- 👏作者简介:大家好,我是爱吃芝士的土豆倪,24届校招生Java选手,很高兴认识大家
- 📕系列专栏:Spring源码、JUC源码、Kafka原理、分布式技术原理
- 🔥如果感觉博主的文章还不错的话,请👍三连支持👍一下博主哦
- 🍂博主正在努力完成2023计划中:源码溯源,一探究竟
- 📝联系方式:nhs19990716,加我进群,大家一起学习,一起进步,一起对抗互联网寒冬👀
文章目录
- Zookeeper watcher
- 为什么学习源码
- watcher
- 图解
- 源码实现
Zookeeper watcher
为什么学习源码
公司要调用一个第三方的接口进行一个操作,但是这个操作可能会比较耗时,需要一段时间来响应,在第三方接口不能去修改的情况下,想去提升性能。
在这个过程中我们有很多方法去解决它,包括定时轮询,做事件响应机制,异步化的方式,即便第三方没办法修改的情况下,我们也可以在自己这边形成一个循环,形成一个高效的循环去处理这个调用。
在分析问题的时候,我们所学的事件的机制、异步化、基于线程的生产者消费者模型,其实它可以在刚刚的场景中去使用,比如我们发起这个请求,他可以将其放置在队列中,通过线程去和对应的接口做远程通信,这时我们可以解决我们这端的并发量的问题,他们第三方在不改变的情况下,我们这端某种程度上提升了一定的吞吐量,然后基于事件的机制就是我们调用第三方接口给返回的时候,基于这个返回结果发送一个通知去告诉调用者结果处理完了,你去拿这个结果做后续的处理
watcher
在api中,如果我们的客户端需要去实现watcher,就想zk做注册中心,配置中心的情况下,我们都需要实现在zk server上的配置变更和服务地址变更的通知 要去告诉我们的客户端,所有的客户端,你的数据发生了变化你需要采取一些行动,其实这就是一个通知的机制。
// standrd 标准监听 (一次性监听)ZooKeeper zooKeeper=new ZooKeeper("192.168.216.128:2181", 5000, new Watcher() {@Overridepublic void process(WatchedEvent watchedEvent) {//表示连接成功之后,会产生的回调时间}});
Stat stat=new Stat();
zooKeeper.getData("/first", new DataWatchListener(),stat); //针对当前节点class DataWatchListener implements Watcher{@Overridepublic void process(WatchedEvent watchedEvent) {String path=watchedEvent.getPath();//再次注册监听try {zooKeeper.getData(path,this,new Stat());} catch (KeeperException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}// 在3.6.1 还有着新的监听 持久化监听 和 持久化递归监听
// 持久化监听:只需要注册一次事件
// 持久化递归监听:其子节点发生变化,都会触发监听// 默认情况下,是递归持久化监听
ZooKeeper.addWatch("path",new DataWatchListener(),Add.WatchMode.PERSISTENT_RECURSIVE)
图解
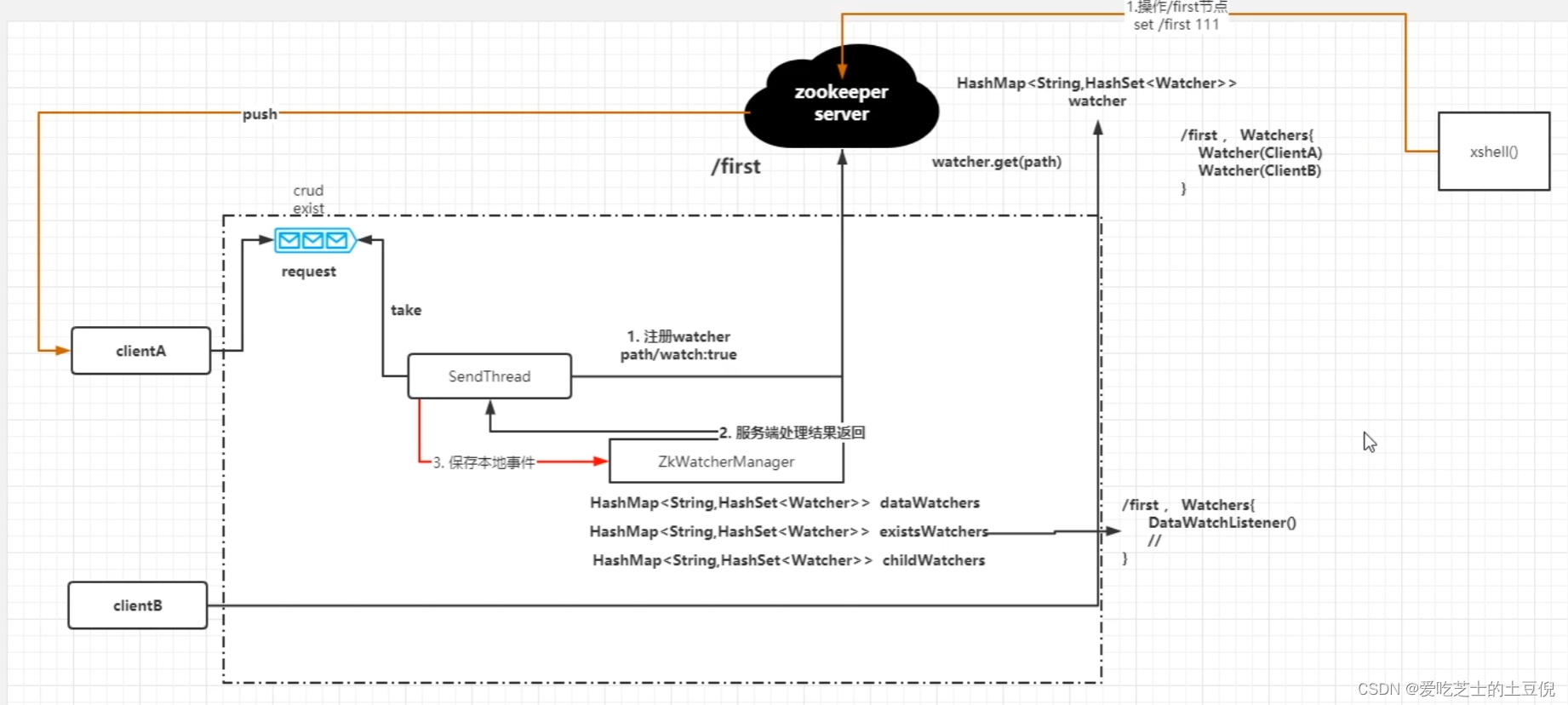
首先客户端要发起一个请求,客户端所有的请求先发到阻塞队列中,然后一个 SendThread线程 去轮询队列,通过take的方式,可以发现异步的方式能够很大程度上的提升整个的处理性能,发送过来的任务是一个request,它里面可以包括 crud exist等,我们后续的请求实际上就是NIO,实际上会将请求转换成序列化以后,自己会实现一个序列化机制,然后将这个请求发送到服务端,这个请求要做的就是 注册 watcher 带的内容是 path/watch:true,发送到服务端之后,因为客户端和服务端建立好连接以后,会维持这个会话,所以最终服务端会保存这个watcher,将其存储在HashMap中。
之所以是HashMap<String,HashSet> 是因为可能有多个客户端。
当注册成功会给一个返回,并且这个动作是异步化的操作。
然后客户端这边也需要存储一个事件的管理 提供了一个类 ZkWatcherManager,通过一些集合去存储客户端那边锁对应的watcher
当我们通过xshell来修改zk上对应监听的路径节点时,此时会触发对应节点的变化,服务端会判断这个节点是否存在监听,也就是在这个hashmap中查询是否有watcher。
因为之间说过zk服务端和客户端实际上存在着一个会话,所以,最后直接push发送给客户端即可
通过上图可以发现,所有和网络通信相关的,都是采用异步(生产者消费者模型)
当然上图中还有一些地方没有说清除,具体如下:
当ZooKeeper服务器检测到某个Znode的状态发生变化时,会向对该Znode注册了Watcher的客户端发送一个通知消息。这个通知消息包含了变化的类型(例如数据内容的变化、子节点的变化等)以及该Znode的最新状态信息。
当客户端接收到Watcher通知后,它会根据通知消息中的信息进行相应的处理。具体地,如果客户端的ZkWatcherManager中有对应的Watcher对象,就会调用该Watcher的process方法来处理通知消息。在process方法中,客户端可以根据变化的类型和最新的状态信息来进行相应的操作。
举个例子,假设客户端在启动时对一个Znode注册了一个数据内容变化的Watcher。当该Znode的数据内容发生变化时,ZooKeeper服务器会向该客户端发送一个通知消息,并在消息中指明变化的类型是“数据内容的变化”,同时包含最新的数据内容。客户端的ZkWatcherManager会找到对应的Watcher对象,并调用它的process方法。在process方法中,客户端可以根据最新的数据内容进行相应的操作,比如重新获取数据内容、重新注册Watcher等。
源码实现
zookeeper.exists();
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public Stat exists(final String path, Watcher watcher) throws KeeperException, InterruptedException {final String clientPath = path;PathUtils.validatePath(clientPath); //节点校验// the watch contains the un-chroot pathWatchRegistration wcb = null;if (watcher != null) {wcb = new ExistsWatchRegistration(watcher, clientPath);}final String serverPath = prependChroot(clientPath);//请求头RequestHeader h = new RequestHeader();h.setType(ZooDefs.OpCode.exists);//请求对象ExistsRequest request = new ExistsRequest();request.setPath(serverPath); //firstrequest.setWatch(watcher != null); //true/false//response返回对象SetDataResponse response = new SetDataResponse();// cnxn 网络通信的负责处理的类ReplyHeader r = cnxn.submitRequest(h, request, response, wcb);if (r.getErr() != 0) {//返回的错误码去判断返回的结果if (r.getErr() == KeeperException.Code.NONODE.intValue()) {return null;}throw KeeperException.create(KeeperException.Code.get(r.getErr()), clientPath);}//返回statareturn response.getStat().getCzxid() == -1 ? null : response.getStat();}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public ReplyHeader submitRequest(RequestHeader h,Record request,Record response,WatchRegistration watchRegistration,WatchDeregistration watchDeregistration) throws InterruptedException {ReplyHeader r = new ReplyHeader();//构建Packet 数据包,主要是需要传递的内容(queuePacket 实际上在这里是要将一个数据包发送到队列中,这符合我么图解中说明的那样)Packet packet = queuePacket(h,r,request,response,null,null,null,null,watchRegistration,watchDeregistration);synchronized (packet) {// 加锁if (requestTimeout > 0) { //如果携带了请求超时时间. 带超时时间的等待// Wait for request completion with timeoutwaitForPacketFinish(r, packet);} else {// Wait for request completion infinitelywhile (!packet.finished) { //只要packet没有处理完成,那么一直调用wait等待。packet.wait(); //阻塞}}}if (r.getErr() == Code.REQUESTTIMEOUT.intValue()) {sendThread.cleanAndNotifyState();}return r;}---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public Packet queuePacket(RequestHeader h,ReplyHeader r,Record request,Record response,AsyncCallback cb,String clientPath,String serverPath,Object ctx,WatchRegistration watchRegistration,WatchDeregistration watchDeregistration) {Packet packet = null;// Note that we do not generate the Xid for the packet yet. It is// generated later at send-time, by an implementation of ClientCnxnSocket::doIO(),// where the packet is actually sent.packet = new Packet(h, r, request, response, watchRegistration);packet.cb = cb;packet.ctx = ctx;packet.clientPath = clientPath;packet.serverPath = serverPath;packet.watchDeregistration = watchDeregistration;// The synchronized block here is for two purpose:// 1. synchronize with the final cleanup() in SendThread.run() to avoid race// 2. synchronized against each packet. So if a closeSession packet is added,// later packet will be notified.synchronized (state) {if (!state.isAlive() || closing) {conLossPacket(packet);} else {// If the client is asking to close the session then// mark as closingif (h.getType() == OpCode.closeSession) {closing = true;}//添加到阻塞队列outgoingQueue.add(packet);}}// 唤醒处于阻塞在selector.select上的线程// 那么sendThread是在哪里初始化的呢?sendThread.getClientCnxnSocket().packetAdded();return packet;}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------//在zookeeper的构造方法里面
public ZooKeeper(String connectString,int sessionTimeout,Watcher watcher,boolean canBeReadOnly,HostProvider aHostProvider) throws IOException {this(connectString, sessionTimeout, watcher, canBeReadOnly, aHostProvider, null);}public ZooKeeper(.........// 客户端和服务端的一个连接cnxn = createConnection(connectStringParser.getChrootPath(),hostProvider,sessionTimeout,this,watchManager,getClientCnxnSocket(),canBeReadOnly);cnxn.start();}public void start() {//发送线程sendThread.start();//事件线程(触发事件的线程,// 也就是说当服务端触发了事件通知到客户端之后,客户端需要从本地的事件列表中去读取watcher,并且进行回调)eventThread.start();}// 后续就是一堆nio netty等流程的内容,暂不关注---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------public void processPacket(ServerCnxn cnxn, ByteBuffer incomingBuffer) throws IOException {// We have the request, now process and setup for nextInputStream bais = new ByteBufferInputStream(incomingBuffer);BinaryInputArchive bia = BinaryInputArchive.getArchive(bais);RequestHeader h = new RequestHeader();h.deserialize(bia, "header"); //反序列化headercnxn.incrOutstandingAndCheckThrottle(h);incomingBuffer = incomingBuffer.slice();//根据请求类型进行不同的处理if (h.getType() == OpCode.auth) {// 授权} else if (h.getType() == OpCode.sasl) {processSasl(incomingBuffer, cnxn, h);} else {if (shouldRequireClientSaslAuth() && !hasCnxSASLAuthenticated(cnxn)) {ReplyHeader replyHeader = new ReplyHeader(h.getXid(), 0, Code.SESSIONCLOSEDREQUIRESASLAUTH.intValue());cnxn.sendResponse(replyHeader, null, "response");cnxn.sendCloseSession();cnxn.disableRecv();} else {Request si = new Request(cnxn, cnxn.getSessionId(), h.getXid(), h.getType(), incomingBuffer, cnxn.getAuthInfo());int length = incomingBuffer.limit();if (isLargeRequest(length)) {// checkRequestSize will throw IOException if request is rejectedcheckRequestSizeWhenMessageReceived(length);si.setLargeRequestSize(length);}si.setOwner(ServerCnxn.me);submitRequest(si); //提交请求(异步有关系)}}}public void submitRequest(Request si) {enqueueRequest(si);}public void enqueueRequest(Request si) {// 有点类似限流的逻辑if (requestThrottler == null) {synchronized (this) {try {while (state == State.INITIAL) {wait(1000);}} catch (InterruptedException e) {LOG.warn("Unexpected interruption", e);}if (requestThrottler == null) {throw new RuntimeException("Not started");}}}requestThrottler.submitRequest(si);}public void submitRequest(Request request) {if (stopping) {//如果服务端在终止的过程,则删除这个请求LOG.debug("Shutdown in progress. Request cannot be processed");dropRequest(request);} else {submittedRequests.add(request);}}---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// 此时终于找到了一直轮询的线程了public void run() {try {while (true) {if (killed) {break;}// 到这里 一个典型的生产者消费者的方式才很清晰Request request = submittedRequests.take();if (Request.requestOfDeath == request) {break;}if (request.mustDrop()) {continue;}// Throttling is disabled when maxRequests = 0//节流阀是否处于关闭状态,=0表示关闭if (maxRequests > 0) {while (!killed) {if (dropStaleRequests && request.isStale()) {// Note: this will close the connectiondropRequest(request);ServerMetrics.getMetrics().STALE_REQUESTS_DROPPED.add(1);request = null;break;}//限流动作if (zks.getInProcess() < maxRequests) {break;}//等待.throttleSleep(stallTime);}}if (killed) {break;}// A dropped stale request will be nullif (request != null) {if (request.isStale()) {ServerMetrics.getMetrics().STALE_REQUESTS.add(1);}zks.submitRequestNow(request);}}} catch (InterruptedException e) {LOG.error("Unexpected interruption", e);}int dropped = drainQueue();LOG.info("RequestThrottler shutdown. Dropped {} requests", dropped);}public void submitRequestNow(Request si) {if (firstProcessor == null) {synchronized (this) {try {// Since all requests are passed to the request// processor it should wait for setting up the request// processor chain. The state will be updated to RUNNING// after the setup.while (state == State.INITIAL) {wait(1000);}} catch (InterruptedException e) {LOG.warn("Unexpected interruption", e);}if (firstProcessor == null || state != State.RUNNING) {throw new RuntimeException("Not started");}}}try {touch(si.cnxn);boolean validpacket = Request.isValid(si.type);if (validpacket) { //如果packet合法setLocalSessionFlag(si);//通过一个处理器链来处理这个请求// PrepRequestProcessor(SyncRequestProcessor(FinalRequestProcessor))//firstProcessor.processRequest(si);
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------//构建一个请求处理链路//单机环境的处理链路:PrepRequestProcessor(SyncRequestProcessor(FinalRequestProcessor))protected void setupRequestProcessors() {//最终的处理器RequestProcessor finalProcessor = new FinalRequestProcessor(this);//SyncRequestProcessor 同步处理器 将数据同步到本地磁盘RequestProcessor syncProcessor = new SyncRequestProcessor(this, finalProcessor);// 同步处理器最终会有一个 写入到快照文件,也就是需要设置自己的磁盘同步策略// 其实就是性能 和 一致性的取舍问题((SyncRequestProcessor) syncProcessor).start();//PrepRequestProcessor 预处理器firstProcessor = new PrepRequestProcessor(this, syncProcessor);((PrepRequestProcessor) firstProcessor).start();}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------if (si.cnxn != null) {incInProcess();}} else {LOG.warn("Received packet at server of unknown type {}", si.type);// Update request accounting/throttling limitsrequestFinished(si);new UnimplementedRequestProcessor().processRequest(si);}} catch (MissingSessionException e) {LOG.debug("Dropping request.", e);// Update request accounting/throttling limitsrequestFinished(si);} catch (RequestProcessorException e) {LOG.error("Unable to process request", e);// Update request accounting/throttling limitsrequestFinished(si);}}---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------case OpCode.exists: {lastOp = "EXIS";// TODO we need to figure out the security requirement for this!ExistsRequest existsRequest = new ExistsRequest();ByteBufferInputStream.byteBuffer2Record(request.request, existsRequest);path = existsRequest.getPath();if (path.indexOf('\0') != -1) {throw new KeeperException.BadArgumentsException();}//通过zk得到stat// 从这里可以看出来前面图解中说到的HashMap 里面的 Set<Watcher> 中存储的watcher其实是网络对象// 之所以这样去实现当path发生变化的时候,需要告诉所有的监视者,记住这个网络连接将数据返回出去就行了。Stat stat = zks.getZKDatabase().statNode(path, existsRequest.getWatch() ? cnxn : null);rsp = new ExistsResponse(stat);requestPathMetricsCollector.registerRequest(request.type, path);break;}public Stat statNode(String path, Watcher watcher) throws KeeperException.NoNodeException {Stat stat = new Stat();DataNode n = nodes.get(path);// 到这里才到图解中注册的流程if (watcher != null) {//服务端的注册的流程dataWatches.addWatch(path, watcher);}if (n == null) {throw new KeeperException.NoNodeException();}synchronized (n) {n.copyStat(stat);}updateReadStat(path, 0L);return stat;}public boolean addWatch(String path, Watcher watcher) {/*** watcher 表示当前的一个注册监听的一个连接* path 表示监听的路径*/return addWatch(path, watcher, WatcherMode.DEFAULT_WATCHER_MODE);}STANDARD(false, false),PERSISTENT(true, false),PERSISTENT_RECURSIVE(true, true);public static final WatcherMode DEFAULT_WATCHER_MODE = WatcherMode.STANDARD;// 接下来就是自然而然的保存了// 表示节点到watcher集合的映射private final Map<String, Set<Watcher>> watchTable = new HashMap<>();// 表示从watcher到所有节点的映射private final Map<Watcher, Set<String>> watch2Paths = new HashMap<>();public synchronized boolean addWatch(String path, Watcher watcher, WatcherMode watcherMode) {if (isDeadWatcher(watcher)) {LOG.debug("Ignoring addWatch with closed cnxn");return false;}Set<Watcher> list = watchTable.get(path);if (list == null) {// don't waste memory if there are few watches on a node// rehash when the 4th entry is added, doubling size thereafter// seems like a good compromiselist = new HashSet<>(4);// 保存watchTable.put(path, list);}list.add(watcher);Set<String> paths = watch2Paths.get(watcher);if (paths == null) {// cnxns typically have many watches, so use default cap herepaths = new HashSet<>();watch2Paths.put(watcher, paths);}//设置监听模式watcherModeManager.setWatcherMode(watcher, path, watcherMode);return paths.add(path);}// 此时就完成了整个服务端的一个保存---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// 在SendThread中 有一个叫readResponse 的方法void readResponse(ByteBuffer incomingBuffer) throws IOException {ByteBufferInputStream bbis = new ByteBufferInputStream(incomingBuffer);BinaryInputArchive bbia = BinaryInputArchive.getArchive(bbis);ReplyHeader replyHdr = new ReplyHeader();replyHdr.deserialize(bbia, "header");switch (replyHdr.getXid()) {case PING_XID:......case AUTHPACKET_XID:......case NOTIFICATION_XID:......default:break;}// If SASL authentication is currently in progress, construct and// send a response packet immediately, rather than queuing a// response as with other packets.if (tunnelAuthInProgress()) {GetSASLRequest request = new GetSASLRequest();request.deserialize(bbia, "token");zooKeeperSaslClient.respondToServer(request.getToken(), ClientCnxn.this);return;}Packet packet;synchronized (pendingQueue) {if (pendingQueue.size() == 0) {throw new IOException("Nothing in the queue, but got " + replyHdr.getXid());}packet = pendingQueue.remove();}/** Since requests are processed in order, we better get a response* to the first request!*/try {if (packet.requestHeader.getXid() != replyHdr.getXid()) {packet.replyHeader.setErr(KeeperException.Code.CONNECTIONLOSS.intValue());throw new IOException("Xid out of order. Got Xid " + replyHdr.getXid()+ " with err " + replyHdr.getErr()+ " expected Xid " + packet.requestHeader.getXid()+ " for a packet with details: " + packet);}packet.replyHeader.setXid(replyHdr.getXid());packet.replyHeader.setErr(replyHdr.getErr());packet.replyHeader.setZxid(replyHdr.getZxid());if (replyHdr.getZxid() > 0) {lastZxid = replyHdr.getZxid();}if (packet.response != null && replyHdr.getErr() == 0) {packet.response.deserialize(bbia, "response");}LOG.debug("Reading reply session id: 0x{}, packet:: {}", Long.toHexString(sessionId), packet);} finally {finishPacket(packet);}}在zookeeper.class中
public void register(int rc) {if (shouldAddWatch(rc)) {//如果服务端已经建立了映射关系,则需要在客户端建立好关系Map<String, Set<Watcher>> watches = getWatches(rc);synchronized (watches) {Set<Watcher> watchers = watches.get(clientPath);if (watchers == null) {watchers = new HashSet<Watcher>();watches.put(clientPath, watchers);}watchers.add(watcher);}}}/*
后续的流程,如果服务端返回成功的话,那么就保存好了,此时关系就建立好了,而触发监听的方式。服务端在一个地方发现数据发生变更的时候,直接在服务端找到一个对应的watcher,去推送消息就行了,客户端收到消息,判断消息类型,根据映射关系去找到watcher回调即可。
*/