1.找出两个链表的交点
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists (Easy)
Leetcode / 力扣
例如以下示例中 A 和 B 两个链表相交于 c1:
A: a1 → a2↘c1 → c2 → c3↗ B: b1 → b2 → b3
但是不会出现以下相交的情况,因为每个节点只有一个 next 指针,也就只能有一个后继节点,而以下示例中节点 c 有两个后继节点。
A: a1 → a2 d1 → d2↘ ↗c↗ ↘ B: b1 → b2 → b3 e1 → e2
要求时间复杂度为 O(N),空间复杂度为 O(1)。如果不存在交点则返回 null。
设 A 的长度为 a + c,B 的长度为 b + c,其中 c 为尾部公共部分长度,可知 a + c + b = b + c + a。
当访问 A 链表的指针访问到链表尾部时,令它从链表 B 的头部开始访问链表 B;同样地,当访问 B 链表的指针访问到链表尾部时,令它从链表 A 的头部开始访问链表 A。这样就能控制访问 A 和 B 两个链表的指针能同时访问到交点。
如果不存在交点,那么 a + b = b + a,以下实现代码中pa和pb会同时为 null,从而退出循环。
public class Solution {public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {ListNode pa = headA, pb = headB;while(pa != pb){pa = (pa == null ? headB : pa.next);pb = (pb == null ? headA : pb.next);}return pa;}
}2.翻转链表
206. Reverse Linked List (Easy)
Leetcode / 力扣
双指针迭代
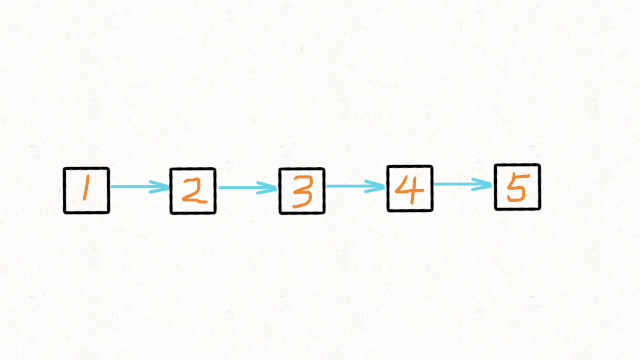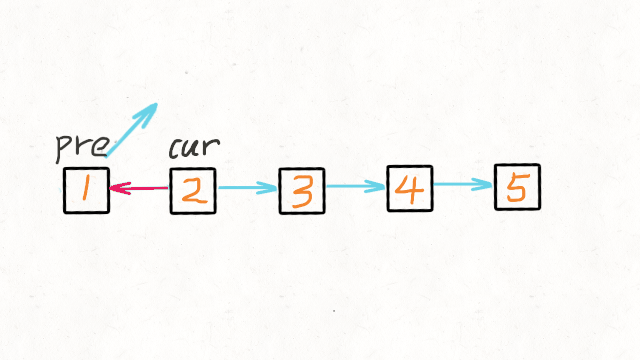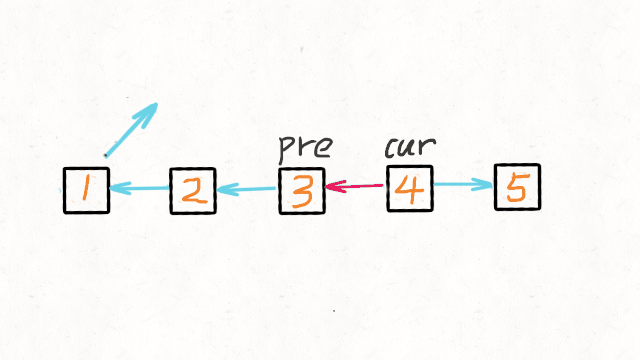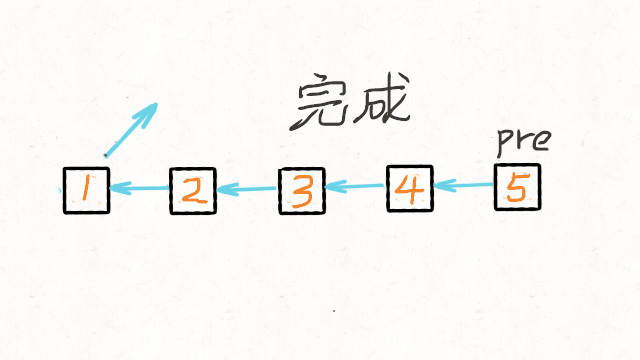
我们可以申请两个指针,第一个指针叫 pre,最初是指向 null 的。
第二个指针 cur 指向 head,然后不断遍历 cur。
每次迭代到 cur,都将 cur 的 next 指向 pre,然后 pre 和 cur 前进一位。
都迭代完了(cur 变成 null 了),pre 就是最后一个节点了。
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {ListNode pre = null, cur = head;while(cur != null){ListNode tmp = cur.next;cur.next = pre;pre = cur;cur = tmp;}return pre;}
}3.归并两个有序的链表
21. Merge Two Sorted Lists (Easy)
Leetcode / 力扣
class Solution {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {ListNode p1 = list1, p2 = list2;ListNode list3 = new ListNode(-1), p3 = list3;while(p1 != null && p2 != null){if(p1.val <= p2.val){p3.next = p1;p3 = p3.next;p1 = p1.next;}else{p3.next = p2;p3 = p3.next;p2 = p2.next;}}if(p1 != null){p3.next = p1;}else{p3.next = p2;}return list3.next;}
}4. 从有序链表中删除重复节点
83. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List (Easy)
Leetcode / 力扣
class Solution {public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {ListNode p = head;while(p.next != null){if(p.val == (p.next).val){p.next = p.next.next;}else{p = p.next;}}return head;}
}