一、接口鉴权方案分析
1、接口鉴权方案
目前大部分接口鉴权方案,一般都是采用 【用户-角色-权限】模型。
将接口与权限进行编码死绑定,同时角色与权限进行动态绑定,用户与角色也进行动态绑定。
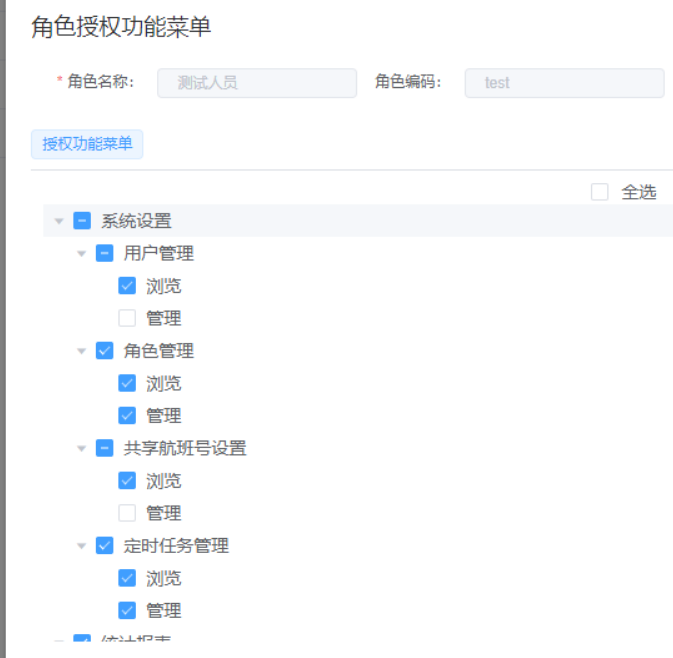
2、角色分配权限树
创建用户之后,用户可以分配多个角色。
创建角色之后,通过查询代码内置的权限树,进行角色与权限绑定,存入数据库中。
二、编码实战
1、定义权限树与常用方法
使用枚举进行权限的定义,通过四级权限树,将权限分为模块、单元、功能级、接口。接口权限精细分配:
/*** 接口权限枚举定义类*/
public enum AuthPermission {/*** 四级权限树* 1 模块* - 2 功能* - - 3 接口集(一般是Controller)* - - - 4 具体接口(@RequestMapping)**/// 用户管理User("user", "用户", Type.Module),SysUser(User, "系统用户", Type.Unit),SysUserManager(SysUser, "系统用户管理", Type.Bunch),SysUserManagerSelect(SysUserManager, "系统用户查询", Type.Function),SysUserManagerAdd(SysUserManager, "系统用户新增", Type.Function),SysUserManagerUpdate(SysUserManager, "系统用户修改", Type.Function),SysUserManagerDelete(SysUserManager, "系统用户删除", Type.Function),NormalUser(User, "普通用户", Type.Unit),NormalUserManager(NormalUser, "普通用户管理", Type.Bunch),NormalUserManagerSelect(NormalUserManager, "普通用户查询", Type.Function),NormalUserManagerAdd(NormalUserManager, "普通用户新增", Type.Function),NormalUserManagerUpdate(NormalUserManager, "普通用户修改", Type.Function),NormalUserManagerDelete(NormalUserManager, "普通用户删除", Type.Function),// 订单管理Order("order", "订单", Type.Module),OrderConfirm(Order, "下单管理", Type.Unit),OrderConfirmKill(OrderConfirm, "秒杀下单管理", Type.Bunch),OrderConfirmKillAdd(OrderConfirmKill, "秒杀订单新增", Type.Function),OrderConfirmKillDelete(OrderConfirmKill, "秒杀订单删除", Type.Function),OrderConfirmNormal(OrderConfirm, "普通下单管理", Type.Bunch),OrderConfirmNormalAdd(OrderConfirmNormal, "普通订单新增", Type.Function),OrderConfirmNormalDelete(OrderConfirmNormal, "普通订单删除", Type.Function),// ...其他;/*** 功能权限类型*/public enum Type {Module, // 功能模块Unit, // 功能单元Bunch, // 功能接口集Function, // 功能接口}// 模块private final String module;// 名称private final String title;// 父private final AuthPermission parent;// 类型private final Type type;AuthPermission(AuthPermission parent, String title, Type type) {this(parent.module, parent, title, type);}AuthPermission(String title, String module, Type type) {this(module, null, title, type);}AuthPermission(String module, AuthPermission parent, String title, Type type) {this.module = module;this.title = title;this.parent = parent;this.type = type;}public String getModule() {return module;}public String getTitle() {return title;}public AuthPermission getParent() {return parent;}public Type getType() {return type;}
}
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;/*** 接口权限管理类*/
public class AuthPermissionManagement {private static List<AuthArchetype> permissionTree = new ArrayList<>();private static Map<AuthPermission, AuthArchetype> permissionMap = new HashMap<>();static {// 递归设置树// 设置子树recursePermissions(permissionTree, permissionMap, null);}public static void main(String[] args) {// 获取权限树(到时候给前端展示树)System.out.println(Json.toJson(getPermissionTree()));// 校验权限System.out.println(checkPermission(AuthPermission.NormalUserManagerDelete, AuthPermission.NormalUser));System.out.println(checkPermission(AuthPermission.NormalUserManagerDelete, AuthPermission.OrderConfirm));System.out.println(checkPermission(AuthPermission.NormalUserManagerDelete, AuthPermission.NormalUserManagerDelete));}/*** 校验权限 递归* @param userPermission 用户角色权限* @param interfacePermission 接口权限* @return*/public static boolean checkPermission(AuthPermission userPermission, AuthPermission interfacePermission) {if (userPermission == interfacePermission) {return true;}// 有子接口权限也可AuthArchetype authArchetype = permissionMap.get(interfacePermission);if (authArchetype == null) {return false;}return checkChildrenPermission(userPermission, authArchetype);}private static boolean checkChildrenPermission(AuthPermission userPermission, AuthArchetype authArchetype) {if (authArchetype.getName().equals(userPermission.name())) {return true;}if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(authArchetype.getSubPermissions())) {for (AuthArchetype subPermission : authArchetype.getSubPermissions()) {if (subPermission.getName().equals(userPermission.name())) {return true;}// 递归if (checkChildrenPermission(userPermission, subPermission)) {return true;}}}return false;}// 获取权限树public static List<AuthArchetype> getPermissionTree() {return permissionTree;}private static void recursePermissions(List<AuthArchetype> permissionTree, Map<AuthPermission, AuthArchetype> permissionMap, AuthPermission current) {for (AuthPermission permission : AuthPermission.values()) {if (permission.getParent() == current) {AuthArchetype permissionArchetype = new AuthArchetype(permission);if (current == null) {permissionTree.add(permissionArchetype);} else {permissionMap.get(current).addSubPermission(permissionArchetype);}permissionMap.put(permission, permissionArchetype);recursePermissions(permissionTree, permissionMap, permission);}}}public static class AuthArchetype {// nameprivate String name;// 模块private String module;// 名称private String title;// 父private AuthPermission parent;// 类型private AuthPermission.Type type;// 子private List<AuthArchetype> subPermissions;public AuthArchetype(AuthPermission permission) {this.name = permission.name();this.module = permission.getModule();this.title = permission.getTitle();this.parent = permission.getParent();this.type = permission.getType();}public void addSubPermission(AuthArchetype subPermission) {if (this.subPermissions == null) {this.subPermissions = new ArrayList<>();}this.subPermissions.add(subPermission);}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public String getModule() {return module;}public void setModule(String module) {this.module = module;}public String getTitle() {return title;}public void setTitle(String title) {this.title = title;}public AuthPermission getParent() {return parent;}public void setParent(AuthPermission parent) {this.parent = parent;}public AuthPermission.Type getType() {return type;}public void setType(AuthPermission.Type type) {this.type = type;}public List<AuthArchetype> getSubPermissions() {return subPermissions;}public void setSubPermissions(List<AuthArchetype> subPermissions) {this.subPermissions = subPermissions;}}
}2、自定义AOP注解
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Auth {AuthPermission[] value() default {};
}
3、AOP切面类(也可以用拦截器实现)
import org.apache.commons.lang3.ArrayUtils;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.lang.reflect.Method;@Aspect
@Component
public class AuthAdvice {/*** 我们希望的是如果方法上有注解,则对方法进行限制,若方法上无注解,单是类上有注解,那么类上的权限注解对该类下所有的接口生效。*/@Around("@annotation(com.qstcloud.athena.opencourse.auth.Auth) || @within(com.qstcloud.athena.opencourse.auth.Auth)")public Object preAuth(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {if (handleAuth(point)) {return point.proceed();}throw new RuntimeException("权限不足,请求被拒绝");}/*** 逻辑判断,返回true or false* true :权限校验通过* false :权限校验不通过*/private boolean handleAuth(ProceedingJoinPoint point) {MethodSignature ms = point.getSignature() instanceof MethodSignature ? (MethodSignature) point.getSignature() : null;Method method = ms.getMethod();// 读取权限注解,优先方法上,没有则读取类Auth Annotation = getAnnotation(method, Auth.class);// 判断权限AuthPermission[] authPermissions = Annotation.value();if (ArrayUtils.isEmpty(authPermissions)) {// 没有权限树,登录就可以访问return checkLogin();}// 校验当前登录用户,是否包含其中权限之一return checkHasPermission(authPermissions);}/*** 校验当前登录用户,是否包含其中权限之一*/private boolean checkHasPermission(AuthPermission[] authPermissions) {
// User user = UserUtil.getCurrentUser();
// Role role = user.getRole(); // 获取角色// TODO 判断角色中的权限,是否包含接口的权限return ArrayUtils.contains(authPermissions, AuthPermission.NormalUserManagerUpdate);}/*** 判断是否登录*/private boolean checkLogin() {// TODO 从redis或者session中判断是否登录return true;}/*** 读取权限注解,优先方法上,没有则读取类*/private Auth getAnnotation(Method method, Class<Auth> authClass) {Auth annotation = method.getAnnotation(authClass);if (annotation != null) {return annotation;}annotation = method.getDeclaringClass().getAnnotation(authClass);return annotation;}
}4、测试一下
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
@Auth
public class TestController {@GetMapping("/test1")public String test1() {return "success";}@GetMapping("/test2")@Auth(AuthPermission.NormalUserManagerDelete)public String test2() {return "success";}@GetMapping("/test3")@Auth(AuthPermission.NormalUserManagerUpdate)public String test3() {return "success";}
}






![[开源]企业级在线办公系统,基于实时音视频完成在线视频会议功能](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/7d5a07a3d4e524f20c4ea3d5243129c8.png)