面向对象的第一概念:类
类的构成:

类的设计:

创建一个类:
class Human {
public://公有的,对外的void eat();//方法,成员函数void sleep();void play();void work();string getName();//获取对内的数据int getAge();int getSalary();
private://对内的,私有的string name;int age;int salary;
};成员函数及实现
/*
void eat();//方法,成员函数
void sleep();
void play();
void work();
*/void Human::eat() {cout << "我正在吃饭!" << endl;
}
void Human::sleep() {cout << "准备去睡觉吧!" << endl;
}
void Human::play() {cout << "准备玩啥呢!" << endl;
}
void Human::work() {cout << "准备工作" << endl;
}成员数据通过函数调用
实现封装,数据获取get()
/*
成员数据
private://对内的,私有的string name;int age;int salary;*/
/*
调用成员数据的函数
string getName();//获取对内的数据
int getAge();
int getSalary();
*/
//实现对成员数据的获取
string Human::getName() {return name;
}
int Human::getAge() {return age;
}
int Human::getSalary() {return salary;
}成员数据单个设置set()
/*
void setName(string name);//设置对内的数据
void setAge(int age);
void setSalary(int salary);
*/
//this是一个特殊的指针,指向这个对象本身
void Human::setName(string name1) {this->name = name1;
}
void Human::setAge(int age1) {this->age = age1;
}
void Human::setSalary(int salary1) {this->salary = salary1;
}对象:
一个特定"类"的具体实例
Human h1;//h1就是Human这个类的一个对象,一个对象是一个特殊的变量,有丰富的功能和用法,可以通过对象去调用类的成员函数
特点:
具体使用方法:
int main(void) {Human h1;//通过Human类创建一个对象h1.eat();h1.play();h1.sleep();h1.work();//设置成员数据h1.setName("张三");//通过getName()来获取成员数据cout << h1.getName() << endl;//h1.age//直接访问成员数据是无法通过编译的return 0;
}成员数据的初始化:构造函数(自动调用)
作用:
特点:
1: 自动调用 (在创建新对象时,自动调用)2: 构造函数的函数名,和类名相同3:构造函数 没有 返回类型4:可以有多个构造函数(即 函数重载形式 )(大致常用的有四种)
构造函数的种类
每一种构造函数都只有一个
默认构造函数
没有参数的构造函数,称为默认构造函数
合成的默认构造函数
在创建一个对象的时候,(1:当我们没写默认的构造函数时,编译器会自动创建一个"合成的默认构造函数")--->这个值都是随机的,并不准确
仅当数据成员全部使用了“类内初始值”,才宜使用“合成的默认构造函数”
int age = 18;//设置类内初始值(仅C11以上才支持)
//通过getAge()来获取成员数据
cout << h1.getAge() << endl;//使用类内初始值(仅C11以上才支持)
//通过getName()来获取成员数据
cout << h1.getSalary() << endl;//没有使用类内初始值

手动定义默认构造函数
防止编译器自动编译一个合成的默认构造函数
Human();//手动定义默认构造函数
//手动定义的默认构造函数
Human::Human(){
name = "张三";
age = 23;
salary = 25000;
}

自定义带参构造函数(会覆盖类内初始值)
与自定义默认构造函数不同的是,(默认的是在初始化的时候值都是固定的,带参的可以根据不同对象设置不同的初始化值)
this是一个特殊的指针,指向这个对象本身
/*
类内
//手动定义带参的(重载)构造函数
Human(string name,int age,int salary);
*/
/*
类外
//自定义重载构造函数
Human::Human(string name, int age, int salary){this->age = age;//this是一个特殊的指针this->name = name;this->salary = salary;
}
*/
int main(void) {//自定义一个带参的构造函数Human h1("张三",24,25000);//通过Human类创建一个对象h1.eat();h1.play();h1.sleep();h1.work();//通过getName()来获取成员数据cout << h1.getName() << endl;//通过getAge()来获取成员数据cout << h1.getAge() << endl;//通过getName()来获取成员数据cout << h1.getSalary() << endl;//h1.age//直接访问成员数据是无法通过编译的return 0;
} 
拷贝构造函数
合成的拷贝构造函数(一般有问题)

Human h1("张三",24,25000);//通过Human类创建一个对象
Human h2 = h1;//第一种形式:在没有自定义拷贝构造函数时,编译器会默认调用"合成拷贝构造函数"一般有问题
Human h3(h2);//第二种形式//通过getName()来获取成员数据
cout << h1.getName() << endl;
cout << h2.getName() << endl;
cout << h3.getName() << endl;那合成拷贝构造函数的问题
当数据成员是个指针的时候就会出现"浅拷贝"或者"位拷贝"直接复制拷贝对象的所有数据值
#include <iostream>
#include <string>using namespace std;
#define size 16
class Human {
public://公有的,对外的void eat();//方法,成员函数void sleep();void play();void work();void descript();//自定义的默认构造函数Human();//手动定义带参的(重载)构造函数Human(string name,int age,int salary);//手动定义拷贝构造函数//Human(const Human& other);void setName(string name);//设置对内的数据void setAge(int age);void setSalary(int salary);void setAddr(char* addr);string getName();//获取对内的数据int getAge();int getSalary();
private://对内的,私有的string name;int age;//设置类内初始值int salary;char* addr;
};
//成员描述信息
void Human::descript()
{cout << "name: " << getName()<< "age: " << getAge()<< "salary: " << getSalary()<<"addr: "<<addr <<endl;//可以直接访问,只是不安全
}
string Human::getName() {return name;
}
int Human::getAge() {return age;
}
int Human::getSalary() {return salary;
}
//手动定义的默认构造函数
Human::Human(){cout << "手动定义的默认构造函数" << endl;name = "张三";age = 23;salary = 25000;addr = new char[32];strcpy_s(addr, size, "Amecrican");
}
//自定义重载构造函数
Human::Human(string name, int age, int salary){cout << "调用自定义的拷贝构造函数" << endl;this->age = age;this->name = name;this->salary = salary;addr = new char[32];strcpy_s(addr,size, "China");
}
//相当于 Human h2 = h1; //const Human &other = h1;
//Human::Human(const Human& other){
// cout << "调用拷贝构造函数" << endl;
// this->age = other.age;
// this->name = other.name;
// this->salary = other.salary;
//}void Human::setAddr(char* addr)
{if (!addr){return;}strcpy_s(this->addr, size, addr);
}
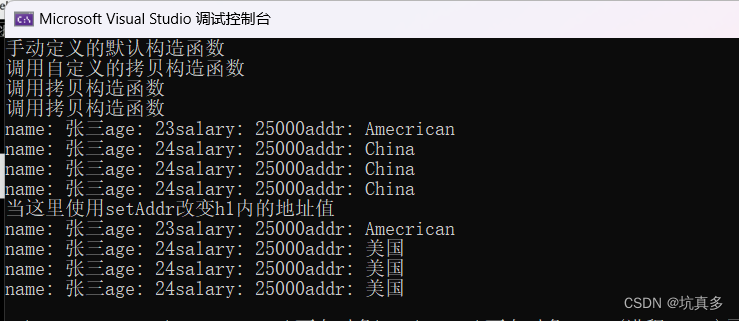
int main(void) {Human h;//自定义一个带参的构造函数Human h1("张三",24,25000);//通过Human类创建一个对象Human h2 = h1;//第一种形式:在没有自定义拷贝构造函数时,编译器会默认调用"合成拷贝构造函数"一般有问题Human h3(h2);//第二种形式h.descript();h1.descript();h2.descript();h3.descript();//当这里使用setAddr改变h1内的地址值cout << "当这里使用setAddr改变h1内的地址值" << endl;h1.setAddr("美国");h.descript();h1.descript();h2.descript();h3.descript();return 0;
}自定义拷贝构造函数(const的引用类型)

#include <iostream>
#include <string>using namespace std;
#define size 16
class Human {
public://公有的,对外的void eat();//方法,成员函数void sleep();void play();void work();void descript();//自定义的默认构造函数Human();//手动定义带参的(重载)构造函数Human(string name,int age,int salary);//手动定义拷贝构造函数Human(const Human& other);void setName(string name);//设置对内的数据void setAge(int age);void setSalary(int salary);void setAddr(char* addr);string getName();//获取对内的数据int getAge();int getSalary();
private://对内的,私有的string name;int age;//设置类内初始值int salary;char* addr;
};
//成员描述信息
void Human::descript()
{cout << "name: " << getName()<< "age: " << getAge()<< "salary: " << getSalary()<<"addr: "<<addr <<endl;//可以直接访问,只是不安全
}
string Human::getName() {return name;
}
int Human::getAge() {return age;
}
int Human::getSalary() {return salary;
}
//手动定义的默认构造函数
Human::Human(){cout << "手动定义的默认构造函数" << endl;name = "张三";age = 23;salary = 25000;addr = new char[32];strcpy_s(addr, size, "Amecrican");
}
//自定义重载构造函数
Human::Human(string name, int age, int salary){cout << "调用自定义的拷贝构造函数" << endl;this->age = age;this->name = name;this->salary = salary;addr = new char[32];strcpy_s(addr,size, "China");
}
//相当于 Human h2 = h1; //const Human &other = h1;
Human::Human(const Human& other){cout << "调用拷贝构造函数" << endl;this->age = other.age;this->name = other.name;this->salary = other.salary;//为addr分配一块独立的内存空间,不进行浅拷贝addr = new char[32];strcpy_s(addr, size, other.addr);
}
void Human::setAddr(char* addr)
{if (!addr){return;}strcpy_s(this->addr, size, addr);
}
int main(void) {Human h;//自定义一个带参的构造函数Human h1("张三",24,25000);//通过Human类创建一个对象Human h2 = h1;//第一种形式:在没有自定义拷贝构造函数时,编译器会默认调用"合成拷贝构造函数"一般有问题Human h3(h2);//第二种形式h.descript();h1.descript();h2.descript();h3.descript();//当这里使用setAddr改变h1内的地址值cout << "当这里使用setAddr改变h1内的地址值" << endl;h1.setAddr("美国");h.descript();h1.descript();h2.descript();h3.descript();return 0;
}调用时机
1:拷贝构造函数作为函数的参数,而非引用类型
如果参数是引用类型的话,函数内是可以直接修改,引用对象的数据值的,但是这种方式是不会创建新的对象的可以节省空间(如果设置不行值被修改,可以将成员函数和引用参数类型都定义为const类型,那么引用的这个对象就无法修改非const的值)禁止值被修改,就和拷贝构造函数一样了)
非引用的话,修改值,那值也是也是新的对象的


/*
//拷贝构造函数作为函数的参数,而非引用类型
//相当于就是Human h2 = h1;
void type1(Human h2) {cout << "拷贝构造函数作为函数的参数,而非引用类型" << endl;cout << "name: " << h2.getName()<< "age: " << h2.getAge()<< "salary: " << h2.getSalary()<< "addr: " << h2.getAddr() << endl;
}*/
/*
//如果时引用的话,是不会创建新的对象
void type2(Human &h2) {//相当于别名cout << "拷贝构造函数作为函数的参数,是引用类型" << endl;cout << "name: " << h2.getName()<< "age: " << h2.getAge()<< "salary: " << h2.getSalary()<< "addr: " << h2.getAddr() << endl;
}
*/int main(void) {Human h;//自定义一个带参的构造函数Human h1("张三",24,25000);//通过Human类创建一个对象//调用拷贝构造函数时机1:拷贝构造函数作为函数的参数,而非引用类型//type1(h1);type2(h1);return 0;
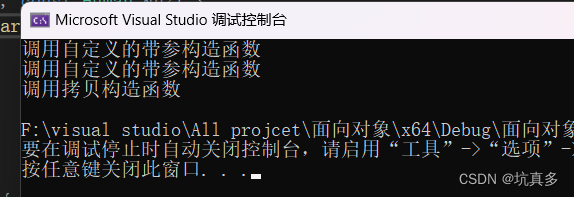
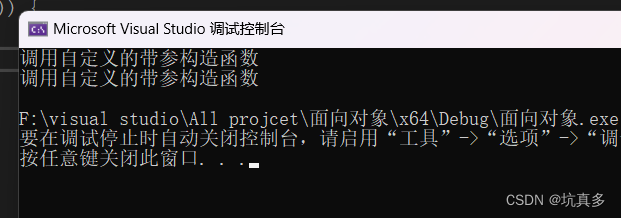
}2:函数的返回类型是类,而不是引用类型

#include <iostream>
#include <string>using namespace std;
#define size 16
class Human {
public://公有的,对外的void eat();//方法,成员函数void sleep();void play();void work();void descript();//自定义的默认构造函数Human();//手动定义带参的(重载)构造函数Human(string name,int age,int salary);//手动定义拷贝构造函数Human(const Human& other);void setName(string name);//设置对内的数据void setAge(int age);void setSalary(int salary);void setAddr(char* addr);string getName()const;//获取对内的数据int getAge()const;int getSalary()const;char* getAddr() const;
private://对内的,私有的string name;int age;//设置类内初始值int salary;char* addr;
};
//成员描述信息
void Human::descript()
{cout << "name: " << getName()<< "age: " << getAge()<< "salary: " << getSalary()<<"addr: "<<addr <<endl;//可以直接访问,只是不安全
}
string Human::getName() const {return name;
}
int Human::getAge() const {return age;
}
int Human::getSalary() const {return salary;
}
char* Human::getAddr() const
{return addr;
}
//手动定义的默认构造函数
Human::Human(){cout << "手动定义的默认构造函数" << endl;name = "张三";age = 23;salary = 25000;addr = new char[32];strcpy_s(addr, size, "Amecrican");
}
//自定义重载构造函数
Human::Human(string name, int age, int salary){cout << "调用自定义的带参构造函数" << endl;this->age = age;this->name = name;this->salary = salary;addr = new char[32];strcpy_s(addr,size, "China");
}
//相当于 Human h2 = h1; //const Human &other = h1;
Human::Human(const Human& other){cout << "调用拷贝构造函数" << endl;this->age = other.age;this->name = other.name;this->salary = other.salary;//为addr分配一块独立的内存空间,不进行浅拷贝addr = new char[32];strcpy_s(addr, size, other.addr);//设置值为深拷贝
}
//拷贝构造函数作为函数的参数,而非引用类型
void type1(Human h2) {cout << "拷贝构造函数作为函数的参数,而非引用类型" << endl;cout << "name: " << h2.getName()<< "age: " << h2.getAge()<< "salary: " << h2.getSalary()<< "addr: " << h2.getAddr() << endl;
}
//函数的返回类型是类,参数是对象,而非引用类型
//这个函数会返回一个临时的对象,这个对象会调用拷贝构造函数,加上参数的两个,这里一共会调用三次拷贝构造函数
//这里可以将参数设置为引用类型,避免浪费资源(其他成员函数最好设置为const的类型,避免值无意间自己给修改了)
//返回的类型也可以设置为引用类型,避免创建临时对象
const Human& getBetterMan(const Human &h1, const Human &h2) {if (h1.getSalary() > h2.getSalary()) {return h1;}else {return h2;}
}
void Human::setName(string name1) {this->name = name1;
}
void Human::setAge(int age1) {this->age = age1;
}
void Human::setSalary(int salary1) {this->salary = salary1;
}
void Human::setAddr(char* addr)
{if (!addr){return;}strcpy_s(this->addr, size, addr);
}
int main(void) {//自定义一个带参的构造函数Human h1("张三",24,25000);//通过Human类创建一个对象Human h2("王五", 24, 26000);//调用拷贝构造函数时机1:拷贝构造函数作为函数的参数,而非引用类型getBetterMan(h1,h2);//这个函数会返回一个临时的对象,这个对象会调用拷贝构造函数return 0;
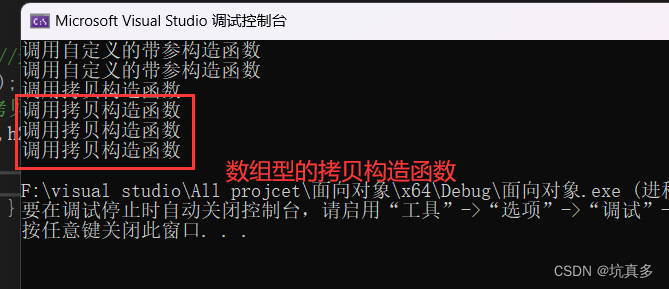
}3:对象是数组:
Human men[] = { h1, h2, h3 }; //调用 3 次拷贝构造函数
赋值构造函数
赋值构造函数和拷贝构造函数的区别
拷贝构造函数是在创建对象的时候,将其他对象拷贝给他,
Human h1 = h2;//这种就是拷贝构造函数
但是当将已经存在的对象进行赋值的就不是拷贝构造函数了,而是调用的赋值构造函数
Human h1,h2;
h1 = h2;//这种就是赋值构造函数
合成的赋值构造函数(浅拷贝)
和拷贝构造函数有点类似

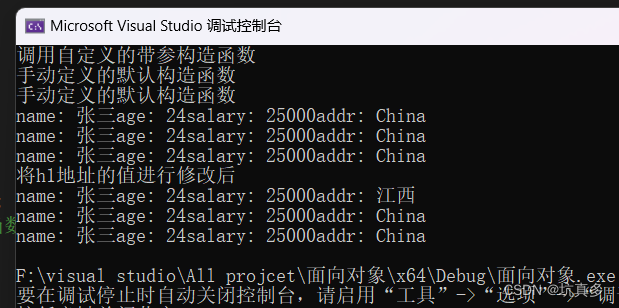
int main(void) {//自定义一个带参的构造函数Human h1("张三", 24, 25000), h2;h2 = h1;h1.descript();h2.descript(); cout << "将h1地址的值进行修改后" << endl;h1.setAddr("江西");h1.descript();h2.descript();return 0;
}自定义赋值构造函数
/*
类内//手动定义赋值构造函数,// 运算符重载"operator ="Human& operator= (const Human & other1);*/
/*
//类外
//赋值构造函数,&Human等同于h1
//const型的 h2
Human &Human::operator= (const Human& other1) {//防止对象给自己赋值if (this == &other1) {//如果对象给自己赋值,就返回对象本身的指针return *this;}//当执行h2 = h1时 //就相当于调用h2.operator =(h1);this->name = other1.name;this->age = other1.age;this->salary = other1.salary;//如果有必要可以先释放原本对象的资源//看情况,因为对象生成的时候本身就有一块内存/*delete addr;addr = new char[64];*/strcpy_s(this->addr, size, other1.addr);//深拷贝//返回对象本身this的引用*this,以方便做链式处理,h3=h2=h1;return *this;//return this 这种只是返回对象的指针,这个对象如果继续给下一个对象赋值的,就是空的
}*/int main(void) {//自定义一个带参的构造函数Human h1("张三", 24, 25000), h2,h3;h3 = h2 = h1;//没有自定义赋值构造函数时,就是"浅拷贝"h1.descript();h2.descript(); h3.descript();cout << "将h1地址的值进行修改后" << endl;h1.setAddr("江西");h1.descript();h2.descript();h3.descript();return 0;
}析构函数(自动调用)
当对象内部构造函数申请多个内存空间之后,由于这个空间都是在堆空间里,对象消亡之后,堆空间里的内存空间依然存在,又因为在对象内部,使用delete运算符去清空,首先很繁琐,
这时候就要用到析构函数.析构函数是没有参数,没有返回类型的,而且只有一个
构造函数申请了多少空间,就释放多少空间
一个波浪线+类名();:~Human();,可以看出,谁先调用完,谁就先释放

Human::~Human() {//这里加个this,谁来调用就返回这个对象的指针,在其他对象中也加入就可以判断调用的先后顺序cout << "调用析构函数" << this<<endl;delete addr;
}int main(void) {//自定义一个带参的构造函数Human h1("张三", 24, 25000), h2,h3;h3 = h2 = h1;//没有自定义赋值构造函数时,就是"浅拷贝"h1.descript();h2.descript(); h3.descript();cout << "将h1地址的值进行修改后" << endl;h1.setAddr("江西");h1.descript();h2.descript();h3.descript();return 0;
}this指针:
是一个特殊的指针,放回这个对象本身,this指针是属于实例对象,不能访问静态方法(不属于某一个实例对象,属于共有的,大众的,由类直接调用)
第一种用法:
void Human::setName(string name1) {this->name = name1;
}
void Human::setAge(int age1) {this->age = age1;
}
void Human::setSalary(int salary1) {this->salary = salary1;
}第二三种用法:引用和指针
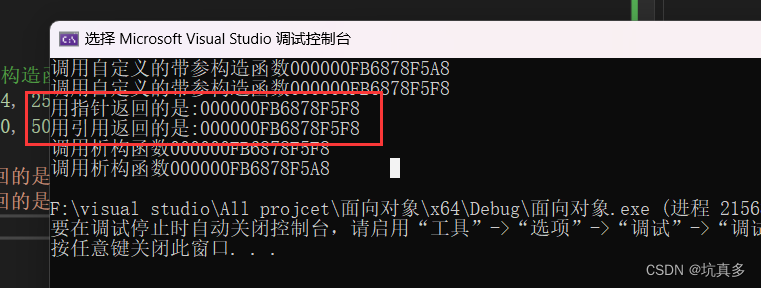
//this指针的用法两种
const Human* comBetterMan(const Human*);
const Human& comBetterMan1(const Human&);/*
//当返回对象是指针时
const Human *Human::comBetterMan(const Human *other) {if (this->getSalary() >other->getSalary()) {return this;}else {return other;}
}
//当返回对象是引用时
const Human& Human::comBetterMan1(const Human&other) {if (this->getSalary() > other.getSalary()) {return *this;}else {return other;}
}
*/
int main(void) {//自定义一个带参的构造函数Human h1("张三", 24, 25000);Human h2("李四", 40, 50000);cout << "用指针返回的是:" << h1.comBetterMan(&h2) << endl;cout << "用引用返回的是:" << &h1.comBetterMan1(h2) << endl;return 0;
}类文件的分离
分为定义(.h的文件中)和实现(.cpp文件中)两个部分和一个主函数(main)文件.cpp
.h中
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;class Human {
public://公有的,对外的void eat();//方法,成员函数void sleep();void play();void work();void descript();//自定义的默认构造函数Human();~Human();//手动定义带参的(重载)构造函数Human(string name, int age, int salary);//手动定义拷贝构造函Human(const Human& other);//手动定义赋值构造函数,// 运算符重载"operator ="Human& operator= (const Human& other1);void setName(string name);//设置对内的数据void setAge(int age);void setSalary(int salary);void setAddr(char* addr);//this指针的用法两种const Human* comBetterMan(const Human*);const Human& comBetterMan1(const Human&);string getName()const;//获取对内的数据int getAge()const;int getSalary()const;char* getAddr() const;
private://对内的,私有的string name;int age;//设置类内初始值int salary;char* addr;
};实现 .cpp中代码
#include "Human.h"
#define size 16
string Human::getName() const {return name;
}
int Human::getAge() const {return age;
}
int Human::getSalary() const {return salary;
}
char* Human::getAddr() const
{return addr;
}
//手动定义的默认构造函数
Human::Human() {cout << "手动定义的默认构造函数" << this << endl;name = "张三";age = 23;salary = 25000;addr = new char[32];strcpy_s(addr, size, "Amecrican");
}
//自定义重载构造函数
Human::Human(string name, int age, int salary) {cout << "调用自定义的带参构造函数" << this << endl;this->age = age;this->name = name;this->salary = salary;addr = new char[32];strcpy_s(addr, size, "China");
}
//相当于 Human h2 = h1; //const Human &other = h1;
Human::Human(const Human& other) {cout << "调用拷贝构造函数" << endl;this->age = other.age;this->name = other.name;this->salary = other.salary;//为addr分配一块独立的内存空间,不进行浅拷贝addr = new char[32];strcpy_s(addr, size, other.addr);//设置值为深拷贝
}//如果时引用的话,是不会创建新的对象
//void type2(const Human& h2) {//相当于别名
// cout << "拷贝构造函数作为函数的参数,是引用类型" << endl;
// //h2.setAddr("芜湖");//可以修改值,定义为const就不能修改了
// cout << "name: " << h2.getName()
// << "age: " << h2.getAge()
// << "salary: " << h2.getSalary()
// << "addr: " << h2.getAddr() << endl;
//}
//函数的返回类型是类,而非引用类型,,参数是对象,而非引用类型
//这个函数会返回一个临时的对象,这个对象会调用拷贝构造函数,加上参数的两个,这里一共会调用三次拷贝构造函数
//这里可以将参数设置为引用类型,避免浪费资源(其他成员函数最好设置为const的类型,避免值无意间自己给修改了)
//返回的类型也可以设置为引用类型,避免创建临时对象
const Human& getBetterMan(const Human& h1, const Human& h2) {if (h1.getSalary() > h2.getSalary()) {return h1;}else {return h2;}
}
//赋值构造函数,&Human等同于h1
//const型的 h2
Human& Human::operator= (const Human& other1) {cout << "调用赋值构造函数" << this << endl;//防止对象给自己赋值if (this == &other1) {//如果对象给自己赋值,就返回对象本身的指针return *this;}//当执行h2 = h1时 //就相当于调用h2.operator =(h1);this->name = other1.name;this->age = other1.age;this->salary = other1.salary;//如果有必要可以先释放原本对象的资源//看情况,因为对象生成的时候本身就有一块内存delete addr;addr = new char[64];strcpy_s(this->addr, size, other1.addr);//深拷贝//返回对象本身的引用,以方便做链式处理,h3=h2=h1;return *this;//return this 这种只是返回对象的指针,这个对象如果继续给下一个对象赋值的,就是空的
}
void Human::setName(string name1) {this->name = name1;
}
void Human::setAge(int age1) {this->age = age1;
}
void Human::setSalary(int salary1) {this->salary = salary1;
}
void Human::setAddr(char* addr)
{if (!addr) {return;}strcpy_s(this->addr, size, addr);
}
//当返回对象是指针时
const Human* Human::comBetterMan(const Human* other) {if (this->getSalary() > other->getSalary()) {return this;}else {return other;}}//当返回对象是引用时
const Human& Human::comBetterMan1(const Human& other) {if (this->getSalary() > other.getSalary()) {return *this;}else {return other;}
}
Human::~Human() {//这里加个this,谁来调用就返回这个对象的指针,在其他对象中也加入就可以判断调用的先后顺序cout << "调用析构函数" << this << endl;delete addr;
}主函数.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "Human.h"
using namespace std;
#define size 16
//成员描述信息
void Human::descript() {cout << "name: " << getName()<< "age: " << getAge()<< "salary: " << getSalary()<< "addr: " << addr << endl;//可以直接访问,只是不安全
}//拷贝构造函数作为函数的参数,而非引用类型
void type1(Human h2) {cout << "拷贝构造函数作为函数的参数,而非引用类型" << endl;cout << "name: " << h2.getName()<< "age: " << h2.getAge()<< "salary: " << h2.getSalary()<< "addr: " << h2.getAddr() << endl;
}int main(void) {//自定义一个带参的构造函数Human h1("张三", 24, 25000);Human h2("李四", 40, 50000);cout << "用指针返回的是:" << h1.comBetterMan(&h2) << endl;cout << "用引用返回的是:" << &h1.comBetterMan1(h2) << endl;return 0;
}static关键字
弥补使用全局变量不方便,破坏程序的封装性,就是用静态
对于非 const 的类静态成员
头文件.h
class Human{public:
......
private:
....
static int count;
....
};实现文件.cpp//初始化静态成员
//对于非 const 的类静态成员,只能在类的实现文件中初始化。
int Human::count = 0;
const 类静态成员
可以在类内设置初始值,也可以在类的实现文件中设置初始值。(但是 不要同时在这两个地方初始化,只能初始化 1 次)
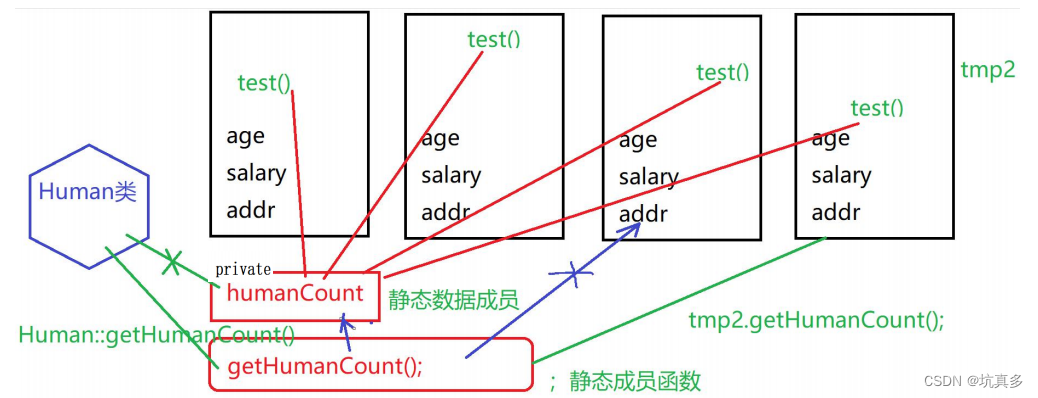
类的静态方法:别人可以访问他,但是他不能访问别人
优点:可以节省创建对象来调用成员函数,因为静态的成员函数可以用类来调用1. 可以直接通过 类来访问【更常用】 ,也可以通过 对象(实例)来访问 。/ 直接通过类名来访问静态方法!
// 用法:类名::静态方法2. 在类的静态方法中,不能访问普通数据成员和普通成员函数(对象的数据成员和成员函数)静态方法中,只能访问静态数据成员静态方法的实现,不能加 static
#pragma once
......
class Human {
public:
......
static int getCount();
......
};实现文件中
//静态方法的实现,不能加 static
int Human::getCount() {
// 静态方法中,不能访问实例成员(普通的数据成员)
// cout << age;
// 静态方法中,不能访问 this 指针,因为 this 指针是属于实例对象的
// cout << this;
//静态方法中,只能访问静态数据成员
return count;
}//静态方法:别人可以访问他,但是他不能访问别人
void test() {
cout << "总人数: ";
// ??? 没有可用的对象来访问 getCount()
// 直接通过类名来访问静态方法!
// 用法:类名::静态方法
cout << Human::getCount();
}int main(void) {//自定义一个带参的构造函数Human h1("张三", 24, 25000);Human h2("李四", 40, 50000);//可以通过类名访问静态成员方法,也可以通过实例对象cout << Human::getCount() << endl;cout << h1.getCount() << endl;return 0;
}所有的成员函数(),都可以访问静态数据成员。
类可以直接访问public静态数据成员(Human::count 非法)但是不能访问私有的静态数据成员
对象可以直接访问静态成员函数
类可以直接访问静态成员函数
在类的静态成员函数(类的静态方法)内部,不能直接访问 this 指针和对象的数据成员!
const关键字
const成员数据
只能读不能写
初始化:
设置类内初始值,(C11以上版本支持)
const char BloodType = 'B';
使用构造函数的初始化列表:一个冒号+const成员('初始值')
Human::Human(string name, int age, int salary):BloodType('A')
如何做到灵活初始化,用带参的构造函数的参数列表里定义一个形参,去表示初始化列表里的值
/*
Human(string name, int age, int salary,string BloodType);
const string BloodType = "B";
*/
实现文件
//在定义的对象的时候就可以灵活的设置初始值了
Human::Human(string name, int age, int salary,string BloodType):BloodType(BloodType) {
}int main(void) {//自定义一个带参的构造函数Human h1("张三", 24, 25000,"AB");Human h2("李四", 40, 50000,"A");h1.descript();h2.descript();return 0;
}const成员函数
如果一个成员函数内部,不会修改任何数据成员,就把它定义为 const 成员函数。
const方法只能调用const方法,非const可以调用const方法
void descript() const;
//成员描述信息
void Human::descript() const{//这个函数里面就不能修改数据cout << "name: " << getName()<< "age: " << getAge()<< "salary: " << getSalary()<< "addr: " << addr << "bloodType:"<<BloodType << endl;//可以直接访问,只是不安全
}int main(void) {//自定义一个带参的构造函数const Human h1("张三", 24, 25000,"AB");//const对象可以访问const的成员函数Human h2("李四", 40, 50000,"A");//也可以访问const的成员函数h1.descript();h2.descript();return 0;
}组合和聚合
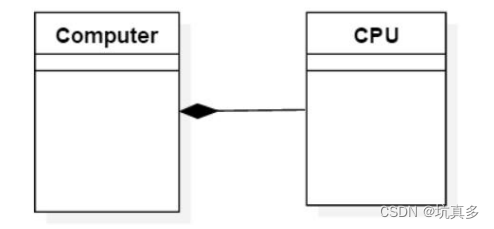
组合:类里添加其他类
#pragma once
#include "Cpu.h"
class Computer{
public:Computer();~Computer();
private:Cpu cpu;//Cpu和Computer之间,就是"组合"//Cpu *cpu;使用指针int hardDisk;//硬盘int memory;//内存
};组合:构造函数初始化值:
调用外类的成员数据之间通过外部类名调用,
//this->cpu = Cpu(cpuBrand, cpuVersion);
通过初始化列表
// :cpu(cpuBrand,cpuVersion)//使用初始化列表
cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;如果调用这个函数就返回这个函数
使用指针调用外类和使用对象来调用外类效果一样
错误 C2040 “Computer::cpu”:“Cpu *”与“Cpu”的间接寻址级别不同
当报错这个,有可能是写的两种调用方式名字重名

(Cpu.h)Cpu(const char *brand = "intel",const char *version = "i7");Cpu::Cpu(const char *brand, const char *version){this->brand = brand;this->version = version;cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;//如果调用该函数就返回这个函数
}(Computer.h)
Computer(const char *cpuBrand,const char *cpuVersion,const int hardDisk,const int memory );Computer::Computer(const char* cpuBrand, const char* cpuVersion,const int hardDisk, const int memory):cpu(cpuBrand,cpuVersion)//使用初始化列表
{//调用外类的成员数据之间通过外部类名调用,//this->cpu = Cpu(cpuBrand, cpuVersion);//this->cpu =new Cpu(cpuBrand, cpuVersion);//如果外类是指针this->hardDisk = hardDisk;this->memory = memory;cout << __FUNCTION__ << endl;
}
Computer::~Computer{delete cpu;//如果外类是指针,就需要释放
}主文件#include "Computer.h"
#include <iostream>
void test() {Computer h1("intel","i9",1000,8);
}int main(void) {test();return 0;
}组合的概念:
一起生成一起消亡,拥有者需要对被拥有者负责,是一种比较强的关系,是整体与部分的关系。
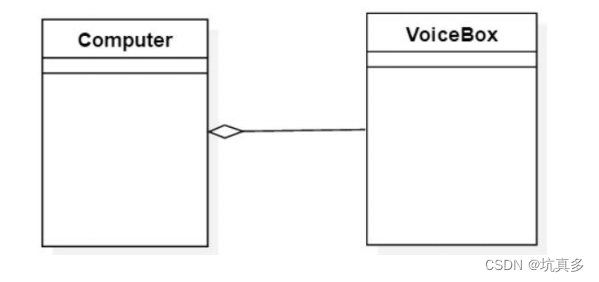
聚合
聚合不是组成关系,被包含的对象,也可能被其他对象包含。拥有者,不需要对被拥有的对象的生命周期负责。
头文件
class VoiceBox;VoiceBox *vioceBox;//computer和vioceBox之间,就是"聚合"void addBox(VoiceBox *vioceBox1);//创建一个成员函数,不和构造函数放在一起实现文件
void Computer::addBox(VoiceBox* vioceBox1) {this->vioceBox = vioceBox1;
}主文件
#include "Computer.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "VoiceBox.h"
void test(VoiceBox *h2) {Computer h1("intel","i9",1000,8);h1.addBox(h2);
}int main(void) {VoiceBox box;test(&box);return 0;
}