目录
无向图的连通分量个数
单纯求出了连通分量个数
能具体返回哪几个点是同一个连通分量
路径问题
单源路径问题
从某个顶点到另一个顶点的路径问题
检测无向图中的环
二分图的检测
无向图的连通分量个数
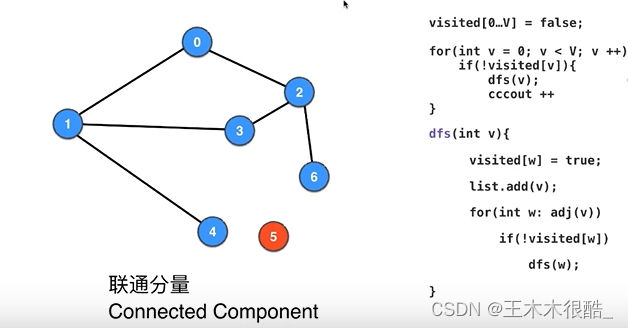
单纯求出了连通分量个数
import java.util.ArrayList;public class CC {private Graph G;private int[] visited;private int cccount = 0;public CC(Graph G){this.G = G;visited = new int[G.V()];for(int i = 0; i < visited.length; i ++)visited[i] = -1;for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)if(visited[v] == -1){dfs(v, cccount);cccount ++;}}private void dfs(int v, int ccid){visited[v] = ccid;for(int w: G.adj(v))if(visited[w] == -1)dfs(w, ccid);}public int count(){
// for(int e: visited)
// System.out.print(e + " ");
// System.out.println();return cccount;}public boolean isConnected(int v, int w){G.validateVertex(v);G.validateVertex(w);return visited[v] == visited[w];}public ArrayList<Integer>[] components(){ArrayList<Integer>[] res = new ArrayList[cccount];for(int i = 0; i < cccount; i ++)res[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)res[visited[v]].add(v);return res;}public static void main(String[] args){Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");CC cc = new CC(g);System.out.println(cc.count());System.out.println(cc.isConnected(0, 6));System.out.println(cc.isConnected(5, 6));ArrayList<Integer>[] comp = cc.components();for(int ccid = 0; ccid < comp.length; ccid ++){System.out.print(ccid + " : ");for(int w: comp[ccid])System.out.print(w + " ");System.out.println();}}
}能具体返回哪几个点是同一个连通分量
import java.util.ArrayList;public class CC{private Graph G;private boolean[] visited;private int cccount = 0;
public CC(Graph G){this.G = G;visited = new int[G.V()];
for(int i = 0; i < visited.length; i++)
{visited[i] = -1;
}
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++){if(visited[V] == -1){dfs(v, ccount);cccount++;}}
private void dfs(int v, int ccid){visited[v] = ccid;
for(int w : G.adj(v)){if(visited[w] == -1){dfs(w, ccid);}}}
public int count(){for(int e : visited){System.out.print(e + " ");
}System.out.println();return cccount;}
public static void main(String[] args){Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");CC cc = new GraphDFS(g);System.out.println(cc.count());}}
}路径问题
单源路径问题

import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;public class SingleSourcePath {private Graph G;private int s;private int[] pre;public SingleSourcePath(Graph G, int s){this.G = G;this.s = s;pre = new int[G.V()];for(int i = 0; i < pre.length; i ++)pre[i] = -1;dfs(s, s);}private void dfs(int v, int parent){pre[v] = parent;for(int w: G.adj(v))if(pre[w] == -1)dfs(w, v);}public boolean isConnectedTo(int t){G.validateVertex(t);return pre[t] != -1;}public Iterable<Integer> path(int t){ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();if(!isConnectedTo(t)) return res;int cur = t;while(cur != s){res.add(cur);cur = pre[cur];}res.add(s);Collections.reverse(res);return res;}public static void main(String[] args){Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");SingleSourcePath sspath = new SingleSourcePath(g, 0);System.out.println("0 -> 6 : " + sspath.path(6));System.out.println("0 -> 5 : " + sspath.path(5));}
}从某个顶点到另一个顶点的路径问题
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;public class Path {private Graph G;private int s, t;private int[] pre;private boolean[] visited;public Path(Graph G, int s, int t){G.validateVertex(s);G.validateVertex(t);this.G = G;this.s = s;this.t = t;visited = new boolean[G.V()];pre = new int[G.V()];for(int i = 0; i < pre.length; i ++)pre[i] = -1;dfs(s, s);for(boolean e: visited)System.out.print(e + " ");System.out.println();}private boolean dfs(int v, int parent){visited[v] = true;pre[v] = parent;if(v == t) return true;for(int w: G.adj(v))if(!visited[w])if(dfs(w, v))return true;return false;}public boolean isConnected(){return visited[t];}public Iterable<Integer> path(){ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();if(!isConnected()) return res;int cur = t;while(cur != s){res.add(cur);cur = pre[cur];}res.add(s);Collections.reverse(res);return res;}public static void main(String[] args){Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");Path path = new Path(g, 0, 6);System.out.println("0 -> 6 : " + path.path());Path path2 = new Path(g, 0, 5);System.out.println("0 -> 5 : " + path2.path());Path path3 = new Path(g, 0, 1);System.out.println("0 -> 1 : " + path3.path());}
}检测无向图中的环
思路:找到一个已经被访问过的结点,并且这个结点不是当前节点的上一个结点。
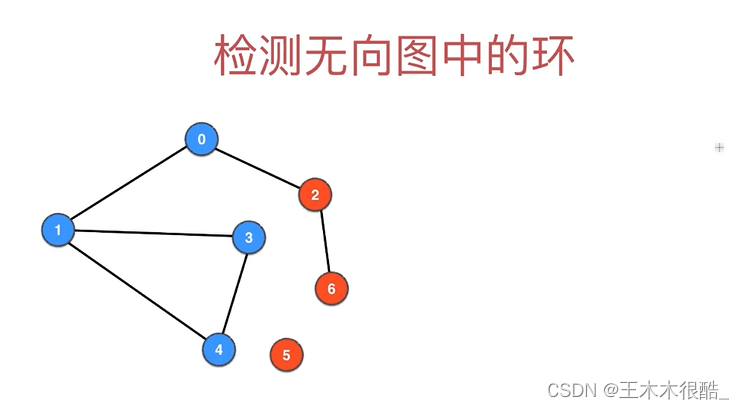
public class CycleDetection {private Graph G;private boolean[] visited;private boolean hasCycle = false;public CycleDetection(Graph G){this.G = G;visited = new boolean[G.V()];for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)if(!visited[v])if(dfs(v, v)){hasCycle = true;break;}}// 从顶点 v 开始,判断图中是否有环private boolean dfs(int v, int parent){visited[v] = true;for(int w: G.adj(v))if(!visited[w]){if(dfs(w, v)) return true;}else if(w != parent)return true;return false;}public boolean hasCycle(){return hasCycle;}public static void main(String[] args){Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");CycleDetection cycleDetection = new CycleDetection(g);System.out.println(cycleDetection.hasCycle());Graph g2 = new Graph("g2.txt");CycleDetection cycleDetection2 = new CycleDetection(g2);System.out.println(cycleDetection2.hasCycle());}
}二分图的检测
思路:从某一点开始逐个染色。

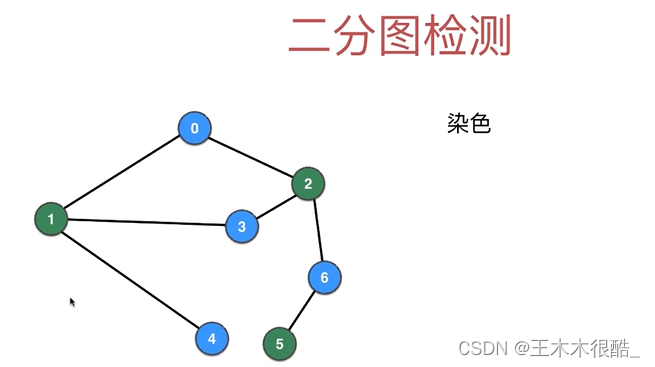
import java.util.ArrayList;public class BipartitionDetection {private Graph G;private boolean[] visited;private int[] colors;private boolean isBipartite = true;public BipartitionDetection(Graph G){this.G = G;visited = new boolean[G.V()];colors = new int[G.V()];for(int i = 0; i < G.V(); i ++)colors[i] = -1;for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)if(!visited[v])if(!dfs(v, 0)){isBipartite = false;break;}}private boolean dfs(int v, int color){visited[v] = true;colors[v] = color;for(int w: G.adj(v))if(!visited[w]){if(!dfs(w, 1 - color)) return false;}else if(colors[w] == colors[v])return false;return true;}public boolean isBipartite(){return isBipartite;}public static void main(String[] args){Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");BipartitionDetection bipartitionDetection = new BipartitionDetection(g);System.out.println(bipartitionDetection.isBipartite);// trueGraph g2 = new Graph("g2.txt");BipartitionDetection bipartitionDetection2 = new BipartitionDetection(g2);System.out.println(bipartitionDetection2.isBipartite);// falseGraph g3 = new Graph("g3.txt");BipartitionDetection bipartitionDetection3 = new BipartitionDetection(g3);System.out.println(bipartitionDetection3.isBipartite);// true}
}




![[SWPUCTF 2021 新生赛]hardrce_3 无字母rce 自增](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5f5c72fe9635453089d754ac4c0902ee.png)