一、线程接力
编写一个应用程序,除了主线程外,还有三个线程:first、second和third。first负责模拟一个红色的按钮从坐标(10,60)运动到(100,60);second负责模拟一个绿色的按钮从坐标(100,60)运动到(200,60)。third线程负责模拟一个蓝色的按钮从坐标(200,60)运动到(300,60)。
阅读并分析以下程序,将程序中的代码补充完整,编译并运行程序,查看结果。
package Demo01;import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;public class MoveButton extends Frame implements Runnable, ActionListener {// 用Thread类声明first,second,third三个线程对象Thread first, second, third;Button redButton, greenButton, blueButton, startButton;int distance = 10;MoveButton() {// 分别创建first,second,third三个线程,用当前窗口做为该线程的目标对象first = new Thread(this);second = new Thread(this);third = new Thread(this);redButton = new Button();greenButton = new Button();blueButton = new Button();redButton.setBackground(Color.red);greenButton.setBackground(Color.green);blueButton.setBackground(Color.blue);startButton = new Button("start");startButton.addActionListener(this);setLayout(null);add(redButton);redButton.setBounds(10, 60, 15, 15);add(greenButton);greenButton.setBounds(100, 60, 15, 15);add(blueButton);blueButton.setBounds(200, 60, 15, 15);add(startButton);startButton.setBounds(200, 100, 30, 30);setTitle("线程接力");setBounds(0, 0, 10, 200);setVisible(true);validate();addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {System.exit(0);}});}public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {try {// 分别启动三个线程first.start();second.start();third.start();} catch (Exception exp) {}}public void run() {while (true) {// 判断当前占有CPU资源的线程是否是firstif (Thread.currentThread() == first) {moveComponent(redButton);try {Thread.sleep(20);} catch (Exception exp) {}}
// 判断当前占有CPU资源的线程是否是secondif (Thread.currentThread() == second) {moveComponent(greenButton);try {Thread.sleep(10);} catch (Exception exp) {}}
// 判断当前占有CPU资源的线程是否是thirdif (Thread.currentThread() == third) {moveComponent(blueButton);try {Thread.sleep(20);} catch (Exception e) {}}}}public synchronized void moveComponent(Component b) {if (Thread.currentThread() == first) {while (distance > 100 && distance <= 300)try {wait();} catch (Exception exp) {}distance = distance + 1;b.setLocation(distance, 60);if (distance >= 100) {b.setLocation(10, 60);notifyAll();}}if (Thread.currentThread() == second) {while ((distance >= 10 && distance < 100) || (distance >200 && distance <= 300))try {wait();} catch (Exception exp) {}distance = distance + 1;b.setLocation(distance, 60);if (distance > 200) {b.setLocation(100, 60);notifyAll();}}if (Thread.currentThread() == third) {while (distance >= 10 && distance < 200)try {wait();} catch (Exception exp) {}distance = distance + 1;b.setLocation(distance, 60);if (distance > 300) {distance = 10;b.setLocation(200, 60);notifyAll();}}}public static void main(String[] args) {new MoveButton().setLocationRelativeTo(null);}
}
二、线程的控制
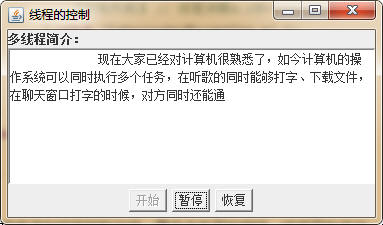
编写一个程序,动画显示文本域中的字符串。在窗体的南面添加三个按钮,为程序添加线程控制功能,要求点击开始按钮(startBtn),线程开始启动,文字逐个显示,并且将按钮状态改变为禁用(因为线程不能重复启动);点击暂停按钮(pauseBtn),线程暂停,文字显示停止;点击恢复按钮(resumeBtn),线程恢复运行,文字继续显示。当线程执行完毕后,恢复开始按钮的状态为可用。程序运行界面如下图所示:
package Demo01;import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.border.BevelBorder;public class RunnableDemo extends JFrame implements Runnable, ActionListener {private JTextArea textArea; // 文本域组件JLabel label;Button startBtn, pauseBtn, resumeBtn;Panel panel;Thread thread;boolean move = false;// 动画显示的文本字符串private String introduction = "现在大家已经对计算机很熟悉了,如今计算机的操作" + "系统可以同时执行多个任务,在听歌的同时能够打字、下载文件,在聊天窗口打"+ "字的时候,对方同时还能通过视频看到你;听到你。这一切都是使用多任务实现" + "的,Java语言使用多线程实现一个程序中的多个任务同时运行。程序员可以在程"+ "序中执行多个线程,每一个线程完成一个功能,并与其他线程并发执行,这种机" + "制被称为多线程。";public static void main(String args[]) {new RunnableDemo().setLocationRelativeTo(null); // 创建本类实例对象}public RunnableDemo() {setTitle("线程的控制");label = new JLabel("多线程简介:"); // 标签组件getContentPane().add(label, BorderLayout.NORTH);// 添加标签到窗体 textArea = new JTextArea("\t"); // 初始化文本域组件textArea.setBorder(new BevelBorder(BevelBorder.LOWERED));// 设置边框textArea.setLineWrap(true); // 设置自动折行getContentPane().add(textArea, BorderLayout.CENTER);// 添加文本域组件到文本框startBtn = new Button("开始");pauseBtn = new Button("暂停");resumeBtn =new Button("恢复");startBtn.addActionListener(this);pauseBtn.addActionListener(this);resumeBtn.addActionListener(this);panel = new Panel();panel.add(startBtn);panel.add(pauseBtn);panel.add(resumeBtn);getContentPane().add(panel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);setBounds(0, 0, 383, 225); // 设置窗体大小位置setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);setVisible(true); // 显示窗体}/** Runnable接口方法,是线程的执行方法 */@Overridepublic void run() {textArea.setText("\t");String[] intros = introduction.split(""); // 将字符串分割为数组for (String ch : intros) { // ForEach遍历字符串数组while (!move) {try {synchronized (this) {wait();}} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}textArea.append(ch); // 添加一个字符到文本域try {Thread.sleep(100); // 线程休眠0.1秒} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}startBtn.setEnabled(true);}@Overridepublic void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {if (e.getSource() == startBtn) {thread = new Thread(this);thread.start();move = true;startBtn.setEnabled(false);} else if (e.getSource() == pauseBtn) {move = false;} else if (e.getSource() == resumeBtn) {move = true;synchronized (this) {notifyAll();}}}
}







![[Linux版本Debian系统]安装cuda 和对应的cudnn以cuda 12.0为例](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8dc2005cc7104af4a6e54310a0158187.png)