在Java开发中经常遇到list结构数据的处理,如List的合并或拆分,记录下来,方便备查。
一、List 合并
两个list数据的合并处理,可使用Java8 新特性的stream流,根据实际需要遍历取值。
1、定义 UserInfo 对象
订单的相关字段如下所示。
public class UserInfo {Long orderId;Long skuId;String skuName;Long spuId;String spuName;public Long getOrderId() {return orderId;}public void setOrderId(Long orderId) {this.orderId = orderId;}public Long getSkuId() {return skuId;}public void setSkuId(Long skuId) {this.skuId = skuId;}public String getSkuName() {return skuName;}public void setSkuName(String skuName) {this.skuName = skuName;}public Long getSpuId() {return spuId;}public void setSpuId(Long spuId) {this.spuId = spuId;}public String getSpuName() {return spuName;}public void setSpuName(String spuName) {this.spuName = spuName;}
}
2、构造List 对象
两个List 对象,内容分别如下:
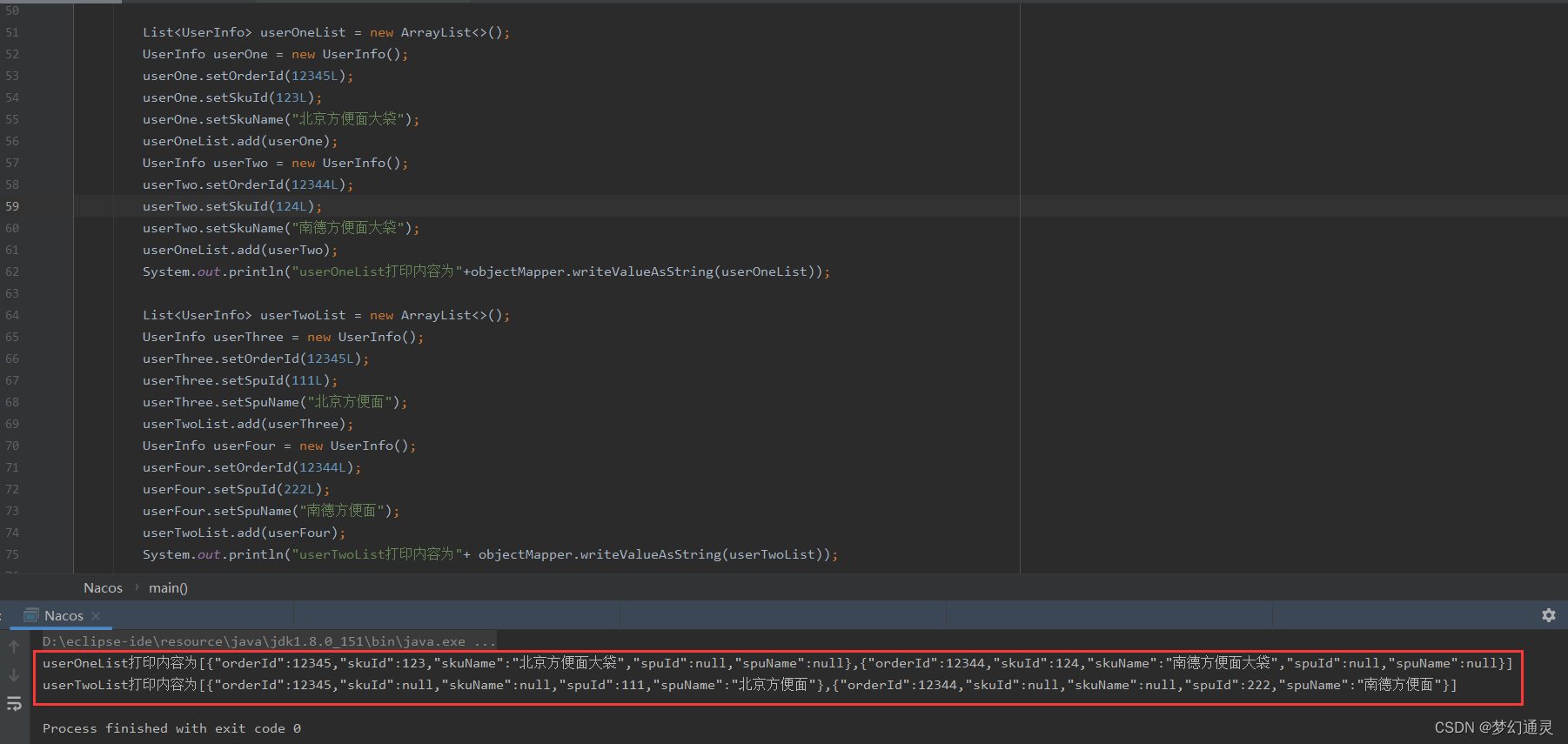
第一个 userOneList 中UserInfo包含3个字段,订单号orderId,商品ID skuId和 商品名称skuName;
第二个 userTwoList 中UserInfo包含3个字段,订单号orderId,产品ID spuId和 产品名称spuName;
两个合并为新的list,包含所有5个字段。
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;// 创建ObjectMapper实例
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
List<UserInfo> userOneList = new ArrayList<>();
UserInfo userOne = new UserInfo();
userOne.setOrderId(12345L);
userOne.setSkuId(123L);
userOne.setSkuName("北京方便面大袋");
userOneList.add(userOne);
UserInfo userTwo = new UserInfo();
userTwo.setOrderId(12344L);
userTwo.setSkuId(124L);
userTwo.setSkuName("南德方便面大袋");
userOneList.add(userTwo);
System.out.println("userOneList打印内容为"+objectMapper.writeValueAsString(userOneList));List<UserInfo> userTwoList = new ArrayList<>();
UserInfo userThree = new UserInfo();
userThree.setOrderId(12345L);
userThree.setSpuId(111L);
userThree.setSpuName("北京方便面");
userTwoList.add(userThree);
UserInfo userFour = new UserInfo();
userFour.setOrderId(12344L);
userFour.setSpuId(222L);
userFour.setSpuName("南德方便面");
userTwoList.add(userFour);
System.out.println("userTwoList打印内容为"+ objectMapper.writeValueAsString(userTwoList));
遍历结果如下图所示。
思路:利用 Stream 遍历第一个list,并筛选过滤第二个list中bean 订单ID一致的对象,进行赋值操作。
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;// 两个list合并
List<UserInfo> tolatAllList = userOneList.stream().map(one -> {userTwoList.stream().filter(two -> Objects.equals(one.getOrderId(), two.getOrderId())).forEach(two -> {one.setSpuId(two.getSpuId());one.setSpuName(two.getSpuName());});return one;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("合并后tolatAllList打印其内容为"+ objectMapper.writeValueAsString(tolatAllList));
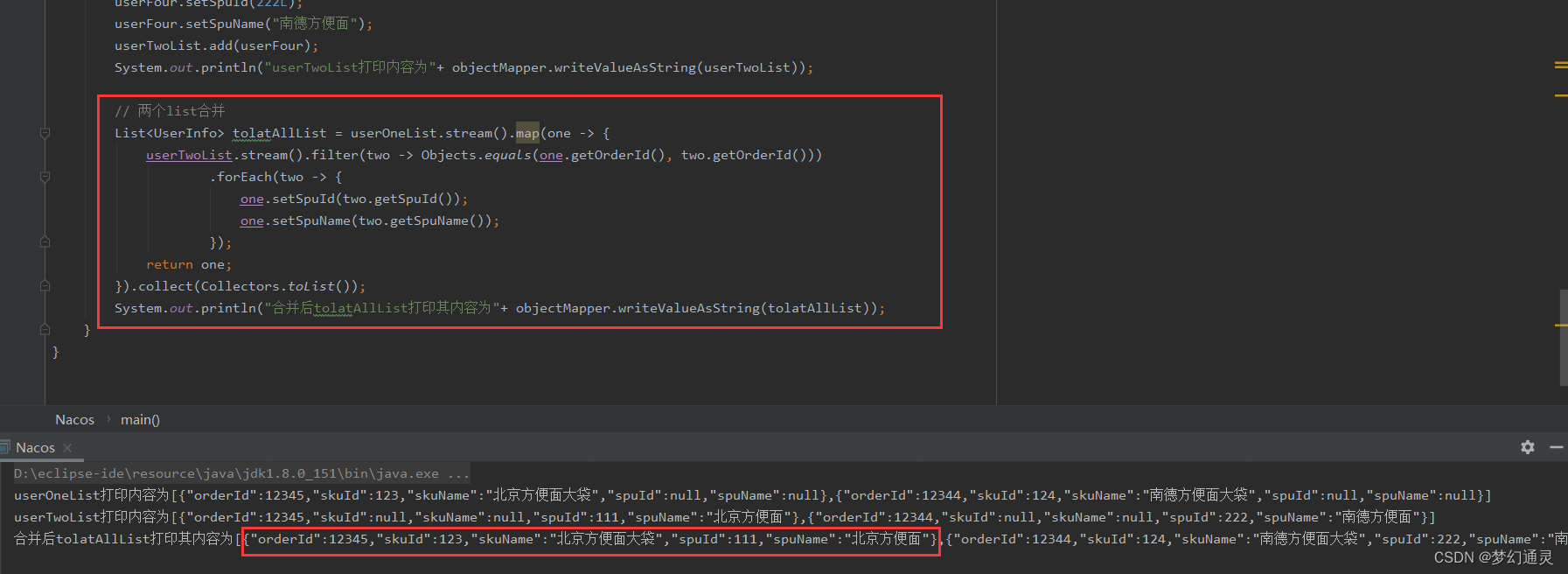
执行以上代码,遍历结果如下所示,则可发现新的list包含两个list的信息。
二、List 拆分
对于大List的操作处理是很消耗性能,可将其拆分为小一些的List进行处理。
提取拆分的公共util类,splitList 方法
/*** 切分list* @param sourceList* @param groupSize 每组定长* @return*/public static List<List<UserInfo>> splitList(List<UserInfo> sourceList, int groupSize) {int length = sourceList.size();// 计算可以分成多少组int num = (length + groupSize - 1) / groupSize;List<List<UserInfo>> newList = new ArrayList<>(num);for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {// 开始位置int fromIndex = i * groupSize;// 结束位置int toIndex = (i + 1) * groupSize < length ? (i + 1) * groupSize : length;newList.add(sourceList.subList(fromIndex, toIndex));}return newList;}
调用如下所示。
List<UserInfo> userTwoList = new ArrayList<>();
UserInfo userThree = new UserInfo();
userThree.setOrderId(12345L);
userThree.setSpuId(111L);
userThree.setSpuName("北京方便面");
userTwoList.add(userThree);
UserInfo userFour = new UserInfo();
userFour.setOrderId(12344L);
userFour.setSpuId(222L);
userFour.setSpuName("南德方便面");
userTwoList.add(userFour);
UserInfo userFive = new UserInfo();
userFive.setOrderId(12343L);
userFive.setSpuId(333L);
userFive.setSpuName("豫竹方便面");
userTwoList.add(userFive);
UserInfo userSix = new UserInfo();
userSix.setOrderId(12342L);
userSix.setSpuId(444L);
userSix.setSpuName("小浣熊方便面");
userTwoList.add(userSix);
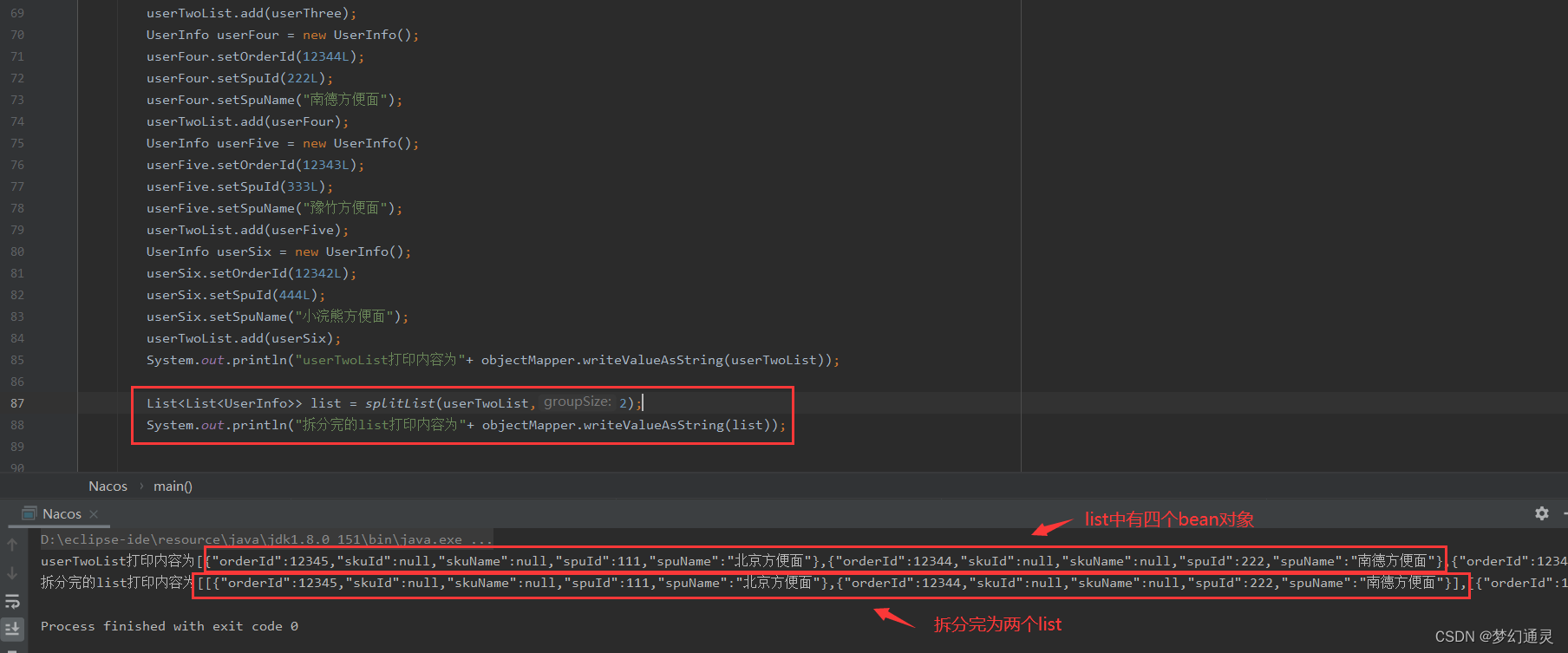
System.out.println("userTwoList打印内容为"+ objectMapper.writeValueAsString(userTwoList));List<List<UserInfo>> list = splitList(userTwoList,2);
System.out.println("拆分完的list打印内容为"+ objectMapper.writeValueAsString(list));// 调用方法
List<List<UserInfo>> list = splitList(userTwoList,2);
System.out.println("拆分完的list打印内容为"+ objectMapper.writeValueAsString(list));
方法执行拆分结果如下图所示。
以上即 List的合并和拆分,仅做参考,可留言交流。