_ImportModule)
- 获取函数对象(PyObject_GetAttrString)
- 调用函数对象(PyObject_CallObject)
- 结束python接口调用,释放资源(Py_Finalize)
在call_python.py里面添加代码:
def test():print("hello python to C++")
然后在main.cpp里面进行调用:
int main()
{//1.初始化python接口Py_Initialize();if (!Py_IsInitialized){std::cout << "python init failed" << std::endl;return 1;}//2.导入依赖库PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");//执行py单条语句//3.初始化python系统文件路径,以便访问到python源码文件所在的路径PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('./script')");//4.调用python源码文件,只写文件名,不用写后缀PyObject* module = PyImport_ImportModule("call_python");if (module == nullptr){std::cout << "module not found: call_python" << std::endl;return 1;}//5.获取python文件里面的函数PyObject* test = PyObject_GetAttrString(module, "test");if (!test || !PyCallable_Check(test)){std::cout << "function not found: test" << std::endl;return 1;}//6.调用函数,函数对象与传入参数PyObject_CallObject(test, nullptr);Py_Finalize();return 0;
}2.2 调用Python代码有参与有返回值的函数
C++调用python有参并有返回的函数流程:
- 初始化python接口(Py_Initialize)
- 导入依赖库 (PyRun_SimpleString)
- 初始化python系统文件路径(PyRun_SimpleString)
- 调用python文件名(PyImport_ImportModule)
- 获取函数对象(PyObject_GetAttrString)
- 传递参数(PyTuple_New,Py_BuildValue)
- 调用函数对象(PyObject_CallObject)
- 接收函数返回值(PyArg_Parse)
- 结束python接口初始化(Py_Finalize)
在call_python.py里面添加代码:
def add(a, b):c = a + bprint(f"{a} + {b} = {c}")return c
然后在main.cpp里面进行调用:
#include <iostream>
#include <Python.h>int main()
{// 1、初始化python接口Py_Initialize();if (!Py_IsInitialized()){std::cout << "python init failed" << std::endl;return 1;}// 2、初始化python系统文件路径,保证可以访问到 .py文件PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('./script')");// 3、调用python文件名,不用写后缀PyObject* module = PyImport_ImportModule("call_python");if (module == nullptr){std::cout << "module not found: call_python" << std::endl;return 1;}// 4、调用函数PyObject* func = PyObject_GetAttrString(module, "add");if (!func || !PyCallable_Check(func)){std::cout << "function not found: add" << std::endl;return 1;}// 5、给 python 传递参数// 函数调用的参数传递均是以元组的形式打包的, 2表示参数个数// 如果函数中只有一个参数时,写1就可以了PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(2);// 0:第一个参数,传入 int 类型的值 1PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, Py_BuildValue("i", 1));// 1:第二个参数,传入 int 类型的值 2PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, Py_BuildValue("i", 2));// 6、使用C++的python接口调用该函数PyObject* ret = PyObject_CallObject(func, args);// 7、接收python计算好的返回值int result;// i表示转换成int型变量。// 在这里,最需要注意的是:PyArg_Parse的最后一个参数,必须加上“&”符号PyArg_Parse(ret, "i", &result);std::cout << "return is " << result << std::endl;// 8、结束python接口初始化Py_Finalize();return 0;
}
2.3 调用Python代码类
C++调用python类流程:
- 初始化python接口(Py_Initialize)
- 初始化python系统文件路径(PyRun_SimpleString)
- 调用python文件名(PyImport_ImportModule)
- 获取类(PyObject_GetAttrString)
- 根据类构造函数实例化对象(PyEval_CallObject)
- 获取实例的函数对象(PyObject_GetAttrString)
- 传递参数(PyTuple_New,Py_BuildValue)
- 调用函数对象(PyObject_CallObject)
- 接收函数返回值(PyArg_Parse)
- 结束python接口初始化(Py_Finalize)
在call_python.py里面添加代码:
class Person:def __init__(self, name, age):self.name = nameself.age = agedef foo(self):print(f"my name is {self.name}, my age is {self.age}")
然后在main.cpp里面进行调用:
#include <iostream>
#include <Python.h>int main()
{// 1、初始化python接口Py_Initialize();if (!Py_IsInitialized()){std::cout << "python init failed" << std::endl;return 1;}// 2、初始化python系统文件路径,保证可以访问到 .py文件PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('./script')");// 3、调用python文件名,不用写后缀PyObject* module = PyImport_ImportModule("call_python");if (module == nullptr){std::cout << "module not found: call_python" << std::endl;return 1;}// 4、获取类PyObject* cls = PyObject_GetAttrString(module, "Person");if (!cls){std::cout << "class not found: Person" << std::endl;return 1;}// 5、给类构造函数传递参数// 函数调用的参数传递均是以元组的形式打包的, 2表示参数个数// 如果函数中只有一个参数时,写1就可以了PyObject* args = PyTuple_New(2);// 0:第一个参数,传入 int 类型的值 1PyTuple_SetItem(args, 0, Py_BuildValue("s", "jack"));// 1:第二个参数,传入 int 类型的值 2PyTuple_SetItem(args, 1, Py_BuildValue("i", 18));// 6、根据类名实例化对象PyObject* obj = PyObject_CallObject(cls, args);// 7、根据对象得到成员函数PyObject* func = PyObject_GetAttrString(obj, "foo");if (!func || !PyCallable_Check(func)){std::cout << "function not found: foo" << std::endl;return 1;}// 8、使用C++的python接口调用该函数PyObject_CallObject(func, nullptr);// 9、结束python接口初始化Py_Finalize();return 0;
}