6-2.求二叉树的高度
本题要求给定二叉树的高度。
函数接口定义:
int GetHeight( BinTree BT );typedef struct TNode *Position;
typedef Position BinTree;
struct TNode{ElementType Data;BinTree Left;BinTree Right;
};要求函数返回给定二叉树BT的高度值。
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef char ElementType;
typedef struct TNode *Position;
typedef Position BinTree;
struct TNode{ElementType Data;BinTree Left;BinTree Right;
};BinTree CreatBinTree(); /* 实现细节忽略 */
int GetHeight( BinTree BT );int main()
{BinTree BT = CreatBinTree();printf("%d\n", GetHeight(BT));return 0;
}
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
输出样例(对于图中给出的树):
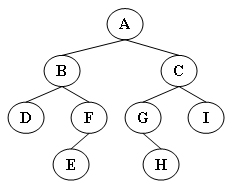
4求树的高度的代码
/*分治思想求二叉树的高度
1.bt为空,则高度为0
2.bt非空,其高度应为其左右子树高度的最大值加1
*/
int GetHeight( BinTree BT )
{int hl,hr,h;if(BT!=NULL){hl=GetHeight(BT->Left);hr=GetHeight(BT->Right);h=hl>hr?hl:hr;return h+1;} elsereturn 0;//若为空树
}R6-1 求采用邻接矩阵作为存储结构的无向图各顶点的度
本题要求实现一个函数,输出无向图每个顶点的数据元素的值,以及每个顶点度的值。
函数接口定义:
void degree(MGraph G);G为采用邻接矩阵作为存储结构的无向图。
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#define MVNum 100 //最大顶点数
typedef struct{ char vexs[MVNum]; //存放顶点的一维数组 int arcs[MVNum][MVNum]; //邻接矩阵 int vexnum,arcnum; //图的当前顶点数和边数
}MGraph;
void degree(MGraph G);
void CreatMGraph(MGraph *G);/* 创建图 */
int main()
{MGraph G;CreatMGraph(&G);degree(G);return 0;
}
void CreatMGraph(MGraph *G)
{int i,j,k;scanf("%d%d",&G->vexnum,&G->arcnum);getchar();for(i=0;i<G->vexnum;i++)scanf("%c",&G->vexs[i]);for(i=0;i<G->vexnum;i++)for(j=0;j<G->vexnum;j++)G->arcs[i][j]=0;for(k=0;k<G->arcnum;k++){ scanf("%d%d",&i,&j); G->arcs[i][j]=1; G->arcs[j][i]=1; }
}/* 请在这里填写答案 */输入样例:
例如无向图

第一行给出图的顶点数n和边数e。第二行给出n个字符,表示n个顶点的数据元素的值。后面是e行,给出每一条边的两个顶点编号。
4 5
ABCD
0 1
0 2
1 2
1 3
2 3输出样例:
输出n个顶点的元素值,顶点的数据类型为字符型。以及各顶点的度值
A:2
B:3
C:3
D:2
求各定点的度的代码
void degree(MGraph G)
{int i,j;for(i=0;i<G.vexnum;i++){int du=0;for(j=0;j<G.vexnum;j++){if(G.arcs[i][j]==1)//如果G.arcs[i][j]!=0,du++; {du++;}}printf("%c:%d\n",G.vexs[i],du);}
}R6-1 求链式表的表长
本题要求实现一个函数,求链式表的表长。
函数接口定义:
int Length( List L );L是给定单链表,函数Length要返回链式表的长度。
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef int ElementType;
typedef struct LNode *PtrToLNode;
struct LNode {ElementType Data;PtrToLNode Next;
};
typedef PtrToLNode List;List Read(); /* 细节在此不表 */int Length( List L );int main()
{List L = Read();printf("%d\n", Length(L));return 0;
}/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */输入样例:
1 3 4 5 2 -1
输出样例:
5
求表长代码
int Length( List L )
{LNode *p;p=L->Next;int len=0;while(p!=NULL){p=p->Next;len++;}return len;
}R6-2 求二叉树的深度
本题要求实现一个函数,可返回二叉树的深度。
函数接口定义:
int Depth(BiTree T);
T是二叉树树根指针,函数Depth返回二叉树的深度,若树为空,返回0。
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct BiTNode
{ElemType data;struct BiTNode *lchild, *rchild;
}BiTNode, *BiTree;BiTree Create();/* 细节在此不表 */int Depth(BiTree T);int main()
{BiTree T = Create();printf("%d\n", Depth(T));return 0;
}
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */输入样例:
输入为由字母和'#'组成的字符串,代表二叉树的扩展先序序列。例如对于如下二叉树,输入数据:
AB#DF##G##C##
输出样例(对于图中给出的树):
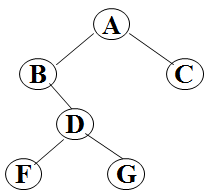
4代码:
int Depth(BiTree T)
{int hl=0,hr=0,h;if(T){hl=Depth(T->lchild);hr=Depth(T->rchild);h=hl>hr?hl:hr;//其高度为左右子树高度的最大值+1 return h+1;}elsereturn 0;
}R6-2 顺序表的查找操作
本题要求实现一个函数,要求从顺序表中查找指定元素,并返回第一个查找成功的元素在表中的位置序号,若查找失败,则返回0;
函数接口定义:
int LocateElem(SqList L,ElemType e);
其中SqList结构定义如下:
typedef struct{ElemType *elem;int length;}SqList;```### 裁判测试程序样例:
```c++
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXSIZE 5
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct{ElemType *elem;int length;}SqList;
void InitList(SqList &L);/*细节在此不表*/
int LocateElem(SqList L,ElemType e);int main()
{SqList L;InitList(L);ElemType e;int p;scanf("%d",&e);p=LocateElem(L,e);printf("The position of %d in SequenceList L is %d.",e,p);return 0;
}/* 请在这里填写答案 */输入格式:
输入数据有1行,首先给出以-1结束的顺序表元素值(不超过100个,-1不属于顺序表元素),然后是待查找的元素值。所有数据之间用空格分隔。
输入样例:
2 6 4 9 13 -1 2输出样例:
The position of 2 in SequenceList L is 1.代码:
int LocateElem(SqList L,ElemType e)
{int i;for(i=0;i<L.length;i++){if(L.elem[i]==e)//L.elem[i] {return i+1;}} return 0;
}R6-1 二叉树叶结点计数
实现一个函数,返回二叉树bt中叶结点的数量。
题目保证二叉树中所有元素均为整数。
裁判测试程序样例:
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct BinTree{int data;struct BinTree *left;struct BinTree *right;
};
struct BinTree* createNode(int item){ //创建结点/* 函数实现细节省略*/
}
struct BinTree* findNode(struct BinTree *bt, int item){ //查找结点/* 函数实现细节省略*/
}
int insert(struct BinTree *bt, int parent, int dir, int item){ //插入结点/* 实现细节仅供参考 */struct BinTree *tmp;tmp = findNode(bt, parent);if(!tmp) return 0;if(dir == 0){if(tmp->left) return 0;tmp->left = createNode(item);if(tmp->left == NULL) return 0;} else{if(tmp->right) return 0;tmp->right = createNode(item);if(tmp->right == NULL) return 0;}return 1;
}
struct BinTree* createBinTree(){ //创建二叉树/* 实现细节仅供参考 */int total, data;scanf("%d", &total);if(total == 0) return NULL;scanf("%d", &data);struct BinTree *bt;bt = createNode(data);if(!bt) return NULL;int parent, dir;for(int i=1; i<total; i++){scanf("%d%d%d", &parent, &dir, &data);insert(bt, parent, dir, data);}return bt;
}
int countLeaves(struct BinTree *bt);
int main(){struct BinTree *bt1, *bt2;bt1 = createBinTree();bt2 = createBinTree();printf("%d\n",countLeaves(bt1));printf("%d\n",countLeaves(bt2));return 0;
}/* 你提交的代码将被嵌入在这儿 */输入样例:

对于图片中的两棵二叉树以及样例测试程序的输入方式:
3
30
30 0 10
30 1 25
4
30
30 0 10
30 1 25
25 0 20输出样例:
对于样例测试程序的输出方式:
2
2代码:
/*统计二叉树中叶子结点的数目并没,有次序要求,
可以用三种遍历中的任意一种来完成.
一、后序遍历统计
叶子结点:既没有左孩子,又没有右孩子
*/
int countLeaves(struct BinTree *bt)
{int cnt=0;if(bt!=NULL){countLeaves(bt->leftt);countLeaves(bt->right);if(bt->left==NULL&&bt->right==NULL){cnt++;}} return cnt;
}
/*
方法二:采用分治方法,如果二叉树为空树,返回0,
如果二叉树只有一个结点 ,返回1
否则为左右子树叶子结点的和
*/
int countLeaves(struct BinTree *bt)
{int count=0;if(bt==NULL)return 0;else if(bt->left==NULL && bt->right==NULL)return count+1;else{count=countLeaves(bt->left)+countLeaves(bt->right);return count;}
}R6-1 按值查找单链表
本题要求实现一个函数,Locate_LinkList(LinkList L, datatype x)函数是在带头结点单链表中查找值为x的结点。函数须返回找到结点的指针,没有找到返回空。
函数接口定义:
LNode *Locate_LinkList(LinkList L, datatype x);
其中 L 和 x 都是用户传入的参数。 L 是单链表的头指针; x 是需要查找的值。函数须返回找到结点的指针,没有找到返回空。
裁判测试程序样例:
在这里给出函数被调用进行测试的例子。例如:
#define FLAG -1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
typedef int datatype;
typedef struct node
{datatype data;struct node *next;
}LNode, *LinkList;LinkList Creat_LinkList();/*这里忽略函数的实现*/LNode *Locate_LinkList(LinkList L, datatype x);int main()
{LinkList L;LNode *p=NULL;int x; L = Creat_LinkList();if(L == NULL){ printf("L=NULL,error!"); return 0; }scanf("%d",&x);if(p=Locate_LinkList(L,x)) printf("%d",p->data);else printf("NOT");return 0;
}/* 请在这里填写答案 */输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 -1
8
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
8代码:
LNode *Locate_LinkList(LinkList L, datatype x)
{LNode *p;p=L->next;while(p!=NULL&&p->data!=x)//当它不为空并这个数据值不等于x {p=p->next;//则找下一个 }return p;//返回找到该节点的指针
}R6-1 二叉树的遍历
本题要求给定二叉树的4种遍历。
函数接口定义:
void InorderTraversal( BinTree BT );
void PreorderTraversal( BinTree BT );
void PostorderTraversal( BinTree BT );
void LevelorderTraversal( BinTree BT );
要求4个函数分别按照访问顺序打印出结点的内容,格式为一个空格跟着一个字符
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef char ElementType;
typedef struct TNode *Position;
typedef Position BinTree;
struct TNode{ElementType Data;BinTree Left;BinTree Right;
};BinTree CreatBinTree(); /* 实现细节忽略 */
void InorderTraversal( BinTree BT );
void PreorderTraversal( BinTree BT );
void PostorderTraversal( BinTree BT );
void LevelorderTraversal( BinTree BT );int main()
{BinTree BT = CreatBinTree();printf("Inorder:"); InorderTraversal(BT); printf("\n");printf("Preorder:"); PreorderTraversal(BT); printf("\n");printf("Postorder:"); PostorderTraversal(BT); printf("\n");printf("Levelorder:"); LevelorderTraversal(BT); printf("\n");return 0;
}
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */输出样例(对于图中给出的树):
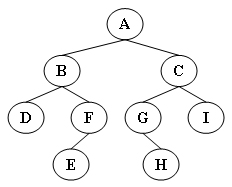
Inorder: D B E F A G H C I
Preorder: A B D F E C G H I
Postorder: D E F B H G I C A
Levelorder: A B C D F G I E H
void InorderTraversal( BinTree BT )//中序遍历 (左 根 右)
{if(BT!=NULL){InorderTraversal(BT->Left);printf(" %c",BT->Data);InorderTraversal(BT->Right);}
}
void PreorderTraversal( BinTree BT )//前序遍历 (根 左 右)
{if(BT!=NULL){printf(" %c",BT->Data);PreorderTraversal(BT->Left);PreorderTraversal(BT->Right); }
}
void PostorderTraversal( BinTree BT )//后序遍历 (左 右 根)
{if(BT!=NULL){PostorderTraversal(BT->Left);PostorderTraversal(BT->Right);printf(" %c",BT->Data);}
}
void LevelorderTraversal( BinTree BT )//层序遍历
{BinTree a[11000];a[0]=BT;int len=1;if(!BT){return;}while(1){if(len==0)return ;int pos=0;BinTree b[11000];for(int i=0;i<len;i++){if(a[i]!=NULL)printf(" %c",a[i]->Data);if(a[i]->Left!=NULL)b[pos++]=a[i]->Left;if(a[i]->Right!=NULL)b[pos++]=a[i]->Right; }len=pos;for(i=0;i<len;i++)a[i]=b[i];}
}