大家好,我是晴天学长,这是很重要的贪心思维题,哈希的存法和小根堆的表示很重要。
1) .通关

2) .算法思路
通关
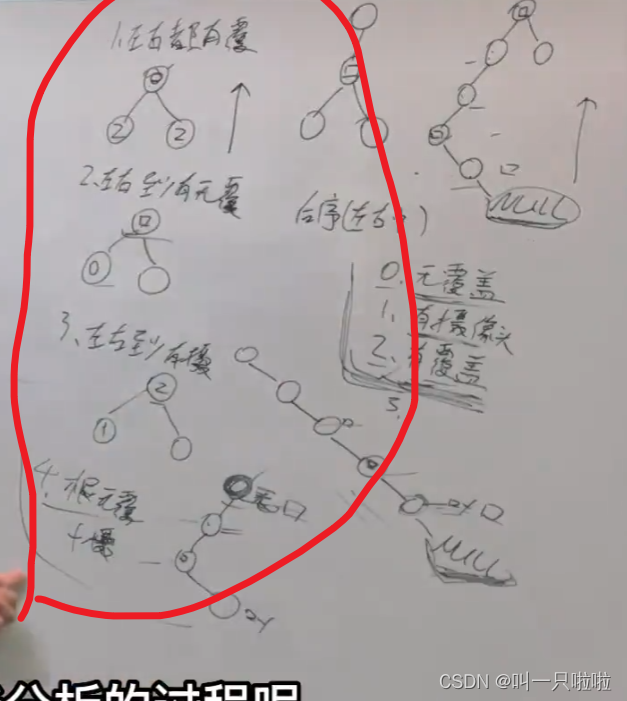
用hash(int[])存点的子节点并按输入顺序存关卡的号码(输入顺序就是)
列如:key:父节点
难度 经验 关卡
优先队列存难度和节点
1.接受数据和初始经验。(用快读)。
2.判断第1关能过不。
3.把第1关的子节点放入队列
4.从队列中取出元素
5.挑战成功再把子元素丢入队列中
6.ans++;
3).算法步骤
1.从输入中读取关卡数量 n 和初始经验值 sum。
2.读取第一关的难度、关卡和经验值,并将其存储在map中。
3.如果初始经验值小于第一关的经验值要求,则输出0并返回。
4.增加初始经验值并增加答案计数器。
5.循环读取剩余的关卡信息,并将其存储在map中。
6.创建一个小顶堆(优先队列)queue,并将第一关的子节点放入小顶堆。
7.循环处理小顶堆中的关卡节点,直到小顶堆为空。
8.从小顶堆中取出一个关卡节点,比较当前经验值是否小于关卡节点的难度要求,如果是,则输出答案计数器并返回。
9.增加经验值并增加答案计数器。
10.如果当前关卡有子节点,则将子节点放入小顶堆。
11.输出最终的答案计数器。
4). 代码实例
package LanQiaoTest.大小堆;import java.util.*;//变种广搜
public class 通关_小顶堆 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);Map<Integer, List<int[]>> map = new HashMap<>();//关卡int ans = 0;int n = scanner.nextInt();//经验值int sum = scanner.nextInt();//存第一关int temp = scanner.nextInt();int temp1 = scanner.nextInt();int temp2 = scanner.nextInt();map.put(temp, new ArrayList<>());map.get(temp).add(new int[]{0, temp1, temp2});int[] temp3 = map.get(temp).get(0);if (sum < temp3[2]) {System.out.println(ans);return;}sum += temp3[1];ans++;//存子节点了for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {//父节点int a = scanner.nextInt();//挑战成功的经验值int b = scanner.nextInt();//难度int c = scanner.nextInt();if (!map.containsKey(a)) {map.put(a, new ArrayList<>());}//父节点 难度 关卡 经验值map.get(a).add(new int[]{c, i + 1, b});}//用优先队列(默认小根堆)PriorityQueue<Integer[]> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> (a[0] - b[0]));//把第一关的子节点丢入小根堆for (int i = 0; i < map.get(1).size(); i++) {int[] temp4 = map.get(1).get(i);//难度 关卡 经验值queue.offer(new Integer[]{temp4[0], temp4[1], temp4[2]});}// 开始闯关while (!queue.isEmpty()) {//难度 关卡 经验值Integer[] temp5 = queue.poll();//对比if (sum < temp5[0]) {System.out.println(ans);return;}sum += temp5[2];ans++;//把闯的关的子节点丢入小根堆if (map.containsKey(temp5[1])) {for (int i = 0; i < map.get(temp5[1]).size(); i++) {int[] temp6 = map.get(temp5[1]).get(i);queue.offer(new Integer[]{temp6[0], temp6[1], temp6[2]});}}}System.out.println(ans);scanner.close();}
}4).总结
- 小根堆的表示(在贪心题中经常使用)
- 哈希表的正确使用。
试题链接: