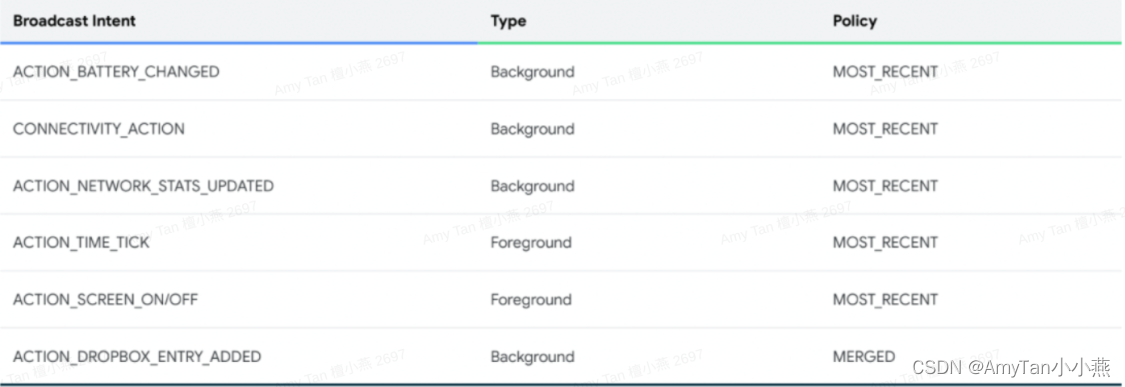
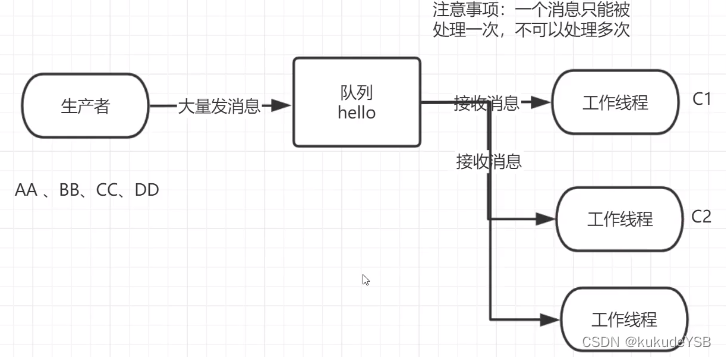
工作队列
注意事项:一个消息只能被处理一次,不可以处理多次
轮询分发信息
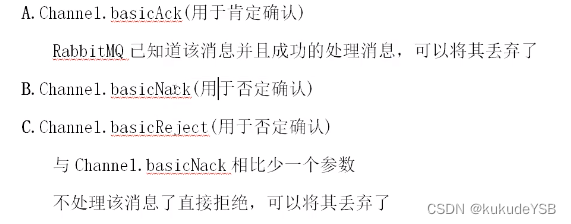
消息应答
消费者在接收到消息并且处理该消息之后,告诉rabbitmq它已经处理了,rabbitmq可以把该消息删除了。倘若mq没有收到应答,mq会将消息转发给其他消费者
- 自动应答:
- 需要在高吞吐和数据传输安全性方面做权衡
- 没有对消息数据进行限制
- 仅适合在消费者可以高效并以某种速率能够处理这些信息的情况下使用。
- 手动应答:
- 应答方式:
- 应答方式:
- 自动应答在消息接收到以后即做出应答,但若接收以后还需其他操作,对应答无影响。所以当消费者接收到消息,但是在消息处理完之前就已经挂掉了,但是由于自动应答,使得mq会认为已经处理完,并删除该消息。
- 手动应答可以写在消息处理的最后,即使出现异常,也能防止mq删除消息。
持久化
防止RabbitMQ崩溃导致的消息丢失,我们需要将队列和消息都标记为持久化
- 队列持久化
重启队列不会消失,但是消息可能会消失 - 消息持久化
但是不能确保消息一定持久化成功,因为可能在保存到磁盘的过程中,发送故障,导致丢失//设置生产者发送消息为持久化消息(要求保存到磁盘中) 保存在内存中channel.basicPublish("", QUEUE_NAME, MessageProperties.PERSISTENT_TEXT_PLAIN, message.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
不公平分发(“多劳多得”)
// 设置不公平分发
channel.basicQos(1);
预取值
//设置预取值
int prefetchCount = 5;
channel.basicQos(prefetchCount);
发布确认
当生产者发送消息到队列中以后,队列需要向生产者返回信息确认
当满足以下要求时,可以达到消息不丢失
- 设置要求队列必须持久化
- 设置要求队列中的消息必须持久化
- 发布确认
- 开启发布确认
//开启发布确认
channel.confirmSelect();
- 单个发布确认
- 同步确认发布的方式
- 缺点:发布速度特别的慢
- 实现:在每条消息发送结束以后就进行确认
- 批量发布确认
- 发布速度快
- 缺点:无法获取出现异常的消息
- 实现:在所有消息发送结束以后再进行消息确认
- 异步发布确认
- 发布速度快
- 实现:
ConcurrentSkipListMap<Long, String> map = new ConcurrentSkipListMap<>(); //消息确认成功 回调函数 ConfirmCallback ackCallback = (deliveryTag, multiple) -> {System.out.println("收到消息:" + deliveryTag);if (multiple){//删除已经确认的消息,剩下的就是未确认的消息了ConcurrentNavigableMap<Long, String> concurrentNavigableMap = map.headMap(deliveryTag);concurrentNavigableMap.clear();}else {map.remove(deliveryTag);} }; //消息确认失败 回调函数 ConfirmCallback nackCallback = (deliveryTag, multiple) -> {System.out.println("未收到消息:" + deliveryTag); }; channel.addConfirmListener(ackCallback, nackCallback); for( int i = 1 ; i <= MESSAGE_COUNT ; i ++ ){String s = String.valueOf(i);channel.basicPublish("", queueName, null, s.getBytes());map.put(channel.getNextPublishSeqNo(), s); }
交换机
RabbitMQ消息传递模型的核心思想是:生产者生产的消息从不回直接发送到队列。实际上,通常生产者甚至都不知道这些信息传递到了哪些队列中。
相反,生产者只能讲消息发送到交换机。
- 概念:交换机工作的内容非常简单,一方面它接收来自生产者的消息,另一方面讲它们推入队列。交换机必须确切知道如何处理收到的消息。是应该把这些消息放到特定队列还是说把他们到许多队列中还是说应该丢弃它们。者就由交换机得类型来决定了
- 类型:
- 直接
- 主题
- 标题
- 扇出
- 无名exchange
临时队列
具有随机名称的队列,一旦断开了消费者的连接,队列将被自动删除
绑定
binding其实是exchange和queue之间的桥梁,它告诉我们exchange和那个队列进行了绑定关系。
Fanout交换机(直接交换机)
- 介绍:将接收到的所有消息广播到它知道的所有队列中。系统中默认有些exchange类型
Direct交换机(扇出交换机)
根据routingKey来绑定队列
- 多重绑定
它绑定的多个队列的key如果都相同,表现和效果就和Fanout类似
Topics交换机(主题交换机)
主题交换机的routing-Key不能随意写,必须满足一定的要求。它必须是一个单调列表,以点号隔开
- “*”可以代替一个单词
- “#”可以代替零个或多个单词
死信队列
由某些特定的原因导致queue中的某些消息无法被消费,这样的消息如果没有后续的处理,就变成了死信,有死信自然就成了死信队列
- 死信来源:
- 消息TTL过期
- 队列达到最大长度(队列满了,无法再添加数据到mq中)
- 消息被拒绝(basic.reject或basic.nack)并且requeue=false.
延迟队列
延迟队列就是用来存放需要在指定时间被处理的元素的队列
整合Spring
- 创建springboot项目
- 添加配置类
<dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId><scope>test</scope></dependency><!-- 非Spring版本依赖--> <!--<!– rabbitmq依赖客户端–>--> <!-- <dependency>--> <!-- <groupId>com.rabbitmq</groupId>--> <!-- <artifactId>amqp-client</artifactId>--> <!-- <version>5.8.0</version>--> <!-- </dependency>--><!--<!– 操作文件流的一个依赖–>--> <!-- <dependency>--> <!-- <groupId>commons-io</groupId>--> <!-- <artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>--> <!-- <version>2.6</version>--> <!-- </dependency>--><!-- Spring版本依赖--> <!-- RabbitMQ依赖--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>com.alibaba</groupId><artifactId>fastjson</artifactId><version>1.2.60</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>io.springfox</groupId><artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId><version>3.0.0</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>io.springfox</groupId><artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId><version>3.0.0</version></dependency><!-- RabbitMQ测试依赖--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.amqp</groupId><artifactId>spring-rabbit-test</artifactId><scope>test</scope></dependency></dependencies> - 编写配置类(这里对ip进行修改即可)
spring:rabbitmq:host: 192.168.221.128port: 5672username: adminpassword: root - 编写配置文件类
package com.config;import org.springframework.amqp.core.*; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map;/*** @author Joy Yang*/ @Configuration public class TtlQueueConfig {public static final String X_EXCHANGE = "X";public static final String QUEUE_A = "QA";public static final String QUEUE_B = "QB";public static final String Y_DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE = "Y";public static final String DEAD_LETTER_QUEUE = "QD";// 声明 xExchange@Bean("xExchange")public DirectExchange xExchange(){return new DirectExchange(X_EXCHANGE);}// 声明 xExchange@Bean("yExchange")public DirectExchange yExchange(){return new DirectExchange(Y_DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE);}//声明队列 A ttl 为 10s 并绑定到对应的死信交换机@Bean("queueA")public Queue queueA(){Map<String, Object> args = new HashMap<>(3);//声明当前队列绑定的死信交换机args.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", Y_DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE);//声明当前队列的死信路由 keyargs.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "YD");//声明队列的 TTLargs.put("x-message-ttl", 10000);return QueueBuilder.durable(QUEUE_A).withArguments(args).build();}// 声明队列 A 绑定 X 交换机@Beanpublic Binding queueaBindingX(@Qualifier("queueA") Queue queueA,@Qualifier("xExchange") DirectExchange xExchange){return BindingBuilder.bind(queueA).to(xExchange).with("XA");}//声明队列 B ttl 为 40s 并绑定到对应的死信交换机@Bean("queueB")public Queue queueB(){Map<String, Object> args = new HashMap<>(3);//声明当前队列绑定的死信交换机args.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", Y_DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE);//声明当前队列的死信路由 keyargs.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "YD");//声明队列的 TTLargs.put("x-message-ttl", 40000);return QueueBuilder.durable(QUEUE_B).withArguments(args).build();}//声明队列 B 绑定 X 交换机@Beanpublic Binding queuebBindingX(@Qualifier("queueB") Queue queue1B,@Qualifier("xExchange") DirectExchange xExchange){return BindingBuilder.bind(queue1B).to(xExchange).with("XB");}//声明死信队列 QD@Bean("queueD")public Queue queueD(){return new Queue(DEAD_LETTER_QUEUE);}//声明死信队列 QD 绑定关系@Beanpublic Binding deadLetterBindingQAD(@Qualifier("queueD") Queue queueD,@Qualifier("yExchange") DirectExchange yExchange){return BindingBuilder.bind(queueD).to(yExchange).with("YD");} } - 编写生产者代码
package com.controller;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import java.util.Date;@Slf4j @RequestMapping("ttl") @RestController public class SendMsgController {@Autowiredprivate RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;@GetMapping("sendMsg/{message}")public void sendMsg(@PathVariable String message){log.info("当前时间:{},发送一条信息给两个 TTL 队列:{}", new Date(), message);rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("X", "XA", "消息来自 ttl 为 10S 的队列: "+message);rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("X", "XB", "消息来自 ttl 为 40S 的队列: "+message);} } - 编写消费者代码
package com.consumer;import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Date;@Slf4j @Component public class DeadLetterQueueConsumer {@RabbitListener(queues = "QD")public void receiveD(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {String msg = new String(message.getBody());System.out.println(msg);log.info("当前时间:{},收到死信队列信息{}", new Date().toString(), msg);} }
延迟队列优化
- 不限制过期时间的消息队列
- 实现:声明队列时不对时间进行限制,发送信息时设置过期时间
@Component public class MsgTtlQueueConfig {public static final String Y_DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE = "Y";public static final String QUEUE_C = "QC";//声明队列 C 死信交换机@Bean("queueC")public Queue queueB(){Map<String, Object> args = new HashMap<>(3);//声明当前队列绑定的死信交换机args.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", Y_DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE);//声明当前队列的死信路由 keyargs.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "YD");//没有声明 TTL 属性return QueueBuilder.durable(QUEUE_C).withArguments(args).build();}//声明队列 B 绑定 X 交换机@Beanpublic Binding queuecBindingX(@Qualifier("queueC") Queue queueC,@Qualifier("xExchange") DirectExchange xExchange){return BindingBuilder.bind(queueC).to(xExchange).with("XC");@GetMapping("sendExpirationMsg/{message}/{ttlTime}") public void sendMsg(@PathVariable String message,@PathVariable String ttlTime) {rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("X", "XC", message, correlationData ->{correlationData.getMessageProperties().setExpiration(ttlTime);return correlationData;});log.info("当前时间:{},发送一条时长{}毫秒 TTL 信息给队列 C:{}", new Date(),ttlTime, message); }- 对于这种形式的延迟队列,因为RabbitMQ只会检查第一个消息是否过期,如果过期则丢到死信队列,但是
如果第一个消息的延时时间很长,而第二个消息的延时时长很短,第二个消息并不会优化得到执行。
插件实现延迟队列
-
安装延迟插件
- 在官网上下载 插件下载地址

- 选择对应版本 我这里选的时3.8.0
- 将文件复制到指定位置,并进入该文件路径
[root@localhost opt]# cp rabbitmq_delayed_message_exchange-3.8.0.ez /usr/lib/rabbitmq/lib/rabbitmq_server-3.8.8/plugins [root@localhost opt]# cd /usr/lib/rabbitmq/lib/rabbitmq_server-3.8.8/plugins- 安装插件
[root@localhost plugins]# rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_delayed_message_exchange- 启动rabbitmq
[root@localhost plugins]# systemctl restart rabbitmq-server- 判断是否成功
-
插件实现延迟队列得机制
- 基于死信实现消息延迟时,消息发送延迟得地点是队列TTL
由于保留了队列得性质“先进先出”,所以前面得消息会堵塞后面得消息 - 基于插件实现消息延迟时,消息延迟地点为交换机
- 基于死信实现消息延迟时,消息发送延迟得地点是队列TTL
-
实现
配置文件编写:
package com.config;import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;/*** 插件实现消息延迟** @author : 杨世博* @date: Created in 22:20 2023/10/10*/
@Configuration
public class DelayedQueueConfig {/*** 队列*/public static final String DELAYED_QUEUE_NAME = "delayed.queue";/*** 延迟交换机*/public static final String DELAYED_EXCHANGE_NAME = "delayed.exchange";/*** routingKey*/public static final String DELAY_ROUTING_KEY = "delayed.routing.key";/*** 声明队列*/@Beanpublic Queue delayedQueue(){return new Queue(DELAYED_QUEUE_NAME);}/*** 声明交换机*/@Beanpublic CustomExchange delayedExchange(){Map<String, Object> arguments = new HashMap<>();arguments.put("x-delayed-type", "direct");/*** 1. 交换机的名称* 2. 交换机的类型* 3. 是否需要持久化* 4. 是否需要自动删除* 5. 其他的参数*/return new CustomExchange(DELAYED_EXCHANGE_NAME, "x-delayed-message", true, true, arguments);}/*** 绑定*/@Beanpublic Binding delayedQueueBindingDelayedExchange(@Qualifier("delayedExchange")DirectExchange directExchange,@Qualifier("delayedQueue")Queue delayedQueue){return BindingBuilder.bind(delayedQueue).to(directExchange).with(DELAY_ROUTING_KEY);}
}
生产者
public static final String DELAYED_EXCHANGE_NAME = "delayed.exchange";
public static final String DELAYED_ROUTING_KEY = "delayed.routing.key";
@GetMapping("sendDelayMsg/{message}/{delayTime}")
public void sendMsg(@PathVariable String message,@PathVariable Integer delayTime) {rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(DELAYED_EXCHANGE_NAME, DELAYED_ROUTING_KEY, message,correlationData ->{correlationData.getMessageProperties().setDelay(delayTime);return correlationData;});log.info(" 当 前 时 间 : {}, 发送一条延迟 {} 毫秒的信息给队列 delayed.queue:{}", newDate(),delayTime, message);
}
消费者
@Slf4j
@Component
public class DelayedQueueConsumer {public static final String DELAYED_QUEUE_NAME = "delayed.queue";@RabbitListener(queues = DELAYED_QUEUE_NAME)public void receiveDelayedQueue(Message message){String msg = new String(message.getBody());log.info("当前时间:{},收到延时队列的消息:{}", new Date().toString(), msg);}
}
发布确认高级
当交换机与队列宕机时,将生产者发送的信息进行缓存,定时任务对未成功投递的信息进行重新投递
- 配置文件类编写
package com.config;import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;/*** 发布确认(高级)** @author : 杨世博* @date: Created in 20:23 2023/10/11*/
@Configuration
public class ConfirmConfig {/*** 交换机*/public static final String CONFIRM_EXCHANGE_NAME = "confirm_exchange";/*** 队列*/public static final String CONFIRM_QUEUE = "confirm_queue";/*** RoutingKey*/public static final String CONFIRM_ROUTING_KEY = "confirm_Routing_Key";/*** 声明交换机*/@Bean("confirmExchange")public DirectExchange confirmExchange(){return new DirectExchange(CONFIRM_EXCHANGE_NAME);}/*** 声明队列*/@Bean("confirmQueue")public Queue confirmQueue(){return QueueBuilder.durable(CONFIRM_QUEUE).build();}/*** 绑定*/@Beanpublic Binding queueBindingExchange(@Qualifier("confirmQueue")Queue confirmQueue,@Qualifier("confirmExchange")DirectExchange directExchange){return BindingBuilder.bind(confirmQueue).to(directExchange).with(CONFIRM_ROUTING_KEY);}
}
- 生产者编写
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;@GetMapping("/sendMessage/{message}")
public void sendMessage(@PathVariable String message){CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData("1");rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(ConfirmConfig.CONFIRM_EXCHANGE_NAME, ConfirmConfig.CONFIRM_ROUTING_KEY, message, correlationData);log.info("发送信息内容:{}", message);
}
- 消费者编写
@Slf4j
@Component
public class Consumer {@RabbitListener(queues = ConfirmConfig.CONFIRM_QUEUE)public void receiveConfirmMessage(Message message){String msg = new String(message.getBody());log.info("接收到的队列confirm.queue消息:{}", msg);}
}
- 回调接口
/*** 回调接口** @author : 杨世博* @date: Created in 21:21 2023/10/11*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MyCellBack implements RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback, RabbitTemplate.ReturnCallback {@Autowiredprivate RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;@PostConstructpublic void init(){//注入rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(this);rabbitTemplate.setReturnCallback(this);}/*** 交换机确认回调方法* 1. 发送消息 交换机接收了 回调* 1.1 correlationData 保存回调消息的ID及相关消息* 1.2 交换机收到消息 ack = true* 1.3 cause null* 2. 发消息 交换机接收失败 回调* 2.1 correlationData 保存回调消息的ID及相关消息* 2.2 交换机收到消息 ack = false* 2.3 cause 失败的原因*/@Overridepublic void confirm(CorrelationData correlationData, boolean ack, String cause) {String id = correlationData != null ? correlationData.getId() : "";if (ack){log.info("交换机已经收到Id为:{}的信息", id);}else {log.info("交换机还未收到Id为:{}的消息,由于原因:{}", id,cause);}}/*** 可以在当消息传递过程中不可达目的地时将消息返回给生产者* 只有不可达目的的时候 才进行回退*/@Overridepublic void returnedMessage(Message message, int replyCode, String replyText, String exchange, String routingKey) {log.error("消息:{},被交换机{}退回,退回原因:{},路由Key:{}",new String(message.getBody()), exchange, replyText, routingKey);}
}
- 配置文件
spring:rabbitmq:host: 192.168.221.128port: 5672username: adminpassword: rootpublisher-confirm-type: correlatedpublisher-returns: true
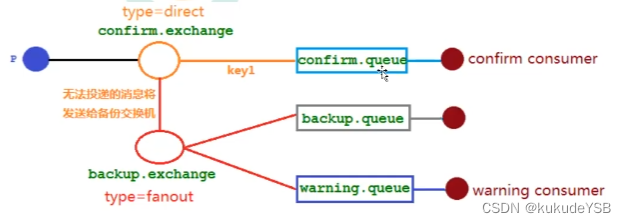
备份交换机
当主交换机宕机时,会将消息发送到备份交换机,再将消息备份,并进行报警
当备份交换机和发布确认同时开启时,备份交换机优先
实现
- 编写配置类文件代码
@Configuration
public class ConfirmConfig {/*** 交换机*/public static final String CONFIRM_EXCHANGE_NAME = "confirm_exchange";/*** 队列*/public static final String CONFIRM_QUEUE = "confirm_queue";/*** RoutingKey*/public static final String CONFIRM_ROUTING_KEY = "confirm_routing_key";/*** 备份交换机*/public static final String BACKUP_EXCHANGE_NAME = "backup_exchange_name";/*** 备份队列*/public static final String BACKUP_QUEUE = "backup_queue";/*** 报警队列*/public static final String WARNING_QUEUE = "warning_queue";/*** 声明交换机*/@Bean("confirmExchange")public DirectExchange confirmExchange(){return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange(CONFIRM_EXCHANGE_NAME).durable(true).withArgument("alternate-exchange", BACKUP_EXCHANGE_NAME).build();}/*** 声明队列*/@Bean("confirmQueue")public Queue confirmQueue(){return QueueBuilder.durable(CONFIRM_QUEUE).build();}/*** 绑定*/@Beanpublic Binding queueBindingExchange(@Qualifier("confirmQueue")Queue confirmQueue,@Qualifier("confirmExchange")DirectExchange directExchange){return BindingBuilder.bind(confirmQueue).to(directExchange).with(CONFIRM_ROUTING_KEY);}/*** 创建备份交换机*/@Bean("backupExchange")public FanoutExchange backupExchange(){return new FanoutExchange(BACKUP_EXCHANGE_NAME);}/*** 声明备份队列*/@Bean("backupQueue")public Queue backupQueue(){return QueueBuilder.durable(BACKUP_QUEUE).build();}/*** 声明报警队列*/@Bean("warningQueue")public Queue warningQueue(){return QueueBuilder.durable(WARNING_QUEUE).build();}/*** 备份交换机绑定备份队列*/@Beanpublic Binding backupQueueBindingExchange(@Qualifier("backupQueue")Queue backupQueue,@Qualifier("backupExchange")FanoutExchange backupExchange){return BindingBuilder.bind(backupQueue).to(backupExchange);}/*** 备份交换机绑定报警队列*/@Beanpublic Binding warningQueueBindingExchange(@Qualifier("warningQueue")Queue warningQueue,@Qualifier("backupExchange")FanoutExchange backupExchange) {return BindingBuilder.bind(warningQueue).to(backupExchange);}
}
- 警报消费者编写
@Slf4j
@Component
public class WarningConsumer {/*** 接收报警消息*/@RabbitListener(queues = ConfirmConfig.WARNING_QUEUE)public void receiveWarningMsg(Message message){String msg = new String(message.getBody());log.error("报警发现不可路由消息:{}", msg);}
}
幂等性
幂等性:
用户对于同一操作发起的一次请求或者多次请求的结果是一致的,不会因为多次点击而产生了副作用。
- 消息重复消费
消费者在消费 MQ 中的消息时,MQ 已把消息发送给消费者,消费者在给 MQ 返回 ack 时网络中断,
故 MQ 未收到确认信息,该条消息会重新发给其他的消费者,或者在网络重连后再次发送给该消费者,但
实际上该消费者已成功消费了该条消息,造成消费者消费了重复的消息。 - 解决思路
使用一个全局ID,每次消费时用该id先判断该消息是否消费过- 唯一 ID+指纹码机制
指纹码:我们的一些规则或者时间戳加别的服务给到的唯一信息码,它并不一定是我们系统生成的,基本都是由我们的业务规则拼接而来,但是一定要保证唯一性,然后就利用查询语句进行判断这个 id 是否存在数据库中,优势就是实现简单就一个拼接,然后查询判断是否重复;劣势就是在高并发时,如果是单个数据库就会有写入性能瓶颈当然也可以采用分库分表提升性能,但也不是我们最推荐的方式。 - Redis 原子性
利用 redis 执行 setnx 命令,天然具有幂等性。从而实现不重复消费
- 唯一 ID+指纹码机制
优先级队列
- 使用场景
订单催付
我们的客户在天猫下的订单,淘宝会及时将订单推送给我们,如果在用户设定的时间内未付款那么就会给用户推送一条短信提醒,很简单的一个功能对吧,但是,tmall商家对我们来说,肯定是要分大客户和小客户的对吧,比如像苹果,小米这样大商家一年起码能给我们创造很大的利润,所以理应当然,他们的订单必须得到优先处理,而曾经我们的后端系统是使用 redis 来存放的定时轮询,大家都知道 redis 只能用 List 做一个简简单单的消息队列,并不能实现一个优先级的场景,所以订单量大了后采用 RabbitMQ 进行改造和优化,如果发现是大客户的订单给一个相对比较高的优先级,否则就是默认优先级。 - 实现
// 队列中代码添加优先级
Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap();
params.put("x-max-priority", 10);
channel.queueDeclare("hello", true, false, false, params);
// 消息中代码添加优先级
AMQP.BasicProperties properties = new
AMQP.BasicProperties().builder().priority(5).build();
惰性队列
- 正常情况:消息时保存在内存中
- 惰性队列:消息时保存在磁盘中