完整版生产者代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/file.h>
#include <string.h>#define MAXLEN 10
#define ALPHABET 1
#define ALPHABET_START 'a'
#define COUNT_OF_ALPHABET 26
#define DIGIT 2
#define DIGIT_START '0'
#define COUNT_OF_DIGIT 10
#define SIGN_TYPE ALPHABETconst char * fifo_file = "./FIFO.txt";char buf[MAXLEN];int lock_set(int fd, int type){struct flock old_lock, lock;lock.l_whence = SEEK_SET; //加锁区域为文件开始处 lock.l_start = 0;//加锁区域在文件位置的相对偏移量 lock.l_len = 0;//加锁区域长度 lock.l_type = type;//锁的类型 lock.l_pid = -1;fcntl(fd, F_GETLK, &lock);//写入if(lock.l_type != F_UNLCK){//若未解锁 if(lock.l_type == F_RDLCK){//读取锁 printf("Read lock already set by %d\n", lock.l_pid);}else if(lock.l_type == F_WRLCK){printf("Write lock already set by %d\n", lock.l_pid);} } /*上述可能由于不是解锁状态l_type被设置成了相应的锁值下方进行上锁操作时要再次调用type*/ lock.l_type = type;if((fcntl(fd, F_SETLKW, &lock)) < 0){//上锁失败 printf("Lock failed:type = %d\n", lock.l_type);return -1;}switch(lock.l_type){case F_RDLCK:printf("Read lock set by %d\n", getpid());//获取当前进程的IDbreak;case F_WRLCK:printf("Write lock set by %d\n", getpid());break;case F_UNLCK:printf("Release lock by %d\n", getpid());//解锁返回1 return 1;break; }return 0;//上锁返回0
}int product(void){int fd;unsigned int sign_type, sign_start, sign_count, size;static unsigned int counter = 0;//只会执行一次 if((fd = open(fifo_file, O_WRONLY|O_APPEND)) < 0){//只写方式打开 ,追加模式 perror("open error");return -1;}sign_type = SIGN_TYPE;//英文字符集合 switch(sign_type){case ALPHABET:sign_start = ALPHABEF_START;sign_count = COUNT_OF_ALPHABET;//26break;case DIGIT:sign_start = DIGIT_START;sign_count = COUNT_OF_DIGIT;break;default:return -1; }sprintf(buf, "%c", (sign_start + counter));//将字符写入buf缓冲区counter = (counter + 1) % sign_count;lock_set(fd, F_WRLCK);//写锁if((size = write(fd, buf, strlen(buf))) < 0){//打开失败,否者写入 perror("producer:write error");return -1; }lock_set(fd, F_UNLCK);//解锁close(fd);return 0;
}int main(int argc, const char * argv[]){int time_step = 1;//周期 int time_life = 10;//生产数量close(open(fifo_file, O_REONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC, 0664));//创建文件 if(argc > 1){sscanf(argv[1], "%d", &time_step);//将argv[1]转成整数存入time_step中 }if(argc > 2){sscanf(argv[2], "%d", &time_life);} while(time_life --){if(product() < 0){break;} sleep(time_step);}return 0;
}
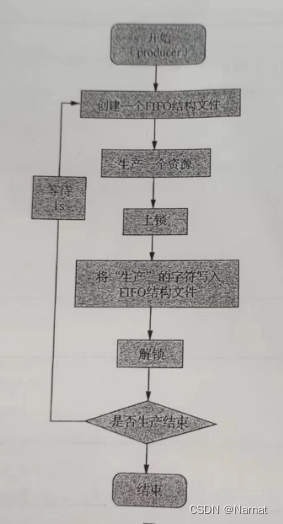
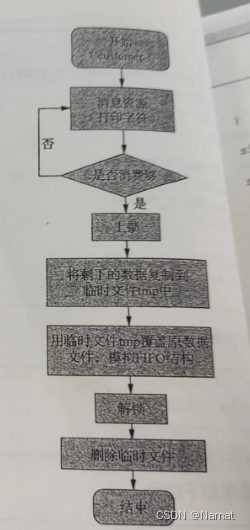
流程:
原版代码有点缺失和问题,添加的代码如下:
原版代码缺少创建文件函数,以及没有对文件清空的函数
每次启动一轮生产,为了方便观察将文件上次生产的内容清空:
close(open(fifo_file, O_REONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC, 0664));//创建文件&清空
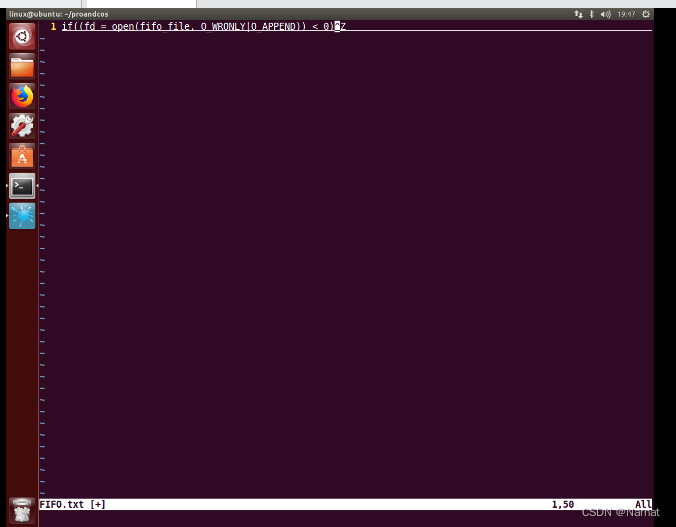
文件打开模式必须是追加模式,否则生产的新数据会覆盖原有数据:
if((fd = open(fifo_file, O_WRONLY|O_APPEND)) < 0)
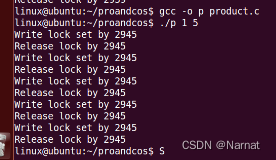
运行效果:
FIFO.txt文件上次运行时残留有数据
生产五个数据:
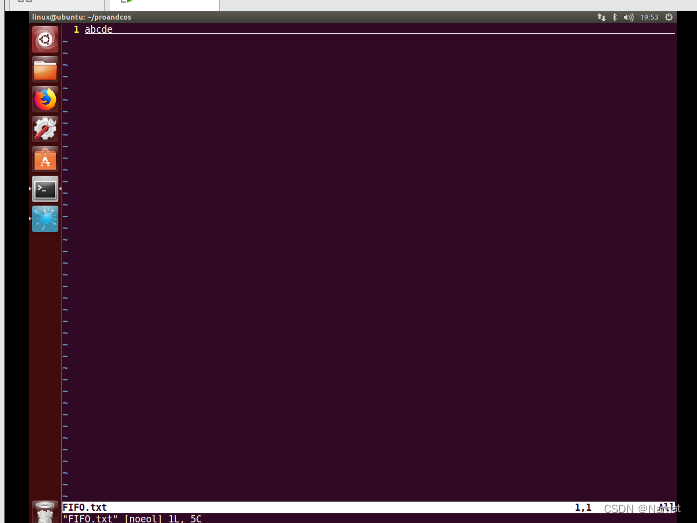
文件之前生产信息被清除,取而代之的是新数据:
完整版消费者代码:
#include <stdio.h>#include <sys/types.h>#include <sys/stat.h>#include <fcntl.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <sys/file.h> #include <string.h>#define MAX_FILE_SIZE 100 * 1024 * 102const char *fifo_file = "./FIFO.txt";const char *temp_file = "./temp";int lock_set(int fd, int type){struct flock old_lock, lock;lock.l_whence = SEEK_SET; //加锁区域为文件开始处 lock.l_start = 0;//加锁区域在文件位置的相对偏移量 lock.l_len = 0;//加锁区域长度 lock.l_type = type;//锁的类型 lock.l_pid = -1;fcntl(fd, F_GETLK, &lock);//写入if(lock.l_type != F_UNLCK){//若未解锁 if(lock.l_type == F_RDLCK){//读取锁 printf("Read lock already set by %d\n", lock.l_pid);}else if(lock.l_type == F_WRLCK){printf("Write lock already set by %d\n", lock.l_pid);}} /*上述可能由于不是解锁状态l_type被设置成了相应的锁值下方进行上锁操作时要再次调用type*/ lock.l_type = type; if((fcntl(fd, F_SETLKW, &lock)) < 0){//上锁失败 printf("Lock failed:type = %d\n", lock.l_type);return -1;}switch(lock.l_type){case F_RDLCK:printf("Read lock set by %d\n", getpid());//获取当前进程的IDbreak; case F_WRLCK:printf("Write lock set by %d\n", getpid());break;case F_UNLCK:printf("Release lock by %d\n", getpid());//解锁返回1 return 1;break;}return 0;//上锁返回0
}int customing(const char * myfifo, int need){int fd;char buf;int counter = 0;if((fd = open(myfifo, O_RDONLY)) < 0){//只读 perror("FunctI/On customing error");return -1;}printf("Enjoy:");lseek(fd, SEEK_SET, 0);while(counter < need){while((read(fd, &buf, 1) == 1) && (counter < need)){//read期望读取的字符数与实际所读一样&&.... fputc(buf, stdout);//打印到显示屏 counter ++;}}fputs("\n", stdout);close(fd);return 0;
} int myfilecopy(const char * sour_file, const char * dest_file, int offset, int count, int copy_mode){int in_file, out_file;int counter = 0;char buff_unit;if((in_file = open(sour_file, O_RDONLY|O_NONBLOCK)) < 0){//非阻塞只读 perror("FunctI/On my filecopy error int source file\n");return -1;}if((out_file = open(dest_file, O_RDWR|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC|O_NONBLOCK, 0664)) < 0){//非阻塞&打开或创建 perror("FUNCTI/O myfilecopy error in destinatI/on file");return -1;}lseek(in_file, offset, SEEK_SET);//设置指针到指定位置while((read(in_file, &buff_unit, 1) == 1) && (counter < count)){//读取 write(out_file, &buff_unit, 1);//写入 counter ++;}close(in_file);close(out_file);return 0;
}int custom(int need){int fd;customing(fifo_file, need);//取if((fd = open(fifo_file, O_RDWR)) < 0){//读写方式打开 perror("FunctI/On myfilecopy error in source_file");return -1;}lock_set(fd, F_WRLCK);//上锁,写入锁 myfilecopy(fifo_file, temp_file, need, MAX_FILE_SIZE, 0);//将第一个文件内容复制到另一个文件,偏移>myfilecopy(temp_file, fifo_file, 0, MAX_FILE_SIZE, 0);lock_set(fd, F_UNLCK);//解锁 unlink(temp_file);//删除 close(fd);return 0;}int main(int argc, const char *argv[]){int customer_capacity = 0;if(argc > 1){sscanf(argv[1], "%d", &customer_capacity);//消费数目写入 }if(customer_capacity > 0){custom(customer_capacity);}return 0;}流程:
这里对open函数进行再次扩充讲解:
当文件被一个进程植入写入锁的时候,另一个进程仍可以通过open函数获取该文件的标志位,但却不能进行read或write函数操作,因为会受到写入锁的阻止
朴素的将写入锁是阻止其他进程对文件的读写操作,而不是open操作

之前一直不理解为什么customing函数中下列语句不会报错,通过用printf函数取点才发现问题
if((fd = open(myfifo, O_RDONLY)) < 0){//只读 perror("FunctI/On customing error");return -1;
}
看来看课本和懂课本是天差地别的
还有一点注意的是:
生产者代码中的:
while(time_life --){if(product() < 0){break;} sleep(time_step);
}
其中:
sleep(time_step);
这个延时语句作用巨大:
lock_set(fd, F_WRLCK);//上锁,写入锁
myfilecopy(fifo_file, temp_file, need, MAX_FILE_SIZE, 0);//将第一个文件内容复制到另一个文件,偏移>
myfilecopy(temp_file, fifo_file, 0, MAX_FILE_SIZE, 0);
lock_set(fd, F_UNLCK);//解锁
其作用是为了让消费者中这个文件挪动语句能有时间完成
同时也用于读取生产出来的字符:
while((read(in_file, &buff_unit, 1) == 1) && (counter < count)){//读取 write(out_file, &buff_unit, 1);//写入 counter ++;}
上述语句在字符未被生产,或者文件被锁住,会一直等待,直到解锁或者有字符被生产
例如文件中生产abc,消费a,所以挪位后为bc
效果:
已生产五个字符:
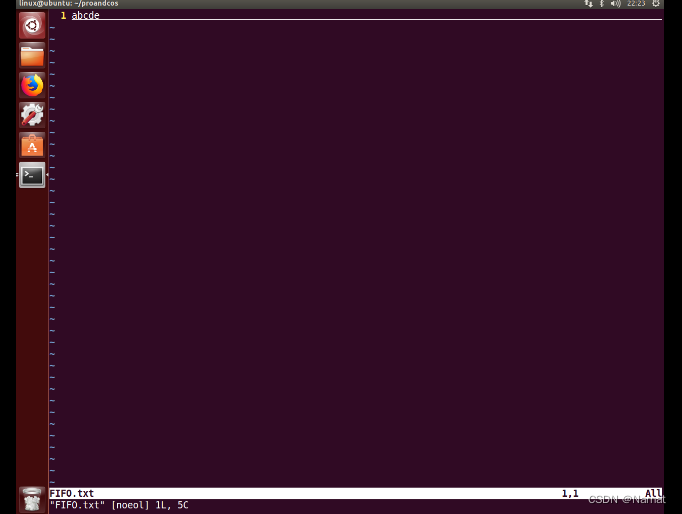
消费四个:
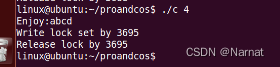
最后剩一个:
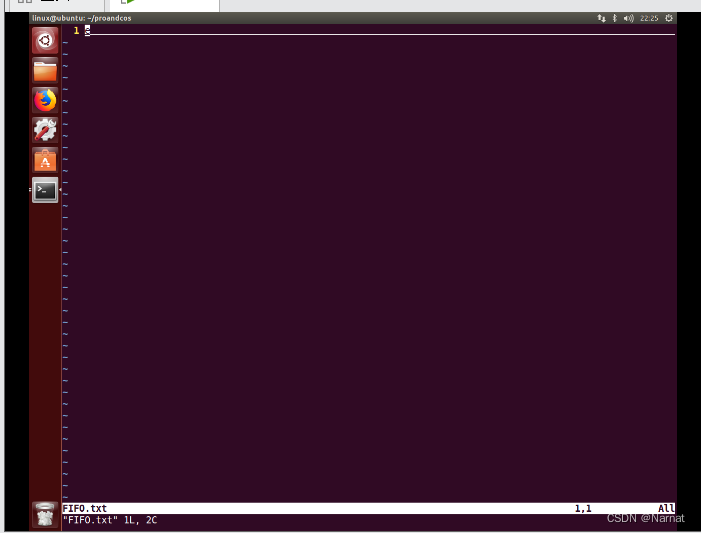
同时进行如下:
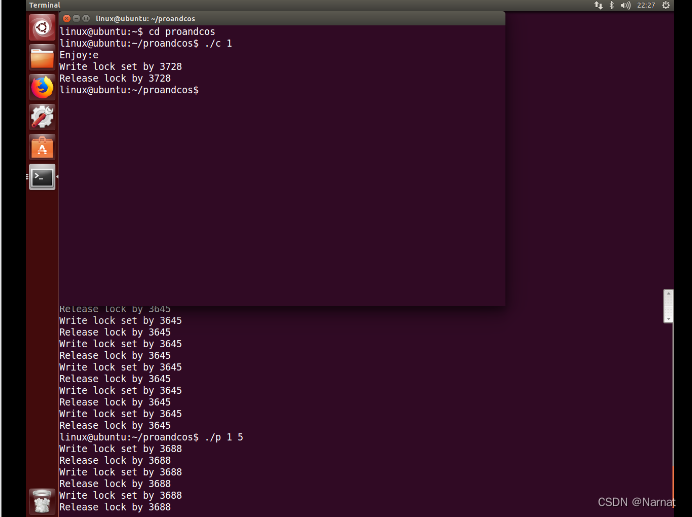
整个文件被锁住,只出现在生产者将生产的字符写入文件和文件挪动这俩操作