一、搭建SSH服务
1、关闭防火墙与SELinux
# 关闭firewalld防火墙 # 临时关闭 systemctl stop firewalld # 关闭开机自启动 systemctl disable firewalld # 关闭selinux # 临时关闭 setenforce 0 # 修改配置文件 永久关闭 vim /etc/selinux/config SELINUX=disabled
2、配置yum源
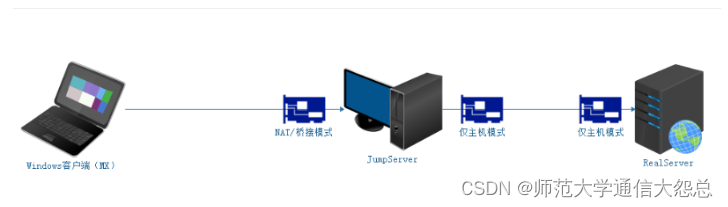
JumpServer配置外网YUM源 => 阿里云
# mv /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo.backup # wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo # yum clean all # yum makecache
RealServer配置本地YUM源 => 把光盘镜像作为仓库(自建YUM仓库)
① 挂载光盘
# mkdir /mnt/cdrom # mount -o ro /dev/sr0 /mnt/cdrom # chmod +x /etc/rc.local # echo 'mount -o ro /dev/sr0 /mnt/cdrom' >> /etc/rc.local
② 编写local.repo文件
# cd /etc/yum.repos.d # vim local.repo [local] name=local yum baseurl=file:///mnt/cdrom enabled=1 gpgcheck=0
3、openssh软件的安装
SSH服务底层的软件名称叫做openssh,open开源,ssh就是ssh服务。openssh属于C/S架构软件,其拥有客户端与服务器端。
客户端:ssh
服务端:openssh-server
安装步骤:
# yum install openssh -y
检查openssh是否安装成功
# rpm -qa |grep openssh 或 # yum list installed |grep openssh
获取openssh生成的文件列表
# rpm -ql openssh-server # 配置文件 /etc/ssh/sshd_config => ssh服务的主配置文件 /etc/sysconfig/sshd # 服务管理脚本 /usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service => systemctl start sshd # 文件共享服务 提供文件上传下载的服务 /usr/libexec/openssh/sftp-server # 二进制文件程序文件 /usr/sbin/sshd # 公钥生成工具 /usr/sbin/sshd-keygen # man手册 /usr/share/man/man5/sshd_config.5.gz /usr/share/man/man8/sftp-server.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/sshd.8.gz
# rpm -ql openssh-clients # 客户端配置文件 /etc/ssh/ssh_config # 远程copy命令 服务器间进行文件传输 /usr/bin/scp # sftp客户端 上传下载文件操作 /usr/bin/sftp /usr/bin/slogin /usr/bin/ssh /usr/bin/ssh-add /usr/bin/ssh-agent /usr/bin/ssh-copy-id /usr/bin/ssh-keyscan # 客户端man手册 /usr/share/man/man1/scp.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1/sftp.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1/slogin.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1/ssh-add.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1/ssh-agent.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1/ssh-copy-id.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1/ssh-keyscan.1.gz /usr/share/man/man1/ssh.1.gz /usr/share/man/man5/ssh_config.5.gz /usr/share/man/man8/ssh-pkcs11-helper.8.gz
4、查看并修改ssh服务端的配置文件
# man 5 sshd_config
RealServer:禁止root账号远程登录
# man 5 sshd_config PermitRootLogin => yes or no,默认为yes 代表允许通过root账号远程登录此服务器
# vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config 38行 PermitRootLogin no
5、sshd服务管理
# systemctl restart sshd => 重启 # systemctl status sshd => 状态 # systemctl stop sshd => 停止 # systemctl start sshd => 启动 # systemctl enable sshd => 开机自启动 # systemctl disable sshd => 开机不自启 # ps -ef |grep sshd => 进程 或 # netstat -tnlp |grep sshd => 端口 或 # ss -naltp |grep sshd
二、SSH服务任务解决方案
1、创建用户并授权
JumpServer跳板机创建用户并授权
第一步:创建用户与用户组(html前端组,tom与jerry)
# 创建html前端组 # groupadd html # 创建组内用户tom与jerry # useradd -g html tom # useradd -g html jerry
第二步:为用户添加密码
# echo 123456 |passwd --stdin tom # echo 123456 |passwd --stdin jerry
第三步:为开发人员创建数据目录并且设置相应的权限
① 创建用户的数据目录:
# mkdir -p /code/html => 前端组 # ll -d /code/html drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 May 24 10:36 /code/html
② 更改目录的文件所属组(更改为html,代表html组内成员可以对这个目录进行管理)
# chgrp -R html /code/html drwxr-xr-x. 2 root html 6 May 24 10:36 /code/html # chmod -R g+w /code/html drwxrwxr-x. 2 root html 6 May 24 10:36 /code/html
③ 添加粘滞位权限,防止误删除操作
# chmod 1770 /code/html drwxrwx--T. 2 root html 6 May 24 10:36 /code/html
2、测试用户权限
测试用户权限是否设置成功,可以结合第1步一起完成
3、禁用root登录
RealServer服务器端:
# vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config PermitRootLogin no
4、更改SSH默认端口
RealServer服务器端:
# vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config 17行 Port 3712
5、重启SSH服务
# systemctl restart sshd 或 # systemctl reload sshd
restart与reload的本质区别:
① restart其实相当于stop然后在start
② reload不停止现有业务,只是重新加载sshd对应的配置文件
6、在RealServer创建一个code账号
# useradd code # echo 123456 |passwd --stdin code
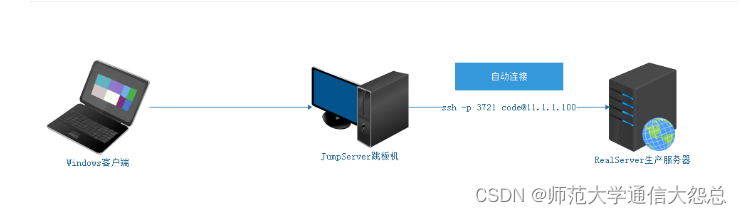
测试:在JumpServer远程连接RealServer
# ssh -p 3721 code@11.1.1.100
7、SSH客户端不验证指纹
第一次连接远程服务器时:
The authenticity of host '11.1.1.100 (11.1.1.100)' can't be established. ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:Y/cQNWWkX15o2MsJ5HOQBI2m8S33qIA+x3zys8J4pOY. ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:76:61:86:8b:d5:ee:bf:9c:60:e6:12:fa:f6:f0:74:36. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?yes Warning: Permanently added '11.1.1.100' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
如果我们不想验证指纹,可以通过更改SSH客户端的配置文件
JumpServer:
# vim /etc/ssh/ssh_config 35行 StrictHostKeyChecking no
8、用专业工具pwgen生成用户密码
在实际生产环境中,其用户密码一定不要手工设置,建议使用专业的密码生成工具如pwgen。
① 安装随机密码生成工具pwgen
② 使用pwgen工具生成随机密码
③ 给账号code设置密码
第一步:创建code开发者账号
# useradd code
第二步:配置EPEL源,安装pwgen工具
# wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo # yum clean all # yum makecache
第三步:安装pwgen密码生成工具
# yum install pwgen -y
第四步:使用pwgen生成随机密码
# pwgen -cnBs1 10 1
扩展:pwgen密码生成器的使用
# pwgen --help # 用法: pwgen 选项参数 长度 生成个数 Usage: pwgen [ OPTIONS ] [ pw_length ] [ num_pw ] # 密码中至少包含一个大写字母 -c or –capitalize # 密码中不包含大写字母 -A or –no-capitalize # 密码中至少包含一个数字 -n or –numerals # 密码中不包含数字 -0 or –no-numerals # 密码中至少包含一个特殊符号 -y or –symbols # 生成完全随机密码 -s or –secure # 密码中不包含歧义字符(例如1,l,O,0) -B or –ambiguous # 使用SHA1 hash给定的文件作为一个随机种子 -H or –sha1=path/to/file[#seed] # 在列中打印生成的密码 -C # 不要在列中打印生成的密码,即一行一个密码 -1 # 不要使用任何元音,以避免偶然的脏话 -v or –no-vowels
三、SSH服务补充
1、scp命令
主要功能:用于Linux系统与Linux系统之间进行文件的传输(上传、下载)
上传:
# scp [选项] 本地文件路径 远程用户名@远程服务器的IP地址:远程文件存储路径 -r : 递归上传,主要针对文件夹 -P : 更换了SSH服务的默认端口必须使用-P选项
下载:
# scp [选项] 远程用户名@远程服务器的IP地址:远程文件路径 本地文件存储路径 -r : 递归上传,主要针对文件夹 -P : 更换了SSH服务的默认端口必须使用-P选项
2、踢出用户
# 查看当前在线用户 w # 踢出某个账号 pkill -kill -t pts/1
四、SSH免密登录解决方案
1、为什么需要免密登录
2、SSH认证原理(基于用户名密码+基于密钥对)
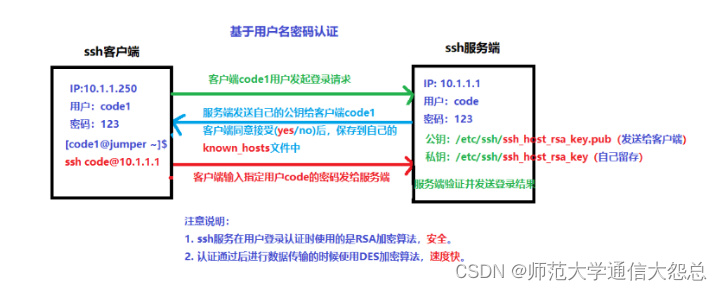
① 回顾基于用户名密码的认证方式
② 基于密钥对(公钥与私钥)的认证方式 => 免密登录
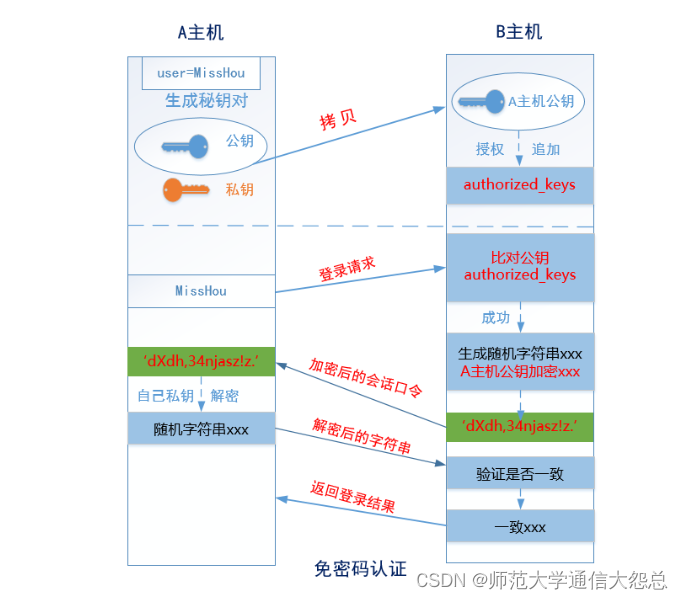
A主机 => JumpServer,B主机 => RealServer
第一步:在A主机(JumpServer)生成一个密钥对(公钥和私钥)
第二步:把A主机的公钥通过网络拷贝到B主机(RealServer)上,然后把其内容追加到B主机的~/.ssh/authorized_keys
第三步:由A主机(JumpServer)向B主机(RealServer)发起登录请求,然后直接在B主机上进行公钥比对(判断A主机的公钥是否已经存储在B主机的authorized_keys文件中),如果存在且正确,则生成一个随机的字符串(如itcast),然后使用A主机的公钥对其加密得到加密的后字符串(如dXdh,34njasz!z.)
第四步:通过网络,由B主机讲刚才生成的加密后的字符串传输给主机A,主机A接收到加密后的字符串以后,使用自己本地存储的私钥进行解密操作(得到itcast)
第五步:把解密得到的itcast发送到B主机,然后验证与刚才生成的字符串是否一致,如果一致,返回登录成功。反之,则返回登录失败。
到此免密登录全部完成!
3、SSH免密登录的具体实现
SSH免密的实现思路一共分为三个步骤(三步走)
第一步:在A主机针对某个账号(tom或jerry)生成公钥与私钥
第二步:使用某些方法把公钥发送到B主机中,然后追加到authorized_keys文件中
第三步:测试是否实现免密登录
☆ 方法一:比较常用(tom)
① 在A主机针对某个账号生成公钥与私钥
# ssh-keygen
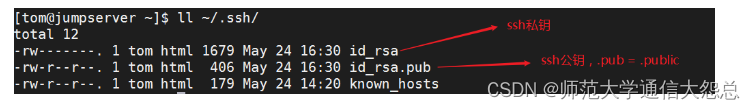
注:如果不想一路确认,可以在ssh-keygen -P "",直接生成公私钥
② 使用ssh-copy-id把公钥文件中的内容传输到服务器端的~/.ssh/authorized_keys文件中
# ssh-copy-id -p 3712 code@11.1.1.100 code@11.1.1.100's password:123456
③ 在JumpServer客户端测试免密登录是否成功
# ssh -p 3721 code@11.1.1.100
☆ 方法二:集群常用(jerry)
① 生成公钥与私钥
# ssh-keygen
② 把id_rsa.pub文件,scp到RealServer服务器端
# scp -P 3721 ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub code@11.1.1.100:/home/code/
③ 在RealServer服务器端,把id_rsa.pub文件中的内容追加到~/.ssh/authorized_keys文件中
# cd ~ # cat id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
注意事项:以上配置也比较简单,但是实际应用时要注意文件的权限
RealServer: ~/.ssh : 700 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys : 600
④ 测试免密是否成功
# ssh -p 3721 code@11.1.1.100