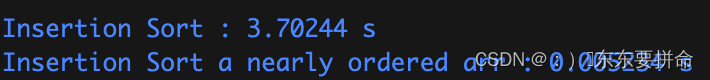
 效果非常的明显
效果非常的明显
下面给出代码截图

再给出原代码
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include "Student.h"
#include "sorttesthelper.h"
using namespace std;template<typename T >void selectionSort( T arr[], int n){for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){//寻找【i,n之间的最小值】int minIndex = i;for( int j = i + 1 ; j < n ; j++)if(arr[j] < arr[minIndex] )minIndex = j;swap( arr[i] , arr[minIndex]);}
}//对插入排序来说,直接从第二个元素开始template<typename T >
void InsertSort( T arr[], int n){for(int i = 1 ; i < n ; i++){T e = arr[i];// j 需要保存元素e应该插入的位置int j;//寻找【i应该插入的位置】,但是注意我们是从后面往前找所以j 要从后往前// for( int j = i ; j > 0 ; j --)// if(arr[j] < arr[j - 1] )// swap(arr[j], arr[j-1]);// else // break;//插入排序的优点是 可以提前 终止循环 所以对于几乎有序的序列 插入排序的性能非常强for( j = i ; j > 0 && arr[j-1] > arr[e]; j --)arr[j] = arr[j-1];arr[j] = arr[e];}
}int main()
{int a[5] = {5,62,3,58,44};selectionSort( a, 5 );for( int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++)cout<<a[i]<< " ";cout<<endl;float b[4] = {4.4,2.3,5.63};selectionSort( b , 3);for( int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++)cout<<b[i]<< " ";cout<<endl;string c[2] = {"z","b"};selectionSort( c , 2);for( int i = 0 ; i < 2 ; i++)cout<<c[i]<< " ";cout<<endl;Student d[3] = {{"D",90} , {"C",89} , { "B", 114}};selectionSort( d , 3);for( int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++)cout<<d[i];cout<<endl;int n = 100000;int *arr = SortTestHelper :: generateRandomArr(n, 0, n) ;int *arr2 = SortTestHelper :: copyIntArray(arr, n);int *arr3 = SortTestHelper :: generateNearlyorderedArr(n, 100);// InsertSort(arr2, n);// SortTestHelper :: printarr(arr2, n);// selectionSort( arr, n );// SortTestHelper :: printarr(arr, n);// SortTestHelper::test_sort("selection Sort", selectionSort, arr,n);SortTestHelper::test_sort("Insertion Sort", InsertSort, arr2,n);SortTestHelper::test_sort("Insertion Sort a nearly ordered arr", InsertSort, arr3,n);delete[] arr;delete[] arr2;return 0;}给出辅助文件
#ifndef SORT_HELPER_H
#define SORT_HELPER_H
//解决ide.h文件的多重引用的问题
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <ctime>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;
namespace SortTestHelper{//生成n个元素的随机数组,每个元素的随机范围为【rangeL, rangeR】int* generateRandomArr(int n, int rangeL, int rangeR){assert( rangeL <= rangeR );int *arr = new int[n];//设置随机种子srand(time(NULL));for(int i = 0; i < n ;i ++)arr[i] = rand()%(rangeR - rangeL + 1) + rangeL;return arr;}int* generateNearlyorderedArr(int n, int swaptimes){int *arr = new int[n];for(int i = 0; i < n ;i ++)arr[i] = i;//设置随机种子srand(time(NULL));for(int i = 0; i < swaptimes ; i ++){int posx = rand()%n;int posy = rand()%n;swap( arr[posx], arr[posy] );}return arr;}template<typename T >void printarr(T arr[], int n){for( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++)cout<<arr[i]<< " ";cout<<endl;return;}//我们也希望写一个辅助函数来帮我们判断 函数的正确性template<typename T >bool isSorted(T arr[], int n){for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)if (arr[i]> arr[i+1])return false;return true;}template<typename T >// 我们希望之后传入的都是函数名字 指针和测试用例void test_sort( string sortNmae, void(*sort)(T[], int), T arr[], int n){clock_t startTime = clock();sort(arr,n);clock_t endTime = clock();assert( isSorted(arr, n ));//每一秒中时钟周期运行的个数 最后输出的程序 运行的多少秒cout<< sortNmae << " : "<<double(endTime - startTime)/ CLOCKS_PER_SEC << " s " <<endl;return;}int* copyIntArray(int a[], int n){int* arr = new int[n];copy(a, a + n, arr);return arr;}}#endif //SORT_HELPER_H