一、什么是SpringDoc
SpringDoc注解的使用,它是基于OpenAPI 3和Swagger 3的现代化解决方案,相较于旧版的Swagger2(SpringFox),SpringDoc提供了更简洁、更直观的注解方式。
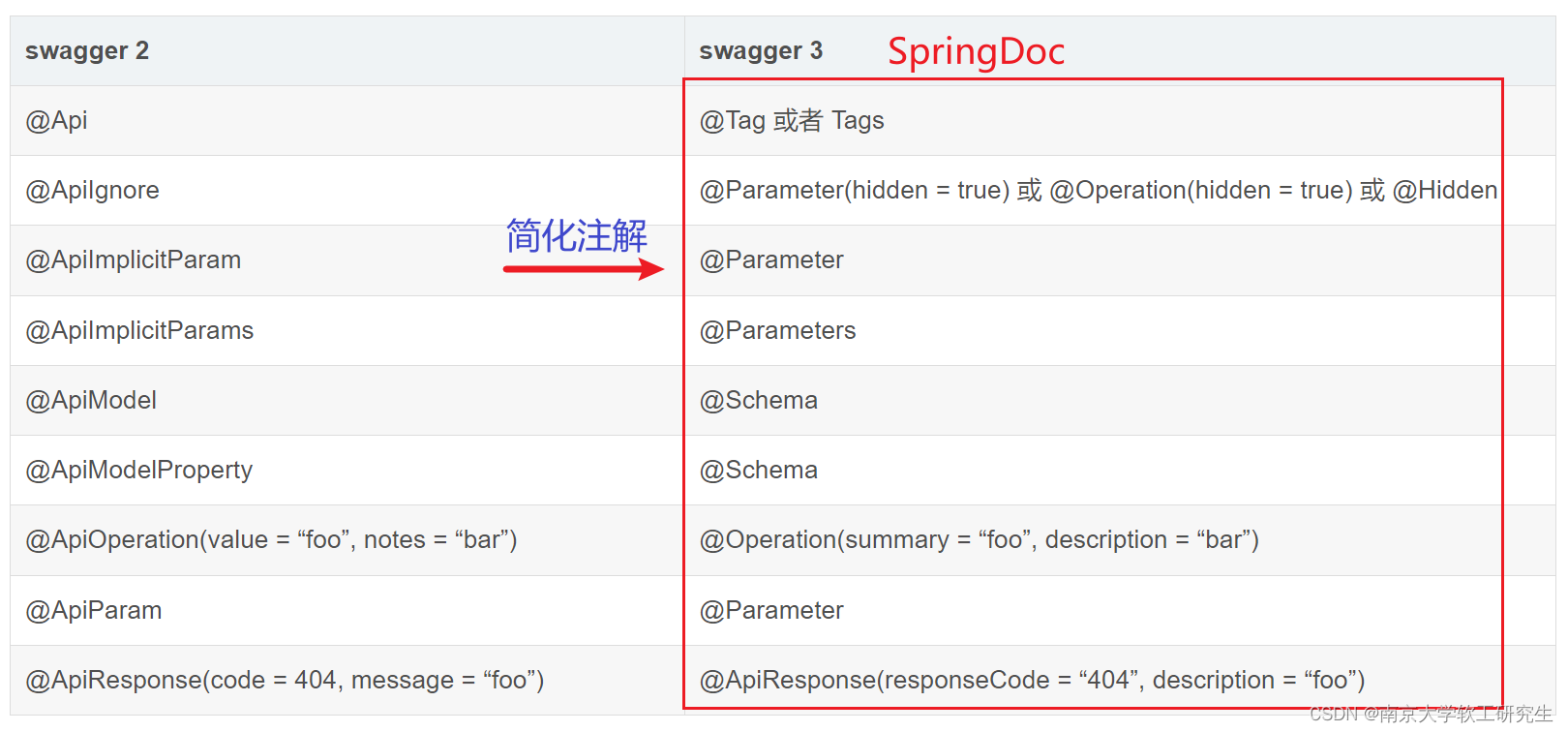
二、SpringDoc的注解分类
2.1 作用于类的注解
1. @Tag
用于说明或定义的标签。也可以作用于方法上
部分参数:
name:名称
description:描述
@Tag(name = "用户接口", description = "用户管理相关接口")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {}
2. @Hidden
某个元素(API操作、实体类属性等)是否在 API 文档中隐藏。当我们想要隐藏某些不必要的信息时,可以使用@Parameter(hidden = true)、@Operation(hidden = true)或者@Hidden注解。
3. @ApiResponse
API 的响应信息。也可以作用于方法上,一般常用于方法上
部分参数:
responseCode:响应的 HTTP 状态码
description:响应信息的描述
content:响应的内容
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "200", description = "查询成功", content = @Content(schema = @Schema(implementation = User.class)))
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "404", description = "查询失败")
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<User> getUserById(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {// ...
}
4. @Schema
用于描述实体类属性的描述、示例、验证规则等,比如 POJO 类及属性。
部分参数:
name:名称
title:标题
description:描述
example:示例值
required:是否为必须
format:属性的格式。如 @Schema(format = “email”)
maxLength 、 minLength:指定字符串属性的最大长度和最小长度
maximum 、 minimum:指定数值属性的最大值和最小值
pattern:指定属性的正则表达式模式
type: 数据类型(integer,long,float,double,string,byte,binary,
boolean,date,dateTime,password),必须是字符串。
如 @Schema=(type=“integer”)
implementation :具体的实现类,可以是类本身,也可以是父类或实现的接口。
@Tag(name = "用户", description = "用户实体类")
@Data
public class User {@Schema(name = "用户id", type = "long")private Long id;@Schema(name = "用户名", type = "long")private String name;@Schema(name = "密码", type = "password", minLength = "6", maxLength = "20")private String password;
}
2.2 作用于方法上
1. @Operation
描述 API 操作的元数据信息。常用于 controller 的方法上
部分参数:
summary:简短描述
description :更详细的描述
hidden:是否隐藏
tags:标签,用于分组API
operationId:操作的唯一标识符,建议使用唯一且具有描述性的名称
parameters:指定相关的请求参数,使用 @Parameter 注解来定义参数的详细属性。
requestBody:指定请求的内容,使用 @RequestBody 注解來指定请求的类型。
responses:指定操作的返回内容,使用 @ApiResponse 注解定义返回值的详细属性。
@Operation(summary = "操作摘要",description = "操作的详细描述",operationId = "operationId",tags = "tag1",parameters = {@Parameter(name = "param1", description = "参数1", required = true),@Parameter(name = "param2", description = "参数2", required = false)},requestBody = @RequestBody(description = "请求描述",required = true,content = @Content(mediaType = "application/json",schema = @Schema(implementation = RequestBodyModel.class))),responses = {@ApiResponse(responseCode = "200", description = "成功", content = @Content(mediaType = "application/json", schema = @Schema(implementation = ResponseModel.class))),@ApiResponse(responseCode = "400", description = "错误", content = @Content(mediaType = "application/json", schema = @Schema(implementation = ErrorResponseModel.class)))}
)
// @Tag(name = "标签1")
// @ApiResponses(value = {
// @ApiResponse(responseCode = "200", description = "成功", content = @Content(mediaType = "application/json", schema = @Schema(implementation = ResponseModel.class))),
// @ApiResponse(responseCode = "400", description = "錯誤", content = @Content(mediaType = "application/json", schema = @Schema(implementation = ErrorResponseModel.class)))
//})
public void Operation() {// 逻辑
}2. @Parameter
用于描述 API 操作中的参数
部分参数:
name : 指定的参数名
in:参数来源,可选 query、header、path 或 cookie,默认为空,表示忽略
ParameterIn.QUERY 请求参数
ParameterIn.PATH 路径参数
ParameterIn.HEADER header参数
ParameterIn.COOKIE cookie 参数
description:参数描述
required:是否必填,默认为 false
schema :参数的数据类型。如 schema = @Schema(type = “string”)
@Operation(summary = "根据用户名查询用户列表")
@GetMapping("/query/{username}")
public List<User> queryUserByName(@Parameter(name = "username", in = ParameterIn.PATH,description = "用户名",required = true) @PathVariable("username") String userName) {return new ArrayList<>();
}
3. @Parameters
包含多个 @Parameter 注解,指定多个参数。
@Parameters({@Parameter(name = "param1",description = "description",required = true,in = ParameterIn.PATH,schema = @Schema(type = "string")),@Parameter(name = "param2",description = "description",required = true,in = ParameterIn.QUERY,schema = @Schema(type = "integer"))
})
4. @RequestBody @Content
内容注解。
部分参数:
mediaType:内容的类型。比如:application/json
schema:内容的模型定义,使用 @Schema 注解指定模型的相关信息。
@Operation(requestBody = @RequestBody(description = "请求描述",required = true,content = @Content(mediaType = "application/json",schema = @Schema(implementation = RequestBodyModel.class)))
)
public void Operation() {// 逻辑
}
三、场景配置
3.1 类及 pojo 上
@Tag(name = "用户", description = "用户交互载体")
@Data
public class User {@Schema(name = "用户id", type = "string")private String id;@Schema(name = "用户名", type = "string")private String name;@Schema(name = "密码", type = "string")private String password;
}3.2 Controller 上
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
@Tag(name = "用户管理", description = "用户数据增删改查")
public class UserController {@Autowiredprivate UserService userService;@GetMapping("/{id}")@Operation(summary = "根据ID,查询用户",parameters = {@Parameter(name = "id", required = true, in = ParameterIn.PATH)},responses = {@ApiResponse(responseCode = "200",description = "成功",content = @Content(mediaType = "application/json", schema = @Schema(implementation = User.class))),@ApiResponse(responseCode = "400", description = "错误", content = @Content(mediaType = "application/json"))})public User getUserById(@PathVariable Long id) {return userService.getUserById(id);}
}

![[C#]C# OpenVINO部署yolov8图像分类模型](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/34b8d5a956c6466782ce9b0b6d8f9f0a.jpeg)