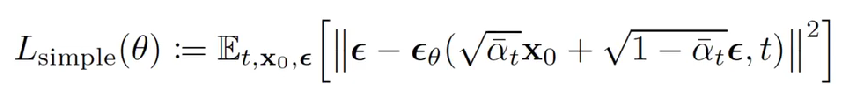1 Title
Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models(Jonathan Ho、Ajay Jain、Pieter Abbeel)
2 Conclusion
This paper present high quality image synthesis results using diffusion probabilistic models,
a class of latent variable models inspired by considerations from nonequilibrium thermodynamics.The best results are obtained by training on a weighted variational bound designed according to a novel connection between diffusion probabilistic models and denoising score matching with Langevin dynamics, and our models naturally admit a progressive lossy decompression scheme that can be interpreted as a generalization of autoregressive decoding
3 Good Sentences
1、A diffusion probabilistic model which we will call a “diffusion model” for brevity is a parameterized Markov chain trained using variational inference to produce samples matching the data after finite time.(The essence of the DDPM model)
2、Diffusion models are straightforward to define and efficient to train, but to the best of our knowledge,there has been no demonstration that they are capable of generating high quality samples. We show that diffusion models actually are capable of generating high quality samples, sometimes better than the published results on other types of generative models.(The significance of this work)
3、These terms train the network to denoise data with very small amounts of noise, so it is beneficial to down-weight them so that the network can focus on more difficult denoising tasks at larger t terms. We will see in our experiments that this reweighting leads to better sample quality.(The role of parameter restructuring techniques)
DDPM的主要过程如图所示,共有两个阶段,第一个阶段是从x0到xT,叫做扩散过程,第二个阶段是反过来,叫做重构过程。
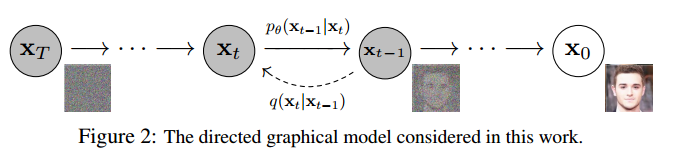
扩散过程就是不断向加噪声,最终得到xT,xT符合标准高斯分布(也就是正态分布)。
重构过程则是从一个标准的高斯分布不断降噪,得到一个清晰的图片。
整个DDPM的核心假设是马尔科夫链假设,即变换过程只与前一状态有关,与更前的状态无关,这样的话,可以简化一些复杂的概率分布,比如
这个公式中的条件概率中,给定条件x0就可以被忽略,因为xt的状态只与xt-1时的状态有关。
进而,以下公式成了文章的精华:
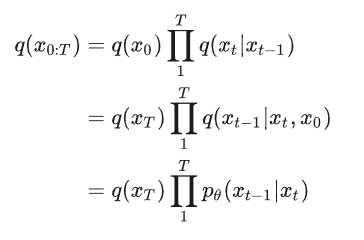
第一行就是扩散过程,第二行则是重构过程,而第三行是重构的真正方式(因为第二行并不适用,目的就是得到x0,公式中都有x0,岂不是闭合了),所以最终DDPM的核心就在于![]() ,其中,p可以转换成只包含xt和噪声
,其中,p可以转换成只包含xt和噪声两个变量的公式。
DDPM选择预测,其目标函数如下: