一、 问题描述
在计算机科学与数学中,一个排序算法(英语:Sorting algorithm)是一种能将一串资料依照特定排序方式排列的算法。最常用到的排序方式是数值顺序以及字典顺序。有效的排序算法在一些算法(例如搜索算法与合并算法)中是重要的,如此这些算法才能得到正确解答。排序算法也用在处理文字资料以及产生人类可读的输出结果。基本上,排序算法的输出必须遵守下列两个原则:
- 输出结果为递增序列(递增是针对所需的排序顺序而言)
- 输出结果是原输入的一种排列、或是重组
——Wiki百科
在计算机科学中,排序算法是一种常见的算法任务,它的目标是将一组数据按照一定的顺序排列,通常是升序或降序。不同的排序算法可以根据不同的性能指标(例如执行时间、内存使用等)在不同的情况下表现出不同的性能特点。因此,我们需要一个程序来比较多种排序算法在给定数据集上的性能。
解决方案:我们将创建一个多种排序算法的比较程序,该程序具有以下功能:
- 随机生成数据集:程序将生成一个包含随机整数的数据集,以便对排序算法进行测试。
- 多种排序算法的实现:程序将实现多种排序算法,包括但不限于冒泡排序、插入排序、选择排序、快速排序、归并排序、希尔排序和堆排序。
- 计时性能比较:程序将使用不同的排序算法对生成的数据集进行排序,并记录每种算法的执行时间。
- 显示比较结果:程序将展示每种排序算法的执行时间,以便用户可以比较它们的性能。
用户将能够运行程序,选择不同的排序算法来测试,并获得性能比较的结果,从而更好地了解不同排序算法的优势和不足之处。这个程序可以帮助学生和研究者学习和理解排序算法的性能特点,以及在不同应用场景中选择合适的算法。
二、 设计思路
以下是项目目录结构图:
SortAlgorithms/
├── include/
│ ├── SortAlgorithm.h
│ ├── BubbleSort.h
│ ├── InsertionSort.h
│ ├── SelectionSort.h
│ ├── QuickSort.h
│ ├── MergeSort.h
│ ├── ShellSort.h
│ ├── HeapSort.h
│ └── STLsort.h
├── src/
│ ├── BubbleSort.cpp
│ ├── InsertionSort.cpp
│ ├── SelectionSort.cpp
│ ├── QuickSort.cpp
│ ├── MergeSort.cpp
│ ├── ShellSort.cpp
│ ├── HeapSort.cpp
│ └── STLsort.cpp
├── mainwindow.h
├── mainwindow.ui
├── mainwindow.cpp
└── main.cpp
- 创建排序算法抽象类和具体排序算法类:
创建一个抽象类(例如 SortAlgorithm),其中包含一个纯虚拟的 sort 函数,用于在具体的排序算法子类中实现。每个排序算法都将作为一个具体子类来实现这个接口,以确保每个算法都有相同的接口,便于比较。 - 生成随机测试数据:
设计一个函数来生成随机的测试数据集,这样每个排序算法都将使用相同的输入数据进行比较。这些数据应该包括不同大小的数组以及不同分布(例如随机、升序、降序)的数据,以测试每个算法的性能。 - 计时比较算法性能:
使用计时器来测量每个排序算法在不同输入数据上的执行时间。你可以使用 clock() 函数来实现计时功能,确保获得精确的执行时间。 - 主程序:
在主程序中,初始化待比较算法类的实例,并将不同排序算法的实例添加到其中。
调用各排序算法,进行排序,并输出耗时结果。 - Qt图形化界面:
运用Qt 创建图形化界面,提供交互与结果呈现。
三、 数据结构设计
排序算法抽象类(SortAlgorithm):
这是一个抽象基类,包含了所有排序算法的共同接口。其中,最重要的函数是 sort,用于对输入的数据进行排序。
排序算法子类:
对于每一种排序算法(例如冒泡排序、插入排序、选择排序、快速排序、归并排序、希尔排序、),都创建一个子类,继承自抽象类 SortAlgorithm,并实现 sort 函数。每个子类将包含算法的具体实现逻辑。
冒泡排序 (Bubble Sort):
冒泡排序是一种简单的比较排序算法,它通过不断交换相邻的元素将最大(或最小)的元素逐步移动到数组的末尾。
插入排序 (Insertion Sort):
插入排序是一种逐步构建有序序列的排序算法,它从未排序的元素中逐个取出元素并将其插入已排序的部分。
选择排序 (Selection Sort):
选择排序是一种简单的排序算法,它每次选择未排序部分中的最小(或最大)元素,并将其交换到已排序部分的末尾。
快速排序 (Quick Sort):
快速排序是一种分治排序算法,它通过选择一个元素作为基准,将数组分为两个子数组,然后递归地对子数组进行排序。
归并排序 (Merge Sort):
归并排序也是一种分治排序算法,它将数组递归分为两个子数组,然后将这些子数组合并成一个有序数组。
希尔排序 (Shell Sort):
希尔排序是一种改进的插入排序,它通过对数组的多个子序列进行排序,逐渐减小子序列的间隔,最终得到一个有序序列。
堆排序 (Heap Sort):
堆排序使用堆数据结构来排序数组,它首先将数组转换为一个最大堆或最小堆,然后逐个取出堆顶元素。
主程序(main):
主程序用于初始化排序算法的实例、性能比较器类,创建测试数据,然后调用比较函数,对不同排序算法进行性能比较。最后,展示比较结果供用户分析。
四、 功能函数设计
- generateRandomArray 函数:这个函数用于生成随机整数数组,它接受三个参数,分别是数组的大小 size、最小值 minValue 和最大值 maxValue。函数内部使用 rand 函数生成指定范围内的随机整数,并将这些整数存储在一个 vector 中,然后返回该 vector。
- main 函数:主函数首先初始化随机数种子,然后要求用户输入数据量大小 size,并生成一个包含随机整数的数组 Data。接着,它创建了一个包含各种排序算法对象的 vector,然后遍历这些排序算法,对随机生成的数组进行排序,并记录排序时间。最后,它输出每种排序算法的名称和执行时间。
- 各个排序算法的类和函数:代码中定义了多个排序算法的类,如 BubbleSort、InsertionSort 等,每个类都继承自 SortAlgorithm 基类,并实现了 sort 函数和 getName 函数。这些函数用于执行排序和获取排序算法的名称。
- SortAlgorithm 基类:这是一个抽象基类,包含纯虚函数 sort 用于执行排序和 getName 用于获取排序算法名称。其他排序算法的类都继承自这个基类。
五、 程序代码
// main.cpp#include "mainwindow.h"
#include <QApplication>int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {QApplication a(argc, argv);MainWindow w;w.setWindowTitle("DS 课程设计 zdy229074447");w.show();return a.exec();
}
// mainwindow.h#ifndef MAINWINDOW_H
#define MAINWINDOW_H#include <QMainWindow>QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
namespace Ui {class MainWindow;
}
QT_END_NAMESPACEclass MainWindow: public QMainWindow {Q_OBJECT
public:MainWindow(QWidget *parent = nullptr);~MainWindow();void onButtonConfirmClicked();
private:Ui::MainWindow *ui;
};#endif // MAINWINDOW_H
// mainwindow.cpp#include <QtWidgets>
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include "ui_mainwindow.h"
#include "include/SortAlgorithm.h"
#include "include/BubbleSort.h"
#include "include/InsertionSort.h"
#include "include/SelectionSort.h"
#include "include/QuickSort.h"
#include "include/MergeSort.h"
#include "include/ShellSort.h"
#include "include/HeapSort.h"
#include "include/STLsort.h"
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>// 产生随机数据
vector<int> generateRandomArray(int size, int minValue, int maxValue) {vector<int> arr;for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {int randomNum = rand() % (maxValue - minValue + 1) + minValue;arr.push_back(randomNum);}return arr;
}MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent): QMainWindow(parent), ui(new Ui::MainWindow) {ui->setupUi(this);// 查找输入框和按钮,并进行相应的设置或连接信号槽QLineEdit *inputDataSize = this->findChild<QLineEdit *>("Input_DataSize");QPushButton *buttonConfirm = this->findChild<QPushButton *>("Button_Confirm");if (inputDataSize) {inputDataSize->setPlaceholderText("请输入");}if (buttonConfirm) {// 连接按钮的点击信号到适当的槽函数connect(buttonConfirm, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &MainWindow::onButtonConfirmClicked);}
}// 槽函数,用于处理按钮点击事件
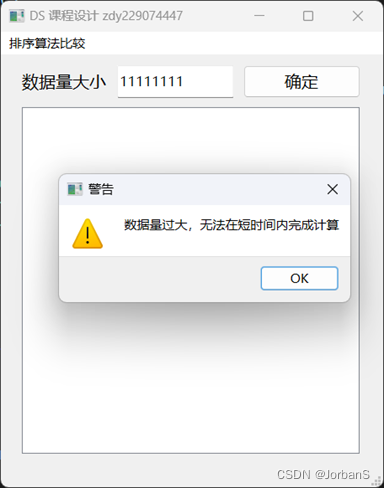
void MainWindow::onButtonConfirmClicked() {QLineEdit *inputDataSize = this->findChild<QLineEdit *>("Input_DataSize");if (inputDataSize) {QString dataSize = inputDataSize->text();if (dataSize.length() == 0) {QMessageBox warningBox;warningBox.setIcon(QMessageBox::Warning);warningBox.setWindowTitle("警告");warningBox.setText("未输入任何数据");warningBox.exec(); // 显示对话框并等待用户关闭return;}vector<SortAlgorithm*> sortAlgorithms; // 使用的排序算法if (dataSize.length() >= 8 || dataSize.toInt() > 2e6) {QMessageBox warningBox;warningBox.setIcon(QMessageBox::Warning);warningBox.setWindowTitle("警告");warningBox.setText("数据量过大,无法在短时间内完成计算");warningBox.exec(); // 显示对话框并等待用户关闭return;} else if (dataSize.toInt() <= 50000) {sortAlgorithms.push_back(new BubbleSort());sortAlgorithms.push_back(new InsertionSort());sortAlgorithms.push_back(new SelectionSort);}sortAlgorithms.push_back(new QuickSort);sortAlgorithms.push_back(new MergeSort);sortAlgorithms.push_back(new ShellSort);sortAlgorithms.push_back(new HeapSort);sortAlgorithms.push_back(new STLsort);srand(time(NULL));int minValue = -0x3f3f3f3f;int maxValue = 0x3f3f3f3f;vector<int> Data = generateRandomArray(dataSize.toInt(), minValue, maxValue);QTableWidget *tableResult = this->findChild<QTableWidget *>("Table_Result");if (tableResult) {tableResult->setRowCount(sortAlgorithms.size()); // 设置表格的行数tableResult->setColumnCount(2); // 设置表格的列数tableResult->setHorizontalHeaderLabels(QStringList() << "排序算法" << "执行用时/s");int row = 0;for (auto sortAlgorithm : sortAlgorithms) {vector<int> data(Data);clock_t startTime = clock(); // 打时间戳计时sortAlgorithm->sort(data);clock_t endTime = clock();double executionTime = double(endTime - startTime) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;QTableWidgetItem *algorithmItem = new QTableWidgetItem(QString::fromStdString(sortAlgorithm->getName()));QTableWidgetItem *timeItem = new QTableWidgetItem(QString::number(executionTime, 'f', 3));tableResult->setItem(row, 0, algorithmItem);tableResult->setItem(row, 1, timeItem);row ++;}}}
}MainWindow::~MainWindow() {delete ui;
}
// BubbleSort.h#ifndef BUBBLE_SORT_H
#define BUBBLE_SORT_H#include "SortAlgorithm.h"class BubbleSort: public SortAlgorithm {
public:void sort(vector<int>& arr) override;string getName() const override;
};#endif // BUBBLE_SORT_H
// HeapSort.h#ifndef HEAPSORT_H
#define HEAPSORT_H#include "SortAlgorithm.h"class HeapSort: public SortAlgorithm {
private:void heapify(vector<int>& arr, int n, int i);
public:void sort(vector<int>& arr) override;string getName() const override;
};#endif // HEAPSORT_H
// InsertionSort.h#ifndef INSERTION_SORT_H
#define INSERTION_SORT_H#include "SortAlgorithm.h"class InsertionSort: public SortAlgorithm {
public:void sort(vector<int>& arr) override;string getName() const override;
};#endif // NSERTION_SORT_H
// MergeSort.h#ifndef MERGE_SORT_H
#define MERGE_SORT_H#include "SortAlgorithm.h"class MergeSort: public SortAlgorithm {
private:void merge(vector<int>& arr, int l, int mid, int r);void mergeSort(vector<int>& arr, int l, int r);
public:void sort(vector<int>& arr) override;string getName() const override;
};#endif // MERGE_SORT_H
// QuickSort.h#ifndef QUICK_SORT_H
#define QUICK_SORT_H#include "SortAlgorithm.h"class QuickSort: public SortAlgorithm {
private:void quickSort(vector<int>& arr, int l, int r);
public:void sort(vector<int>& arr) override;string getName() const override;
};#endif // QUICK_SORT_H
// STLsort.h#ifndef STLSORT_H
#define STLSORT_H#include "SortAlgorithm.h"class STLsort: public SortAlgorithm {
public:void sort(vector<int>& arr) override;string getName() const override;
};#endif // STLSORT_H
// SelectionSort.h#ifndef SELECTION_SORT_H
#define SELECTION_SORT_H#include "SortAlgorithm.h"class SelectionSort: public SortAlgorithm {
public:void sort(vector<int>& arr) override;string getName() const override;
};#endif // SELECTION_SORT_H
// ShellSort.h#ifndef SHELLSORT_H
#define SHELLSORT_H#include "SortAlgorithm.h"class ShellSort: public SortAlgorithm {
public:void sort(vector<int>& arr) override;string getName() const override;
};#endif // SHELLSORT_H
// SortAlgorithm.h#ifndef SORT_ALGORITHM_H
#define SORT_ALGORITHM_H#include <vector>
#include <string>using namespace std;class SortAlgorithm {
public:virtual void sort(vector<int>& arr) = 0;virtual string getName() const = 0;
};#endif // SORT_ALGORITHM_H
// BubbleSort.cpp#include "../include/BubbleSort.h"void BubbleSort::sort(vector<int>& arr) {int n = arr.size();for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i ++)for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j ++)if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1])swap(arr[j], arr[j + 1]);
}string BubbleSort::getName() const {return "Bubble Sort";
}
// HeapSort.cpp#include "../include/HeapSort.h"void HeapSort::sort(vector<int>& arr) {int n = arr.size();// 建堆for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i --)heapify(arr, n, i);for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i --) {// 从堆顶取出元素swap(arr[0], arr[i]);heapify(arr, i, 0);}
}void HeapSort::heapify(vector<int>& arr, int n, int i) {int maxIndex = i;int l = i * 2 + 1;int r = i * 2 + 2;if (l < n && arr[l] > arr[maxIndex])maxIndex = l;if (r < n && arr[r] > arr[maxIndex])maxIndex = r;if (maxIndex != i) {swap(arr[i], arr[maxIndex]);heapify(arr, n, maxIndex);}
}string HeapSort::getName() const {return "Heap Sort";
}
// InsertionSort.cpp#include "../include/InsertionSort.h"void InsertionSort::sort(vector<int>& arr) {int n = arr.size();for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++) {int key = arr[i];int j = i - 1;while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {arr[j + 1] = arr[j];j --;}arr[j + 1] = key;}
}string InsertionSort::getName() const {return "Insertion Sort";
}
// MergeSort.cpp#include "../include/MergeSort.h"void MergeSort::sort(vector<int>& arr) {int l = 0, r = arr.size() - 1;mergeSort(arr, l, r);
}void MergeSort::merge(vector<int>& arr, int l, int mid, int r) {int n1 = mid - l + 1;int n2 = r - mid;vector<int> L(n1), R(n2);for (int i = 0; i < n1; i ++) L[i] = arr[l + i];for (int i = 0; i < n2; i ++) R[i] = arr[mid + 1 + i];int i = 0, j = 0, k = l;while (i < n1 && j < n2) {if (L[i] <= R[j]) arr[k ++] = L[i ++];else arr[k ++] = R[i ++];}while (i < n1) arr[k ++] = L[i ++];while (j < n2) arr[k ++] = R[j ++];
}void MergeSort::mergeSort(vector<int>& arr, int l, int r) {if (l >= r) return;int mid = l + r >> 1; // 位运算mergeSort(arr, l, mid);mergeSort(arr, mid + 1, r);merge(arr, l, mid, r);
}string MergeSort::getName() const {return "Merge Sort";
}
// QuickSort.cpp#include "../include/QuickSort.h"void QuickSort::sort(vector<int>& arr) {int l = 0, r = arr.size() - 1;quickSort(arr, l, r);
}void QuickSort::quickSort(vector<int>& arr, int l, int r) {if (l >= r) return;int pivot = arr[r]; // 取 arr[r] 为分界点int i = l - 1;for (int j = l; j <= r - 1; j ++)if (arr[j] <= pivot) {i ++;swap(arr[i], arr[j]);}swap(arr[i + 1], arr[r]);int inter = i + 1;quickSort(arr, l, inter - 1);quickSort(arr, inter + 1, r);
}string QuickSort::getName() const {return "Quick Sort";
}
// STLsort.cpp#include "../include/STLsort.h"
#include <algorithm>void STLsort::sort(vector<int>& arr) {std::sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());
}string STLsort::getName() const {return "STLsort";
}
// SelectionSort.cpp#include "../include/SelectionSort.h"void SelectionSort::sort(vector<int>& arr) {int n = arr.size();for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i ++) {int minIndex = i;for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j ++)if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex])minIndex = j;swap(arr[i], arr[minIndex]);}
}string SelectionSort::getName() const {return "Selecton Sort";
}
// ShellSort.cpp#include "../include/ShellSort.h"void ShellSort::sort(vector<int>& arr) {int n = arr.size();for (int gap = n / 2; gap > 0; gap >>= 1)for (int i = gap; i < n; i ++) {int tmp = arr[i];int j;for (j = i; j >= gap && arr[j - gap] > tmp; j -= gap)arr[j] = arr[j - gap];arr[j] = tmp;}
}string ShellSort::getName() const {return "Shell Sort";
}
// mainwindows.ui<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ui version="4.0"><class>MainWindow</class><widget class="QMainWindow" name="MainWindow"><property name="geometry"><rect><x>0</x><y>0</y><width>363</width><height>435</height></rect></property><property name="windowTitle"><string>MainWindow</string></property><widget class="QWidget" name="centralwidget"><widget class="QPushButton" name="Button_Confirm"><property name="geometry"><rect><x>230</x><y>10</y><width>111</width><height>31</height></rect></property><property name="styleSheet"><string notr="true">font: 12pt "Microsoft YaHei UI";</string></property><property name="text"><string>确定</string></property></widget><widget class="QLineEdit" name="Input_DataSize"><property name="geometry"><rect><x>110</x><y>10</y><width>111</width><height>31</height></rect></property><property name="styleSheet"><string notr="true">font: 10pt "Microsoft YaHei UI";</string></property></widget><widget class="QLabel" name="label"><property name="geometry"><rect><x>20</x><y>10</y><width>91</width><height>31</height></rect></property><property name="text"><string><html><head/><body><p><span style=" font-size:12pt;">数据量大小</span></p></body></html></string></property></widget><widget class="QTableWidget" name="Table_Result"><property name="geometry"><rect><x>20</x><y>50</y><width>321</width><height>331</height></rect></property><property name="styleSheet"><string notr="true">font: 10pt "Microsoft YaHei UI";</string></property></widget></widget><widget class="QStatusBar" name="statusbar"/><widget class="QMenuBar" name="menubar"><property name="geometry"><rect><x>0</x><y>0</y><width>363</width><height>24</height></rect></property><widget class="QMenu" name="menu"><property name="title"><string>排序算法比较</string></property></widget><addaction name="menu"/></widget></widget><resources/><connections/>
</ui>
六、 运行结果及分析
未输入内容时
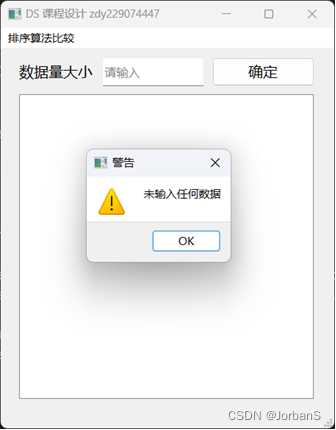
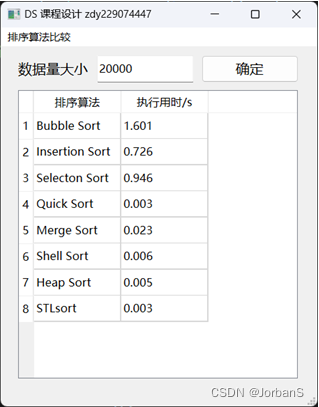
dataSize = 20000 时
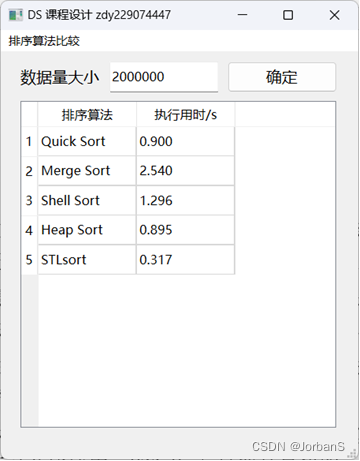
dataSize = 2000000 时
dataSize > 2000000 时
- Bubble Sort(冒泡排序):排序时间最长,执行用时约为 1.601 秒,这是因为冒泡排序是一种简单但效率较低的排序算法,其时间复杂度为 O(n^2),在大规模数据上性能较差。
- Insertion Sort(插入排序):稍快于冒泡排序,执行用时约为 0.726 秒。插入排序也是一种简单的排序算法,其时间复杂度也为 O(n^2),对于较小规模的数据效果较好。
- Selection Sort(选择排序):执行用时约为 0.946 秒,比冒泡排序慢一些,但仍然是一种基本的排序算法,时间复杂度也为 O(n^2)。
- Quick Sort(快速排序):执行用时非常快,仅为 0.003 秒。快速排序是一种高效的排序算法,其平均时间复杂度为 O(nlogn),在大规模数据上表现良好。
- Merge Sort(归并排序):执行用时约为 0.023 秒,与快速排序相比略慢。归并排序也是一种稳定的排序算法,其时间复杂度为 O(nlogn)。
- Shell Sort(希尔排序):执行用时约为 0.006 秒,介于插入排序和快速排序之间。希尔排序是一种改进的插入排序算法,其时间复杂度也在平均情况下为 O(n^1.3)。
- Heap Sort(堆排序):执行用时约为 0.005 秒,与归并排序和希尔排序相近。堆排序是一种不稳定的排序算法,其时间复杂度为 O(nlogn),但常数因子较小。
- STL sort(C++标准库中的排序算法):执行用时约为 0.003 秒,是所有算法中执行时间最短的,这是因为C++标准库中的排序算法通常高度优化,能够在不同情况下选择最合适的排序策略,因此性能较好。
总体而言,快速排序、归并排序和堆排序在大规模数据上表现良好,执行时间较短,而冒泡排序、插入排序和选择排序在大规模数据上效率较低。C++标准库中的排序算法通常是首选,因为它们是经过高度优化的。排序算法的选择应根据具体应用场景和数据规模来决定。
七、 设计心得
- 抽象基类的使用:在这个设计中,使用了抽象基类 SortAlgorithm 来定义排序算法的接口。这种抽象基类的使用使得添加新的排序算法变得非常容易,只需创建一个新的派生类,并实现 sort 和 getName 函数即可。这种设计符合面向对象的原则,使代码更加模块化和可扩展。
- 随机数据生成:生成随机数据用于性能测试是一个重要的步骤。这个程序中使用了 rand 函数来生成随机整数,但需要注意的是,这种方式生成的数据可能不具备真实数据的特性。在实际应用中,可以考虑使用更复杂的数据生成函数来模拟真实场景。
- 代码结构清晰:代码的模块化和结构清晰,每个排序算法都有自己的类和文件,使得代码易于理解和维护。此外,使用了标准的头文件和源文件分离的方式,有助于代码的组织和管理。
- 性能测试的重要性:通过对不同排序算法进行性能测试,可以更好地理解它们在不同情况下的表现。在实际项目中,性能测试是评估算法是否满足性能要求的重要步骤。这个程序提供了一个简单的性能测试框架,可以方便地扩展和使用。
- 选择合适的排序算法:根据性能测试结果,可以选择合适的排序算法来处理特定的数据集。不同的排序算法适用于不同的场景,因此了解它们的优劣势对于程序优化和性能提升非常重要。
- GUI交互:使用C++Qt编写直观的GUI进行交互,有助于用户的交互。
八、 参考资料
排序简介 OI Wiki (oiwiki.org) https://oi-wiki.org/basic/sort-intro/
排序算法 维基百科,自由的百科全书 (wikipedia.org) https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E6%8E%92%E5%BA%8F%E7%AE%97%E6%B3%95
![[DAU-FI Net开源 | Dual Attention UNet+特征融合+Sobel和Canny等算子解决语义分割痛点]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/8df44dcb68254860bc6cff17be93b66d.png)