MyBatis小技巧
- 一、#{}和${}
- 1.#{}和${}的区别
- 2.什么情况下必须使⽤${}
- 二、别名机制-typeAliases
- 1.typeAlias
- 2.package
- 三、mappers的配置
- 1.mapper
- (1)resource
- (3)URL
- (3)class
- 2.package
- 四、插⼊数据时获取⾃动⽣成的主键
一、#{}和${}
1.#{}和${}的区别
- #{}:先编译sql语句,再给占位符传值,底层是PreparedStatement实现。可以防⽌sql注⼊,⽐较常⽤。
- ${}:先进⾏sql语句拼接,然后再编译sql语句,底层是Statement实现。存在sql注⼊现象。只有在需要进⾏sql语句关键字拼接的情况下才会⽤到。
- 原则:能⽤ #{} 就不⽤ ${}。
2.什么情况下必须使⽤${}
- 当需要进⾏sql语句关键字拼接的时候。必须使⽤${}。
- 案例:
- ① 通过向sql语句中注⼊asc或desc关键字,来完成数据的升序或降序排列。
- ② 拼接表名。
- 业务背景:实际开发中,有的表数据量⾮常庞⼤,可能会采⽤分表⽅式进⾏存储,⽐如每天⽣成⼀张表。表的名字与⽇期挂钩,例如:2022年8⽉1⽇⽣成的表:t_user20220108。2000年1⽉1⽇⽣成的表:t_user20000101。此时前端在进⾏查询的时候会提交⼀个具体的⽇期,⽐如前端提交的⽇期为:2000年1⽉1⽇,那么后端就会根据这个⽇期动态拼接表名为:t_user20000101。有了这个表名之后,将表名拼接到sql语句当中,返回查询结果。
- 使⽤ #{} 会是这样:select * from ‘article’
- 使⽤ ${} 会是这样:select * from article
- ③ 批量删除
- 对应的sql语句:
- delete from t_user where id = 1 or id = 2 or id = 3;
- delete from t_user where id in(1, 2, 3);
- 假设现在使⽤in的⽅式处理,前端传过来的字符串:1, 2, 3
- 使⽤#{} :delete from t_user where id in(‘1, 2, 3’)
- 使⽤${} :delete from t_user where id in(1, 2, 3)
- 对应的sql语句:
- ④ 模糊查询
二、别名机制-typeAliases
- resultType 属性⽤来指定查询结果集的封装类型、parameterType 属性用来指定传递的参数类型(namespace 不能使用别名机制),这个名字太⻓,可以在 mybatis-config.xml ⽂件中使⽤ typeAliases 标签来起别名,包括两种⽅式:
- ⾸先要注意 typeAliases 标签的放置位置,如果不清楚的话,可以看看错误提示信息。
1.typeAlias
<typeAliases><typeAlias type="com.gdb.mybatis.pojo.Car" alias="Car"/>
</typeAliases>
- typeAliases标签中的typeAlias可以写多个。
- typeAlias:
- type属性:指定给哪个类起别名
- alias属性:别名。
- alias属性不是必须的,如果缺省的话,type属性指定的类型名的简类名作为别名。
- alias是⼤⼩写不敏感的。也就是说假设alias=“Car”,再⽤的时候,可以CAR,也可以car,也可以Car,都⾏。
2.package
<typeAliases><package name="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
- 如果⼀个包下的类太多,每个类都要起别名,会导致 typeAlias 标签配置较多,所以 mybatis 又提供 package 的配置⽅式,只需要指定包名,该包下的所有类都⾃动起别名,别名就是简类名。并且别名不区分⼤⼩写。
- package也可以配置多个的。
三、mappers的配置
1.mapper
(1)resource
- 这种⽅式是从类路径中加载配置⽂件,所以这种⽅式要求SQL映射⽂件必须放在resources⽬录下或其⼦
⽬录下。
<mappers><mapper resource="article2.xml"/><mapper resource="com/gdb/mybatis/mapper/article1.xml"/>
</mappers>
(3)URL
- 这种⽅式显然使⽤了绝对路径的⽅式,这种配置对SQL映射⽂件存放的位置没有要求,随意。这种方式的移植性差,一般都不会使用。
<mappers><mapper url="file:///var/mappers/AuthorMapper.xml"/><mapper url="file:///var/mappers/BlogMapper.xml"/><mapper url="file:///var/mappers/PostMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
(3)class
- 如果使⽤这种⽅式必须满⾜以下条件:
-
SQL映射⽂件和mapper接⼝放在同⼀个⽬录下。
- 在resources⽬录下新建:com/powernode/mybatis/mapper【这⾥千万要注意:不能这样新建com.powernode.mybatis.mapper】
- 如果将 xxx.xml 文件放在了 java 目录下,需要在 pom.xml 文件中添加如下配置。
<build><!--配置maven在构建项目的时候除了编译Java源文件以外也编译所有的.xml文件--><resources><resource><directory>src/main/java</directory><includes><include>**/*.xml</include></includes></resource><resource><directory>src/main/resources</directory><includes><include>**/*.*</include></includes></resource></resources> </build> -
SQL映射⽂件的名字也必须和mapper接⼝名⼀致。
-
<mappers><!-- 使⽤映射器接⼝实现类的完全限定类名 --><mapper class="com.gdb.mybatis.mapper.ArticleMapper"/>
</mappers>
2.package
- 如果 class 较多,可以使⽤这种 package 的⽅式,但前提条件和 class 的⽅式⼀样。
<!-- 将包内的映射器接⼝实现全部注册为映射器 -->
<mappers><package name="com.gdb.mybatis.mapper"/>
</mappers>
四、插⼊数据时获取⾃动⽣成的主键
- 插⼊⼀条新的记录之后,⾃动⽣成了主键,⽽这个主键需要在其他表中使⽤时。
- 插⼊⼀个⽤户数据的同时需要给该⽤户分配⻆⾊:需要将⽣成的⽤户的id插⼊到⻆⾊表的user_id字段上。
- 第⼀种⽅式:可以先插⼊⽤户数据,再写⼀条查询语句获取id,然后再插⼊user_id字段。【⽐较麻烦】
- 第⼆种⽅式:mybatis提供了⼀种⽅式更加便捷。
public interface ArticleMapper {int insert(Article row);
}
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.gdb.generate.pojo.Article" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">insert into articlevalues(null, #{userId}, #{title}, #{summary}, #{readCount}, #{createTime}, #{updateTime})
</insert>
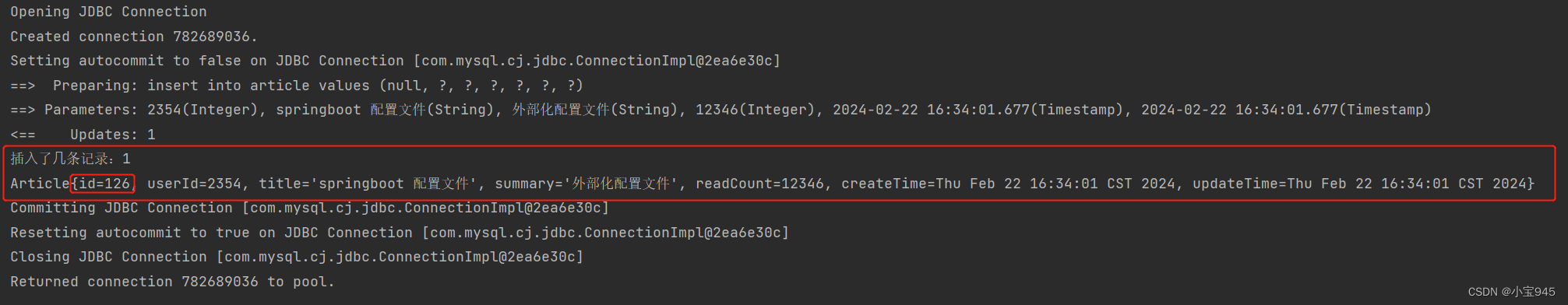
- useGenerateKeys = “true” 使用自动生成的主键
- keyProperty = “id” 指定主键值赋值给对象的那个属性。这个就表示将主键值赋值给 Article 对象的 id 属性。
import com.gdb.generate.mapper.ArticleMapper;
import com.gdb.generate.pojo.Article;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.Test;import java.util.Date;public class GeneratorTest {@Testpublic void testGenerator() throws Exception {SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"));SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();ArticleMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(ArticleMapper.class);// 增Article article = new Article(null, 2354, "springboot 配置文件", "外部化配置文件", 12346, new Date(), new Date());int count = mapper.insert(article);System.out.println("插⼊了⼏条记录:" + count);System.out.println(article);sqlSession.commit();sqlSession.close();}
}