目录
一、yum仓库
1. yum仓库介绍
1.1 简介
1.2 实现过程
1.3 实现安装服务
2. yum配置文件及命令
2.1 yum配置文件
2.1.1 yum主配置文件
2.1.2 仓库设置文件
2.1.3 日志文件
2.2 yum命令详解
2.2.1 查询
2.2.2 yum安装升级
2.2.3 软件卸载
3. 搭建仓库的方式
3.1 搭建本地yum仓库
3.2 搭建阿里云仓库 (http方式外网环境)
3.3 ftp方式搭建云仓库
3.4 http方式搭建
二、nfs共享
1. 简介
2. 原理
3. NFS软件介绍
4. NFS共享配置文件格式
5. 搭建过程
三、工作环境常见问题
1. 自行打包后建立元数据
2. epel源本地
3. 离线安装软件
4. 升级内核
5. 访问不同服务器获得相同的数据
一、yum仓库
1. yum仓库介绍
1.1 简介
yum是一个基于RPM包(是Red-Hat Package Manager红帽软件包管理器的缩写)构建的软件更新机制,能够自动解决软件包之间的依赖关系。解决了日常工作中的大量查找安装依赖包的时间。
1.2 实现过程

yum实现需要安装包:
- 光驱自带,挂载提供软件包
- 网络下载到本地
- 直接通过网络
yum需要依赖于环境,依赖于服务端和客户端,允许跨网络 :
服务器:
- RPM包 (Packages文件夹中)
- 元数据(repodata文件夹:目录(软件的目录),软件的依赖关系,软件的位置)
客户端的配置文件中:
- baseurl=地址一定要写到这两个文件夹 repodata packages 的上级目录
最终形成两个文件夹Packages (包文件夹一般取名packages)和 repodata(元数据文件夹)
仓库类型:
- 光盘的仓库基本仓库,比较常用的
- epel扩展仓库,比较新
1.3 实现安装服务

2. yum配置文件及命令
2.1 yum配置文件
2.1.1 yum主配置文件
位置:/etc/yum.conf
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/yum.conf1 [main]2 cachedir=/var/cache/yum/$basearch/$releasever
#yum下载的RPM包的缓存目录,$basearch代表硬件架构,$releasever系统版本比如73 keepcache=0 #是否保存缓存:0代表不保存,1代表保存4 debuglevel=2 #调试级别5 logfile=/var/log/yum.log #日志文件位置6 exactarch=1 #是否允许不同版本的rpm安装7 obsoletes=1 #update的一个参数是否可以允许旧版本的运行8 gpgcheck=1 #验证秘钥9 plugins=1 #是否允许插件:1代表可以10 installonly_limit=5 #保存几个内核:5代表5个11 bugtracker_url=http://bugs.centos.org/set_project.php?project_id=23&ref=http://bugs.centos.org/bug_report_pag e.php?category=yum12 distroverpkg=centos-releaseyum的repo配置文件中可用的变量:
$releasever: 当前OS的发行版的主版本号,如:8,7,6
$arch: CPU架构,如:aarch64, i586, i686,x86_64等
$basearch:系统基础平台;i386, x86_64
$contentdir:表示目录,比如:centos-8,centos-7
$YUM0-$YUM9:自定义变量2.1.2 仓库设置文件
位置:/etc/yum.repos.d/*.repo
[root@localhost ~]# ls /etc/yum.repos.d/
CentOS-Base.repo CentOS-Debuginfo.repo CentOS-Media.repo CentOS-Vault.repo
CentOS-CR.repo CentOS-fasttrack.repo CentOS-Sources.repo
#这里默认的yum仓库是centos官方的yum源,需要联网才可以使用2.1.3 日志文件
[root@localhost ~]# cat /var/log/yum.log
Jan 16 10:02:07 Installed: vsftpd-3.0.2-29.el7_9.x86_64
#查看日志文件2.2 yum命令详解
| 命令 | 不加关键字 | 加入关键词、软件包、软件包组 |
|---|---|---|
| yum list | 显示所有可用包 | 单个的可安装包 |
| yum info | 显示所有可用包的信息 | 单个具体的信息 |
| yum search | \ | 模糊查找所有的相关信息 |
| yum provides | \ | 精确查找 |
| yum grouplist | 显示所有可用包组 | 显示具体的包组 |
| yum groupinfo | 显示所有的包组具体信息 | 显示具体的包组的具体信息 |
| yum install | \ | 安装具体软件包 |
| yum groupinstall | \ | 安装具体软件包组 |
| yum update | 所有软件升级 | 具体软件升级 |
| yum group update | 所有包组升级 | 具体包组升级 |
| yum remove | \ | 卸载具体软件 |
| yum groupremove | \ | 卸载具体包组软件 |
| yum history | 查看当前yum操作历史 | \ |
| yum history undo | 加入序号卸载序号里安装的软件 | \ |
| yum history redo | 加入序号重新执行序号里的操作 | \ |
2.2.1 查询
yum list [软件名]:显示可用的安装包,如不加软件名是显示所有的可用包
[root@localhost ~]# yum list *httpd*
#包含httpd的软件包yum info [软件名]:显示安装包详细信息
[root@localhost ~]# yum info httpd
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile* base: mirrors.ustc.edu.cn* extras: mirrors.ustc.edu.cn* updates: mirrors.ustc.edu.cn
可安装的软件包
名称 :httpd
架构 :x86_64
版本 :2.4.6
发布 :99.el7.centos.1
大小 :2.7 M
源 :updates/7/x86_64
简介 : Apache HTTP Server
网址 :http://httpd.apache.org/
协议 : ASL 2.0
描述 : The Apache HTTP Server is a powerful, efficient, and extensible: web server.yum search <关键词>:根据关键字查找软件安装包,相当于你只知道这个包里的某个关键字会全部给你匹配出来
[root@localhost ~]# yum search ftp
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile* base: mirrors.ustc.edu.cn* extras: mirrors.ustc.edu.cn* updates: mirrors.ustc.edu.cn
=============================================== N/S matched: ftp ================================================
ftp.x86_64 : The standard UNIX FTP (File Transfer Protocol) client
lftp-scripts.noarch : Scripts for lftp
syslinux-tftpboot.noarch : SYSLINUX modules in /var/lib/tftpboot, available for network booting
tftp.x86_64 : The client for the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP)
tftp-server.x86_64 : The server for the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP)
vsftpd.x86_64 : Very Secure Ftp Daemon
vsftpd-sysvinit.x86_64 : SysV initscript for vsftpd daemon
curl.x86_64 : A utility for getting files from remote servers (FTP, HTTP, and others)
lftp.i686 : A sophisticated file transfer program
lftp.x86_64 : A sophisticated file transfer program
wget.x86_64 : A utility for retrieving files using the HTTP or FTP protocolsyum provides <关键词>:知道某个命令却不知道具体的包可以用此命令查找
[root@localhost ~]# yum provides httpd
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile* base: mirrors.ustc.edu.cn* extras: mirrors.ustc.edu.cn* updates: mirrors.ustc.edu.cn
httpd-2.4.6-95.el7.centos.x86_64 : Apache HTTP Server
源 :baseyum grouplist [包组名] :安装包组的查询,不加包组名就是显示所有
yum groupinfo <包组名>:不加包组名显示全部
2.2.2 yum安装升级
yum install [软件名]
[root@localhost ~]# yum install httpd
#安装软件包,yum install安装http服务 yum groupinstall <包组名>
[root@localhost ~]# yum group install gnome desktop -y
#包组安装,安装可视化界面yum updata:更新包组,可以单个也可以全部后面加具体包组名称就是单个更新,不加就是全部更新;但首先要有更新的包组库否则也无法更新。
yum groupdata:组包更新和单个安装包更新差不多
2.2.3 软件卸载
yum remove <软件名>:卸载已安装的软件必须加软件名
yum groupremove <包组名>:同软件包卸载
yum history:查看历史的使用记录
[root@localhost ~]# yum history
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
ID | 登录用户 | 日期和时间 | 操作 | 变更数
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------3 | root <root> | 2024-01-16 15:04 | Install | 5 2 | root <root> | 2024-01-16 10:02 | Install | 1 1 | 系统 <空> | 2024-01-09 21:30 | Install | 1318选择ID,可以使用yum history undo 3进行卸载,这样对比remove好处是可以将所有的依赖都删除
案例:将ID3卸载
[root@localhost ~]# yum history undo 3
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
Undoing transaction 3, from Tue Jan 16 15:04:42 2024依赖安装 apr-1.4.8-7.el7.x86_64 @base依赖安装 apr-util-1.5.2-6.el7_9.1.x86_64 @updates安装 httpd-2.4.6-99.el7.centos.1.x86_64 @updates依赖安装 httpd-tools-2.4.6-99.el7.centos.1.x86_64 @updates依赖安装 mailcap-2.1.41-2.el7.noarch @base
正在解决依赖关系
--> 正在检查事务
---> 软件包 apr.x86_64.0.1.4.8-7.el7 将被 删除
---> 软件包 apr-util.x86_64.0.1.5.2-6.el7_9.1 将被 删除
---> 软件包 httpd.x86_64.0.2.4.6-99.el7.centos.1 将被 删除
---> 软件包 httpd-tools.x86_64.0.2.4.6-99.el7.centos.1 将被 删除
---> 软件包 mailcap.noarch.0.2.1.41-2.el7 将被 删除
……[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# yum history info 3
#查看第三次具体安装了什么再次使用yum history查看多了一条4记录是卸载记录
[root@localhost ~]# yum history
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
ID | 登录用户 | 日期和时间 | 操作 | 变更数
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------4 | root <root> | 2024-01-16 15:07 | Erase | 5 3 | root <root> | 2024-01-16 15:04 | Install | 5 2 | root <root> | 2024-01-16 10:02 | Install | 1 1 | 系统 <空> | 2024-01-09 21:30 | Install | 1318
history list如果后悔卸载可以使用两种方式:
yum history redo 3 (重新安装一遍
yum history undo 4(反悔卸载等于重新安装一遍)
3. 搭建仓库的方式
软件仓库的提供方式 FTP服务:
- ftp://ip地址/站点里路径
- HTTP服务:http://域名或者ip地址/站点里的路径
- 本地目录:file://绝对路径 (file:///mnt 此处第三个/为根目录)
3.1 搭建本地yum仓库
Linux配置本地yum仓库及编译安装nginx-CSDN博客
3.2 搭建阿里云仓库 (http方式外网环境)
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
[root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# mkdir bak
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# mv *.repo bak/
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# vim ali.repo
[ali]
name=aliyun
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/centos/7/os/x86_64/
gpgcheck=0
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# yum clean all
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# yum makecache
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# yum repolist
已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
源标识 源名称 状态
ali aliyun 10,072
repolist: 10,0723.3 ftp方式搭建云仓库
Linux网络文件共享服务-CSDN博客
3.4 http方式搭建
Linux网络文件共享服务-CSDN博客
先前搭建yum仓库相关已做过介绍,这里就不做赘述 。
二、nfs共享
1. 简介
NFS(Network File System 网络文件服务)文件系统(软件)文件的权限NFS是一种基于TCP/IP 传输的网络文件系统协议,最初由Sun公司开发。 通过使用NFS协议,客户机可以像访问本地目录一样访问远程服务器中的共享资源NFS也是NAS存储设备必然支持的一种协议。
2. 原理
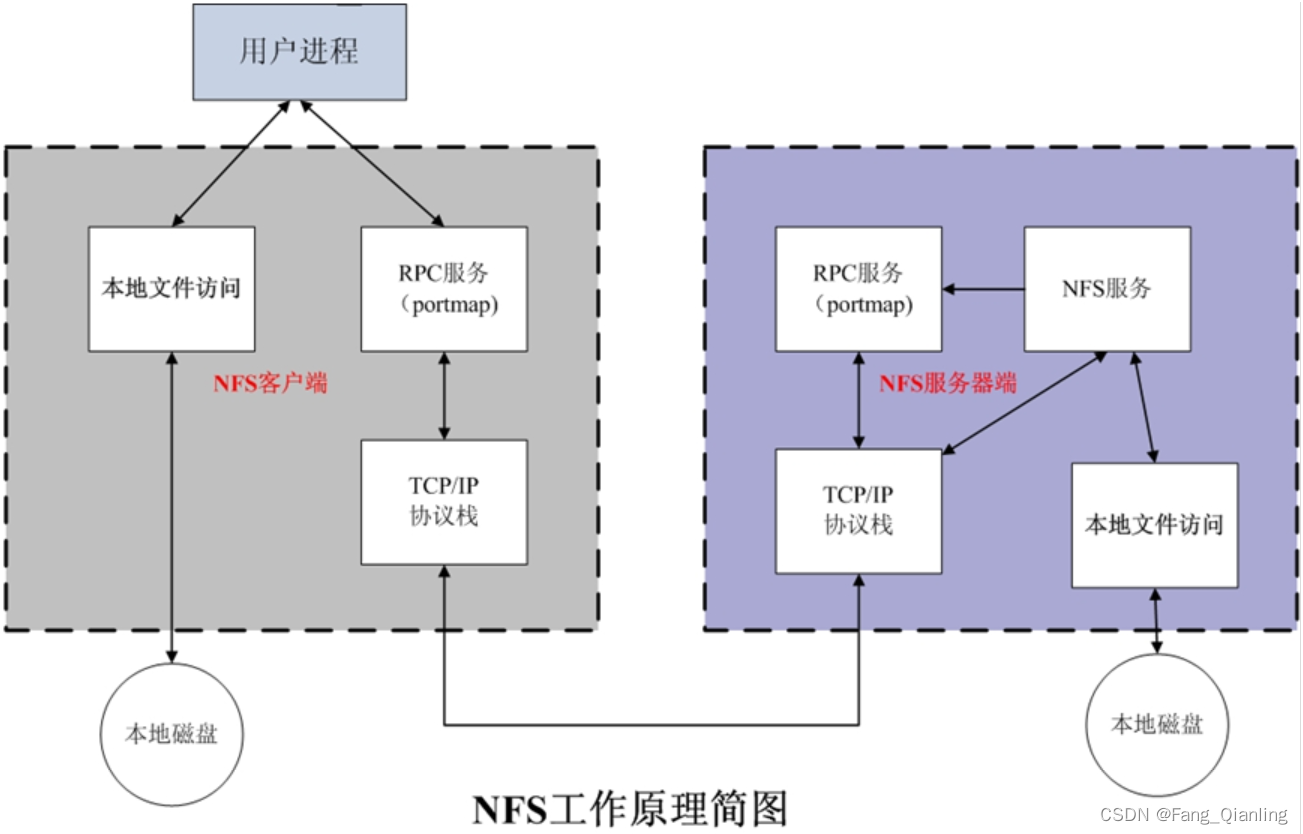
当客户端通过网络协议连接服务端,由于NFS服务端口号是随机的,所以要先连rpcbind这个程序(固定端口号111),然后通过rpcbind再连接NFS服务端。每当NFS服务启动时会报告自己的端口号给rpcbind。
3. NFS软件介绍
软件包:nfs-utils(包括服务器端和客户端);相关软件包:rpcbind(必须)。二者存在依赖关系。nfs端口号不固定,RPC端口号111。
4. NFS共享配置文件格式
主配置文件:/etc/exports
共享目录 主机,可以访问的主机地址(权限)
/share *
#wildcards:主机名通配,例如:*.magedu.com,IP不可以netgroups:NIS域的主机组,@group_name每个条目指定目录导出到的哪些主机,及相关的权限和选项:
默认选项:(ro,sync,root_squash,no_all_squash)
ro,rw 只读和读写
async 异步,数据变化后不立即写磁盘,先写入到缓冲区中,过一段时间再写入磁盘,性能高,安全性低
sync(1.0.0后为默认)同步,数据在请求时立即写入共享存储磁盘,性能低,安全性高
root_squash (默认)远程root映射为nfsnobody,UID为65534,CentOS8 为nobody,CentOS
7以前的版本为nfsnobody
no_root_squash 远程root映射成NFS服务器的root用户
all_squash 所有远程用户(包括root)都变成nfsnobody,CentOS8 为nobody
no_all_squash (默认)保留共享文件的UID和GID
anonuid和anongid 指明匿名用户映射为特定用户UID和组GID,而非nobody,可配合all_squash使用
/data/nfs1 *(rw,all_squash,anonuid=1002,anongid=1002)
5. 搭建过程
服务端创建共享目录,服务端挂载共享目录:
服务端:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -q nfs-utils
nfs-utils-1.3.0-0.48.el7.x86_64
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -q rpcbind
rpcbind-0.2.0-42.el7.x86_64
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start rpcbind #开启rpcbind即可,会呼叫nfs
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /share
[root@localhost ~]# cp /etc/passwd /share
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/exports
/share *
[root@localhost ~]# exportfs -r #重新加载配置文件
[root@localhost ~]# exportfs -v #显示本机服务端的共享目录
/share <world>(ro,sync,wdelay,hide,no_subtree_check,sec=sys,secure,root_squash,no_all_squash)
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start nfs客户端:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start rpcbind
[root@localhost ~]# showmount -e 192.168.190.100 #查看服务端共享文件目录
Export list for 192.168.190.100:
/share *
[root@localhost ~]# mount 192.168.190.100:/share /mnt
[root@localhost ~]# df -h | grep mnt
192.168.190.100:/share 50G 3.3G 47G 7% /mnt
[root@localhost ~]# ls /mnt
passwd客户端创建文件:
服务端:
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/exports
/share *(rw) #添加读写权限
[root@localhost ~]# chmod 777 /share/ #给文件夹添加读写权限
[root@localhost ~]# ll -d /share/
drwxrwxrwx. 2 root root 20 1月 16 17:58 /share/
[root@localhost ~]# exportfs -r客户端:
[root@localhost mnt]# touch 1.txt
[root@localhost mnt]# ls
1.txt passwd超级管理员root用户削权:
服务端:
[root@localhost ~]# cd /share/
[root@localhost share]# ll
总用量 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 nfsnobody nfsnobody 0 1月 16 18:02 1.txt #客户端root创建用户显示nfsnobody
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2101 1月 16 17:58 passwd客户端:
[root@localhost mnt]# su fql
[fql@localhost mnt]$ ls
1.txt passwd
[fql@localhost mnt]$ touch 2.txt服务端:
[root@localhost share]# ll
总用量 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 nfsnobody nfsnobody 0 1月 16 18:02 1.txt
-rw-rw-r--. 1 fql fql 0 1月 16 18:08 2.txt #普通用户fql创建文件的用户依然是fql
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2101 1月 16 17:58 passwd
#由此可见,nfs共享超级管理员创建的文件会被削权取消root用户压榨削权:
服务端:
[root@localhost share]# exportfs -v
/share <world>(rw,sync,wdelay,hide,no_subtree_check,sec=sys,secure,root_squash,no_all_squash)
[root@localhost share]# vim /etc/exports
/share *(rw,no_root_squash)
#no_root_squash代表关闭将root用户映射成匿名用户,取消削权客户端:
[root@localhost mnt]# touch 3.txt服务端:
[root@localhost share]# ll
总用量 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 nfsnobody nfsnobody 0 1月 16 18:02 1.txt
-rw-rw-r--. 1 fql fql 0 1月 16 18:08 2.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nfsnobody nfsnobody 0 1月 16 18:16 3.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2101 1月 16 17:58 passwd #文件属主root
指明匿名用户映射为特定用户UID和组GID,而非nobody:
服务端:
[root@localhost share]# useradd -u 1002 lisi
[root@localhost share]# passwd lisi
/share *(rw,anonuid=1002,anongid=1002)
[root@localhost share]# vim /etc/exports
share *(rw,all_squash,anonuid=1002,anongid=1002)
[root@localhost share]# exportfs -r
[root@localhost share]# exportfs -v
/share <world>(rw,sync,wdelay,hide,no_subtree_check,anonuid=1002,anongid=1002,sec=sys,secure,root_squash,all_squash)客户端:
[root@localhost mnt]# touch 4.txt
[root@localhost mnt]# su fql
[fql@localhost mnt]$ touch 5.txt服务端:
[root@localhost share]# ll
总用量 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 nfsnobody nfsnobody 0 1月 16 18:02 1.txt
-rw-rw-r--. 1 fql fql 0 1月 16 18:08 2.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nfsnobody nfsnobody 0 1月 16 18:16 3.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 lisi lisi 0 1月 16 18:33 4.txt #任何用户压榨成属主lisi
-rw-rw-r--. 1 lisi lisi 0 1月 16 18:33 5.txt #任何用户压榨成属主lisi
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2101 1月 16 17:58 passwd三、工作环境常见问题
1. 自行打包后建立元数据
#将新软件以“rpm”结尾的安装包移动到规定目录下,软件包找开发要,模拟将tree的安装包放到规定目录下,在建立元数据
[root@localhost ~]# mount /dev/sr0 /mnt/
mount: /dev/sr0 写保护,将以只读方式挂载
[root@localhost ~]# cd /mnt
[root@localhost mnt]# ls
CentOS_BuildTag EULA images LiveOS repodata RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-Testing-7
EFI GPL isolinux Packages RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7 TRANS.TBL
[root@localhost mnt]# mkdir -p /data/tree/Packages
[root@localhost mnt]# cp /mnt/Packages/tree-1.6.0-10.el7.x86_64.rpm /data/tree/Packages/
[root@localhost tree]# cd /data/tree/Packages/
[root@localhost Packages]# ls
tree-1.6.0-10.el7.x86_64.rpm
[root@localhost Packages]# cd ../../
[root@localhost data]# createrepo -v tree
[root@localhost data]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# mkdir bak
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# mv *.repo bak
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# vim tree.repo
[tree]
name=tree
baseurl=file:///data/tree
gpgcheck=0
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]#yum clean all
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]#yum makecache
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]#yum list
[root@localhost ~]#yum install -y tree
2. epel源本地
适用场景:没有外网又想使用这个epel源
[root@localhost ~]#yum install epel-release -y
#安装epel源,生成epel仓库文件
[root@localhost ~]# reposync -r epel -p /data/
#下载同步epel源,根据epel仓库文件去找目录3. 离线安装软件
[root@localhost ~]# yum install nginx --downloadonly --downloaddir=/data/
--downloadonly #只下载相关包默认至某一目录
--downloaddir=绝对目录路径 #下载到某一目录
[root@localhost ~]# ls /data
epel nginx-filesystem-1.20.1-10.el7.noarch.rpm
nginx-1.20.1-10.el7.x86_64.rpm openssl11-libs-1.1.1k-6.el7.x86_64.rpm4. 升级内核
[root@localhost ~]# yum install https://www.elrepo.org/elrepo-release-7.0-4.el7.elrepo.noarch.rpm -y
[root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# ls
CentOS-Base.repo CentOS-Debuginfo.repo CentOS-Media.repo CentOS-Vault.repo epel.repo
CentOS-CR.repo CentOS-fasttrack.repo CentOS-Sources.repo elrepo.repo epel-testing.repo
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# vim elrepo.repo
28 [elrepo-kernel]
35 enabled=1 #将仓库配置文件的内核库打开即可
[root@localhost ~]# uname -r
3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# yum list *kernel*
#查看其他内核版本,然后安装其他内核版本即可
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# yum install -y kernel-lt.x86_64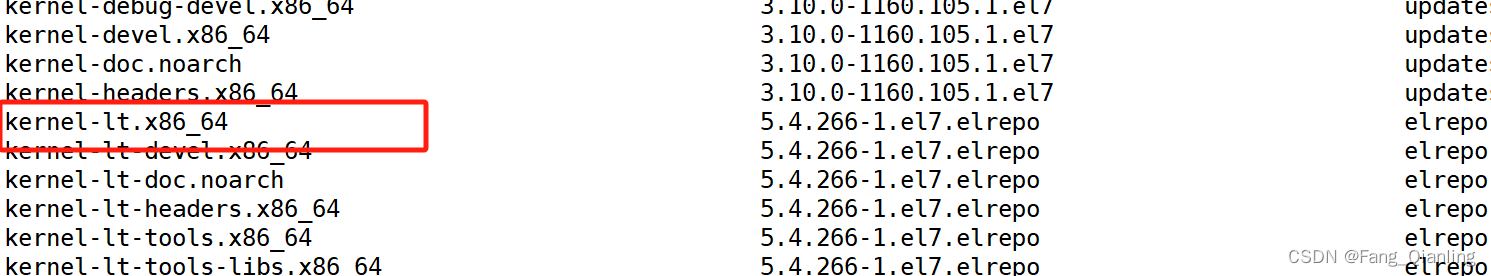
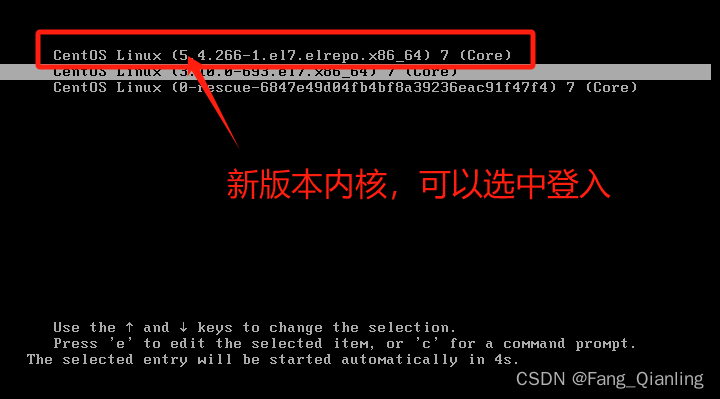
5. 访问不同服务器获得相同的数据
环境:服务器1:192.168.190.101,服务器2:192.168.190.102,nfs存储服务器:192.168.190.100
nfs存储服务端:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
[root@localhost ~]# yum install -y httpd
[root@localhost ~]# cd /var/www/html
[root@localhost html]# vim index.html
fql服务器1:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
[root@localhost ~]# yum install -y httpd
[root@localhost ~]# cd /var/www/html
[root@localhost html]# vim index.html
101服务器2:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
[root@localhost ~]# yum install -y httpd
[root@localhost ~]# cd /var/www/html
[root@localhost html]# vim index.html
102此时,访问各自服务器只能看见对应内容:
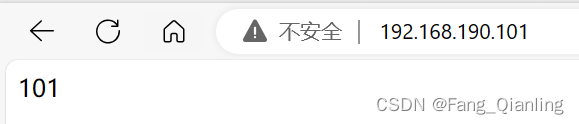
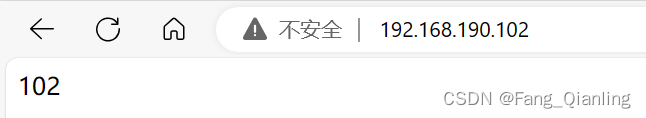
挂载:
nfs存储服务端:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /data
[root@localhost ~]# cd /data
[root@localhost data]# vim index.html
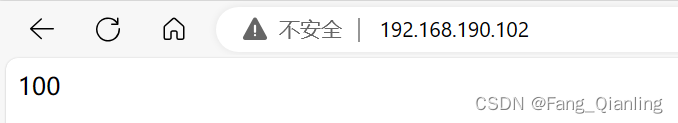
100
[root@localhost data]# vim /etc/exports
/data *
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start rpcbind
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start nfs
[root@localhost data]# exportfs -r
[root@localhost data]# exportfs -v服务器1:
[root@localhost html]# mount 192.168.190.100:/data /var/www/html/服务器2:
[root@localhost html]# mount 192.168.190.100:/data /var/www/html/实现访问多个服务器获得同样的数据:
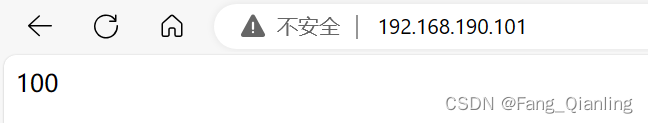




![P9852 [ICPC2021 Nanjing R] Windblume Festival 题解(SPJ)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/f201e201ff0db7cd247536f9feb85d5b.png)