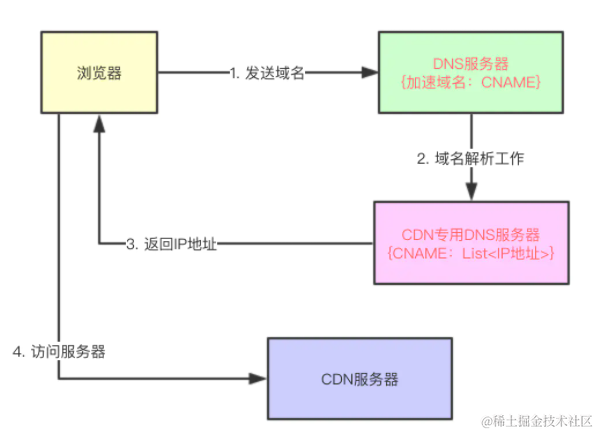
想要精通算法和SQL的成长之路 - 找到最终的安全状态
- 前言
- 一. 找到最终的安全状态
- 1.1 初始化邻接图
- 1.2 构建反向邻接图
- 1.3 BFS遍历
- 1.4 完整代码
前言
想要精通算法和SQL的成长之路 - 系列导航
一. 找到最终的安全状态
原题链接
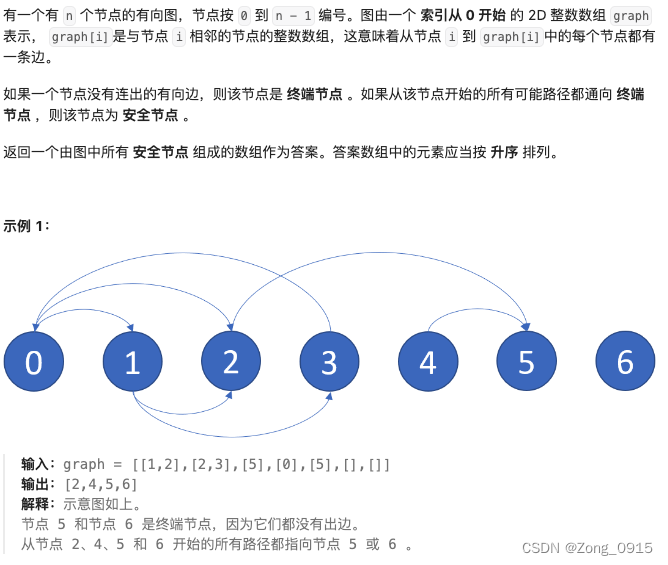
我们从题目中可以看出来:
- 出度为0的,就是终端节点。
- 如果存在路径通向终端节点,那么该节点就是安全节点。那么终端节点本身也可以作为安全节点。
- 而题目要求我们返回的是安全节点。
- 满足题目要求的节点,一定是和终端节点相连的节点。
思路如下:
- 我们构建有向邻接图,并且统计出度。
- 出度为0的丢到队列中。
- 每层循环,处理出度为0的节点(终端节点),我们反向拿到它的前置节点(因此构建邻接图的时候要反向构建有向邻接图), 更新它的出度。若前置节点的出度为0,说明它之前就是一个安全节点,现在成为了终端节点。
- 遍历完毕之后,再遍历一遍出度数组,把所有出度为0的节点更新到结果集中即可。
1.1 初始化邻接图
int n = graph.length;
// 初始化邻接图和出度数组
List<Integer>[] adj = new ArrayList[n];
int[] outDegree = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
1.2 构建反向邻接图
// 构建邻接图和出度数组,这里的索引就是一条有向边的起点。
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {// 出度的个数,就是二维的长度outDegree[i] = graph[i].length;// 反向构建邻接图for (int j = 0; j < graph[i].length; j++) {adj[graph[i][j]].add(i);}
}
1.3 BFS遍历
// 将出度为0的入队
LinkedList<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if (outDegree[i] == 0) {queue.offer(i);}
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int size = queue.size();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {Integer cur = queue.poll();// adj[cur] 就是 pre --> 终端节点,拿到的所有 prefor (Integer pre : adj[cur]) {// 出度 -1,若为0,继续入队if (--outDegree[pre] == 0) {queue.offer(pre);}}}
}
1.4 完整代码
public class Test802 {public List<Integer> eventualSafeNodes(int[][] graph) {int n = graph.length;// 初始化邻接图和出度数组List<Integer>[] adj = new ArrayList[n];int[] outDegree = new int[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();}// 构建邻接图和出度数组,这里的索引就是一条有向边的起点。for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {// 出度的个数,就是二维的长度outDegree[i] = graph[i].length;// 反向构建邻接图for (int j = 0; j < graph[i].length; j++) {adj[graph[i][j]].add(i);}}// 将出度为0的入队LinkedList<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if (outDegree[i] == 0) {queue.offer(i);}}while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int size = queue.size();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {Integer cur = queue.poll();// adj[cur] 就是 pre --> 终端节点,拿到的所有 prefor (Integer pre : adj[cur]) {// 出度 -1,若为0,继续入队if (--outDegree[pre] == 0) {queue.offer(pre);}}}}// 最终出度为0的全部加入到结果集中ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if (outDegree[i] == 0) {res.add(i);}}return res;}
}