文章目录
- 【LeetCode高频SQL50题-基础版】打卡第6天:第31~35题
- ⛅前言
- 员工的直属部门
- 🔒题目
- 🔑题解
- 判断三角形
- 🔒题目
- 🔑题解
- 连续出现的数字
- 🔒题目
- 🔑题解
- 指定日期的产品价格
- 🔒题目
- 🔑题解
- 最后一个进入巴士的人
- 🔒题目
- 🔑题解
【LeetCode高频SQL50题-基础版】打卡第6天:第31~35题
⛅前言
在这个博客专栏中,我将为大家提供关于 LeetCode 高频 SQL 题目的基础版解析。LeetCode 是一个非常受欢迎的编程练习平台,其中的 SQL 题目涵盖了各种常见的数据库操作和查询任务。对于计算机科班出身的同学来说,SQL 是一个基础而又重要的技能。不仅在面试过程中经常会遇到 SQL 相关的考题,而且在日常的开发工作中,掌握 SQL 的能力也是必备的。
本专栏的目的是帮助读者掌握 LeetCode 上的高频 SQL 题目,并提供对每个题目的解析和解决方案。我们将重点关注那些经常出现在面试中的题目,并提供一个基础版的解法,让读者更好地理解问题的本质和解题思路。无论你是准备找工作还是提升自己的技能,在这个专栏中,你可以学习到很多关于 SQL 的实践经验和技巧,从而更加深入地理解数据库的操作和优化。
我希望通过这个专栏的分享,能够帮助读者在 SQL 的领域里取得更好的成绩和进步。如果你对这个话题感兴趣,那么就跟随我一起,开始我们的 LeetCode 高频 SQL 之旅吧!
- 博客主页💖:知识汲取者的博客
- LeetCode高频SQL100题专栏🚀:LeetCode高频SQL100题_知识汲取者的博客-CSDN博客
- Gitee地址📁:知识汲取者 (aghp) - Gitee.com
- 题目来源📢:高频 SQL 50 题(基础版) - 学习计划 - 力扣(LeetCode)全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
员工的直属部门
🔒题目
题目来源:1789.员工的直属部门

🔑题解
- 考察知识点:
unionunion:将两个结果集合并成一个结果集,回对合并后的结果集进行去重
分析:首先我们需要明确我们最终想要得到的结果是什么?
- 定位最终问题:最终得到的结果是员工 ID 及其直属部门 ID
- 对最终的问题进行分解:我们可以明确,员工可以分为两类,一类是属于多个部门的,但是有一个部门被标记为直属部门;另一类员工属于一个部门,并且没有标记为直属部门
- 逐个击破子问题,然后将结果合并即可
解题的主要思想:先明确最终的结果,将最终的结果这个大问题分解为多个子问题,然后对子问题进行逐个击破,这种方法在编程中很常见,就是所谓的分治思想
1)对于属于多个部门的员工
select employee_id , department_id
from Employee
where primary_flag = 'Y';
| employee_id | department_id |
| ----------- | ------------- |
| 2 | 1 |
| 4 | 3 |
2)对于属于一个部门的员工
select employee_id , department_id
from Employee
group by employee_id
having count(*) = 1;
温馨提示:这里可以使用 count(primary_flag) 作为过滤条件,但是 count(字段) 的性能比 count(*) 的性能要低
| employee_id | department_id |
| ----------- | ------------- |
| 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 3 |
3)将上面两个子问题的结果集使用 union 进行合并
select employee_id , department_id
from Employee
where primary_flag = 'Y';
union
select employee_id , department_id
from Employee
group by employee_id
having count(*) = 1
知识拓展
union 和 union all的区别
- union会对数据进行去重,union all 不会对数据进行去重
- union all 比 union 要快
本题不能使用 union all 的原因是,单个部门的 primary_flag 可以为 Y,这种情况会存在重复记录,所以需要使用 union 进行去重
判断三角形
🔒题目
题目来源:610.判断三角形

🔑题解
- 考察知识点:
case whencase when类似于 Java中的switch语句
分析:这一题的难点在于,如果我们按照以往的惯性思维,三角形的判断”两边之和大于第三边,两边只差小于第三边“,这样来实现三角形的判断是很复杂的,我们这里采用另一种判断方法,任意两边之和大于第三边来判断是否是一个三角形,这样实现起来就简单多了
select *,casewhen x + y > z and x + z > y and y + z > x then 'Yes'else 'No'end 'triangle'
from triangle;
也可以使用 if 去做
select *, if(x + y > z and x + z > y and y + z > x, 'Yes', 'No') triangle
from Triangle
温馨提示:按照SQL编写规范,尽量少用 select * 这样的查询,这里我就偷一个小懒
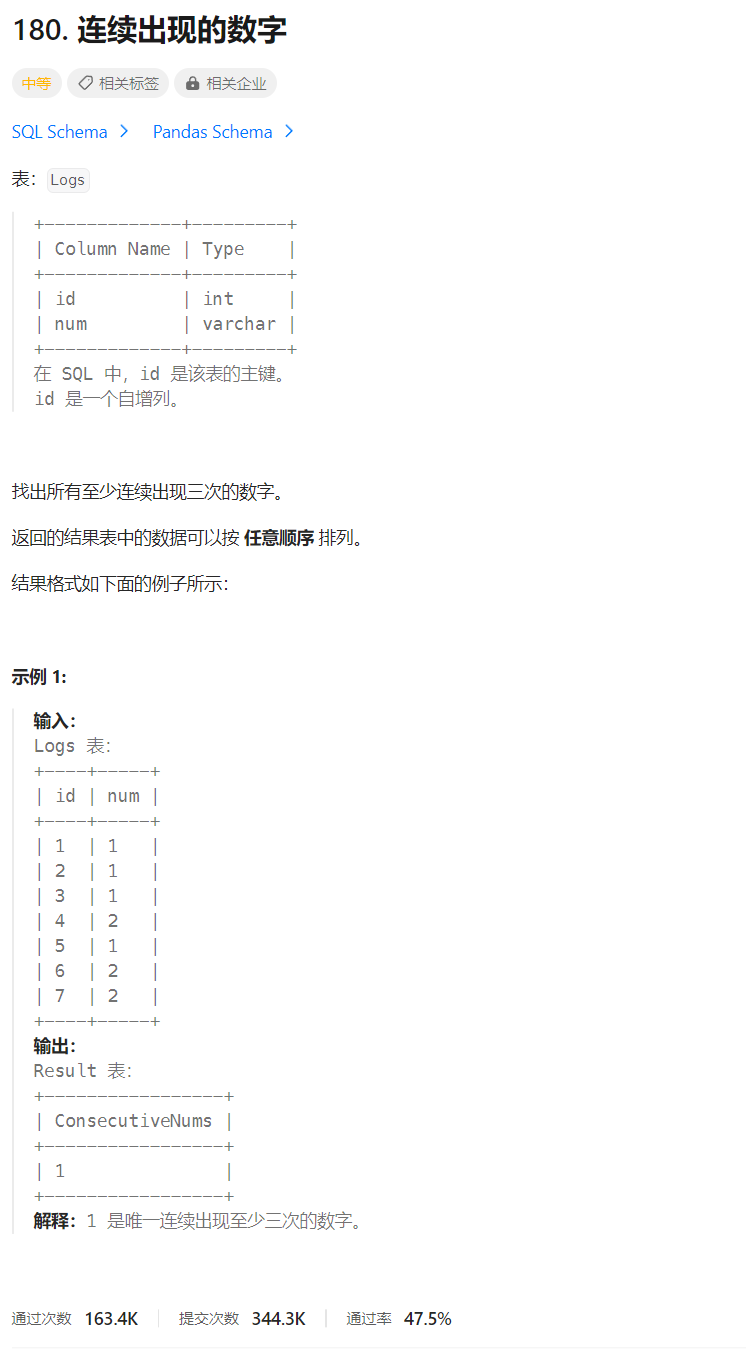
连续出现的数字
🔒题目
题目来源:180.连续出现的数字
🔑题解
- 考察知识点:
自连接
分析:最直接的方式,就是进行一个自我判断,判断是否存在三个id是连续的。那么如何判断三个id是否连续呢?
由于连续的id插值是1,我们只需要判断三个间隔为1的id,他们的num值是否相等即可,下面是SQL
select distinct l1.num ConsecutiveNums
from Logs l1, Logs l2, Logs l3
where l1.id = l2.id - 1 and l2.id = l3.id - 1 and l1.num = l2.num and l2.num = l3.num;
此外,这里还提供一种更先进的解法:
分析:通过窗口函数 row_number 实现,该窗口函数会按照指定的列值按照大小进行排名。利用这个性质即可巧妙的实现判断是否存在一个数连续出现3次,甚至更加灵活,可以判断一个数出现 n 次,这比前面那种方法更加优秀,但是必须是MySQL8才能够使用
- 通过 row_number 窗口函数,对每一行的行号进行一个排序,然后对 num 进行一个排序
- 我们可以知道如果数是连续的,那么 行号的序号 和 num的序号 差值是恒定的
- 利用差值恒定的性质,我们可以进行
对于窗口函数不太了解的推荐阅读这篇文章:一文带你快速了解上手MySQL8新增的窗口函数
1)通过窗口函数查出每一行的行号,还有 num 的排名
select id,num,row_number() over() row_num,row_number() over(partition by num order by id) num_rank
from Logs;
| id | num | row_num | num_rank |
| -- | --- | ------- | -------- |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 4 |
| 4 | 2 | 4 | 1 |
| 6 | 2 | 6 | 2 |
| 7 | 2 | 7 | 3 |
2)我们需要将 所有相同 num 同时满足 差值相等 的列全都采用 group by 进行聚合
elect l.num ConsecutiveNums, l.row_num
from (select id,num,row_number() over() row_num,row_number() over(partition by num order by id) num_rankfrom Logs
) l
group by l.num, (l.row_num - l.num_rank);
| ConsecutiveNums | row_num |
| --------------- | ------- |
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 5 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 2 | 6 |
3)上面由于 group by 并不能将所有 num 相同的,因为group by 会进行两次分组,先按照 num 进行分组,还需要进行一个去重
elect distinct l.num ConsecutiveNums
from (select id,num,row_number() over() row_num,row_number() over(partition by num order by id) num_rankfrom Logs
) l
group by l.num, (l.row_num - l.num_rank);
| ConsecutiveNums |
| --------------- |
| 1 |
| 2 |
4)然后过滤分组中记录数量超过3的记录即可
select distinct l.num ConsecutiveNums
from (select id,num,row_number() over() row_num,row_number() over(partition by num order by id) num_rankfrom Logs
) l
group by l.num, (l.row_num - l.num_rank)
having count(*) >= 3
此时这个SQL就很通用了,可以查询出任意连续出现次数的 num
指定日期的产品价格
🔒题目
题目来源:1164.指定日期的产品价格

🔑题解
- 考察知识点:
子查询、max、左连接、group by
分析:我们需要明确我们的最终目标,是查询出所有日期在 ‘2019-08-16’ 时的产品的价格,这里有是非重要的关键点:
- 产品在当天(2019-08-16) 存在变动价格,那么价格就是当天的
- 产品在没有在当天进行价格变动,但是当天之前存在价格变动,那么价格是距离当天最近的价格
- 产品没有在当天进行价格变动,也没有在当天之前进行价格变动,但是在当天之后存在价格变动,那么价格直接是10,因为每次价格的变动都是在之前的基础上增加10
综合以上三点,我们可以将产品分为两大类
- 一大类是产品价格变动时间 <= 2019-08-16,这类产品的价格将会是最大时间处的价格
- 一大类就是产品价格变动时间 > 2019-08-16,这类产品的价格直接是10
PS:这个题考察的知识点比较多,也比较综合,刚开始写都没啥头绪┭┮﹏┭┮,现在复写了两遍,渐渐有感觉了,下次遇到这类型的题目应该是会有思路的,可以说刷题获得的不仅有知识,还有经验
1)查询出第一大类的产品
select product_id, max(change_date)
from products
where change_date <= '2019-08-16'
group by product_id;
| product_id | max(change_date) |
| ---------- | ---------------- |
| 1 | 2019-08-16 |
| 2 | 2019-08-14 |
2)通过产品的 id 和 变动时间筛选出第一大类产品的价格
select product_id, new_price
from products
where (product_id, change_date) in (select product_id, max(change_date)from productswhere change_date <= '2019-08-16'group by product_id
);
| product_id | new_price |
| ---------- | --------- |
| 2 | 50 |
| 1 | 35 |
3)查询出所有产品的id,我们通过这个这个id与2)的结果进行左连接,这样就能够直接筛选出第二大类的产品了
PS:所有的产品分为两大类,通过
select distinct product_id
from products;
| product_id |
| ---------- |
| 1 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
4)将1)和3)的查询的临时表进行左连接
select *
from (select distinct product_idfrom products
) as p1
left join (select product_id, new_price from productswhere (product_id, change_date) in (select product_id, max(change_date)from productswhere change_date <= '2019-08-16'group by product_id)
) as p2
on p1.product_id = p2.product_id;
| product_id | product_id | new_price |
| ---------- | ---------- | --------- |
| 1 | 1 | 35 |
| 2 | 2 | 50 |
| 3 | null | null |
select p1.product_id, ifnull(p2.new_price, 10) as price
from (select distinct product_idfrom products
) as p1
left join (select product_id, new_price from productswhere (product_id, change_date) in (select product_id, max(change_date)from productswhere change_date <= '2019-08-16'group by product_id)
) as p2
on p1.product_id = p2.product_id
最后一个进入巴士的人
🔒题目
题目来源:1204.最后一个进入巴士的人

🔑题解
- 考察知识点:
窗口函数、limit、order by
我的思路是采用窗口函数
1)使用窗口函数新增一列
select *, sum(weight) over(order by turn) sum
from queue;
| person_id | person_name | weight | turn | sum |
| --------- | ----------- | ------ | ---- | ---- |
| 5 | Alice | 250 | 1 | 250 |
| 3 | Alex | 350 | 2 | 600 |
| 6 | John Cena | 400 | 3 | 1000 |
| 2 | Marie | 200 | 4 | 1200 |
| 4 | Bob | 175 | 5 | 1375 |
| 1 | Winston | 500 | 6 | 1875 |
2)对窗口函数生成的表进行操作,即可
select person_name
from (select *, sum(weight) over(order by turn) sumfrom queue
) q
where sum <= 1000
order by sum desc
limit 1;
上面那种方法只适用于MySQL8或MySQL8以后的版本,因为窗口函数是MySQL8新增的,这里再提供一种MySQL5可以使用的版本,主要是利用用户变量来作实现weight的累加
1)
select person_name, @pre := @pre + weight sum
from Queue, (select @pre := 0) tmp
order by turn
备注:这里的(select @pre := 0) tmp主要用于初始化用户变量
| person_name | sum |
| ----------- | ---- |
| Alice | 250 |
| Alex | 600 |
| John Cena | 1000 |
| Marie | 1200 |
| Bob | 1375 |
| Winston | 1875 |
2)
select q.person_name
from (select person_name, @pre := @pre + weight sumfrom Queue, (select @pre := 0) tmporder by turn
) q
where q.sum <= 1000
order by q.sum desc
limit 1;