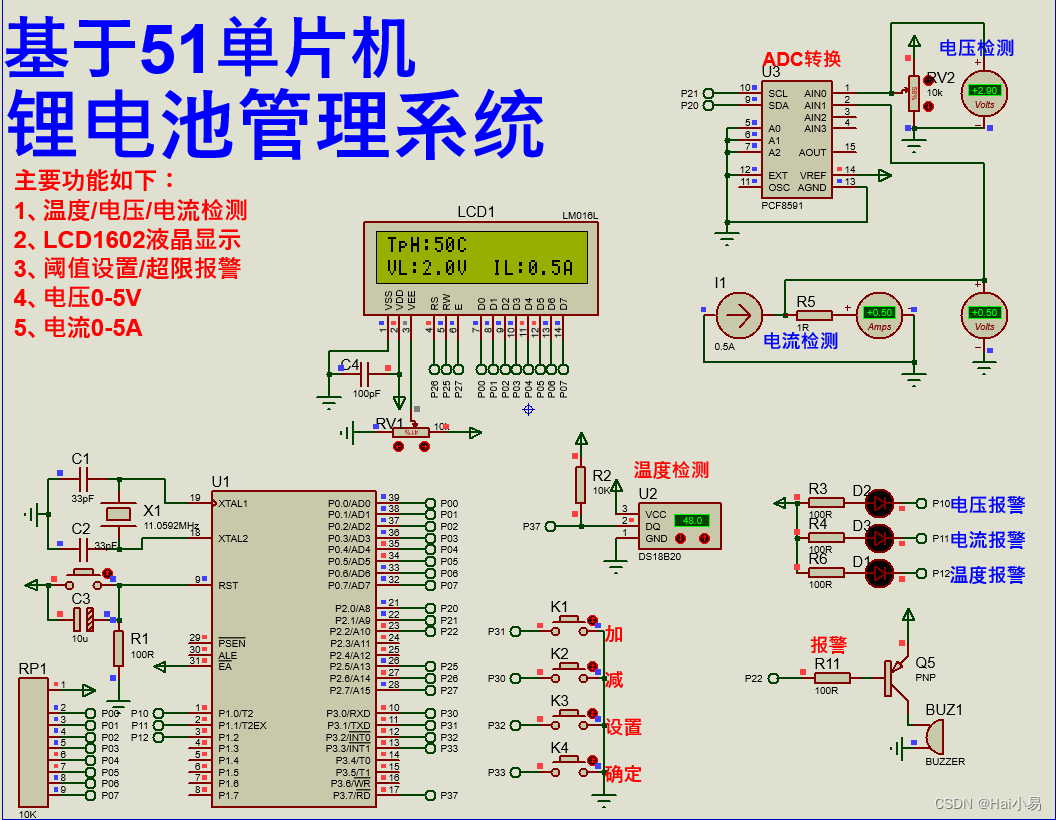
- 一、相关API的handler
- 二、RestBulkAction,组装bulkRequest调用TransportBulkAction
- 三、TransportBulkAction 会把数据分发到数据该到的数据节点
- 1、把数据按分片分组,按分片分组数据再发送到指定的数据节点
- (1) 计算此文档发往哪个分片
- 1)根据索引是否是分区索引,返回不同的索引路由对象
- 2) 文档没有id会自动给文档创建id
- 3)根据不同的索引路由对象,id和routing决定此文档发往哪个分片
- (2)、通过taskManager注册Task执行action.execute发送到数据节点
- 四、数据节点(TransportShardBulkAction)处理处理来自主节点的数据
- 1、针对此节点上索引分片进行操作
- (1) 组装Engine.Index
- (2)先添加到Lucene,成功后再添加到translog
下面的图来自ElasticSearch——刷盘原理流程,这篇文章主要讲的是客户端发送
bulk命令到保存到Lucene和translog的过程源码,不涉及到把数据刷到磁盘的逻辑,也不讲解存储在Lucene的数据结构
一、相关API的handler
在ActionModule.java中
//主节点处理谁分发到不同数据节点node的逻辑actions.register(BulkAction.INSTANCE, TransportBulkAction.class);//node节点接收到主节点分发的数据后的处理actions.register(TransportShardBulkAction.TYPE, TransportShardBulkAction.class);//主节点接收客户端的请求的handerregisterHandler.accept(new RestBulkAction(settings));
二、RestBulkAction,组装bulkRequest调用TransportBulkAction
public class RestBulkAction extends BaseRestHandler {@Overridepublic List<Route> routes() {return List.of(new Route(POST, "/_bulk"),new Route(PUT, "/_bulk"),new Route(POST, "/{index}/_bulk"),new Route(PUT, "/{index}/_bulk"),Route.builder(POST, "/{index}/{type}/_bulk").deprecated(TYPES_DEPRECATION_MESSAGE, RestApiVersion.V_7).build(),Route.builder(PUT, "/{index}/{type}/_bulk").deprecated(TYPES_DEPRECATION_MESSAGE, RestApiVersion.V_7).build());}@Overridepublic RestChannelConsumer prepareRequest(final RestRequest request, final NodeClient client) throws IOException {if (request.getRestApiVersion() == RestApiVersion.V_7 && request.hasParam("type")) {request.param("type");}BulkRequest bulkRequest = new BulkRequest();String defaultIndex = request.param("index");String defaultRouting = request.param("routing");FetchSourceContext defaultFetchSourceContext = FetchSourceContext.parseFromRestRequest(request);String defaultPipeline = request.param("pipeline");String waitForActiveShards = request.param("wait_for_active_shards");if (waitForActiveShards != null) {bulkRequest.waitForActiveShards(ActiveShardCount.parseString(waitForActiveShards));}Boolean defaultRequireAlias = request.paramAsBoolean(DocWriteRequest.REQUIRE_ALIAS, null);bulkRequest.timeout(request.paramAsTime("timeout", BulkShardRequest.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT));bulkRequest.setRefreshPolicy(request.param("refresh"));bulkRequest.add(request.requiredContent(),defaultIndex,defaultRouting,defaultFetchSourceContext,defaultPipeline,defaultRequireAlias,allowExplicitIndex,request.getXContentType(),request.getRestApiVersion());return channel -> client.bulk(bulkRequest, new RestStatusToXContentListener<>(channel));}
}
@Overridepublic void bulk(final BulkRequest request, final ActionListener<BulkResponse> listener) {execute(BulkAction.INSTANCE, request, listener);}
其中BulkAction.INSTANCE会通过最上面的actions转到TransportBulkAction.class
三、TransportBulkAction 会把数据分发到数据该到的数据节点
public class TransportBulkAction extends HandledTransportAction<BulkRequest, BulkResponse> {@Overrideprotected void doExecute(Task task, org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.BulkRequest bulkRequest, ActionListener<org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.BulkResponse> listener) {/** 这是在传输过程中调用的,因此我们可以快速检查索引内存压力,但我们不想让传输线程保持繁忙。然后,一旦我们有了索引压力,* 我们就会分叉到其中一个写入线程池。我们这样做是因为处理批量请求可能会变得昂贵,原因如下:* 在将子请求分派给分片时,我们可能需要压缩它们。LZ4 速度超快,但速度足够慢,最好不要在传输线程上执行此操作,尤其是对于大型子请求。* 我们可以检测到这些情况,然后才分叉,但这要正确处理起来很复杂,而且分叉的开销相当低。*/final int indexingOps = bulkRequest.numberOfActions();final long indexingBytes = bulkRequest.ramBytesUsed();final boolean isOnlySystem = isOnlySystem(bulkRequest, clusterService.state().metadata().getIndicesLookup(), systemIndices);final Releasable releasable = indexingPressure.markCoordinatingOperationStarted(indexingOps, indexingBytes, isOnlySystem);final ActionListener<BulkResponse> releasingListener = ActionListener.runBefore(listener, releasable::close);final String executorName = isOnlySystem ? Names.SYSTEM_WRITE : Names.WRITE;//通过线程池调用threadPool.executor(Names.WRITE).execute(new ActionRunnable<>(releasingListener) {@Overrideprotected void doRun() {doInternalExecute(task, bulkRequest, executorName, releasingListener);}});}protected void doInternalExecute(Task task, org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.BulkRequest bulkRequest, String executorName, ActionListener<BulkResponse> listener) {//省略代码//在开始之前,尝试创建我们在批量处理期间需要的所有索引。// Step 1: 收集请求中的所有索引final Map<String, Boolean> indices = bulkRequest.requests.stream() // 删除请求不应尝试创建索引(如果索引不存在),除非使用外部版本控制.filter(request -> request.opType() != DocWriteRequest.OpType.DELETE|| request.versionType() == VersionType.EXTERNAL|| request.versionType() == VersionType.EXTERNAL_GTE).collect(Collectors.toMap(DocWriteRequest::index, DocWriteRequest::isRequireAlias, (v1, v2) -> v1 || v2));// Step 2: 筛选索引列表以查找当前不存在的索引。final Map<String, IndexNotFoundException> indicesThatCannotBeCreated = new HashMap<>();Set<String> autoCreateIndices = new HashSet<>();ClusterState state = clusterService.state();for (Map.Entry<String, Boolean> indexAndFlag : indices.entrySet()) {final String index = indexAndFlag.getKey();boolean shouldAutoCreate = indexNameExpressionResolver.hasIndexAbstraction(index, state) == false;//只有当我们不要求它是别名时,我们才应该自动创建if (shouldAutoCreate && (indexAndFlag.getValue() == false)) {autoCreateIndices.add(index);}}// Step 3: 创建所有缺失的索引(如果有任何缺失)。在所有创建返回后启动批量if (autoCreateIndices.isEmpty()) {executeBulk(task, bulkRequest, startTime, listener, executorName, responses, indicesThatCannotBeCreated);} else { //省略代码for (String index : autoCreateIndices) {//省略代码,遍历创建索引 }}}void executeBulk(Task task,BulkRequest bulkRequest,long startTimeNanos,ActionListener<BulkResponse> listener,String executorName,AtomicArray<BulkItemResponse> responses,Map<String, IndexNotFoundException> indicesThatCannotBeCreated) {//创建一个BulkOperation对象,执行doRun方法new BulkOperation(task, bulkRequest, listener, executorName, responses, startTimeNanos, indicesThatCannotBeCreated).run();}}1、把数据按分片分组,按分片分组数据再发送到指定的数据节点
private final class BulkOperation extends ActionRunnable<BulkResponse> {@Overrideprotected void doRun() {//省略代码Metadata metadata = clusterState.metadata();//按 ShardId -> Operations 映射对请求进行分组Map<ShardId, List<BulkItemRequest>> requestsByShard = new HashMap<>();//遍历请求的每一条数据for (int i = 0; i < bulkRequest.requests.size(); i++) {DocWriteRequest<?> docWriteRequest = bulkRequest.requests.get(i);//省略代码IndexAbstraction ia = null;//请求是要把文档加入到索引boolean includeDataStreams = docWriteRequest.opType() == DocWriteRequest.OpType.CREATE;try {//给定的请求解析索引ia = concreteIndices.resolveIfAbsent(docWriteRequest);//获取具体的写入索引final Index concreteIndex = docWriteRequest.getConcreteWriteIndex(ia, metadata);//判断索引是否关闭if (addFailureIfIndexIsClosed(docWriteRequest, concreteIndex, i, metadata)) {continue;}//获取索引的路由信息,其中返回的indexRouting是new UnpartitionedIndexRouting indexRouting = concreteIndices.routing(concreteIndex);//这里如果文档没有带id,则会给文档生成一个iddocWriteRequest.process(indexRouting);//获取分片ID 里面IdAndRoutingOnly调用的是Unpartitioned获取分片idint shardId = docWriteRequest.route(indexRouting);//请求和分片ID封装为BulkItemRequest对象,computeIfAbsent是如果不存在则新建List<BulkItemRequest> shardRequests = requestsByShard.computeIfAbsent(new ShardId(concreteIndex, shardId),shard -> new ArrayList<>());//并将其添加到requestsByShard中对应的分片请求列表中。shardRequests.add(new BulkItemRequest(i, docWriteRequest));} catch (ElasticsearchParseException | IllegalArgumentException | RoutingMissingException | ResourceNotFoundException e) {String name = ia != null ? ia.getName() : docWriteRequest.index();BulkItemResponse.Failure failure = new BulkItemResponse.Failure(name, docWriteRequest.id(), e);BulkItemResponse bulkItemResponse = BulkItemResponse.failure(i, docWriteRequest.opType(), failure);responses.set(i, bulkItemResponse);// make sure the request gets never processed againbulkRequest.requests.set(i, null);}}//没有要添加的数据,直接返回了if (requestsByShard.isEmpty()) {listener.onResponse(new BulkResponse(responses.toArray(new BulkItemResponse[responses.length()]), buildTookInMillis(startTimeNanos)));return;}//下面就知道是按照分片ID分别分发请求final AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(requestsByShard.size());String nodeId = clusterService.localNode().getId();for (Map.Entry<ShardId, List<BulkItemRequest>> entry : requestsByShard.entrySet()) {final ShardId shardId = entry.getKey();final List<BulkItemRequest> requests = entry.getValue();BulkShardRequest bulkShardRequest = new BulkShardRequest(shardId,bulkRequest.getRefreshPolicy(),requests.toArray(new BulkItemRequest[requests.size()]));bulkShardRequest.waitForActiveShards(bulkRequest.waitForActiveShards());bulkShardRequest.timeout(bulkRequest.timeout());bulkShardRequest.routedBasedOnClusterVersion(clusterState.version());if (task != null) {bulkShardRequest.setParentTask(nodeId, task.getId());}client.executeLocally(TransportShardBulkAction.TYPE, bulkShardRequest, new ActionListener<>() {//成功后的响应处理@Overridepublic void onResponse(BulkShardResponse bulkShardResponse) {for (BulkItemResponse bulkItemResponse : bulkShardResponse.getResponses()) { if (bulkItemResponse.getResponse() != null) {bulkItemResponse.getResponse().setShardInfo(bulkShardResponse.getShardInfo());}responses.set(bulkItemResponse.getItemId(), bulkItemResponse);}//所有的分片请求都完成后,则完成组装响应报文if (counter.decrementAndGet() == 0) {finishHim();}}//失败的处理逻辑@Overridepublic void onFailure(Exception e) {// create failures for all relevant requestsfor (BulkItemRequest request : requests) {final String indexName = request.index();DocWriteRequest<?> docWriteRequest = request.request();BulkItemResponse.Failure failure = new BulkItemResponse.Failure(indexName, docWriteRequest.id(), e);responses.set(request.id(), BulkItemResponse.failure(request.id(), docWriteRequest.opType(), failure));}//所有的分片请求都完成后,则完成组装响应报文if (counter.decrementAndGet() == 0) {finishHim();}}private void finishHim() {listener.onResponse(new BulkResponse(responses.toArray(new BulkItemResponse[responses.length()]), buildTookInMillis(startTimeNanos)));}});}bulkRequest = null; // allow memory for bulk request items to be reclaimed before all items have been completed允许在所有项目完成之前回收批量请求项的内存}
}
(1) 计算此文档发往哪个分片
其中上面的关键代码块是下面
//获取索引的路由信息,其中返回的indexRouting是new UnpartitionedIndexRouting indexRouting = concreteIndices.routing(concreteIndex);//这里会针对文档的id做一些处理,比如会判断是否存在,不存在是抛异常还是创建一个新的docWriteRequest.process(indexRouting);//获取分片ID 里面IdAndRoutingOnly调用的是Unpartitioned获取分片idint shardId = docWriteRequest.route(indexRouting);
首先indexRouting的对象下面的Partitioned或者Unpartitioned
1)根据索引是否是分区索引,返回不同的索引路由对象
public static IndexRouting fromIndexMetadata(IndexMetadata metadata) {if (false == metadata.getRoutingPaths().isEmpty()) {return new ExtractFromSource(metadata);}//代码检查索引元数据是否是分区索引//如果是,则创建一个分区索引路由对象(Partitioned)并返回if (metadata.isRoutingPartitionedIndex()) {return new Partitioned(metadata);}//以上条件都不满足,则创建一个非分区索引路由对象(Unpartitioned)并返回return new Unpartitioned(metadata);}
2) 文档没有id会自动给文档创建id
@Overridepublic void process(IndexRouting indexRouting) {indexRouting.process(this);}
不管Partitioned还是Unpartitioned都继承自IdAndRoutingOnly
private abstract static class IdAndRoutingOnly extends IndexRouting {@Overridepublic void process(IndexRequest indexRequest) {//往索引添加文档的id不能为空字符串,但是可以为null,后续会自动创建idif ("".equals(indexRequest.id())) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("if _id is specified it must not be empty");}// generate id if not already providedif (indexRequest.id() == null) {indexRequest.autoGenerateId();}}
}
public void autoGenerateId() {assert id == null;assert autoGeneratedTimestamp == UNSET_AUTO_GENERATED_TIMESTAMP : "timestamp has already been generated!";assert ifSeqNo == UNASSIGNED_SEQ_NO;assert ifPrimaryTerm == UNASSIGNED_PRIMARY_TERM;autoGeneratedTimestamp = Math.max(0, System.currentTimeMillis());String uid = UUIDs.base64UUID();id(uid);}
3)根据不同的索引路由对象,id和routing决定此文档发往哪个分片
其中route的接口如下
@Overridepublic int route(IndexRouting indexRouting) {return indexRouting.indexShard(id, routing, contentType, source);}
private abstract static class IdAndRoutingOnly extends IndexRouting {protected abstract int shardId(String id, @Nullable String routing);@Overridepublic int indexShard(String id, @Nullable String routing, XContentType sourceType, BytesReference source) {if (id == null) {throw new IllegalStateException("id is required and should have been set by process");}checkRoutingRequired(id, routing);return shardId(id, routing);}
}其中shardId有两种实现,分别是Partitioned还是Unpartitioned
private static class Unpartitioned extends IdAndRoutingOnly {Unpartitioned(IndexMetadata metadata) {super(metadata);}//优先routing,如果没有则用id@Overrideprotected int shardId(String id, @Nullable String routing) {return hashToShardId(effectiveRoutingToHash(routing == null ? id : routing));}@Overridepublic void collectSearchShards(String routing, IntConsumer consumer) {consumer.accept(hashToShardId(effectiveRoutingToHash(routing)));}}private static class Partitioned extends IdAndRoutingOnly {private final int routingPartitionSize;Partitioned(IndexMetadata metadata) {super(metadata);this.routingPartitionSize = metadata.getRoutingPartitionSize();}//其中routing不能为null@Overrideprotected int shardId(String id, @Nullable String routing) {if (routing == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("A routing value is required for gets from a partitioned index");}int offset = Math.floorMod(effectiveRoutingToHash(id), routingPartitionSize);return hashToShardId(effectiveRoutingToHash(routing) + offset);}@Overridepublic void collectSearchShards(String routing, IntConsumer consumer) {int hash = effectiveRoutingToHash(routing);for (int i = 0; i < routingPartitionSize; i++) {consumer.accept(hashToShardId(hash + i));}}}
下面只看Unpartitioned
/*** Convert a routing value into a hash.* 将路由值转换为哈希值。*/private static int effectiveRoutingToHash(String effectiveRouting) {return Murmur3HashFunction.hash(effectiveRouting);}
/*** Hash function based on the Murmur3 algorithm, which is the default as of Elasticsearch 2.0.* 基于 Murmur3 算法的哈希函数,这是 Elasticsearch 2.0 的默认算法。*/
public final class Murmur3HashFunction {private Murmur3HashFunction() {// no instance}public static int hash(String routing) {final byte[] bytesToHash = new byte[routing.length() * 2];for (int i = 0; i < routing.length(); ++i) {final char c = routing.charAt(i);final byte b1 = (byte) c, b2 = (byte) (c >>> 8);assert ((b1 & 0xFF) | ((b2 & 0xFF) << 8)) == c; // no information lossbytesToHash[i * 2] = b1;bytesToHash[i * 2 + 1] = b2;}return hash(bytesToHash, 0, bytesToHash.length);}public static int hash(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length) {return StringHelper.murmurhash3_x86_32(bytes, offset, length, 0);}
}
/*** Convert a hash generated from an {@code (id, routing}) pair into a* shard id. 将从 {@code (id, routing}) 对生成的哈希转换为分片 ID。*/protected final int hashToShardId(int hash) {return Math.floorMod(hash, routingNumShards) / routingFactor;}
这样就指定了文档的分片id
(2)、通过taskManager注册Task执行action.execute发送到数据节点
client.executeLocally(TransportShardBulkAction.TYPE, bulkShardRequest, new ActionListener<>()
public <Request extends ActionRequest, Response extends ActionResponse> Task executeLocally(ActionType<Response> action,Request request,ActionListener<Response> listener) {return taskManager.registerAndExecute("transport",transportAction(action),request,localConnection,new SafelyWrappedActionListener<>(listener));}
后面的逻辑就不梳理了,直接看TransportShardBulkAction.TYPE
四、数据节点(TransportShardBulkAction)处理处理来自主节点的数据
public class TransportShardBulkAction extends TransportWriteAction<BulkShardRequest, BulkShardRequest, BulkShardResponse> {//这里处理属于属于当前节点分片的数据,请求是从主节点上过来的@Overrideprotected void dispatchedShardOperationOnPrimary(BulkShardRequest request,IndexShard primary,ActionListener<PrimaryResult<BulkShardRequest, BulkShardResponse>> listener) {ClusterStateObserver observer = new ClusterStateObserver(clusterService, request.timeout(), logger, threadPool.getThreadContext());performOnPrimary(request, primary, updateHelper, threadPool::absoluteTimeInMillis, (update, shardId, mappingListener) -> {assert update != null;assert shardId != null;mappingUpdatedAction.updateMappingOnMaster(shardId.getIndex(), update, mappingListener);}, mappingUpdateListener -> observer.waitForNextChange(new ClusterStateObserver.Listener() {//省略代码}}), listener, threadPool, executor(primary), postWriteRefresh, postWriteAction);}}
performOnPrimary 直接看这个
public static void performOnPrimary(org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.BulkShardRequest request,IndexShard primary,UpdateHelper updateHelper,LongSupplier nowInMillisSupplier,MappingUpdatePerformer mappingUpdater,Consumer<ActionListener<Void>> waitForMappingUpdate,ActionListener<PrimaryResult<BulkShardRequest, BulkShardResponse>> listener,ThreadPool threadPool,String executorName,@Nullable PostWriteRefresh postWriteRefresh,@Nullable Consumer<Runnable> postWriteAction) {new ActionRunnable<>(listener) {private final Executor executor = threadPool.executor(executorName);private final BulkPrimaryExecutionContext context = new BulkPrimaryExecutionContext(request, primary);final long startBulkTime = System.nanoTime();@Overrideprotected void doRun() throws Exception {//只要所有的请求没有执行完while (context.hasMoreOperationsToExecute()) {if (executeBulkItemRequest(context,updateHelper,nowInMillisSupplier,mappingUpdater,waitForMappingUpdate,ActionListener.wrap(v -> executor.execute(this), this::onRejection)) == false) {//我们正在等待另一个线程上的映射更新,一旦完成,它将再次调用此操作,因此我们在这里爆发。return;}assert context.isInitial(); // either completed and moved to next or reset 要么完成并移至下一个,要么重置}primary.getBulkOperationListener().afterBulk(request.totalSizeInBytes(), System.nanoTime() - startBulkTime); finishRequest();}@Overridepublic void onRejection(Exception e) {//省略代码}private void finishRequest() {//省略代码}}.run();}
1、针对此节点上索引分片进行操作
static boolean executeBulkItemRequest(BulkPrimaryExecutionContext context,UpdateHelper updateHelper,LongSupplier nowInMillisSupplier,MappingUpdatePerformer mappingUpdater,Consumer<ActionListener<Void>> waitForMappingUpdate,ActionListener<Void> itemDoneListener) throws Exception {//,则获取IndexRequest对象,并创建SourceToParse对象,将相应参数传递给primary的applyIndexOperationOnPrimary方法进行索引操作final IndexRequest request = context.getRequestToExecute();final SourceToParse sourceToParse = new SourceToParse(request.id(),request.source(),request.getContentType(),request.routing(),request.getDynamicTemplates());//把文档数据保存到分片,返回结果保存结果result = primary.applyIndexOperationOnPrimary(version,request.versionType(),sourceToParse,request.ifSeqNo(),request.ifPrimaryTerm(),request.getAutoGeneratedTimestamp(),request.isRetry());//从结果中得到,需要更新索引Mapper的映射,则更新索引的mapperif (result.getResultType() == Engine.Result.Type.MAPPING_UPDATE_REQUIRED) {//省略代码} return true;}
(1) 组装Engine.Index
public Engine.IndexResult applyIndexOperationOnPrimary(long version,VersionType versionType,SourceToParse sourceToParse,long ifSeqNo,long ifPrimaryTerm,long autoGeneratedTimestamp,boolean isRetry) throws IOException {assert versionType.validateVersionForWrites(version);//针对索引的操作,包括更新TransLogreturn applyIndexOperation(getEngine(),UNASSIGNED_SEQ_NO,getOperationPrimaryTerm(),version,versionType,ifSeqNo,ifPrimaryTerm,autoGeneratedTimestamp,isRetry,Engine.Operation.Origin.PRIMARY,sourceToParse);}
private Engine.IndexResult applyIndexOperation(Engine engine,long seqNo,long opPrimaryTerm,long version,@Nullable VersionType versionType,long ifSeqNo,long ifPrimaryTerm,long autoGeneratedTimeStamp,boolean isRetry,Engine.Operation.Origin origin,SourceToParse sourceToParse) throws IOException {assert opPrimaryTerm <= getOperationPrimaryTerm(): "op term [ " + opPrimaryTerm + " ] > shard term [" + getOperationPrimaryTerm() + "]";ensureWriteAllowed(origin);Engine.Index operation;try {//组装indexoperation = prepareIndex(mapperService,sourceToParse,seqNo,opPrimaryTerm,version,versionType,origin,autoGeneratedTimeStamp,isRetry,ifSeqNo,ifPrimaryTerm,getRelativeTimeInNanos());Mapping update = operation.parsedDoc().dynamicMappingsUpdate();if (update != null) {return new Engine.IndexResult(update, operation.parsedDoc().id());}} catch (Exception e) {//省略代码}return index(engine, operation);}
private Engine.IndexResult index(Engine engine, Engine.Index index) throws IOException {active.set(true);final Engine.IndexResult result;final Engine.Index preIndex = indexingOperationListeners.preIndex(shardId, index);try {//省略代码//InternalEngine.index 逐条写入doc// Engine 封装了Lucene和translog的调用,对外提供读写接口.result = engine.index(preIndex);//省略代码} catch (Exception e) {//省略代码indexingOperationListeners.postIndex(shardId, preIndex, e);throw e;}indexingOperationListeners.postIndex(shardId, preIndex, result);return result;}
其中engine.index的子类是InternalEngine.index方法
(2)先添加到Lucene,成功后再添加到translog
@Overridepublic IndexResult index(Index index) throws IOException {assert Objects.equals(index.uid().field(), IdFieldMapper.NAME) : index.uid().field();final boolean doThrottle = index.origin().isRecovery() == false;try (ReleasableLock releasableLock = readLock.acquire()) {//如果是主分片上的操作,则生成新的Index对象if (index.origin() == Operation.Origin.PRIMARY) {index = new Index(index.uid(),index.parsedDoc(),generateSeqNoForOperationOnPrimary(index),index.primaryTerm(),index.version(),index.versionType(),index.origin(),index.startTime(),index.getAutoGeneratedIdTimestamp(),index.isRetry(),index.getIfSeqNo(),index.getIfPrimaryTerm());final boolean toAppend = plan.indexIntoLucene && plan.useLuceneUpdateDocument == false;if (toAppend == false) {advanceMaxSeqNoOfUpdatesOnPrimary(index.seqNo());}} else {//其他分片就标记为已见markSeqNoAsSeen(index.seqNo());}if (plan.indexIntoLucene || plan.addStaleOpToLucene) {//把数据更新到Lucene中indexResult = indexIntoLucene(index, plan);} else {indexResult = new IndexResult(plan.versionForIndexing,index.primaryTerm(),index.seqNo(),plan.currentNotFoundOrDeleted,index.id());}}if (index.origin().isFromTranslog() == false) {final Translog.Location location;//如果更新Lucene成功,则把索引数据放入到translog中if (indexResult.getResultType() == Result.Type.SUCCESS) {location = translog.add(new Translog.Index(index, indexResult));} //省略代码indexResult.setTranslogLocation(location);}//省略代码indexResult.setTook(relativeTimeInNanosSupplier.getAsLong() - index.startTime());indexResult.freeze();return indexResult;}
文档添加到Lucene
import org.apache.lucene.index.IndexWriter;private IndexResult indexIntoLucene(Index index, IndexingStrategy plan) throws IOException {try {if (plan.addStaleOpToLucene) { //添加addStaleDocs(index.docs(), indexWriter);} else if (plan.useLuceneUpdateDocument) { //更新assert assertMaxSeqNoOfUpdatesIsAdvanced(index.uid(), index.seqNo(), true, true);updateDocs(index.uid(), index.docs(), indexWriter);} else {// document does not exists, we can optimize for create, but double check if assertions are runningassert assertDocDoesNotExist(index, canOptimizeAddDocument(index) == false);addDocs(index.docs(), indexWriter);}return new IndexResult(plan.versionForIndexing, index.primaryTerm(), index.seqNo(), plan.currentNotFoundOrDeleted, index.id());} catch (Exception ex) {//省略代码}}private void addStaleDocs(final List<LuceneDocument> docs, final IndexWriter indexWriter) throws IOException {for (LuceneDocument doc : docs) {doc.add(softDeletesField); // soft-deleted every document before adding to Lucene}if (docs.size() > 1) {indexWriter.addDocuments(docs);} else {indexWriter.addDocument(docs.get(0));}}
在写入到transLog日志中,会先转成new Translog.Index 再添加到translog
public Location add(final Operation operation) throws IOException {final ReleasableBytesStreamOutput out = new ReleasableBytesStreamOutput(bigArrays);try {writeOperationWithSize(out, operation);final BytesReference bytes = out.bytes();try (ReleasableLock ignored = readLock.acquire()) {ensureOpen();//省略代码return current.add(bytes, operation.seqNo());}}
} private ReleasableBytesStreamOutput buffer;/***将给定的字节添加到具有指定序列号的转录日志中;返回字节写入到的位置。* @param data the bytes to write 要写入的字节数* @param seqNo the sequence number associated with the operation 与操作关联的序列号* @return the location the bytes were written to 字节写入到的位置* @throws IOException if writing to the translog resulted in an I/O exception*/public Translog.Location add(final BytesReference data, final long seqNo) throws IOException {//首先检查缓冲的字节数是否超过了forceWriteThreshold阈值,如果超过了,则调用writeBufferedOps方法将缓冲的操作写入。long bufferedBytesBeforeAdd = this.bufferedBytes;if (bufferedBytesBeforeAdd >= forceWriteThreshold) {writeBufferedOps(Long.MAX_VALUE, bufferedBytesBeforeAdd >= forceWriteThreshold * 4);}final Translog.Location location;synchronized (this) {ensureOpen();//代码确保buffer不为null,if (buffer == null) {buffer = new ReleasableBytesStreamOutput(bigArrays);}//数据写入缓冲区。然后更新minSeqNo和maxSeqNo的值assert bufferedBytes == buffer.size();final long offset = totalOffset;totalOffset += data.length();data.writeTo(buffer);assert minSeqNo != SequenceNumbers.NO_OPS_PERFORMED || operationCounter == 0;assert maxSeqNo != SequenceNumbers.NO_OPS_PERFORMED || operationCounter == 0;minSeqNo = SequenceNumbers.min(minSeqNo, seqNo);maxSeqNo = SequenceNumbers.max(maxSeqNo, seqNo);//并将seqNo添加到nonFsyncedSequenceNumbers中。操作计数器递增nonFsyncedSequenceNumbers.add(seqNo);operationCounter++;assert assertNoSeqNumberConflict(seqNo, data);//然后使用generation、offset和数据长度创建一个Translog.Location对象。location = new Translog.Location(generation, offset, data.length());//调用operationListener.operationAdded方法通知操作监听器有新的操作添加,并更新bufferedBytes的值。operationListener.operationAdded(data, seqNo, location);bufferedBytes = buffer.size();}return location;}
介绍一下Translog类
/**Translog 是每个索引的分片组件,它以持久的方式记录所有未提交的索引操作。
在 Elasticsearch 中,每个 {@link org.elasticsearch.index.engine.InternalEngine} 都有一个 Translog 实例。
此外,从 Elasticsearch 2.0 开始,引擎还会在每次提交时记录一个 {@link *TRANSLOG_UUID_KEY},以确保 lucene 索引与事务日志文件之间的强关联。
此 UUID 用于防止从属于其他引擎的事务日志中意外恢复。每个 Translog 只有一个 translog 文件打开,供 translog 生成 ID 随时引用的写入。
此 ID 将写入 {@code translog.ckp} 文件,该文件旨在适合单个磁盘块,因此文件的写入是原子的。
检查点文件在 translog 的每个 fsync 操作上写入,并记录写入的操作数、当前 translog 的文件生成、其 fsync 偏移量(以字节为单位)以及其他重要统计信息。当当前转录文件达到特定大小 ({@link IndexSettingsINDEX_TRANSLOG_GENERATION_THRESHOLD_SIZE_SETTING}) 时,或者当新旧操作之间明确分离时(在主要术语更改时),
将重新打开当前文件进行只读,并创建一个新的只写文件。
任何非最新的、只读的 translog 文件总是有一个与之关联的 {@code translog-{gen}.ckp},它是其上一个 {@code translog.ckp} 的同步副本,因此在灾难恢复中,最后一个 fsync 偏移量、操作数等仍会保留。
**/
public class Translog extends AbstractIndexShardComponent implements IndexShardComponent, Closeable {
}
![DocCMS keyword SQL注入漏洞复现 [附POC]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3691cd38256d47f9afbb3dfaedfb1c97.png)