目录
- 动态路由
- 动态路由简介
- 为什么需要动态路由
- 动态路由基本原理
- 路由协议的分类
- 距离向量路由协议
- RIPv1
- RIP简介
- RIPv1的主要特征
- RIPv1的基本配置
- RIPv1配置案例
- 被动接口
- 单播更新
- 使用子网地址
- RIPv2
- RIPv2的基本配置
- RIPv2配置案例
- RIPv2的高级配置
- 与RIPv1的兼容性
- 手工路由汇总
- 触发更新
- MD5认证
动态路由
动态路由简介
为什么需要动态路由
- 如果采用静态路由配置路由器R1,到达主机B的数据包将从路由器R2通过。当路由器R1和R2之间的连接出现故障时,主机A和主机B将无法通信,即使实际上还存在另外一条通路。管理员也可以立即重新配置路由器,改变路由表,使得数据包从路由器R3经过。然而如果这是一个规模庞大的网络(例如是Internet),经常会有链路在断开或恢复,管理员根本无法完成如此庞大的工作。这时可以采用动态路由协议。
- 动态路由协议能够动态地反映网络的状态,当网络发生变化时,网络中的路由器会把这个消息通告给其他的路由器,最终所有的路由器将知道网络的变化,能及时调整路由表,从而保证数据包的正常传输。
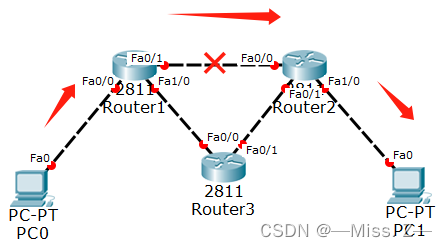
动态路由基本原理
- 动态路由协议的基本思想就是路由器之间要相互交换路由信息,一个动态路由协议都要有两个基本功能:维护自身的路由表、以路由更新的形式将路由信息及时发布给其他路由器。
- 动态路由的基本原理是依靠动态路由协议使得路由器之间能够互相交换路由信息。路由器和路由器之间交换路由信息时要遵守一组规则,这组规则就是动态路由协议。一个路由协议主要包括以下几项内容:
- 如何发送路由更新信息(怎么发送)?
- 更新信息包含哪些内容(发送什么)?
- 什么时候发送这此更新(何时发送)?
- 如何确定更新信息的接收者(发送给谁)?
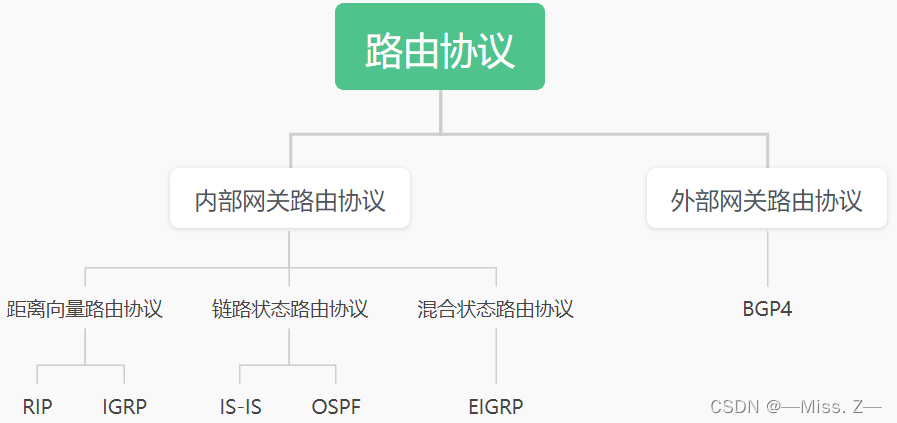
路由协议的分类
路由协议的分类根据路由协议是在什么路由器之间交换路由信息,路由协议可以分为两大类:内部网关协议(Interior Gateway Protocol,IGP)和外部网关协议(Exterior Gateway Protocol,EGP)。

- IGP内部网关协议运行在一个自治系统(Autonomous System,AS)中,该类路由协议用于同一 AS内部的路由器之间交换路由信息。所谓自治系统可被认为是一个公共管理部门下的一组网络设备,例如一个ISP或一个公司的广域网就是一个自治系统。例如RIP、IGRP、EIGRP、OSPF都是IGP。
- EGP外部网关协议运行在各个自治系统之间,该类路由器协议用于不同AS的路由器之间交换路由信息。例如:因特网由成千上万的网络连接而成:各个ISP都有自己的自治系统。但各个自治系统都通过EGP连接在一起。
- 根据路由协议的工作原理,IGP还可以进一步分为距离向量路由(Distance Vector.DV)协议、链路状态路由(Link State,LS)协议和混合路由协议。距离向量路由协议主要有:RIP(Routing Information Protocol,路由信息协议)、IGRP(Interior Gateway Routing Protocol,内部网关路由协议);链路状态路由协议主要有OSPF(Open Shortest Path First,开放的最短路径优先协议)、IS-IS(Intermediate System-toIntermediate System,间系统到中间系统协议)、混合协议主要有EIGRP(Enhanced IGRP,增强型内部网关路由协议)。有的资料把EIGRP归类到距离向量路由协议中。
距离向量路由协议
RIPv1
- RIPv1是有类别路由协议,不支持VLSM和CIDR;RIPv2为无类别路由协议,支持VLSM,支持路由聚合与CIDR。
- RIPv1以广播的形式发送报文;RIPv2支持以广播或者组播(224.0.0.9)方式发送报文。
- RIPv1不支持认证;RIPv2支持明文认证和MD5密文认证。
RIP简介
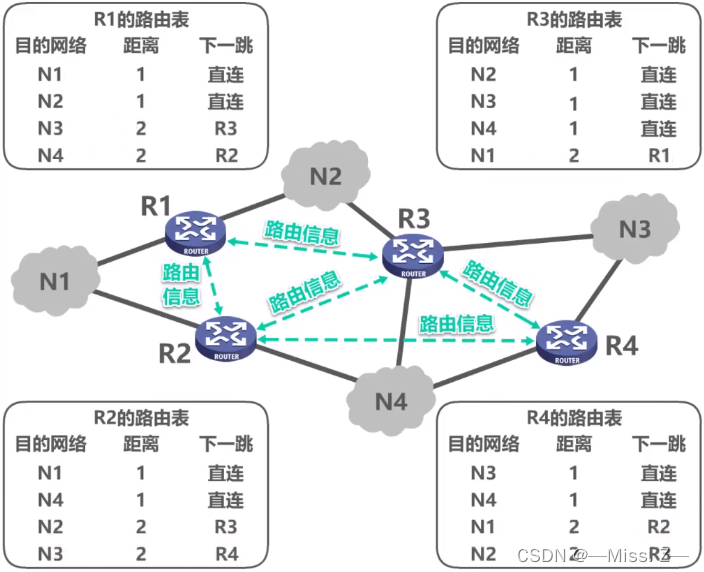
- RIP(Routing Information Protocol,路由信息协议)最大的特点是无论实现原理还是配置方法都非常简单。RIP中路由更新是通过广播(RIPv1)和组播(RIPv2)实现的。默认情况下,路由器每隔30秒利用UDP520端口向与它相连的网络广播自己的路由表,接到广播的路由器将收到的信息添加至自身的路由表中。每个路由器都如此传递路由信息,最终网络上所有的路由器都会得知全部的路由信息。
- 任何距离向量路由协议(如RIP),都有一个问题,即路由器不知道网络的全局情况。路由器必须依靠相邻的路由器来获得网络的可达信息。由于路由更新在网络上传播慢,将会导致网络收敛较慢,造成路由环路。如果网络上有路由环路,信息就会循环传递,永远不能到达目的地。为了避免这个问题,RIP 等距离向量算法通过下面5个机制来避免路由环路。
- 水平分割(Split Horizon)
水平分割保证路由器记住每一条路由信息的来源,并且不在收到这条信息的端口上再次发送它。这是保证不产生路由循环的最基本措施。 - 毒性逆转(Poison Reverse)
当一条路径信息变为无效之后,路由器并不立即将它从路由表中删除,而是将路由条目的度量值标记为16跳,即不可达的度量值将它广播出去。这样虽然增加了路由表的大小,但对消除路由循环很有帮助,它可以立即清除相邻路由器之间的任何环路。 - 定义最大跳数(DefiningaMaximum Count)
RIP的度量是基于跳数的,每经过一台路由器,路径的跳数加一。如此一来,跳数越多,路径就越长,RIP算法会优先选择跳数少的路径。RIP支持的最大跳数是15,跳数为16的网络被认为不可达。 - 触发更新(Triggered Update)
当路由表发生变化时,更新报文立即广播给相邻的所有路由器,而不是等待30秒的更新周期。同样,当一个路由器刚启动RIP时,它广播请求报文,收到此广播的相邻路由器立即应答一个更新报文,而不必等到下一个更新周期。这样,网络拓扑的变化会最快地在网络上传播开,减少了路由循环产生的可能性。RIPv1和RIPv2都支持触发更新。 - 抑制计时(Holddown Timer)
一条路由信息无效之后,一段时间内这条路由都处于抑制状态,即在一定时间内不再接收关于同一目的地址的路由更新,除非有更好的路径。因为路由器从一个网段上得知条路径失效,然后立即在另一个网段上得知这个路由有效。这个有效的信息往往是不正确的,抑制计时避免了这个问题,而且,当一条链路频繁起停时,抑制计时减少了路由的翻转(Flapping),增加了网络的稳定性。
收敛:对于路由协议,网络上的路由器在一条路径不能使用时必须经历决定替代路径的过程,是在最佳路径的判断上所有路由器达到一致的过程。当某个网络事件引起路由可用或不可用时,路由器就发出更新信息。路由更新信息遍及整个网络,引发重新计算最佳路径,最终达到所有路由器一致公认的最佳路径。这个过程即称为收敛。
收敛时间指从网络发生变化开始直到所有路由器识别到变化并针对该变化作出适应为止的这段时间。 收敛慢的路由算法会造成路径循环或网络中断。收敛过程既具协作性,又具独立性。路由器之间既需要共享路由信息,各个路由器也必须独立计算拓扑结构变化对各自路由过程所产生的影响。由于路由器独立更新网络信息以与拓扑结构保持一致,所以,也可以说路由器通过收敛来达成一致。收敛的有关属性包括路由信息的传播速度以及最佳路径的计算方法。可以根据收敛速度来评估路由协议。
收敛速度越快,路由协议的性能就越好。通常,RIP和IGRP收敛较慢,而EIGRP、OSPF和IS-IS收敛较快。
RIP应用于OSI网络七层模型的应用层。
RIPv1的主要特征
RIP最初定义在RFC1058中,它的关键特点包括以下内容:
- 它是距离向量路由协议;
- 它使用跳数作为度量值,而且最大跳数为15,超过15跳,则认为路由不可达,丢弃数据包;
- 采用广播方式(255.255.255.255)进行路由更新;
- 路由更新周期为30秒;
- RIP路由协议的管理距离为120
- 它是有类别的(Classful)路由协议
RIPv1的基本配置
在路由器上配置RIPv1协议分为两个步骤:
(1)启动RIP进程,默认为版本1。
命令语法:Router(config)#router rip
(2)定义要宣告的直连主类网络号。
命令语法:Router(config)#network <network>
第二个network表示网络地址
网络地址是IP地址中网络位不变,主机位置为0的地址(在子网掩码中,网络位全为1,主机位全为0)
由于RIPv1是有类别的协议,所以使用network命令时,只发布A类、B类或C类网络即可。
- distribute-list命令(配置路由过滤)
- 该命令用于指定有路由过滤功能的接口,在被指定的路由器的接口上,既可以过滤其接收的路由更新信息,还可以过滤输出的路由更新信息,它常与“passive-interface”一起使用,这样被指定的接口既可以过滤接收的路由信息,也可阻止该路由器更新信息的输出,即禁止该接口参加RIP。
它的命令格式为“distribute-list <接口>”
例如:router-test(config)#router rip (启动RIP协议)
router-test(config-router)# distribute-list 10 in FastEthemet0/1 (其中 10为已在全局配置模式下配置的访问控制列表,其中定义了路由过滤信息)
router-test(config)#end (end直接退回到特权用户模式)
router-test #
- distance命令 (配置管理距离)。
该命令用来配置或改变RIP的管理距离,管理距离用来测量路由的可信度,该值越小则可信度越高,RIP的默认距离值是120,有效的管理距离值是1 ~255。
它的命令格式为“distanc<管理距离 >”
如在全局配置模式下:
router-test(config) #router rip
router-test(config-router)#distance 100(配置管理距离为100)
router-test(config-router)#exit
router-test(config)#exit
router-test #
RIPv1配置案例
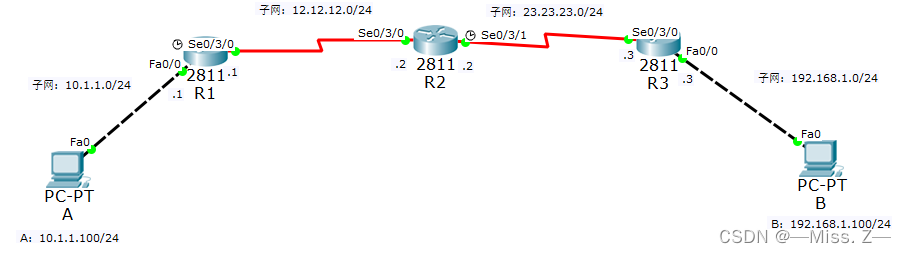
使用RIPv1版本进行配置
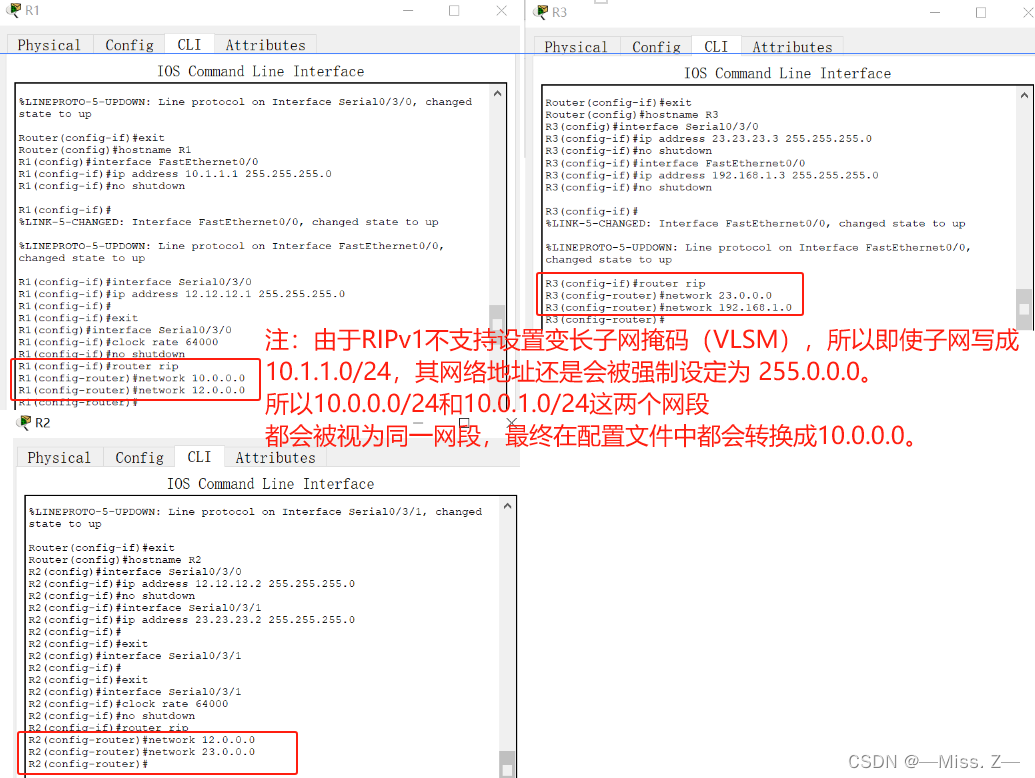
路由器R1的配置:
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#hostname R1
R1(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0
R1(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#interface Serial0/3/0
R1(config-if)#ip address 12.12.12.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#router rip
R1(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0
R1(config-router)#network 12.0.0.0
R1(config-router)#
路由器R2的配置:
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#hostname R2
R2(config)#interface Serial0/3/0
R2(config-if)#ip address 12.12.12.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#interface Serial0/3/1
R2(config-if)#ip address 23.23.23.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#interface Serial0/3/1
R2(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#router rip
R2(config-router)#network 12.0.0.0
R2(config-router)#network 23.0.0.0
R2(config-router)#
路由器R3的配置:
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#hostname R3
R3(config)#interface Serial0/3/0
R3(config-if)#ip address 23.23.23.3 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no shutdown
R3(config-if)#interface FastEthernet0/0
R3(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no shutdown
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#router rip
R3(config-router)#network 23.0.0.0
R3(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0
R3(config-router)#
- 使用“show ip route”命令来查看路由表

- 使用“debug ip rip”可以查看RIP路由协议的动态更新过程。为了立即看到效果,可以使用“clear ip route *”清除路由表。
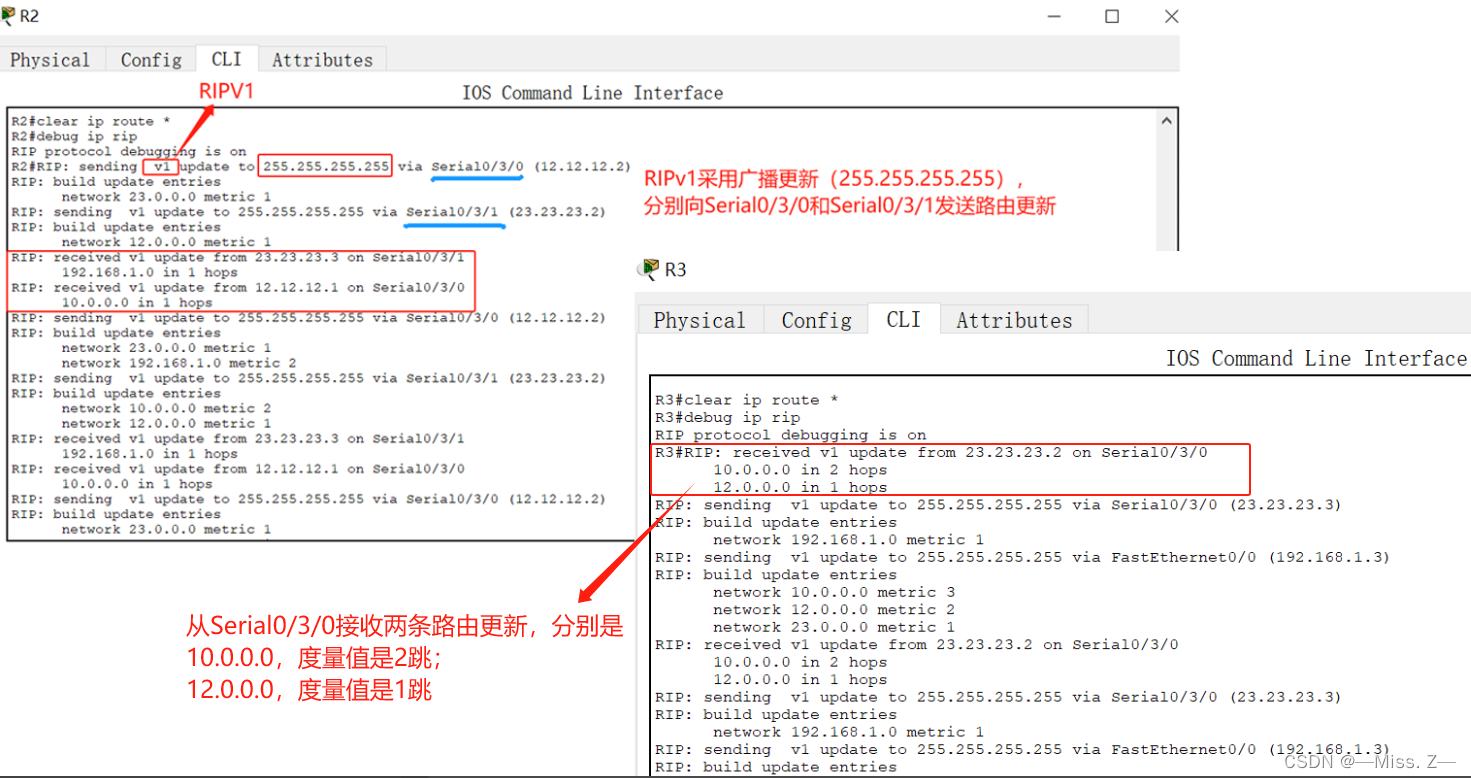
被动接口
- passive-interface命令(配置被动接口)。
所谓被动接口指,在路由器的某个接口上只接收路由更新却不发送路由更新。
它的命令格式为“passive-interface <接口>”
例如:router-test(config)#router rip
router-test(config-router)# passive-interface Serial0/3/0
router-test(config-router)#exit
router-test(config)#exit
router-test #
将R2左侧的Serial0/3/0配置成被动接口:
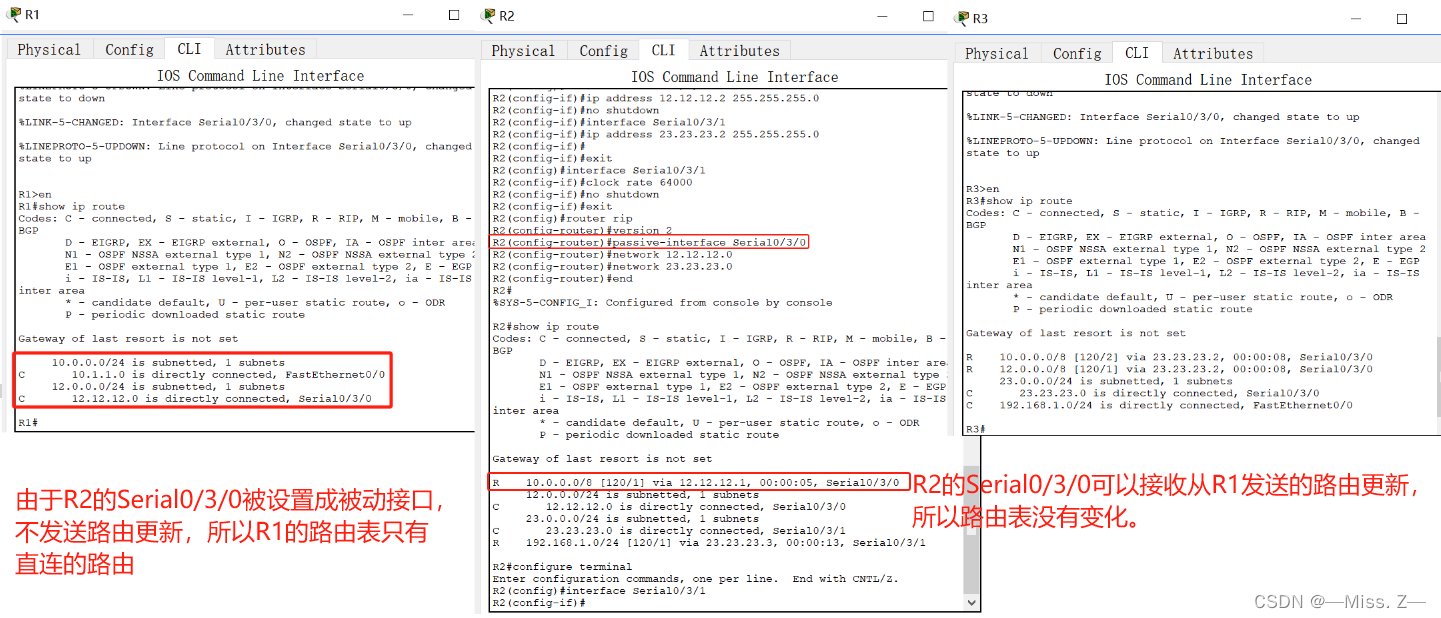
单播更新
- neighbor命令(配置邻居路由器)。
该命令用于指定邻居路由器,这样,在RIP路由器不容许发送广播包或是在网络技术不支持网络广播的特殊情况下,路由器仍可以单播的方式向该邻居路由器发送路由更新信息。
它的命令格式为“neighbor <邻居路由器的IP地址>”
router-test(config) #router rip
router-test(config-router)#neighbor 131.55.101.2
router-test(config-router)#exit
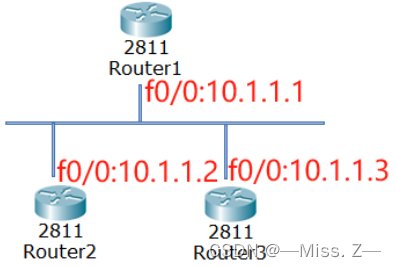
路由器Router1只想把路由更新发送到路由器Router3上,由于RIPv1路由协议采用广播更新,默认情况下,路由更新将发送给以太网上任何一个设备,为了防止这种情况发送,把路由器Router1的f0/0配置成被动接口,然而Router1还想把路由更新发送给Router3,这时候必须采用单播更新,为指定的相邻路由器Router3发送路由更新。
Router1(config)#router rip
Router1(config)#network 10.0.0.0
Router1(config)#passive-interface f0/0Router1(config)#neibor 10.1.1.3
使用子网地址
因为RIPv1的有类别特性,决定了它在路由器更新中不携带子网信息。
例如,当路由器R1向路由器R2发送路由更新10.1.1.0时,它将被自动汇总为10.0.0.0;当路由器R2收到这个更新时,它将丢弃更新,因为它的一个接口连接在网络10.0.0.0上,路由器R2将不接收这条路由。
该问题的解决方案就是整个网络所有地址必须在同一个主类网络,并且需要使用相同长度的子网掩码。这样,在RIPv1的路由更新中也可以传递子网信息了。
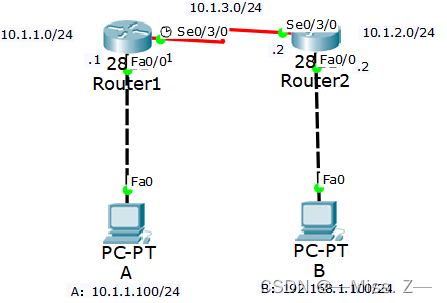
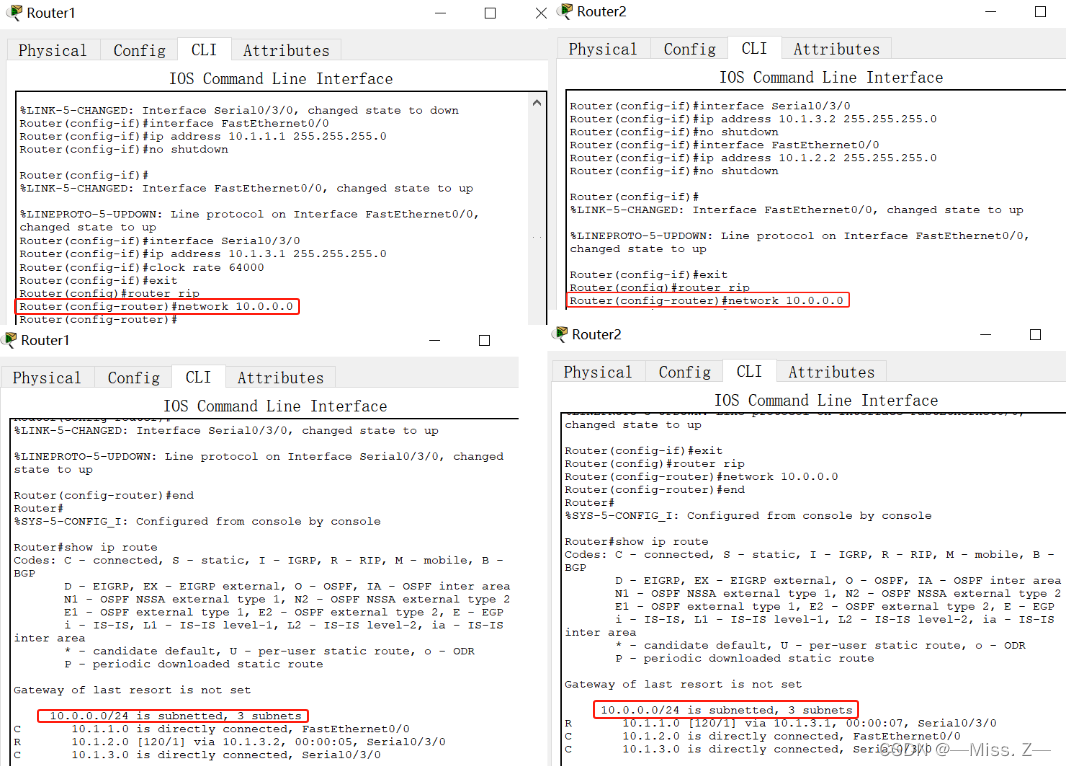
路由器R1的配置:
Router(config-if)#interface FastEthernet0/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#interface Serial0/3/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#clock rate 64000
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#router rip
Router(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0
Router(config-router)#
路由器R2的配置:
Router(config-if)#interface Serial0/3/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 10.1.3.2 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#interface FastEthernet0/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#router rip
Router(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0
从路由器R1和R2的输出可以看出,如果整个网络所有地址都在同一个主类网络,并且网络掩码长度相同,RIPv1确实可以传递子网信息。
RIPv2
RIPv2的基本配置
在路由器上配置RIPv2协议分为四个步骤:
(1)启动RIP进程。
命令语法:Router(config)#router rip
(2)声明版本号。
Router(config-router)#version 2
(3)宣告直连主类网络号
Router(config-router)#network <network-number>
(4)关闭自动汇总
Router(config)#no auto-summary
RIPv2配置案例

使用RIPv2版本进行配置
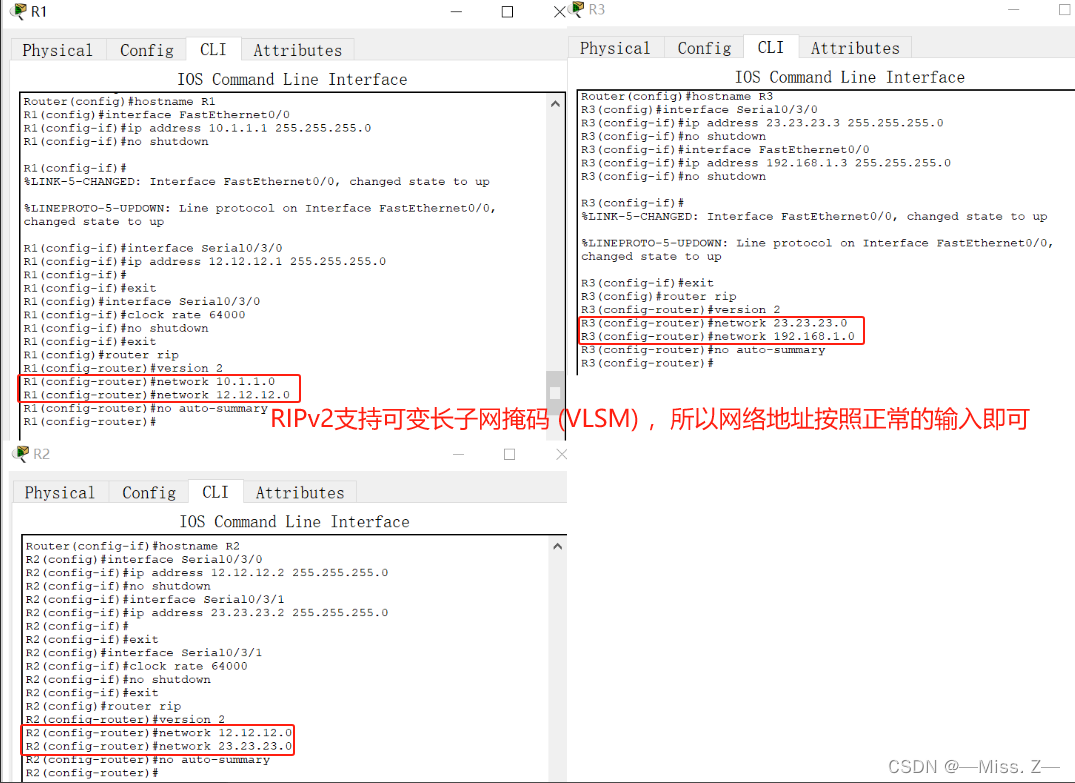
路由器R1的配置:
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#hostname R1
R1(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0
R1(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#interface Serial0/3/0
R1(config-if)#ip address 12.12.12.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#router rip
R1(config-router)#version 2
R1(config-router)#network 10.1.1.0
R1(config-router)#network 12.12.12.0
R1(config-router)#no auto-summary
路由器R2的配置:
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#hostname R2
R2(config)#interface Serial0/3/0
R2(config-if)#ip address 12.12.12.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#interface Serial0/3/1
R2(config-if)#ip address 23.23.23.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#router rip
R2(config-router)#version 2
R2(config-router)#network 12.12.12.0
R2(config-router)#network 23.23.23.0
R2(config-router)#no auto-summary
路由器R3的配置:
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#hostname R3
R3(config)#interface Serial0/3/0
R3(config-if)#ip address 23.23.23.3 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no shutdown
R3(config-if)#interface FastEthernet0/0
R3(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no shutdown
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#router rip
R3(config-router)#version 2
R3(config-router)#network 23.23.23.0
R3(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0
R3(config-router)#no auto-summary
RIPv2支持可变长子网掩码(VLSM),所以网络地址按照正常的输入即可。
测试连通性:主机A和主机B可正常通信

-
RIPv1和RIPv2的路由表对比

-
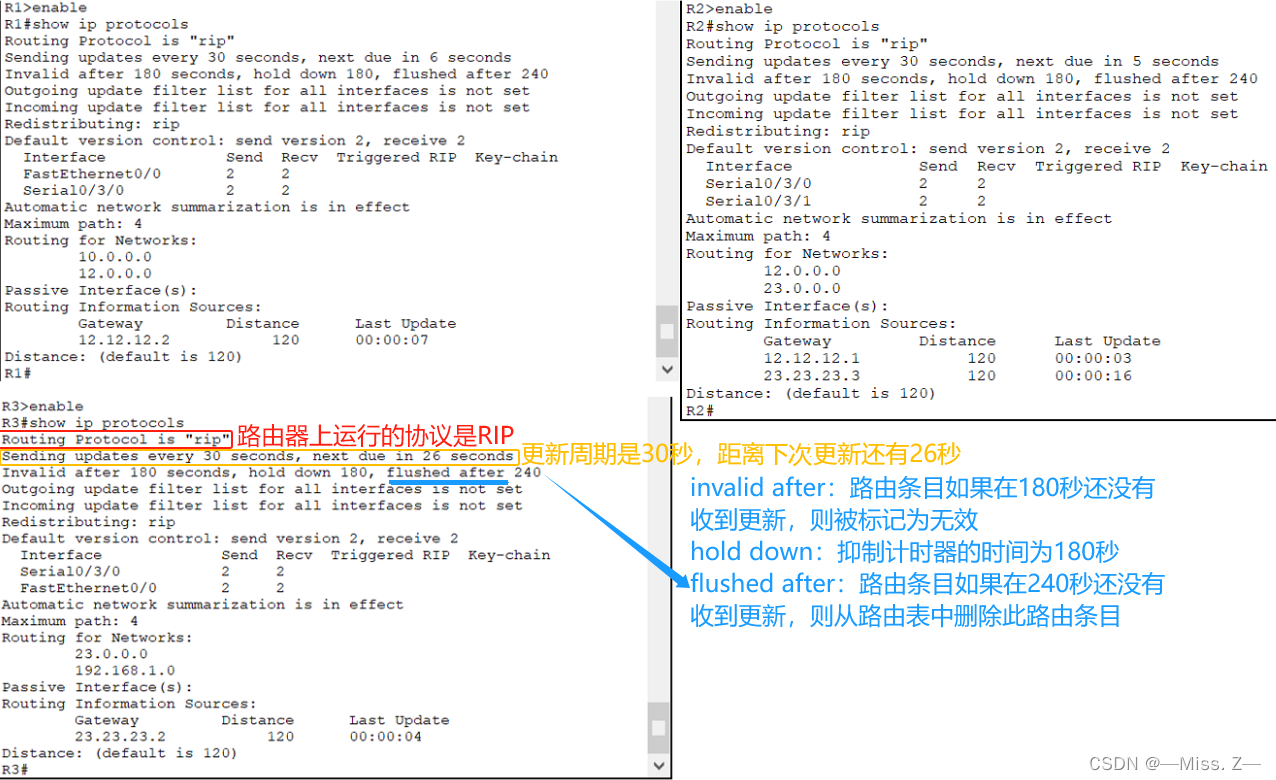
使用“show ip protocols”命令显示路由器上启用的IP路由协议,并对每种协议有用的信息给出一个汇总。
-
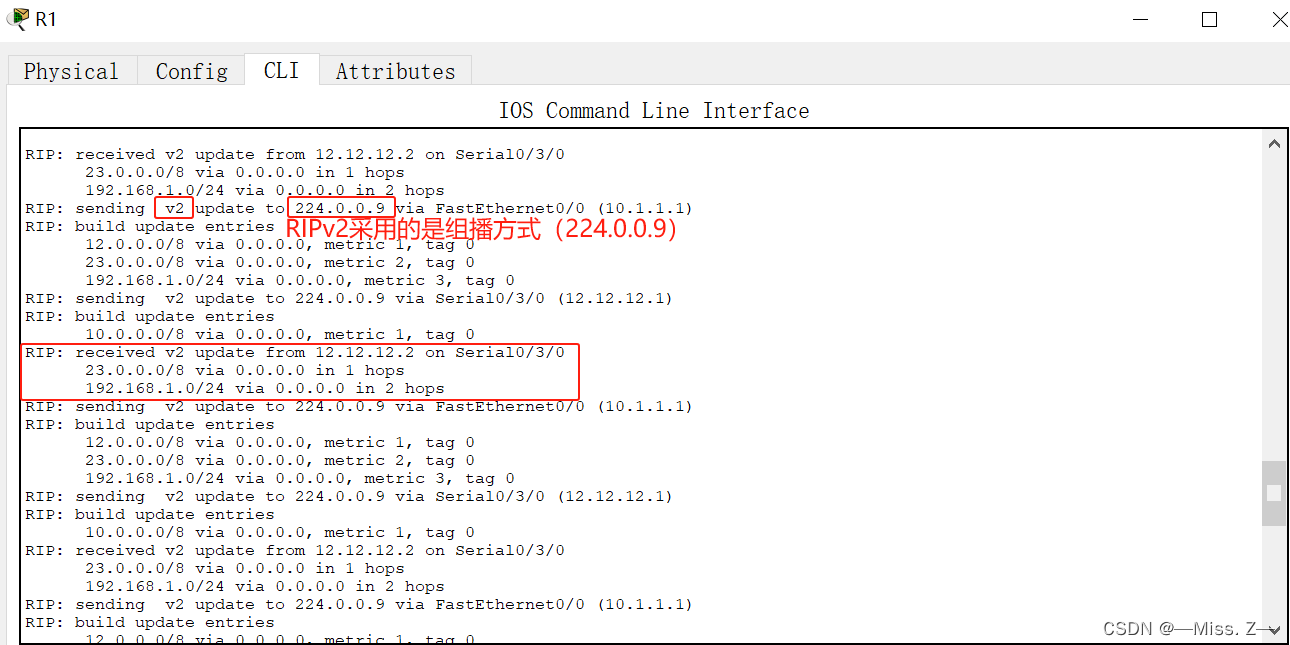
使用“debug ip rip”可以查看RIP路由协议的动态更新过程。
RIPv2的高级配置
输入“ip rip”开头的命令都显示有问题,不知道什么原因,待解决。
与RIPv1的兼容性
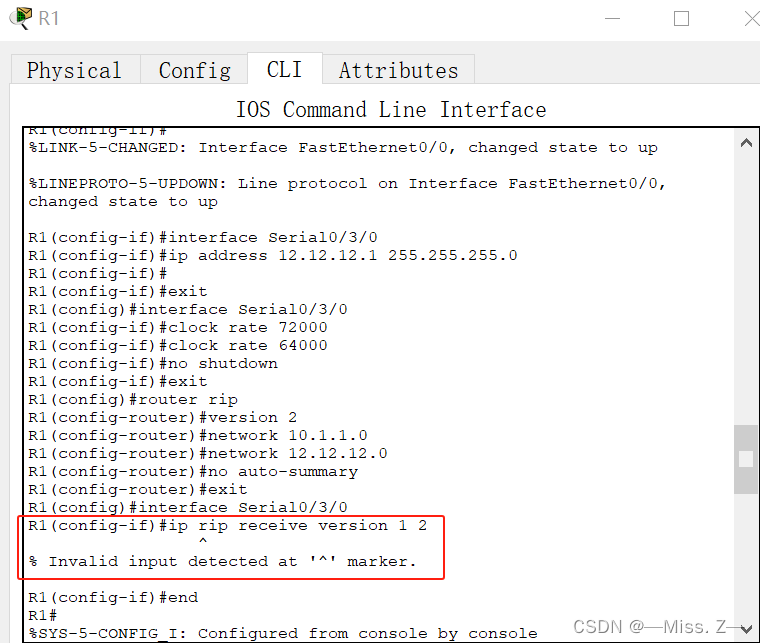
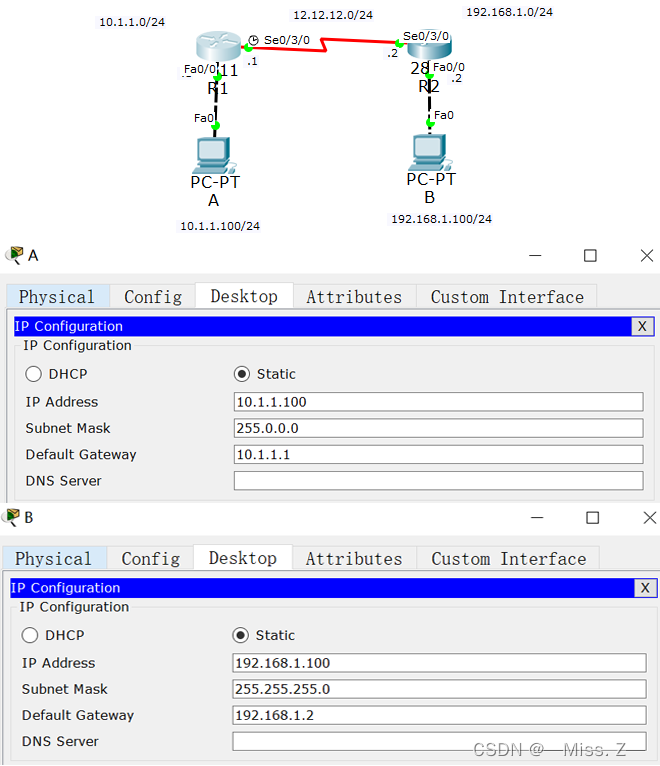
路由器R1的配置:
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#hostname R1
R1(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0
R1(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#interface Serial0/3/0
R1(config-if)#ip address 12.12.12.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#router rip
R1(config-router)#version 2
R1(config-router)#network 10.1.1.0
R1(config-router)#network 12.12.12.0
R1(config-router)#no auto-summary
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#interface Serial0/3/0
R1(config-if)ip rip receive version 1 2
路由器R2的配置:
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#hostname R2
R2(config)#interface Serial0/3/0
R2(config-if)#ip address 12.12.12.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#interface Serial0/3/1
R2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#router rip
R2(config-router)#network 12.0.0.0
R2(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0
R2(config-router)#
手工路由汇总
RIPv2的手工汇总的配置和EIGRP配置基本相同。依然会出现无效命令的提示。
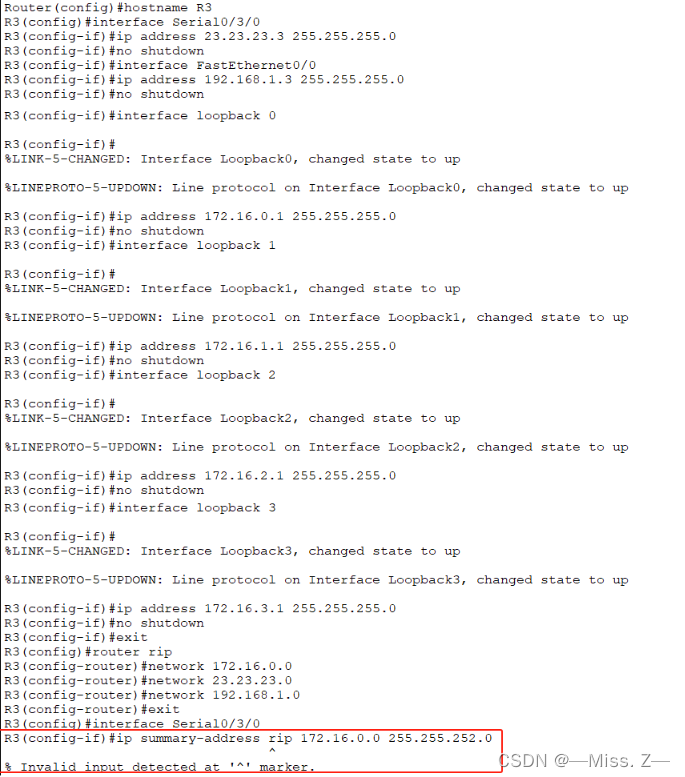
触发更新
RIP路由协议支持触发更新,这也是避免环路的一种方法。实现方法很简单,只需在接口下输入下面命令即可:R1(config-if) # ip rip triggered
注意:ip rip triggered 命令不能在以太口上使用


MD5认证
RIPv2支持明文和密文认证。密文认证是一种比较安全的认证方法,所以,这里仅讨论密文认证。RIPv2密文认证采用MD5认证,认证的配置和EIGRP的认证基本相同。

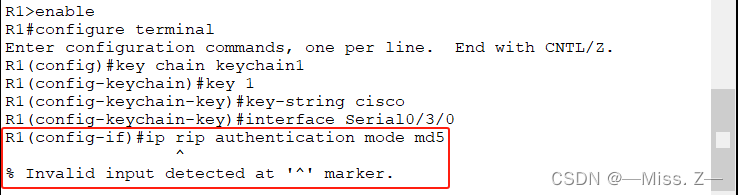
路由器R1的配置:
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#hostname R1
R1(config)#key chain keychain1 (keychain1为钥匙串名称)
R1(config-keychain)#key 1 (设置钥匙1,可以设置多个钥匙)
R1(config-keychain-key)#key-string cisco
R1(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0
R1(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#ip rip authentication mode md5 (打开rip认证,认证模式是明文,还有MD5方式)
R1(config-if)#ip rip authentication key-chain lgm (设置钥匙串名称)
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#interface Serial0/3/0
R1(config-if)#ip address 12.12.12.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R1(config-if)#ip rip authentication mode md5
R1(config-if)#ip rip authentication key-chain lgm
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#router rip
R1(config-router)#version 2
R1(config-router)#network 10.1.1.0
R1(config-router)#network 12.12.12.0
R1(config-router)#no auto-summary
路由器R2的配置:
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#hostname R2
R2(config)#key chain keychain2 (钥匙串名称可以和R1不同)
R2(config-keychain)#key 1 (钥匙ID和钥匙密码必须和R1一致)
R2(config-keychain-key)#key-string cisco
R2(config)#interface Serial0/3/0
R2(config-if)#ip address 12.12.12.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#ip rip authentication mode md5 (模式要设置一样)
R2(config-if)#ip rip authentication key-chain lgm
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#interface Serial0/3/1
R2(config-if)#ip address 23.23.23.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#clock rate 64000
R2(config-if)#ip rip authentication mode md5
R2(config-if)#ip rip authentication key-chain lgm
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#router rip
R2(config-router)#version 2
R2(config-router)#network 12.12.12.0
R2(config-router)#network 23.23.23.0
R2(config-router)#no auto-summary
路由器R3的配置:
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#hostname R3
R3(config)#key chain keychain3 (钥匙串名称可以和R1不同)
R3(config-keychain)#key 1 (钥匙ID和钥匙密码必须和R1一致)
R3(config-keychain-key)#key-string cisco
R3(config)#interface Serial0/3/0
R3(config-if)#ip address 23.23.23.3 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#ip rip authentication mode md5 (模式要设置一样)
R3(config-if)#ip rip authentication key-chain lgm
R3(config-if)#no shutdown
R3(config-if)#interface FastEthernet0/0
R3(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#ip rip authentication mode md5
R3(config-if)#ip rip authentication key-chain lgm
R3(config-if)#no shutdown
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#router rip
R3(config-router)#version 2
R3(config-router)#network 23.23.23.0
R3(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0
R3(config-router)#no auto-summary