一、俩数相加
2.俩数相加(题目链接)
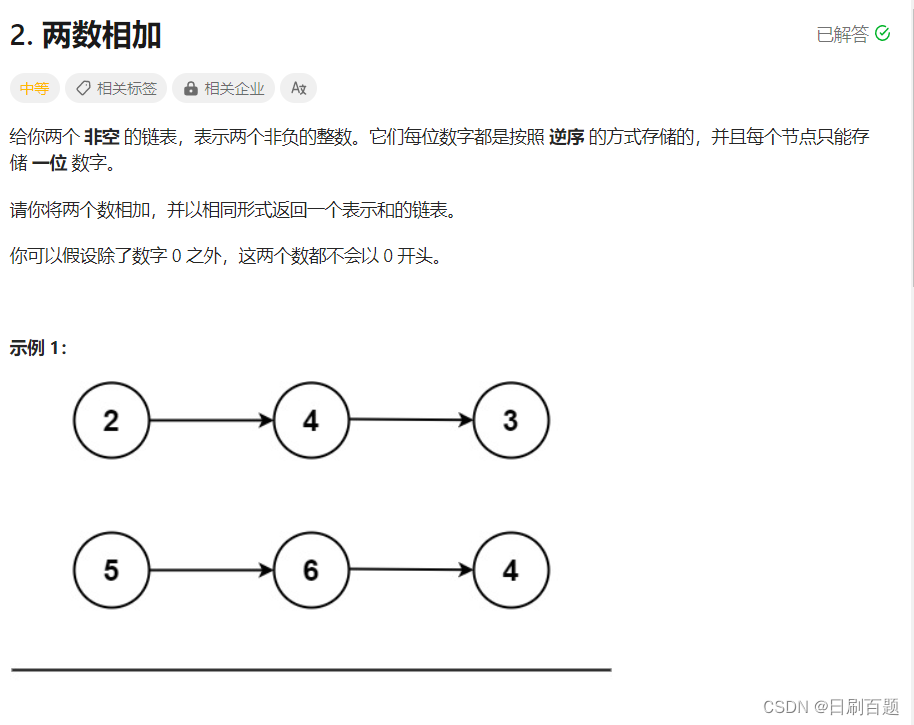
思路:这题题目首先要看懂,以示例1为例 即 342+465=807,而产生的新链表为7->0->8.
可以看成简单的从左向右,低位到高位的加法运算,4+6=10,逢10进1,新链表第三位为3+4+1(第二位进的1),需要注意的的点是当9->9->9和9->9->9->9相加,相当于9->9->9->0和9->9->9->9相加
代码实现:
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/typedef struct ListNode ListNode;ListNode * ListBuyNode(int x){ListNode * node=(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));if(node==NULL){perror("malloc fail:");return NULL;}node->val=x;node->next=NULL;return node;}
struct ListNode* addTwoNumbers(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) {int ret=0;ListNode *head=(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));//带头单链表ListNode*pcur=head;while(l1||l2||ret){if(l1){ret=ret+l1->val;}if(l2){ret=ret+l2->val;}ListNode *node=ListBuyNode(ret%10);pcur->next=node;pcur=pcur->next;if(l1){l1=l1->next;}if(l2){l2=l2->next;}ret=ret/10;}return head->next;
}解析:这里使用的是带头单链表,不用考虑头节点初始化问题;还有一点是:当l1和l2都走完时,还要确定进位是否为0,不为0,新链表还得在加一个节点,储存进位。
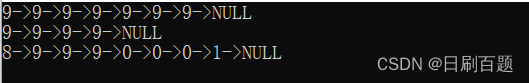
测试及结果:

二、回文链表
234.回文链表(题目链接)

思路:1)将链表内容复制到数组里面;
2)使用双指针法判断是否为回文。
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
bool isPalindrome(struct ListNode* head) {assert(head);int arr[100000]={0};int k=0;ListNode*pcur=head;while(pcur){arr[k]=pcur->val;k++;pcur=pcur->next;}for(int i=0,j=k-1;i<j;i++,j--){if(arr[i]!=arr[j]){return false;}}return true;
}三、相交链表
160.相交链表(题目链接)

思路:这道题的思路比较巧妙,相交链表最关键是节点重合,所以判断条件是节点相等,不是节点的val相等 。
若链表其中一个为NULL,则必定不相交,返回NULL.
分类讨论:
1)链表不相交(假设pheadA的长度为m,headB的长度为n)
1>若m==n,俩链表同时遍历完,相等为NULL
2>若m!=n,headA往后遍历,若遍历结束,则返回到headB的头节点,headB往后遍历,若遍历结束,则返回到headA的头节点,当遍历m+n次,他们都相等为NULL
2)链表相交(假设pheadA的长度为m,headB的长度为n,相交点到headA的头节点距离为a,相交点到headB的头节点距离为b,相交点到末尾的长度为c)
注:a+c=m,b+c=n
1>若m==n,在遍历完第一遍之前,必定有headA==headB!=NULL
2>若m!=n,headA往后遍历,若遍历结束,则返回到headB的头节点,headB往后遍历,若遍历结束,则返回到headA的头节点,当headA遍历a+c+b次,headB遍历b+c+a,同时到达相交点,headA==headB!=NULL
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {ListNode *p1=headA;ListNode*p2=headB;if(p1==NULL){return NULL;}if(p2==NULL){return NULL;}while(p1!=p2){p1 = p1 == NULL ? headB : p1->next;p2 = p2 == NULL ? headA : p2->next;}//p1与p2不相交,则为NULL;p1与p2相交,则为不为NULLif(p1==NULL){return NULL;}return p1;
}四、删除链表倒数第N个节点
19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点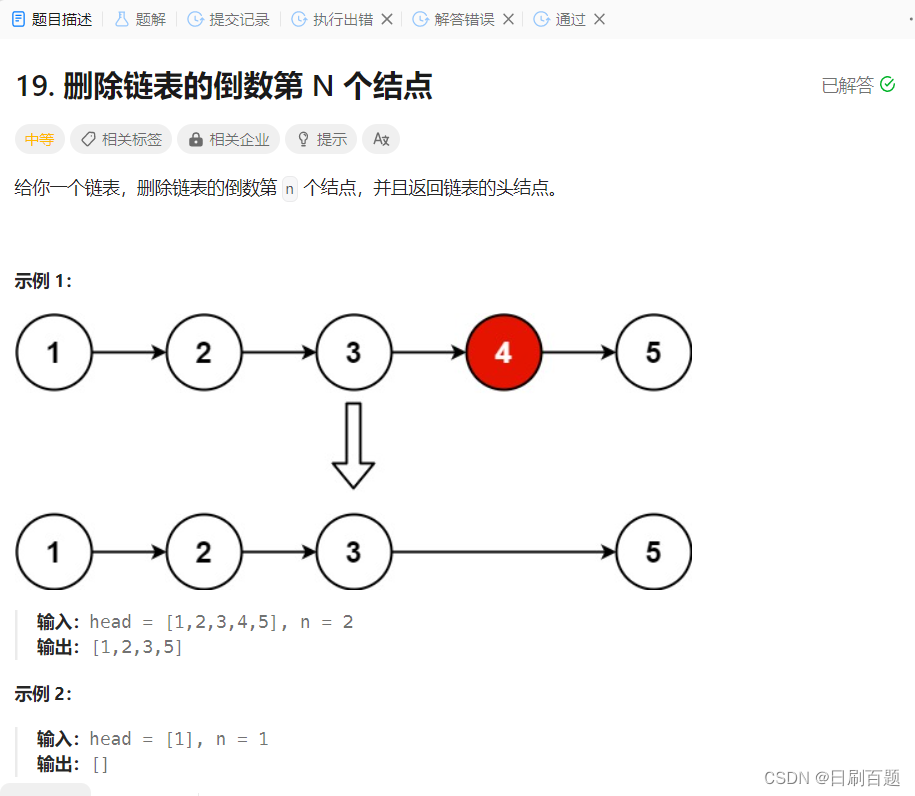
解法一:快慢指针(这里使用无头链表,需要对删除头节点额外考虑)
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(struct ListNode* head, int n) {assert(head);ListNode* fast,*slow;fast=slow=head;if(head->next==NULL)//只有一个节点{free(head);head=NULL;return NULL;}//至少2个节点while(n--){fast=fast->next;}if(fast==NULL)//删除头节点{head=head->next;return head;}while(fast->next){fast=fast->next;slow=slow->next;}ListNode *del=slow->next;slow->next=del->next;free(del);del=NULL;return head;
}优化快慢指针,引进头节点(哑节点)
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(struct ListNode* head, int n) {assert(head);ListNode* fast,*slow;ListNode*node=(ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));node->next=head;fast=slow=node;int m=n+1;while(m--){fast=fast->next;}while(fast){fast=fast->next;slow=slow->next;}ListNode*del=slow->next;slow->next=del->next;free(del);del=NULL;return node->next;
}解法二:遍历链表,找到链表节点数L,用删除指定位置节点方式删除第(L-n+1)个节点即可