赋值运算符重载
运算符重载
日期类实现运算符重载
operator<运算符的实现
Date.h Date.cpp test.cpp 三个文件实现
Date.h#include<iostream>using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1);void Print();bool operator<(const Date& d);private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};Date.cpp#include"Date.h"Date::Date(int year, int month , int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;
}void Date::Print()
{cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)
{if (_year < d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month < d._month){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day){return true;}return false;
}test.cpp
#include"Date.h"void Test1()
{Date d1(2023, 11, 2);Date d2(2023, 11, 3);cout << (d1 < d2) << endl;}int main()
{Test1();return 0;
}
因为d1是自定义出来的对象,运算符不能识别自定义类型对象,只能识别内置类型,因此出现了运算符重载 operator+运算符。根据自己需要来定义返回值的不同 比如上面比较大小 返回真假即可
operator==运算符实现
Date.h
#include<iostream>using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1);void Print();bool operator<(const Date& d);bool operator==(const Date& d);private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};Date.cpp
#include"Date.h"Date::Date(int year, int month , int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;
}void Date::Print()
{cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)
{if (_year < d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month < d._month){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day){return true;}return false;
}bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{return _year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;
}
test.cpp
#include"Date.h"void Test1()
{Date d1(2023, 11, 2);Date d2(2023, 11, 3);cout << (d1 < d2) << endl;cout << (d1 == d2) << endl;
}int main()
{Test1();return 0;
} 当我们实现完前面两个运算符重载以后,剩余的<= >= != >统统可以复用来实现
当我们实现完前面两个运算符重载以后,剩余的<= >= != >统统可以复用来实现
operator> >= <= !=运算符实现
Date.h
#include<iostream>using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1);void Print();bool operator<(const Date& d);bool operator==(const Date& d);bool operator>(const Date& d);bool operator!=(const Date& d);bool operator<=(const Date& d);bool operator>=(const Date& d);private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};Date.cpp
#include"Date.h"Date::Date(int year, int month , int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;
}void Date::Print()
{cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)
{if (_year < d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month < d._month){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day){return true;}return false;
}bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{return _year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;
}bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{return !(*this < d);
}
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d)
{return !(*this == d);
}
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d)
{return *this < d || *this == d;
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d)
{return !(*this < d) || *this == d;
}test.cpp
#include"Date.h"void Test1()
{Date d1(2023, 11, 2);Date d2(2023, 11, 3);cout << (d1 < d2) << endl;cout << (d1 == d2) << endl;cout << (d1 > d2) << endl;cout << (d1 != d2) << endl;cout << (d1 <= d2) << endl;cout << (d1 >= d2) << endl;
}int main()
{Test1();return 0;
}
因为类成员作为函数成员重载时,第一个默认的形参为隐含的Date*const this指针,因此实现完两个运算符重载函数后,直接复用即可,简洁且高效。
日期类除了比较大小有意思之外 那么日期的相减 相加同样也有意义
那么在计算日期相减 相加 就需要知道某个月 包含的天数 某年是否为闰年
这个时候就需要我们的Getmonthday函数的定义
Getmonthday函数实现
Date.cpp
int Date::Getmonthday(int year, int month)
{assert(year >= 1 && month >= 1 && month <= 12);int arry[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };//判断年是否是闰年if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0))){return 29;}return arry[month];
}可以完美帮我们判断闰年 和所对应年 月的天数 方便正确计算 日期的相减相加
也不排除有人会在定义对象的时候给了2023 13 29 月和天显然是不合理的 因此我们需要在成员变量在初始化定义(构造函数)的时候 判断下赋的值正不正确
初始化对象后的判断日期类是否正确
Date.cpp
Date::Date(int year, int month , int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;if (_year < 1 || _month < 1 || _month>12|| _day < 1 || _day>Getmonthday(_year, _month)){cout << "非法日期" << endl;Print();}
}test.cppvoid Test1()
{Date d1(2023, 11, 2);Date d2(2023, 13, 3);}int main()
{Test1();return 0;
}
operator+=运算符实现
d1+=50
Date.cpp
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{_day += day;while (_day > Getmonthday(_year, _month)){_day -= Getmonthday(_year, _month);++_month;if (_month == 13){++_year;_month = 1;}}return *this;
}test.cpp
void Test2()
{Date d1(2023, 11, 2);d1 += 50;d1.Print();}
我们怎么知道最后结果是正确的呢?去网上搜日期计算器就可以了。


先进行天数的相加,再判断天数是否大于Getmonthday函数里面月天数的大小,如果大于就先进行当前月天数的相减 然后再++月,再判断月的条件,因为返回类型为Date,出了作用域还在,因此用引用返回。
d1+50也有意义
operator+运算符实现
Date.cpp
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp += day;return tmp;}test.cpp
void Test2()
{Date d1(2023, 11, 2);/*d1 += 50;*/d1.Print();Date ret = d1 + 50;ret.Print();}
直接复用+=即可,因为是d1+50 d1本身不改变 先创建一个临时变量 用拷贝构造传this最初的值,再复用+=加上天数 返回tmp临时变量 因为tmp出了作用域不存在 固不用引用返回。
反观上面+=和+的运算符重载实现,-=和-的实现方法也类似
operator-=运算符实现
Date.cpp
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{_day -= day;while (_day <= 0){--_month;if (_month == 0){--_year;_month = 12;}_day += Getmonthday(_year, _month);}return *this;
}test.cpp
void Test2()
{Date d1(2023, 11, 2);/*d1 += 50;*/d1 -= 50;d1.Print();/*d1.Print();Date ret = d1 + 50;ret.Print();*/}

operator-运算符实现
Date.cpp
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{Date tmp(*this);tmp -= day;return tmp;
}test.cpp
void Test2()
{Date d1(2023, 11, 2);/*d1 += 50;*//*d1 -= 50;d1.Print();*//*d1.Print();Date ret = d1 + 50;ret.Print();*/Date ret = d1 - 50;d1.Print();ret.Print();}
那么C语言有前置++和后置++ 那么运算符重载自定义对象时怎么分辨呢?
C++之父为了区分前置++和后置++ 在后面++后面加了个int形参
d1++ ++d1 也有意义
operator++(前置)运算符实现
Date.cpp
Date& Date:: operator++()
{*this += 1;return*this;
}test.cpp
void Test2()
{Date d1(2023, 11, 2);/*d1 += 50;*//*d1 -= 50;d1.Print();*//*d1.Print();Date ret = d1 + 50;ret.Print();*//*Date ret = d1 - 50;d1.Print();ret.Print();*/++d1;d1.Print();++d1;d1.Print();}
因为前置++自己本身也会跟着随之改变 所以引用返回this本身。
operator++(后置)运算符实现
Date.cpp
Date Date::operator++(int)
{Date tmp(*this);*this += 1;return tmp;
}test.cpp
void Test3()
{Date d1(2023, 11, 2);d1.Print();d1++;d1.Print();
}
operator--(前置)运算符实现
Date.cpp
Date& Date::operator--()
{*this -= 1;return *this;
}test.cpp
void Test3()
{Date d1(2023, 11, 2);/*d1.Print();d1++;d1.Print();*/--d1;d1.Print();--d1;d1.Print();
}
operator--(后置)运算符实现
Date.cpp
Date Date::operator--(int)
{Date tmp(*this);*this -= 1;return tmp;
}test.cpp
void Test3()
{Date d1(2023, 11, 2);/*d1.Print();d1++;d1.Print();*//*--d1;d1.Print();--d1;d1.Print();*/d1.Print();d1--;d1.Print();} 
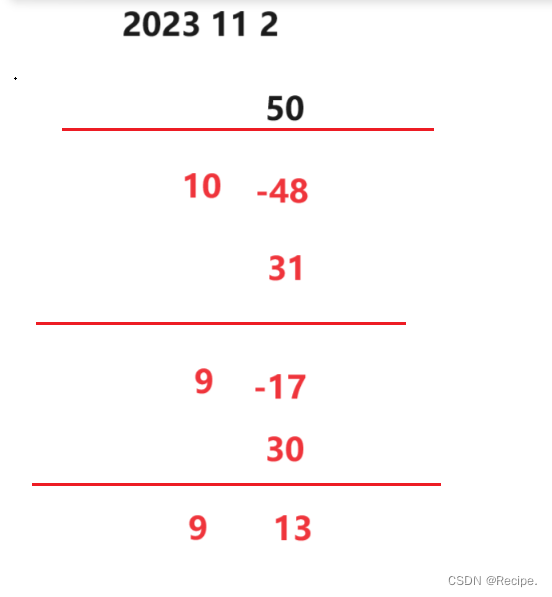
既然日期-天数 日期-月 日期++都有意义 那么日期-日期也有意义
比如计算2023到2024年还有多少天
operator-(日期-日期)
Date.cpp
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{// 假设左大右小int flag = 1;Date max = *this; //this指向d1Date min = d; //d2// 假设错了,左小右大if (*this < d){max = d;min = *this;flag = -1;}int n = 0;while (min != max){++min;++n;}return n * flag;
}test.cpp
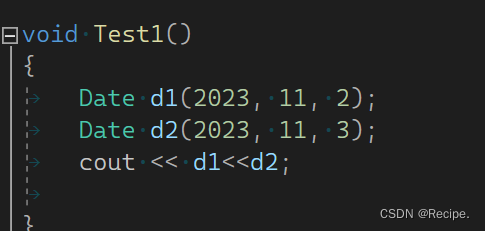
void Test4()
{Date d1(2023, 11, 2);Date d2(2024, 1, 1);cout << (d1 - d2) << endl;
}

但我们在+= 和-=忽略掉了一个问题 就是当给天数 给成负值怎么办?比如d1+=(-50) d1+(-50)
当我们用我们上面实现的+=时
d1+=50 d1=d1+(-50) d1=2-50=-48
void Test4()
{Date d1(2023, 11, 2);//Date d2(2024, 1, 1);d1 += -50;d1.Print();//cout << (d1 - d2) << endl;
}
天数变成了负值 但那个日期计算器人家是能正常计算的
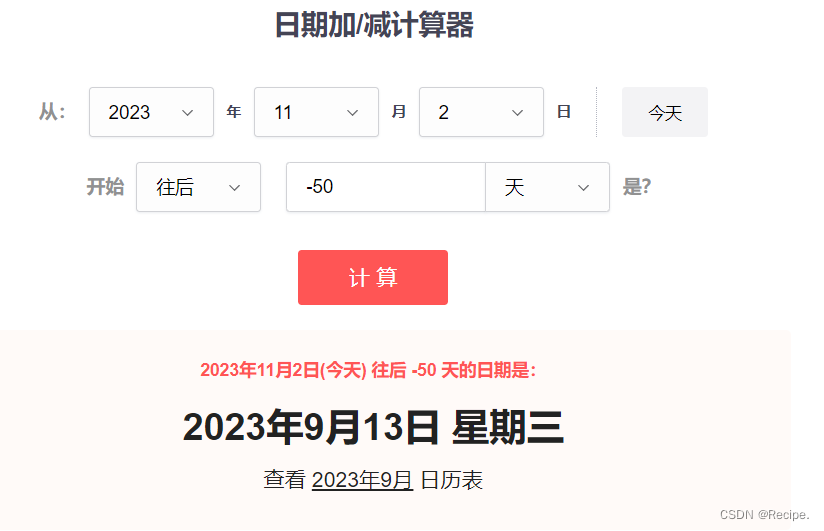
为了能够正确计算负天数,我们只需要加个一个判断条件即可
当天数小于0时 d1+=-50 变成了 d1=d1-(-50) 即d1+=50 d1=d1+50;
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{if (day < 0){return *this -= (-day);}_day += day;while (_day > Getmonthday(_year, _month)){_day -= Getmonthday(_year, _month);++_month;if (_month == 13){++_year;_month = 1;}}return *this;
}
-=也一样加上判断条件即可
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{if (day < 0){return *this += (-day);}_day -= day;while (_day <= 0){--_month;if (_month == 0){--_year;_month = 12;}_day += Getmonthday(_year, _month);}日期类实现全部代码
Date.h
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1);void Print();int Getmonthday(int year, int month);bool operator<(const Date& d)const;bool operator==(const Date& d)const;bool operator>(const Date& d)const;bool operator!=(const Date& d)const;bool operator<=(const Date& d)const;bool operator>=(const Date& d)const;Date& operator+=(int day);Date operator+(int day)const;Date& operator-=(int day);Date operator-(int day)const;Date& operator++();Date operator++(int);Date& operator--();Date operator--(int);int operator-(const Date& d)const;private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};Date.cpp
#include"Date.h"Date::Date(int year, int month , int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;if (_year < 1 || _month < 1 || _month>12|| _day < 1 || _day>Getmonthday(_year, _month)){cout << "非法日期" << endl;Print();}
}void Date::Print()const
{cout << _year << "_" << _month << "_" << _day << endl;
}bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)const
{if (_year < d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month < d._month){return true;}else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day){return true;}return false;
}bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)const
{return _year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;
}bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)const
{return !(*this < d);
}
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d)const
{return !(*this == d);
}
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d)const
{return *this < d || *this == d;
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d)const
{return !(*this < d) || *this == d;
}
int Date::Getmonthday(int year, int month)
{assert(year >= 1 && month >= 1 && month <= 12);int arry[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };//判断年是否是闰年if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0))){return 29;}return arry[month];
}
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{if (day < 0){return *this -= (-day);}_day += day;while (_day > Getmonthday(_year, _month)){_day -= Getmonthday(_year, _month);++_month;if (_month == 13){++_year;_month = 1;}}return *this;
}Date Date::operator+(int day)const
{Date tmp(*this);tmp += day;return tmp;}Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{if (day < 0){return *this += (-day);}_day -= day;while (_day <= 0){--_month;if (_month == 0){--_year;_month = 12;}_day += Getmonthday(_year, _month);}return *this;
}
Date Date::operator-(int day)const
{Date tmp(*this);tmp -= day;return tmp;
}
Date& Date:: operator++()
{*this += 1;return*this;
}Date Date::operator++(int)
{Date tmp(*this);*this += 1;return tmp;
}Date& Date::operator--()
{*this -= 1;return *this;
}
Date Date::operator--(int)
{Date tmp(*this);*this -= 1;return tmp;
}int Date::operator-(const Date& d)const
{// 假设左大右小int flag = 1;Date max = *this; //this指向d1Date min = d; //d2// 假设错了,左小右大if (*this < d){max = d;min = *this;flag = -1;}int n = 0;while (min != max){++min;++n;}return n * flag;
}test.cpp
#include"Date.h"//void Test1()
//{
// /*Date d1(2023, 11, 2);
// Date d2(2023, 13, 3);*/
//
// /*cout << (d1 < d2) << endl;
// cout << (d1 == d2) << endl;
// cout << (d1 > d2) << endl;
// cout << (d1 != d2) << endl;
// cout << (d1 <= d2) << endl;
// cout << (d1 >= d2) << endl;*/
//}//void Test2()
//{
// Date d1(2023, 11, 2);
// /*d1 += 50;*/
// /*d1 -= 50;
// d1.Print();*/
// /*d1.Print();
// Date ret = d1 + 50;
// ret.Print();*/
// /*Date ret = d1 - 50;
// d1.Print();
// ret.Print();*/
// /*++d1;
// d1.Print();
// ++d1;
// d1.Print();*/
//
//}//void Test3()
//{
// Date d1(2023, 11, 2);
// /*d1.Print();
// d1++;
// d1.Print();*/
//
// /*--d1;
// d1.Print();
// --d1;
// d1.Print();*/
// d1.Print();
// d1--;
// d1.Print();
//
//}
void Test4()
{Date d1(2023, 11, 2);//Date d2(2024, 1, 1);d1 += -50;d1.Print();//cout << (d1 - d2) << endl;
}
int main()
{//Test1();//Test2();//Test3();Test4();return 0;
}const成员


加上const后为什么不能打印出来呢?因为这里是权限的放大
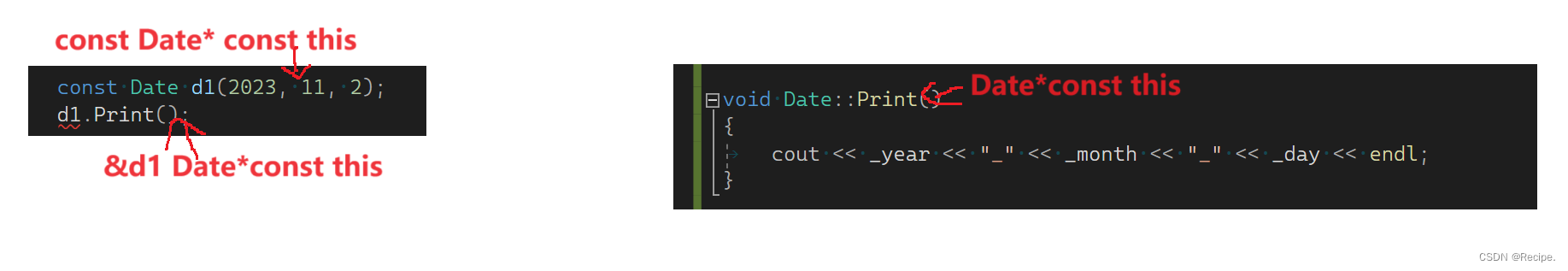
从const Date*const this变成了 Date*const this 形成了权限的放大
那怎么解决呢?祖师爷决定在括号加上一个const(声明和定义后面都要加上)
![]()

当加个const以后 const就修饰了Date*const this变成了const Date*const this const本质是修饰this
从权限的放大变成了权限的平移 就能打印了
那么非const对象能调用const函数吗 ?


答案是可以的,因为Date*const this 变成了 const Date*const this 形成了权限的缩小
权限可以平移和缩小 但不能放大。
那么所有函数都能定义成const函数吗?是不可以的,当需要修改成员变量的成员函数,不能改成const。
但能定义成const的成员函数都应该定义成const
这样const对象和非const对象都可以调用(const权限的平移和const权限的缩小)
要修改成员变量的成员函数,不能定义成const
因此在日期类成员函数在不修改成员变量的成员函数后面都可以加上const
取地址及const取地址操作符重载

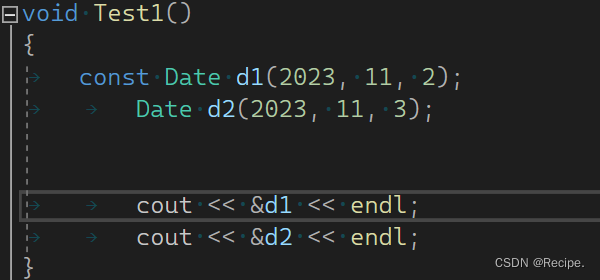
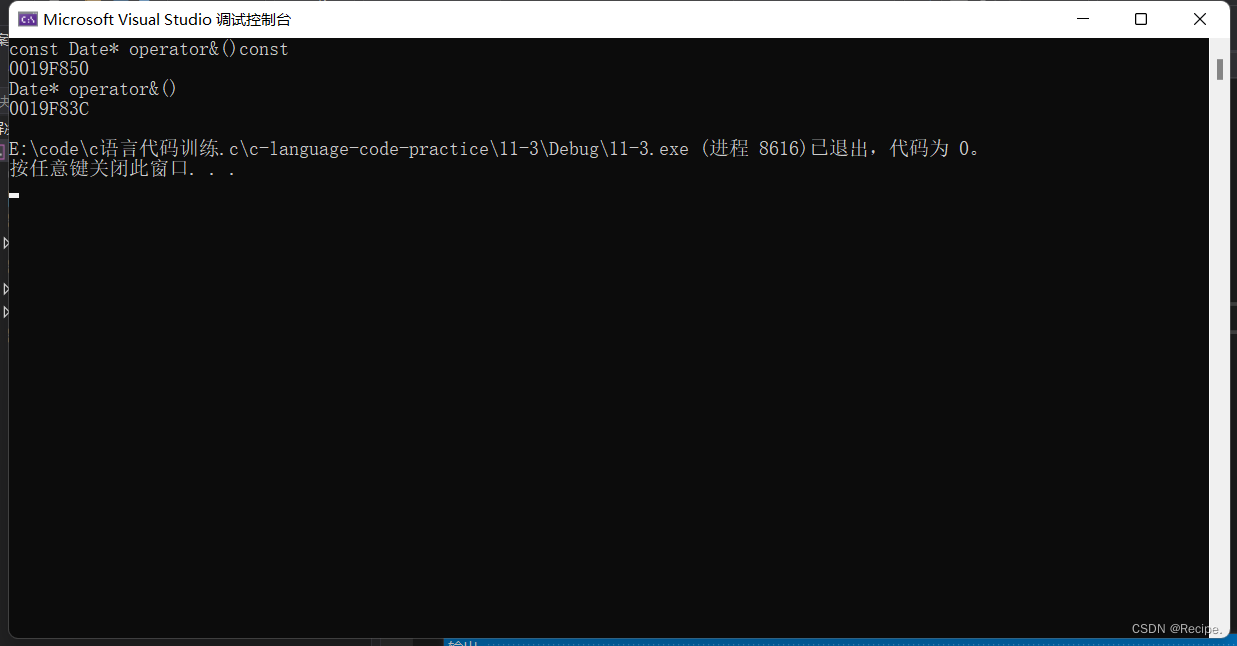 当屏蔽掉非const取地址操作函数,非const会去调用const取地址操作函数
当屏蔽掉非const取地址操作函数,非const会去调用const取地址操作函数

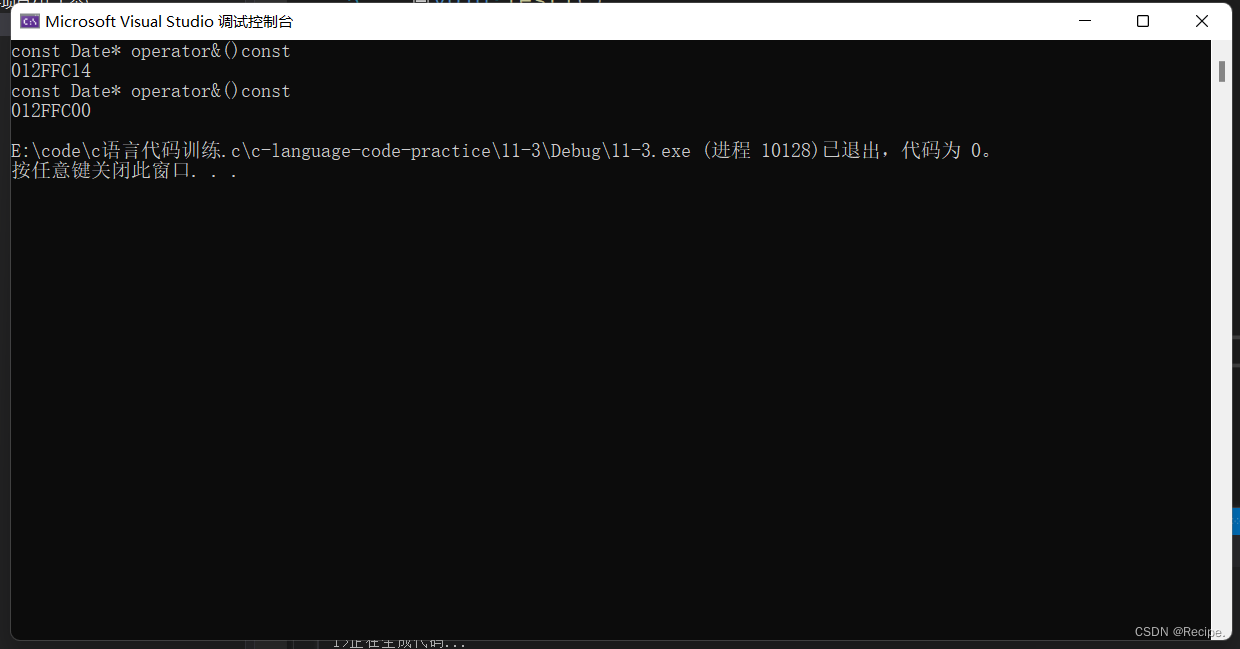
这两个取地址操作符重载一般使用编译器默认生成的就可以。
只有特殊情况,才需要重载,比如想让别人获取到指定的内容!

不想让别人获取地址可以返回空指针nullptr或者返回自己编造的一个地址。

operator实现<<流插入
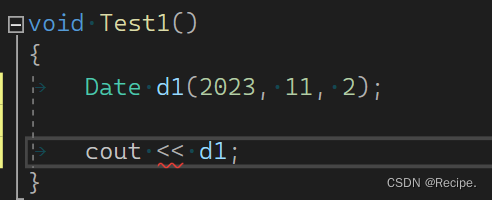
为什么不能打印出d1内容,因为<<不识别自定义类型对象 为什么可以识别内置类型呢?
因为C++已经头文件里面的库函数已经帮忙实现了

为了实现识别自定义类型对象,自己照猫画虎实现一个即可。
Date.h 声明
![]()
Date.cpp 定义
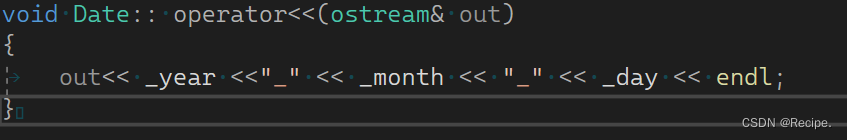
但是它有一个问题,就是访问不了私有成员变量,我们暂且先取消掉private,把成员变量放开

但出现了问题 cout<<d1打印不了 d1<<cout可以打印,这又是为什么呢?


因为双目操作数的运算符,规定第一个参数必须是左操作数(*this),第二个参数必须是右操作数
d1<<cout 转换 d1.operator<<(&d1,cout); cout<<d1 第一个参数是cout 第二个是*this所以不行。
那么为了规定传参,流插入的实现只能在全局进行实现,因为成员函数Date对象默认占据第一个位置。

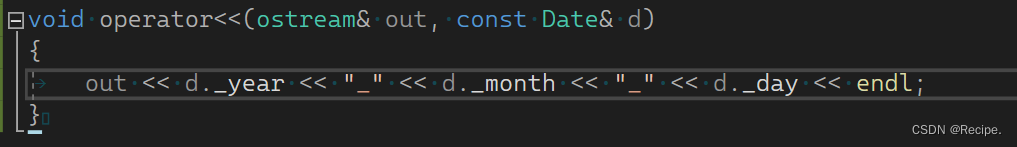

在全局实现又有两个问题,第一个不能访问私有成员变量,第二个不能支持连续插入

我们给流插入返回值就能解决连续cout的问题



那么访问不了私有成员变量怎么解决呢?这时候就要用到我们的友元函数




友元函数就是在类里面成员函数 前面加个friend 表面是友元函数 我和你是好朋友,可以去你家里玩私有物品,比如游戏机 上厕所等。
那么流提取的实现与流插入相仿
operator实现>>流提取


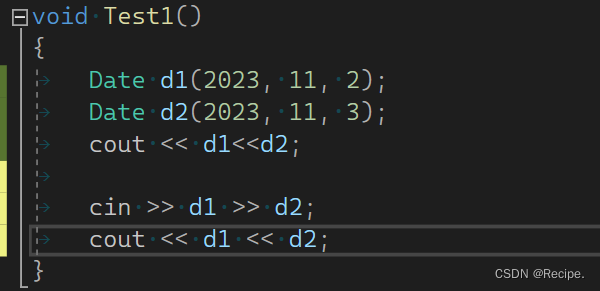
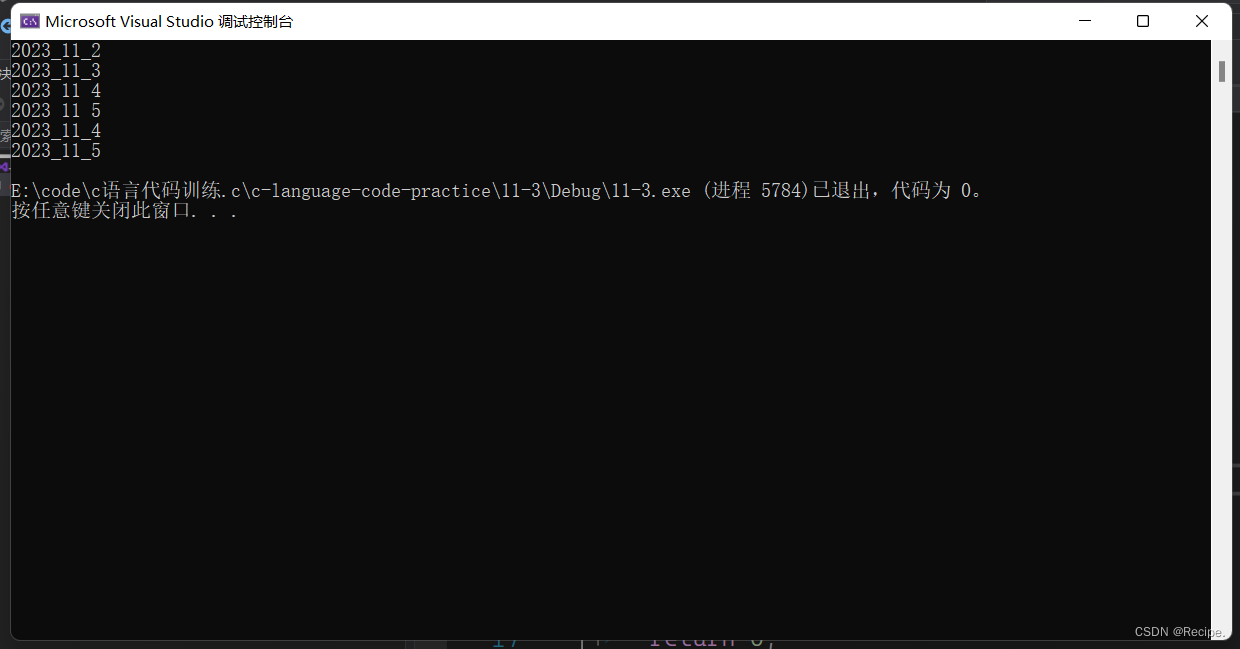 流本质是为了解决,自定义类型的输入和输出问题
流本质是为了解决,自定义类型的输入和输出问题
printf scanf 无法解决自定义类型的输入输出问题面向对象 + 运算符重载解决.
![[GDOUCTF 2023]<ez_ze> SSTI 过滤数字 大括号{等](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/30f4f5ad10ce4733a8a068ccfe2d348f.png)




![[计算机提升] Windows系统软件:娱乐类](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c20ee553600d401c94c476568deafcac.png)