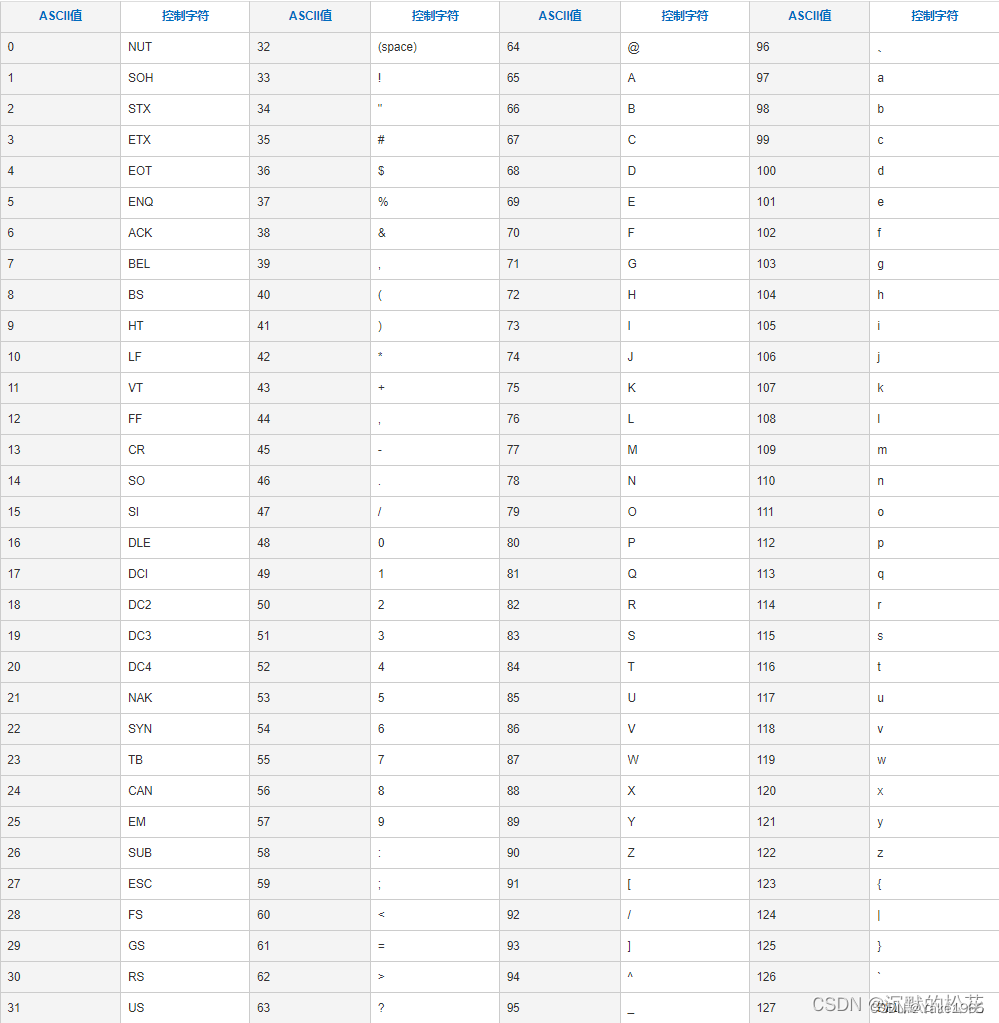
仿照vector手动实现自己的myVector,最主要实现二倍扩容功能
#include <iostream>using namespace std;template<typename T>
class my_vector
{int size;//可存储的容量大小int num;//当前存储的元素个数T* data;//存储数据的空间地址public://无参构造函数my_vector();//有参构造函数my_vector(int n, const T m);//析构函数~my_vector();//拷贝构造my_vector(const my_vector &other);//返回当前的容器大小int get_capacity();//获取容器中的元素个数int get_size();//判空函数bool empty();//添加函数void push_back(const T &val);//向容器中赋值void assign(int n,const T &val);//访问容器中的元素T& at(int loc);//清空容器中的元素void clear();//删除最后一个元素void pop_back();//返回起始位置的引用T& front();//返回最后一个位置的引用T& back();//返回第一个位置的迭代器T* begin();//返回末尾下一个位置的迭代器T* end();//任意插入T* insert(T* p, const T& n);//遍历void show();
};
int main()
{my_vector<int> s1;s1.assign(7,1);cout<<"最大容量"<<s1.get_capacity()<<endl;cout<<"最后一个元素 "<<s1.at(6)<<endl;s1.insert(s1.end(),4);cout<<"最后一个元素 "<<s1.back()<<endl;cout<<"共有元素"<<s1.get_size()<<endl;cout<<"最后一个元素 "<<s1.at(8)<<endl;s1.show();cout<<"最大容量"<<s1.get_capacity()<<endl;s1.pop_back();s1.show();return 0;
}//无参构造
template<typename T>
my_vector<T>::my_vector()
{size=6;num=0;data = new T[6];
}//有参构造
template<typename T>
my_vector<T>::my_vector(int n, const T m)
{size = n;num = n;data = new T[n];for(int i=0;i<n;i++){data[i]= m;}
}template<typename T>
my_vector<T>::~my_vector()
{delete []data;
}//拷贝构造
template<typename T>
my_vector<T>::my_vector(const my_vector &other)
{size = other.size;num = other.num;data = new T[size];for(int i=0;i<other.num;i++){data[i] = other.data[i];}
}//当前容器的大小
template<typename T>
int my_vector<T>::get_capacity()
{return size;
}template<typename T>
int my_vector<T>::get_size()
{return num;
}//判空函数
template<typename T>
bool my_vector<T>::empty()
{if(0 == num){return true;}elsereturn false;
}//添加函数
template<typename T>
void my_vector<T>::push_back(const T &val)
{if(num<size){data[num] = val;num++;}else{T *temp = new T[2*size];size = 2*size;for(int i=0;i<num;i++){temp[i] = data[i];}delete []data;//释放旧的空间data = temp;//指向新的空间temp = nullptr;data[num] = val;num++;}
}//向容器中赋值
template<typename T>
void my_vector<T>::assign(int n, const T &val)
{//判断赋值的个数是否超过最大容量if(n>size){delete [] data;data = nullptr;data = new T [n];size = n;num = n;//赋值for(int i=0;i<n;i++){data[i] = val;}}else{num=n;for(int i=0;i<n;i++){data[i] = val;}}
}//访问元素
template<typename T>
T& my_vector<T>::at(int loc)
{if(loc > num || loc < 0){throw T(1);//越界异常}else{return data[loc-1];}
}//清空所有元素
template<typename T>
void my_vector<T>::clear()
{while (!empty()){pop_back();}}//删除末尾元素
template<typename T>
void my_vector<T>::pop_back()
{if(!empty()){data[num-1] = 0;num--;}elsereturn ;
}//返回第一个位置的引用
template<typename T>
T &my_vector<T>::front()
{return data[0];
}//返回最后一个位置的引用
template<typename T>
T &my_vector<T>::back()
{return data[num-1];
}//返回第一个位置的迭代器
template<typename T>
T *my_vector<T>::begin()
{return &data[0];
}//返回末尾下一个位置的迭代器
template<typename T>
T *my_vector<T>::end()
{return &data[num];
}//任意插入
template<typename T>
T *my_vector<T>::insert(T *p, const T &n)
{int j = 0;while(&data[0]+j != p) //寻找输入的是第几个数据的地址{j++;}if(num == size) //判断当前是否已满{int i = 0;T* data_new = new T[size*2]; //二倍扩容size = size * 2;while(i < num) //将旧区的数据内容赋给新区{data_new[i] = data[i];i++;}delete []data; //释放旧区data = data_new; //指向新区data_new = nullptr; //新指针置空//将指定位置之后的数据全都后移一位for(int k = num,i = j;i < num;i++,k--){data[k] = data[k-1];}data[j] = n; //插入元素num++; //存储数量加1return &data[j];}else if(num < size){//将指定位置之后的数据全都后移一位for(int k = num,i = j;i < num;i++,k--){data[k] = data[k-1];}data[j] = n; //插入元素num++; //存储数量加1return &data[j];}
}//遍历
template<typename T>
void my_vector<T>::show()
{int i = 0;for(;i < num;i++){cout << data[i] << "\t";}cout << endl;
}思维导图: