create-react-app
创建 react 项目的脚手架。
React 基本用法
jsx 语法
变量、表达式
import React from 'react';class JSXBaseDemo extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);this.state = {name: '章三'};}render() {// 获取变量 插值const pElem = <p>{this.state.name}</p>;return pElem;// // 表达式// const exprElem = <p>{this.state.flag ? 'yes' : 'no'}</p>;// return exprElem;}
}export default JSXBaseDemo;
class、style
/* style.css */
.title {font-size: 30px;color: red;
}
import React from 'react';
import './style.css';class JSXBaseDemo extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);this.state = {};}render() {// classconst classElem = <p className="title">设置 css class</p>;return classElem;// // style// const styleData = { fontSize: '30px', color: 'blue' };// const styleElem = <p style={styleData}>设置 style</p>;// // 内联写法,注意 {{ 和 }}// // const styleElem = <p style={{ fontSize: '30px', color: 'blue' }}>设置 style</p>;// return styleElem;}
}export default JSXBaseDemo;
子元素和组件
import React from 'react';
import List from '../List';class JSXBaseDemo extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);this.state = {imgUrl: 'https://img1.mukewang.com/5a9fc8070001a82402060220-140-140.jpg'};}render() {// 子元素const imgElem = <div><p>我的头像</p><img src="xxxx.png"/><img src={this.state.imgUrl}/></div>;return imgElem';// // 加载组件// const componentElem = <div>// <p>JSX 中加载一个组件</p>// <hr />// <List />// </div>;// return componentElem;}
}export default JSXBaseDemo;
原生 html
import React from 'react';class JSXBaseDemo extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);this.state = {};}render() {// 原生 htmlconst rawHtml = '<span>富文本内容<i>斜体</i><b>加粗</b></span>';const rawHtmlData = {__html: rawHtml // 注意,必须是这种格式};const rawHtmlElem = <div><p dangerouslySetInnerHTML={rawHtmlData}></p><p>{rawHtml}</p></div>;return rawHtmlElem;}
}export default JSXBaseDemo;
条件
if else- 三元表达式
- 逻辑运算符:
&&、||
.btn-white {color: #333;
}
.btn-black {background-color: #666;color: #fff;;
}import React from 'react';
import './style.css';class ConditionDemo extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);this.state = {theme: 'black'};}render() {const blackBtn = <button className="btn-black">black btn</button>;const whiteBtn = <button className="btn-white">white btn</button>;// // if else// if (this.state.theme === 'black') {// return blackBtn;// } else {// return whiteBtn;// }// // 三元运算符// return <div>// { this.state.theme === 'black' ? blackBtn : whiteBtn }// </div>;// &&return <div>{ this.state.theme === 'black' && blackBtn }</div>;}
}export default ConditionDemo;
列表渲染
mapkey
import React from 'react';class ListDemo extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);this.state = {list: [{id: 'id-1',title: '标题1'},{id: 'id-2',title: '标题2'},{id: 'id-3',title: '标题3'}]};}render() {return <ul>{this.state.list.map((item, index) => {// 这里的 key 和 Vue 的 key 类似,必填,不能是 index 或 randomreturn <li key={item.id}>index {index}; id {item.id}; title {item.title}</li>;})}</ul>;}
}export default ListDemo;
事件
bind this
- 非严格模式下,
dom事件中的this都是运行时的,就是浏览器执行的,指向的是window - 严格模式下,这里的
this指向undefined
箭头函数为什么能解决 bind this ?
- 箭头函数的
this永远指向上级作用域。 - 箭头函数的
this是在定义函数时绑定的,不是在执行过程中绑定的。 - 也就是说,函数在定义时,
this就继承了定义函数的对象。
import React from 'react';class EventDemo extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);;this.state = {name: 'zhangsan'};// 修改方法的 this 指向this.clickHandler1 = this.clickHandler1.bind(this);}render() {// this - 使用 bindreturn <p onClick={this.clickHandler1}>{this.state.name}</p>;// // this - 使用静态方法// return <p onClick={this.clickHandler2}>// clickHandler2 {this.state.name}// </p>;}clickHandler1() {// console.log('this....', this) // this 默认是 undefinedthis.setState({name: 'lisi'});}// 静态方法,this 指向当前实例clickHandler2 = () => {this.setState({name: 'lisi'});}
}export default EventDemo;
关于 event 参数
import React from 'react';class EventDemo extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);;this.state = {};}render() {// eventreturn <a href="https://imooc.com/" onClick={this.clickHandler3}>click me</a>;}// 获取 eventclickHandler3 = (event) => {// 阻止默认行为event.preventDefault(); // 阻止冒泡event.stopPropagation(); // 指向当前元素,即当前元素触发console.log('target', event.target); // 指向当前元素,假象!!!console.log('current target', event.currentTarget); // 注意,event 其实是 React 封装的。// 可以看 __proto__.constructor 是 SyntheticEvent 组合事件// 不是原生的 Event ,原生的 MouseEventconsole.log('event', event); console.log('event.__proto__.constructor', event.__proto__.constructor);// 原生 event 如下。其 __proto__.constructor 是 MouseEventconsole.log('nativeEvent', event.nativeEvent);// 指向当前元素,即当前元素触发console.log('nativeEvent target', event.nativeEvent.target); // 指向 document !!!console.log('nativeEvent current target', event.nativeEvent.currentTarget;); // 1. event 是 SyntheticEvent ,模拟出来 DOM 事件所有能力// 2. event.nativeEvent 是原生事件对象// 3. 所有的事件,都被挂载到 document 上 (React17 事件绑定到 root 上)// 4. 和 DOM 事件不一样,和 Vue 事件也不一样}
}export default EventDemo;
传递自定义参数
import React from 'react';class EventDemo extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);;this.state = {list: [{id: 'id-1',title: '标题1'},{id: 'id-2',title: '标题2'},{id: 'id-3',title: '标题3'}]};}render() {// 传递参数 - 用 bind(this, a, b)return <ul>{this.state.list.map((item, index) => {return <li key={item.id} onClick={this.clickHandler4.bind(this, item.id, item.title)}>index {index}; title {item.title}</li>;})}</ul>;}// 传递参数// 最后追加一个参数,即可接收 eventclickHandler4(id, title, event) {console.log(id, title);console.log('event', event); }
}export default EventDemo;
组件和 props (类型检查)
受控组件
- 表单的值受
state控制。 value指向state,onChange事件监听,使用setState修改值。
import React from 'react';class FormDemo extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);this.state = {name: 'zhangsan'};}render() {// 受控组件return <div><p>{this.state.name}</p><label htmlFor="inputName">姓名:</label> {/* 用 htmlFor 代替 for */}<input id="inputName" value={this.state.name} onChange={this.onInputChange} /></div>;}onInputChange = (e) => {this.setState({name: e.target.value});}
}export default FormDemo;
表单的使用
import React from 'react';class FormDemo extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);this.state = {name: 'zhangsan',info: '个人信息',city: 'beijing',flag: true,gender: 'male'};}render() {// // 受控组件// return <div>// <p>{this.state.name}</p>// <label htmlFor="inputName">姓名:</label> {/* 用 htmlFor 代替 for */}// <input id="inputName" value={this.state.name} onChange={this.onInputChange}/>// </div>;// textarea - 使用 valuereturn <div><textarea value={this.state.info} onChange={this.onTextareaChange}/><p>{this.state.info}</p></div>;// // select - 使用 value// return <div>// <select value={this.state.city} onChange={this.onSelectChange}>// <option value="beijing">北京</option>// <option value="shanghai">上海</option>// <option value="shenzhen">深圳</option>// </select>// <p>{this.state.city}</p>// </div>;// // checkbox// return <div>// <input type="checkbox" checked={this.state.flag} onChange={this.onCheckboxChange}/>// <p>{this.state.flag.toString()}</p>// </div>;// // radio// return <div>// male <input type="radio" name="gender" value="male" checked={this.state.gender === 'male'} onChange={this.onRadioChange}/>// female <input type="radio" name="gender" value="female" checked={this.state.gender === 'female'} onChange={this.onRadioChange}/>// <p>{this.state.gender}</p>// </div>;}onInputChange = (e) => {this.setState({name: e.target.value});}onTextareaChange = (e) => {this.setState({info: e.target.value});}onSelectChange = (e) => {this.setState({city: e.target.value});}onCheckboxChange = () => {this.setState({flag: !this.state.flag});}onRadioChange = (e) => {this.setState({gender: e.target.value});}
}export default FormDemo;
组件使用
props传递数据props传递函数props类型检查
import React from 'react';
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';class Input extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);this.state = {title: ''};}render() {return <div><input value={this.state.title} onChange={this.onTitleChange}/><button onClick={this.onSubmit}>提交</button></div>;}onTitleChange = (e) => {this.setState({title: e.target.value});}onSubmit = () => {const { submitTitle } = this.props;submitTitle(this.state.title); // 'abc'this.setState({title: ''});}
}// props 类型检查
Input.propTypes = {submitTitle: PropTypes.func.isRequired
};class List extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);}render() {const { list } = this.props;return <ul>{list.map((item, index) => {return <li key={item.id}><span>{item.title}</span></li>;})}</ul>;}
}
// props 类型检查
List.propTypes = {list: PropTypes.arrayOf(PropTypes.object).isRequired
};class Footer extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);}render() {return <p>{this.props.text}{this.props.length}</p>;}
}class TodoListDemo extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);// 状态(数据)提升this.state = {list: [{id: 'id-1',title: '标题1'},{id: 'id-2',title: '标题2'},{id: 'id-3',title: '标题3'}],footerInfo: '底部文字'};}render() {return <div><Input submitTitle={this.onSubmitTitle}/><List list={this.state.list}/><Footer text={this.state.footerInfo} length={this.state.list.length}/></div>;}onSubmitTitle = (title) => {this.setState({list: this.state.list.concat({id: `id-${Date.now()}`,title})});}
}export default TodoListDemo;
state 和 setState
setState
- 不可变值
- 可能是异步更新 (针对
React <= 17)- 直接使用是异步更新,在第二个参数的回调函数中可以拿到最新的
state - 在
setTimeout中使用是同步 - 自定义的
dom事件,是同步的
- 直接使用是异步更新,在第二个参数的回调函数中可以拿到最新的
- 可能会被合并 (针对
React <= 17)- 异步更新,
setState传入的参数是对象,那么在更新前会被合并 - 异步更新,
setState传入的参数是函数,不会被合并
- 异步更新,
import React from 'react';class StateDemo extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);// 第一,state 要在构造函数中定义this.state = {count: 0};}render() {return <div><p>{this.state.count}</p><button onClick={this.increase}>累加</button></div>;}increase = () => {// // 第二,不要直接修改 state ,要使用不可变值 -----------------------// // this.state.count++; // 错误// this.setState({// count: this.state.count + 1 // SCU// });// 操作数组、对象的的常用形式// 第三,setState 可能是异步更新(有可能是同步更新) ------------------// this.setState({// count: this.state.count + 1// }, () => {// // 联想 Vue $nextTick - DOM// // 回调函数中可以拿到最新的 state// console.log('count by callback', this.state.count); // });// console.log('count', this.state.count); // 异步的,拿不到最新值// // setTimeout 中 setState 是同步的// setTimeout(() => {// this.setState({// count: this.state.count + 1// });// console.log('count in setTimeout', this.state.count);// }, 0);// 自己定义的 DOM 事件,setState 是同步的。// 第四,state 异步更新的话,更新前会被合并 --------------------------// // 传入对象,会被合并(类似 Object.assign )。执行结果只一次 +1// this.setState({// count: this.state.count + 1// });// this.setState({// count: this.state.count + 1// });// this.setState({// count: this.state.count + 1// });// 传入函数,不会被合并。执行结果是 +3this.setState((prevState, props) => {return {count: prevState.count + 1};});this.setState((prevState, props) => {return {count: prevState.count + 1};});this.setState((prevState, props) => {return {count: prevState.count + 1};});}// bodyClickHandler = () => {// this.setState({// count: this.state.count + 1// });// console.log('count in body event', this.state.count);// }// componentDidMount() {// // 自己定义的 DOM 事件,setState 是同步的// document.body.addEventListener('click', this.bodyClickHandler);// }// componentWillUnmount() {// // 及时销毁自定义 DOM 事件// document.body.removeEventListener('click', this.bodyClickHandler);// // clearTimeout// }
}export default StateDemo;// -------------------------- 我是分割线 -----------------------------// // 不可变值(函数式编程,纯函数) - 数组
// const list5Copy = this.state.list5.slice();
// list5Copy.splice(2, 0, 'a'); // 中间插入/删除
// this.setState({
// list1: this.state.list1.concat(100), // 追加
// list2: [...this.state.list2, 100], // 追加
// list3: this.state.list3.slice(0, 3), // 截取
// list4: this.state.list4.filter(item => item > 100), // 筛选
// list5: list5Copy // 其他操作
// });
// // 注意,不能直接对 this.state.list 进行 push pop shift unshift splice 等,这样违反不可变值// // 不可变值 - 对象
// this.setState({
// obj1: Object.assign({}, this.state.obj1, {a: 100}),
// obj2: {...this.state.obj2, a: 100}
// })
// // 注意,不能直接对 this.state.obj 进行属性设置,这样违反不可变值
React18 中的 setState
React组件事件:异步更新 + 合并stateDOM事件、setTimeout:异步更新 + 合并stateAutomatic Batching自动批处理
import { useState, useEffect } from 'react';function useStateDemo() { const [value, setValue]= useState(100);function clickHandler() { // // 合并后 +1// setValue(value + 1); // setValue(value + 1); // setValue(value + 1); // console.log(value); // 100 异步更新 setTimeout(() => {// 合并后 +1setValue(value + 1); setValue(value + 1); setValue(value + 1); console.log(value); // 100 异步更新 });} useEffect(() =>{ // 自绑定 DOM 事件 document.getElementById('btn2').addEventListener('click', () => { // 合并后 +1setValue(value + 1); setValue(value + 1); setValue(value + 1); console.log(value); // 100 异步更新 });});return <div> <span>{value}</span> <button onClick={clickHandler}>increase1</button> <button id="btn2">increase2</button> </div>;
}
React <= 17:只有React组件事件才批处理(合并 + 异步)React18:所有事件都自动批处理Automatic Batching
组件生命周期
react 生命周期图示

- 初始化阶段:
constructor - 挂载阶段:
componentDidMount - 更新阶段:
componentDidUpdate - 卸载阶段:
componentWillUnmount
展示不常用的生命周期图示
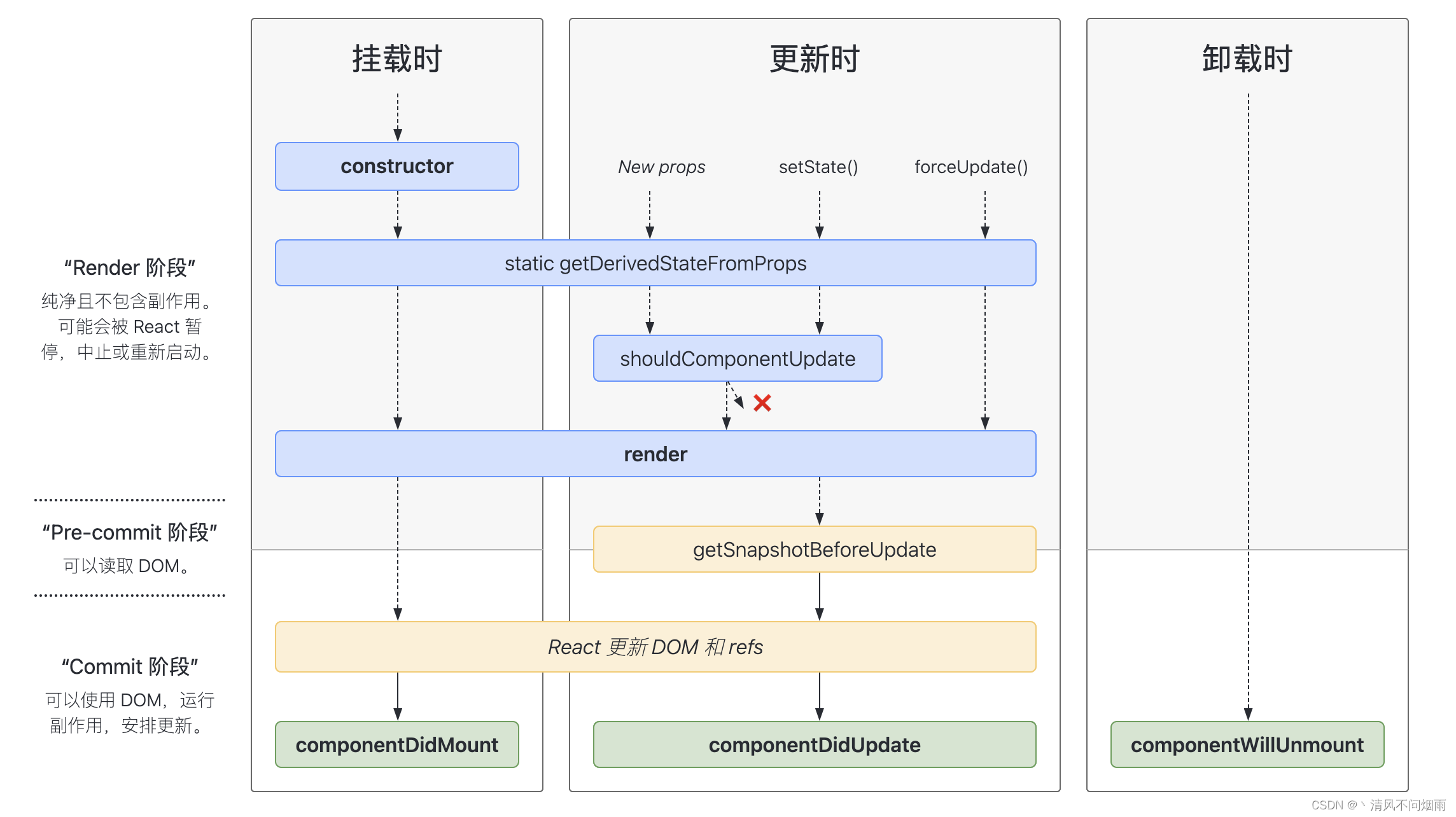
shouldComponentUpdate:可以控制是否更新
父子组件生命周期
- 父组件先
constructor,然后子组件才constructor - 子组件先
componentDidMount,然后父组件componentDidMount - 子组件先
componentDidUpdate,然后父组件componentDidUpdate - 父组件先触发
componentWillUnmout,然后子组件触发componentWillUnmount
FQA
React事件为何bind this?- 非严格模式下,
dom事件中的this都是运行时的,就是浏览器执行的,指向的是window - 严格模式下,这里的
this指向undefined
- 非严格模式下,
- 箭头函数为什么能解决
bind this?- 箭头函数的
this永远指向上级作用域:箭头函数的this是在定义函数时绑定的,不是在执行过程中绑定的。也就是说,函数在定义时,this就继承了定义函数的对象。
- 箭头函数的
react的事件和vue的区别。vue的事件是原生event(MouseEvent),事件是绑定在当前元素上的react的事件是SyntheticEvent,React16事件是绑定在document上的,React17后是绑定在root上的;react获取原生事件是通过event.nativeEvent获取。
react为什么对事件对象进行二次封装?- 兼容各个平台,不仅仅是
DOM,如react native。
- 兼容各个平台,不仅仅是
React17为什么将事件绑定到root上?- 有利于多个
React版本并存(document只有一个,而root可以有多个),例如微前端。
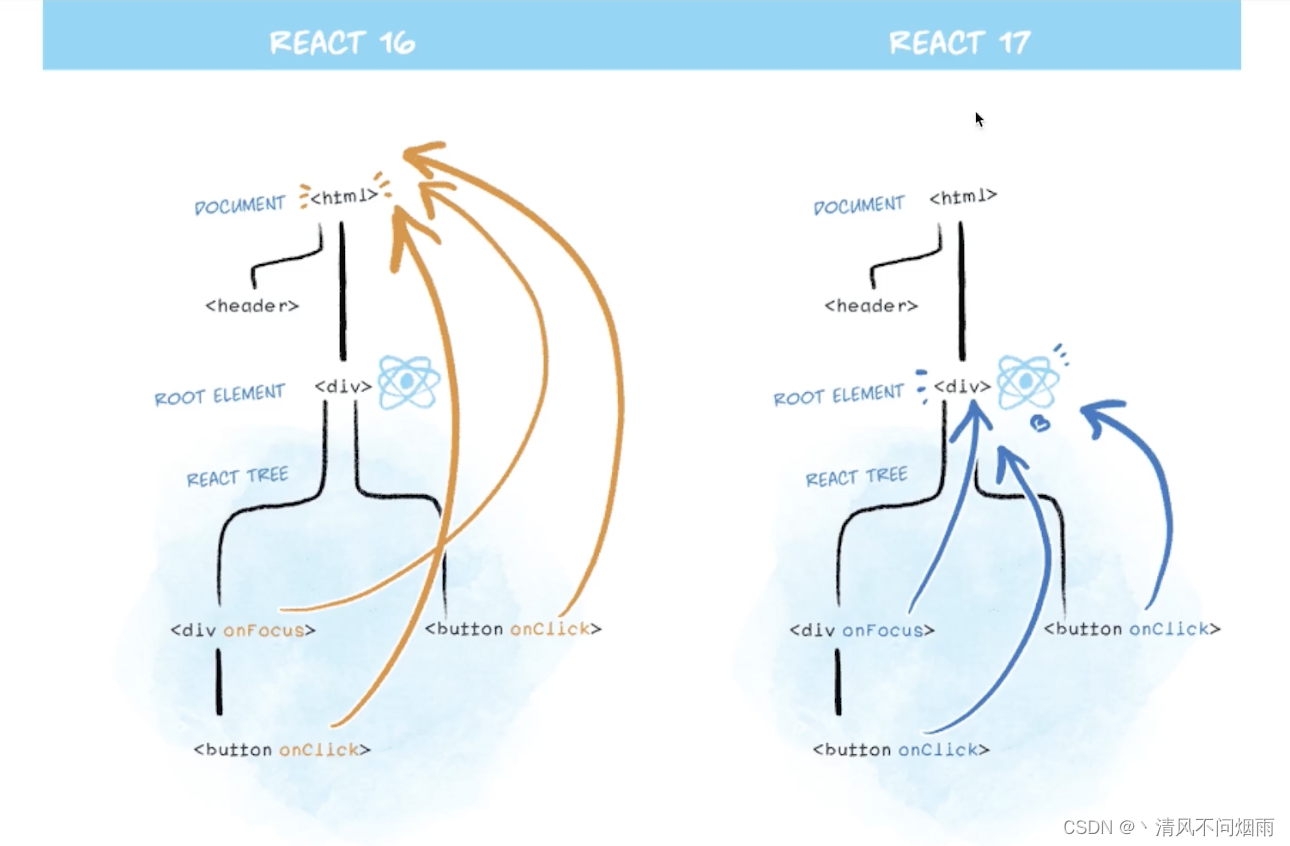
- 有利于多个
- 描述
react组件的生命周期。
- 初始化阶段:
constructor - 挂载阶段:
componentDidMount - 更阶段:
componentDidUpdate - 卸载阶段:
componentWillUnmount - 在更新阶段
componentDidUpdate之前还有一个shouldComponentUpdate:可以控制是否更新
react组件如何通讯?- 父子组件通过
props传递数据 - 可通过
context从顶层组件向子孙组件进行下发数据 - 使用
redux可以全局组件共享状态
- 父子组件通过






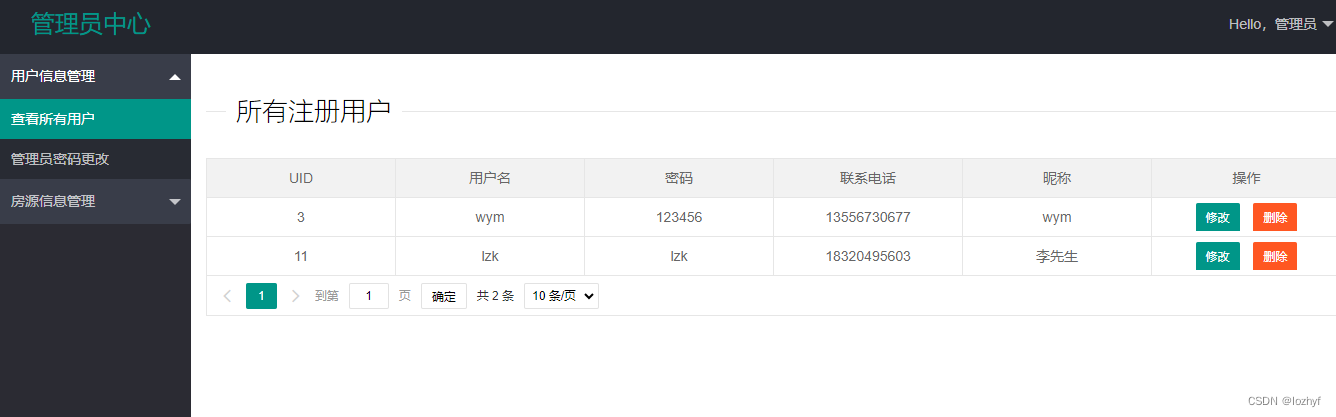
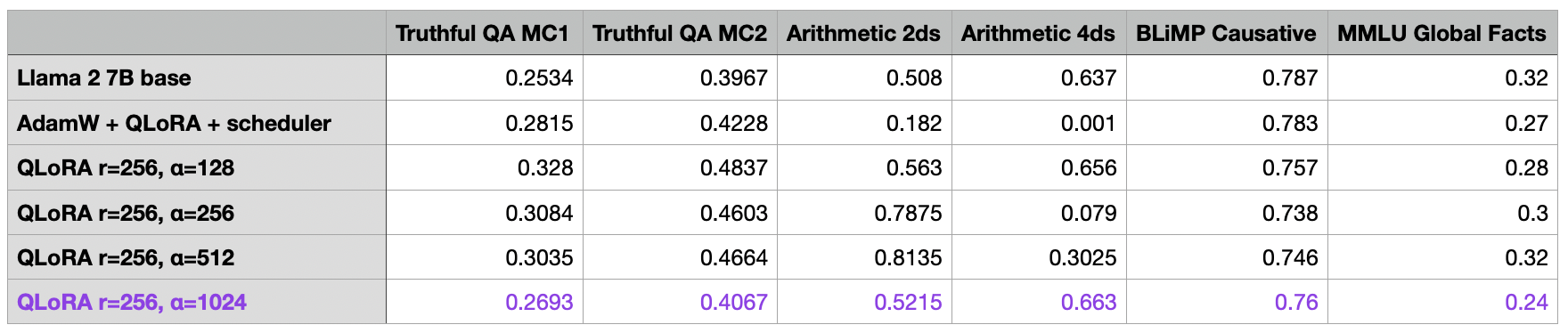
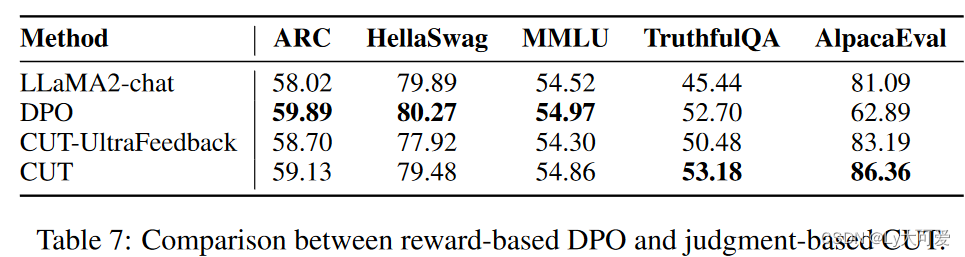
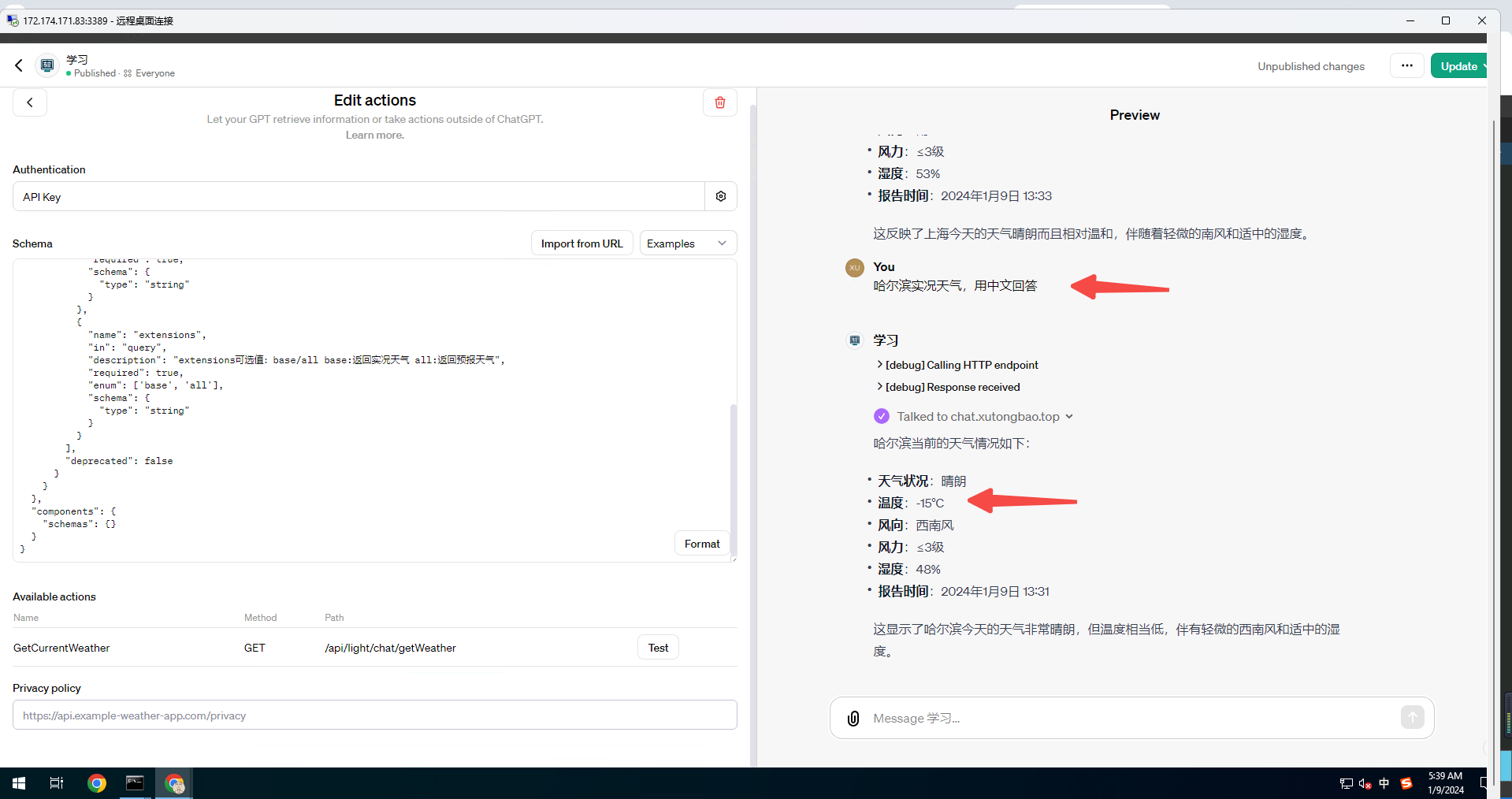
![Flask+Bootstrap4案例[有源码]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/d5fe8abb004c4e3c82825ab5ef38de41.png#pic_center)