2-15 编写一个程序,运行时提示输入一个数字,再把这个数字显示出来。
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main() {// 提示用户输入数字cout << "请输入一个数字: ";// 用于存储用户输入的数字的变量double number;// 从标准输入读取用户输入的数字cin >> number;// 显示用户输入的数字cout << "您输入的数字是: " << number << endl;return 0;
}

2-16 C++语言有哪几种数据类型?简述其值域。编程显示你使用的计算机中的各种数据类型的字节数。
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main() {cout << "整型的大小: " << sizeof(int) << " 字节\n";cout << "长整型的大小: " << sizeof(long) << " 字节\n";cout << "短整型的大小: " << sizeof(short) << " 字节\n";cout << "字符型的大小: " << sizeof(char) << " 字节\n";cout << "单精度浮点型的大小: " << sizeof(float) << " 字节\n";cout << "双精度浮点型的大小: " << sizeof(double) << " 字节\n";cout << "布尔型的大小: " << sizeof(bool) << " 字节\n";// 根据需要添加更多的数据类型return 0;
}
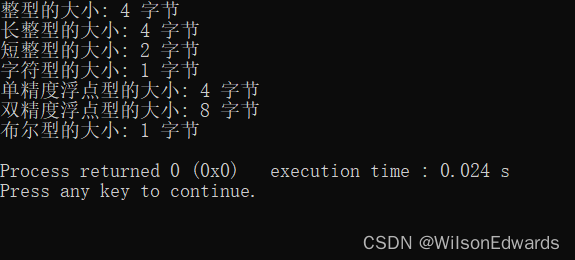
2-17 输出ASCⅡ码为32~127的字符。
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main() {// 输出ASCII码为32~127的字符for (int i = 32; i <= 127; ++i) {cout << char(i) << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
2-25 编写一个完整的程序,实现功能:向用户提问“现在正在下雨吗?”,提示用户输入Y或N。若输入为Y,显示“现在正在下雨。”;若输入为N,显示“现在没有下雨。”;否则继续提问“现在正在下雨吗?”。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>int main() {std::string userInput;do {// 提问用户是否正在下雨std::cout << "现在正在下雨吗?(输入Y或N): ";std::cin >> userInput;// 处理用户输入if (userInput == "Y" || userInput == "y") {std::cout << "现在正在下雨。\n";} else if (userInput == "N" || userInput == "n") {std::cout << "现在没有下雨。\n";} else {std::cout << "无效的输入,请输入Y或N。\n";}} while (userInput != "Y" && userInput != "y" && userInput != "N" && userInput != "n");return 0;
}

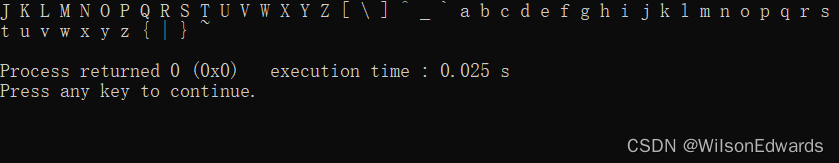
2-26 编写一个完整的程序,运行时向用户提问“你考试考了多少分?(0~100)”,接收输入后判断其等级显示出来。规则如下:
优90≤分数≤100
良80≤分数<90
中60≤分数<80
差0≤分数<60
#include <iostream>int main() {// 提示用户输入分数std::cout << "你考试考了多少分?(0~100): ";// 接收用户输入int score;std::cin >> score;// 判断等级并显示结果if (score >= 90 && score <= 100) {std::cout << "优\n";} else if (score >= 80 && score < 90) {std::cout << "良\n";} else if (score >= 60 && score < 80) {std::cout << "中\n";} else if (score >= 0 && score < 60) {std::cout << "差\n";} else {std::cout << "输入无效,分数应在0~100之间。\n";}return 0;
}
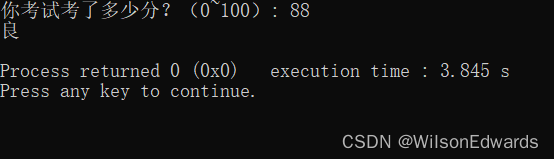
2-27 实现一个简单的菜单程序,运行时显示“Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Selet one:“提醒用户输入,A表示增加,D表示删除,S表示排序,Q表示退出,输入为A、D、S时分别提示“数据已经增加、删除、排序。”输入为Q时程序结束。
(1)要求使用if…else语句进行判断,用break、continue控制程序流程。
(2)要求使用switch语句。
//使用if...else#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>using namespace std;int main() {vector<string> data; // 用于存储数据的向量while (true) {cout << "菜单:A(增加) D(删除) S(排序) Q(退出)\n";char choice;cout << "请选择:";cin >> choice;if (choice == 'A') {// 增加数据string newData;cout << "输入要增加的数据:";cin >> newData;data.push_back(newData);cout << "数据已经增加。\n";} else if (choice == 'D') {// 删除数据if (data.empty()) {cout << "没有数据可以删除。\n";} else {cout << "原始数据:";for (size_t i = 0; i < data.size(); ++i) {cout << data[i] << " ";}cout << "\n输入要删除的数据:";string itemToDelete;cin >> itemToDelete;vector<string>::iterator it = find(data.begin(), data.end(), itemToDelete);if (it != data.end()) {data.erase(it);cout << "数据已经删除。\n";} else {cout << "未找到数据。\n";}}} else if (choice == 'S') {// 排序数据if (data.empty()) {cout << "没有数据可以排序。\n";} else {sort(data.begin(), data.end());cout << "数据已经排序。\n";}} else if (choice == 'Q') {// 退出程序cout << "程序正在退出。\n";break;} else {// 处理无效输入cout << "无效的选择。请键入 A、D、S 或 Q。\n";continue;}// 显示当前数据cout << "当前数据:";for (size_t i = 0; i < data.size(); ++i) {cout << data[i] << " ";}cout << "\n\n";}return 0;
}
// 使用switch语句#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>using namespace std;int main() {vector<string> data; // 用于存储数据的向量char choice;while (true) {cout << "菜单:A(增加) D(删除) S(排序) Q(退出)\n";cout << "请选择:";cin >> choice;switch (choice) {case 'A':case 'a': {// 增加数据string newData;cout << "请输入要增加的数据:";cin >> newData;data.push_back(newData);cout << "数据已经增加。\n";break;}case 'D':case 'd': {// 删除数据if (data.empty()) {cout << "没有数据可以删除。\n";} else {cout << "当前数据:";for (size_t i = 0; i < data.size(); ++i) {cout << data[i] << " ";}cout << "\n请输入要删除的数据:";string itemToDelete;cin >> itemToDelete;size_t indexToDelete = 0;bool found = false;for (size_t i = 0; i < data.size(); ++i) {if (data[i] == itemToDelete) {indexToDelete = i;found = true;break;}}if (found) {data.erase(data.begin() + indexToDelete);cout << "数据已经删除。\n";} else {cout << "未找到数据。\n";}}break;}case 'S':case 's': {// 排序数据if (data.empty()) {cout << "没有数据可以排序。\n";} else {sort(data.begin(), data.end());cout << "数据已经排序。\n";}break;}case 'Q':case 'q':// 退出程序cout << "程序正在退出。\n";return 0;default:// 处理无效输入cout << "无效的选择,请输入A、D、S或Q。\n";}// 显示当前数据cout << "当前数据:";for (size_t i = 0; i < data.size(); ++i) {cout << data[i] << " ";}cout << "\n\n";}return 0;
}

2-28 用穷举法找出1~100的质数并显示出来。分别使用while、do-while、for循环语句实现。
// 使用while循环#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main() {int number = 2;cout << "1~100之间的质数有:";while (number <= 100) {int divisor = 2;bool isPrime = true;while (divisor <= number / 2) {if (number % divisor == 0) {isPrime = false;break;}divisor++;}if (isPrime) {cout << number << " ";}number++;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
//使用do...while语句#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main() {int number = 2;cout << "1~100之间的质数有:";do {int divisor = 2;bool isPrime = true;do {if (number % divisor == 0) {isPrime = false;break;}divisor++;} while (divisor <= number / 2);if (isPrime) {cout << number << " ";}number++;} while (number <= 100);cout << endl;return 0;
}
//使用for循环语句#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main() {cout << "1~100之间的质数有:";for (int number = 2; number <= 100; ++number) {bool isPrime = true;for (int divisor = 2; divisor <= number / 2; ++divisor) {if (number % divisor == 0) {isPrime = false;break;}}if (isPrime) {cout << number << " ";}}cout << endl;return 0;
}
2-30 声明一个表示时间的结构体,可以精确表示年、月、日、小时、分、秒;提示用户输入年、月、日、小时、分、秒的值,然后完整地显示出来
#include <iostream>using namespace std;// 定义表示时间的结构体
struct Time {int year;int month;int day;int hour;int minute;int second;
};int main() {// 创建时间结构体变量Time time;// 提示用户输入时间信息cout << "请输入年份: ";cin >> time.year;cout << "请输入月份: ";cin >> time.month;cout << "请输入日期: ";cin >> time.day;cout << "请输入小时: ";cin >> time.hour;cout << "请输入分钟: ";cin >> time.minute;cout << "请输入秒数: ";cin >> time.second;// 显示完整的时间信息cout << "输入的时间为:" << time.year << "年" << time.month << "月" << time.day << "日 "<< time.hour << "时" << time.minute << "分" << time.second << "秒" << endl;return 0;
}

2-31 在程序中定义一个整型变量,赋以1~100的值,要求用户猜这个数,比较两个数的大小,把结果提示给用户,直到猜对为止。分别使用while、do...while语句实现循环。
//使用while循环#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main() {int targetNumber = 42; // 要猜的数字int userGuess;cout << "猜一猜1~100之间的数字: ";// 使用while循环while (true) {cin >> userGuess;if (userGuess == targetNumber) {cout << "恭喜你,猜对了!" << endl;break; // 结束循环} else if (userGuess < targetNumber) {cout << "猜的数字太小了,请再试一次: ";} else {cout << "猜的数字太大了,请再试一次: ";}}return 0;
}
// 使用do...while语句#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main() {int targetNumber = 42; // 要猜的数字int userGuess;cout << "猜一猜1~100之间的数字: ";// 使用do...while循环do {cin >> userGuess;if (userGuess == targetNumber) {cout << "恭喜你,猜对了!" << endl;} else if (userGuess < targetNumber) {cout << "猜的数字太小了,请再试一次: ";} else {cout << "猜的数字太大了,请再试一次: ";}} while (userGuess != targetNumber);return 0;
}

2-32 口袋中有红、黄、蓝、白、黑5种颜色的球若干个。每次从口袋种取出3个不同颜色的球,问有多少种取法?
#include <iostream>
#include <string>using namespace std;int main() {const int totalColors = 5; // 总颜色数const int ballsPerDraw = 3; // 每次取出的球数string colors[] = {"红", "黄", "蓝", "白", "黑"};int combinationCount = 0;// 循环遍历所有可能的排列for (int color1 = 0; color1 < totalColors; ++color1) {for (int color2 = 0; color2 < totalColors; ++color2) {for (int color3 = 0; color3 < totalColors; ++color3) {if (color1 != color2 && color1 != color3 && color2 != color3) {// 输出当前排列和编号cout << combinationCount + 1 << " ";cout << colors[color1] << " " << colors[color2] << " " << colors[color3] << endl;combinationCount++;}}}}// 输出总的排列数cout << "总共有 " << combinationCount << " 种取法。" << endl;return 0;
}

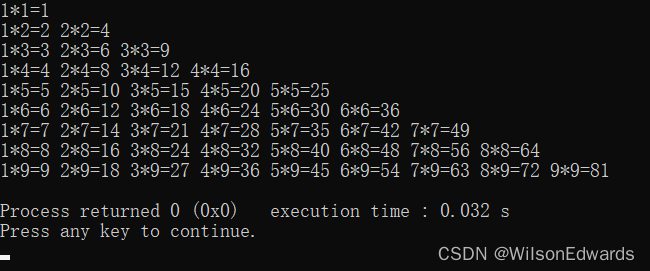
2-33 输出九九乘法表
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//打印九九乘法表
int main(){
int i=0;
int j=0;
for(i=1;i<=9;i++){for(j=1;j<=i;j++){cout<<j<<"*"<<i<<"="<<i*j<<" ";}cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}