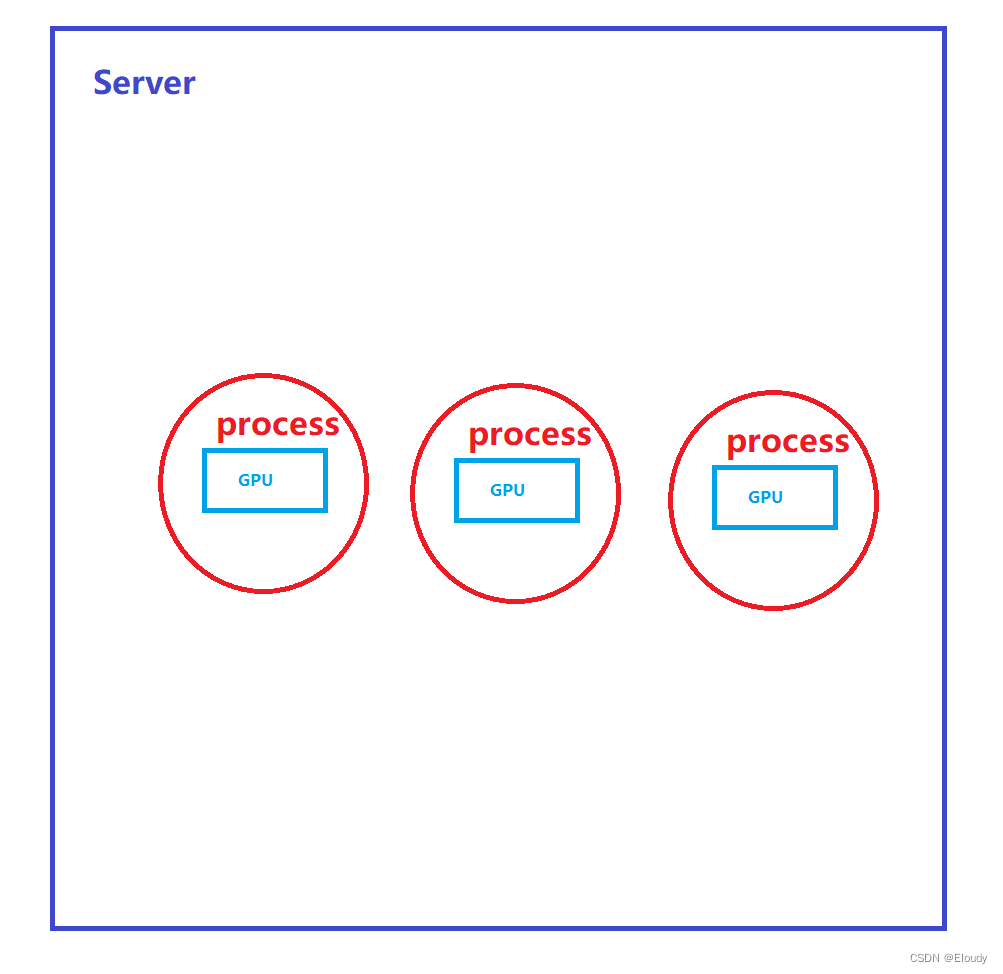
做了部分注释,比较乱
本示例结构:
1,源代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "nccl.h"
#include "mpi.h"
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/time.h>#define SOCKET_SIZE 1#if SOCKET_SIZE
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/tcp.h>
#include <netdb.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <poll.h>
#endifusing namespace std;#define MPI_CHECK(cmd) do { \int e = cmd; \if( e != MPI_SUCCESS ) { \printf("Failed: MPI error %s:%d '%d'\n", \__FILE__,__LINE__, e); \exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \} \
} while(0)#define CUDA_CHECK(cmd) do { \cudaError_t e = cmd; \if( e != cudaSuccess ) { \printf("Failed: Cuda error %s:%d '%s'\n", \__FILE__,__LINE__,cudaGetErrorString(e)); \exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \} \
} while(0)#define NCCL_CHECK(cmd) do { \ncclResult_t r = cmd; \if (r!= ncclSuccess) { \printf("Failed, NCCL error %s:%d '%s'\n", \__FILE__,__LINE__,ncclGetErrorString(r)); \exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \} \
} while(0)/* DJB2a是一种简单的哈希算法,由计算机科学家Daniel J. Bernstein设计。* 它被广泛用于哈希表等数据结构中。该算法通过遍历输入字符串的每个字符,* 并结合一个常数(通常是33),来计算字符串的哈希值。* 它在计算速度和哈希碰撞方面表现良好,但不适用于加密目的。
**/
static uint64_t getHostHash(const char* string) {// Based on DJB2a, result = result * 33 ^ charuint64_t result = 5381;for (int c = 0; string[c] != '\0'; c++){result = ((result << 5) + result) ^ string[c];}return result;
}static void getHostName(char* hostname, int maxlen) {gethostname(hostname, maxlen);//本函数声明于 /usr/include/unistd.hfor (int i=0; i< maxlen; i++) {if (hostname[i] == '.') {hostname[i] = '\0';return;}}
}float max__(float x, float y)
{return x>y? x:y;
}float sum__(float x, float y)
{return x + y;
}void print_vector(float* A, int n)
{for(int i=0; i<n; i++)printf("%.2f ", A[i]);
}void init_dev_vectors(float* A_d, float* B_d, int n, int rank, long long seed)
{float * A = (float*)malloc(n*sizeof(float));float * B = (float*)malloc(n*sizeof(float));//float * M = (float*)malloc(n*sizeof(float));//max[i] = max(A[i], B[i]);//float * S = (float*)malloc(n*sizeof(float));//sum[i] = sum(A[i], B[i]);srand(seed);for(int i=0; i<n; i++){A[i] = (rand()%100)/100.0f;B[i] = (rand()%100)/100.0f;//M[i] = max__(A[i], B[i]);//S[i] = sum__(A[i], B[i]);}printf("\nrank = %d, sendbuff =\n", rank); print_vector(A, n);
// printf("\nrank = %d, Sum =\n", rank); print_vector(S, n);cudaMemcpy(A_d, A, n*sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);cudaMemcpy(B_d, B, n*sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);free(A);free(B);
}void fetch_dev_vector(float* A_d, int n, int rank)
{float* A = (float*)malloc(n*sizeof(float));cudaMemcpy(A, A_d, n*sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);printf("rank = %d, recvbuff =\n", rank);print_vector(A, n);
}void get_seed(long long &seed)
{struct timeval tv;gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);seed = (long long)tv.tv_sec * 1000*1000 + tv.tv_usec;//only second and usecond;printf("useconds:%lld\n", seed);
}int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{int size = 16*16;//32*1024*1024;int myRank, nRanks, localRank = 0;//initializing MPIprintf("argc = %d\n", argc);MPI_CHECK(MPI_Init(&argc, &argv));//本行之后便进入多线程状态,线程数由 mpirun -np 4 ./a.out 的这个4来指定MPI_CHECK(MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myRank));// 本线程的线程序号:myRank = 0, 1, 2, 4-1;MPI_CHECK(MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &nRanks));// 本次启动mpi 程序的总线程数 nRanks==4;cout<< "nRanks="<< nRanks<<endl;//calculating localRank based on hostname which is used in selecting a GPUuint64_t hostHashs[nRanks];//每个rank的主机名字的hash值,占据一个 uint64_t 元素,存储于 hostHashs[myRank] 中;cout<<"nRanks = "<<nRanks<<endl;char hostname[1024];getHostName(hostname, 1024);//cout<<"Host Name is "<<hostname<<endl;hostHashs[myRank] = getHostHash(hostname);printf("myRank = %d, hostHash = %lx\n", myRank, hostHashs[myRank]);MPI_CHECK(MPI_Allgather(MPI_IN_PLACE, 0, MPI_DATATYPE_NULL, hostHashs, sizeof(uint64_t), MPI_BYTE, MPI_COMM_WORLD));//if(myRank==0)if(1){for(int i=0; i<nRanks; i++)printf("myRank = %d, hostHash[%d] = %lx\n", myRank, i, hostHashs[i]);}for (int p=0; p<nRanks; p++) {if (p == myRank) break;if (hostHashs[p] == hostHashs[myRank]) {printf("p=%d\n", p);localRank++;//本进程适合持有本地的第几张 gpu 卡}}printf("myRank = %d, localRank-- = %d\n", myRank, localRank);
/* TCP RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access) GDR (GPU Direct RDMA) 是一种技术,* 它允许在使用RDMA的网络上进行高性能的GPU内存之间的直接数据传输。* 这种技术可以通过网络直接在GPU之间传输数据,而无需将数据先传输到主机内存。* 这有助于减少数据传输的延迟和CPU的参与,从而提高了数据传输的效率。
**/ncclUniqueId id;ncclComm_t comm;float *sendbuff, *recvbuff;cudaStream_t s;//get NCCL unique ID at rank 0 and broadcast it to all othersif (myRank == 0){cout<<"start: id is"<<endl;for(int i=0; i<128; i++){if(id.internal[i]=='\0')break;printf("%d",id.internal[i]);}cout<<"start end"<<endl;ncclGetUniqueId(&id);//ncclGetUniqueId 是获得 an Internet socket address, 即,当前机器的ip和port,作为servercout<<" end: id is "<<endl;for(int i=0; i<128; i++){if(id.internal[i]=='\0')break;printf("%d",id.internal[i]);}cout<<"end end"<<endl;
#if SOCKET_SIZEcout<<"sizeof(sockaddr_in6) = "<<sizeof(sockaddr_in6)<<endl;
#endif}MPI_CHECK(MPI_Bcast((void *)&id, sizeof(id), MPI_BYTE, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD));//将进程0,即root,的 socket 地址,广播给其他进程;//printf("LL:: MPI_Bcast()\n");fflush(stdout);//picking a GPU based on localRank, allocate device buffersCUDA_CHECK(cudaSetDevice(localRank));//每个进程都set一个自己的gpu设备,并从中分配两块显存空间 sendbuff和 recvbuff;CUDA_CHECK(cudaMalloc(&sendbuff, size * sizeof(float)));CUDA_CHECK(cudaMalloc(&recvbuff, size * sizeof(float)));CUDA_CHECK(cudaStreamCreate(&s));//创建本线程自己的streamlong long seed = 0;get_seed(seed);
//void init_dev_vectors(float A_d, int n, float* B_d, int rank, int seed)init_dev_vectors(sendbuff, recvbuff, size, myRank, seed);//initializing NCCLNCCL_CHECK(ncclCommInitRank(&comm, nRanks, id, myRank));//创建一个新的通信子,多线程多进程场景使用。/*********************************************************************************************************** ncclResult_t ncclCommInitRank(ncclComm_t* comm, int nranks, ncclUniqueId commId, int rank)* Creates a new communicator (multi thread/process version).* rank must be between 0 and nranks-1 and unique within a communicator clique.* Each rank is associated to a CUDA device, which has to be set before calling ncclCommInitRank.* ncclCommInitRank implicitly synchronizes with other ranks,* hence it must be called by different threads/processes or use ncclGroupStart/ncclGroupEnd.**********************************************************************************************************///communicating using NCCLNCCL_CHECK(ncclAllReduce((const void*)sendbuff, (void*)recvbuff, size, ncclFloat, /*ncclMax*/ ncclSum, comm, s));//completing NCCL operation by synchronizing on the CUDA streamCUDA_CHECK(cudaStreamSynchronize(s));if(myRank == 1)fetch_dev_vector(recvbuff, size, myRank);//free device buffersCUDA_CHECK(cudaFree(sendbuff));CUDA_CHECK(cudaFree(recvbuff));//finalizing NCCLncclCommDestroy(comm);//finalizing MPIMPI_CHECK(MPI_Finalize());printf("[MPI Rank %d] Success \n", myRank);return 0;
}2,构建
2.1 Makefile
LD_FLAGS := -lnccl -L/usr/local/cuda/lib64 -lcudart -I/usr/local/cuda/includeMPI_FLAGS := -I /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/openmpi/include -L /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/openmpi/lib -lmpi -lmpi_cxxEXE := multiProcess_multiDevice_oneServer_allreduce
#singleProcess_multiDevice_oneServer_allreduce
all: $(EXE)singleProcess_multiDevice_oneServer_allreduce: singleProcess_multiDevice_oneServer_allreduce.cppg++ -g $< -o $@ $(LD_FLAGS)
# singleProcess_multiDevice_oneServer_allreducemultiProcess_multiDevice_oneServer_allreduce: multiProcess_multiDevice_oneServer_allreduce.cppg++ -g $< -o $@ $(LD_FLAGS) $(MPI_FLAGS)
# ../../ex_openmpi/local/bin/mpirun -np 2 ./oneServer_multiDevice_multiThreadmpi_test: mpi_test.cppg++ -g $< -o $@ $(LD_FLAGS) $(MPI_FLAGS).PHONY: clean
clean:-rm $(EXE)2.2 构建
$ make3,运行
../../ex_openmpi/local/bin/mpirun -np 2 ./multiProcess_multiDevice_oneServer_allreduce4,效果

allreduce ncclSum的数学效果,每个进程的recvbuff都满足:
recvbuff[i] = sendbuff_rank0[i] + sendbuff_rank1[i] + ... + sendbuff_rankn-1[i]