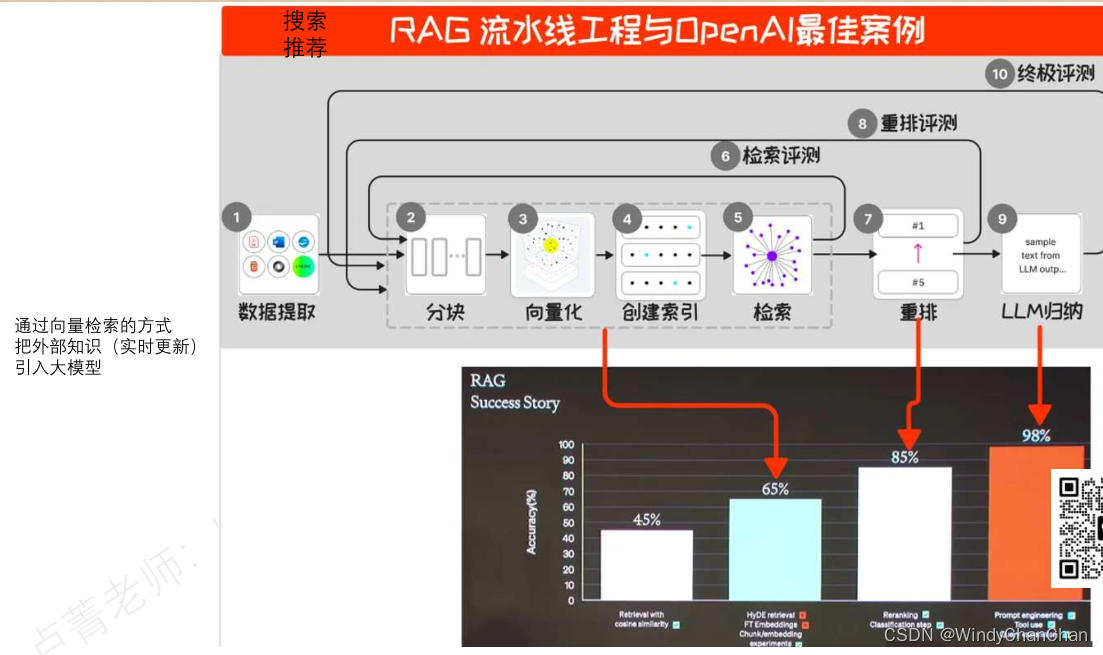
剖析 LinkedList
本文为书籍《Java编程的逻辑》1和《剑指Java:核心原理与应用实践》2阅读笔记
ArrayList随机访问效率很高,但插入和删除性能比较低;LinkedList同样实现了List接口,它的特点与ArrayList几乎正好相反。除了实现了List接口外,LinkedList还实现了Deque和Queue接口,可以按照队列、栈和双端队列的方式进行操作。
2.1 基本用法
LinkedList有两个构造方法:
public LinkedList()
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c)
所以,可以按照下面两种方法创建LinkedList对象:
List<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
List<String> list2 = new LinkedList<>(Arrays.asList(new String[]{"a", "b", "c"}));
同ArrayList一样,LinkedList同样实现了List接口,而List接口扩展了Collection接口,Collection又扩展了Iterable接口,所有这些接口的方法都是可以使用的,使用方法与ArrayList介绍的一样。
与ArrayList不同的是,LinkedList实现了队列接口Queue,所谓队列就类似于日常生活中的各种排队,特点就是先进先出,在尾部添加元素,从头部删除元素,它的接口定义为:
public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E> {/*** Inserts the specified element into this queue if it is possible to do so* immediately without violating capacity restrictions, returning* {@code true} upon success and throwing an {@code IllegalStateException}* if no space is currently available.** @param e the element to add* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})* @throws IllegalStateException if the element cannot be added at this* time due to capacity restrictions* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element* prevents it from being added to this queue* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and* this queue does not permit null elements* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of this element* prevents it from being added to this queue*/boolean add(E e);/*** Inserts the specified element into this queue if it is possible to do* so immediately without violating capacity restrictions.* When using a capacity-restricted queue, this method is generally* preferable to {@link #add}, which can fail to insert an element only* by throwing an exception.** @param e the element to add* @return {@code true} if the element was added to this queue, else* {@code false}* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element* prevents it from being added to this queue* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and* this queue does not permit null elements* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of this element* prevents it from being added to this queue*/boolean offer(E e);/*** Retrieves and removes the head of this queue. This method differs* from {@link #poll() poll()} only in that it throws an exception if* this queue is empty.** @return the head of this queue* @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty*/E remove();/*** Retrieves and removes the head of this queue,* or returns {@code null} if this queue is empty.** @return the head of this queue, or {@code null} if this queue is empty*/E poll();/*** Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue. This method* differs from {@link #peek peek} only in that it throws an exception* if this queue is empty.** @return the head of this queue* @throws NoSuchElementException if this queue is empty*/E element();/*** Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue,* or returns {@code null} if this queue is empty.** @return the head of this queue, or {@code null} if this queue is empty*/E peek();
}Queue扩展了Collection,它的主要操作有三个:
- 在尾部添加元素(
add、offer); - 查看头部元素(
element、peek),返回头部元素,但不改变队列; - 删除头部元素(
remove、poll),返回头部元素,并且从队列中删除。
每种操作都有两种形式,有什么区别呢?区别在于,对于特殊情况的处理不同。特殊情况是指队列为空或者队列为满,为空容易理解,为满是指队列有长度大小限制,而且已经占满了。LinkedList的实现中,队列长度没有限制,但别的Queue的实现可能有。在队列为空时,element和remove会抛出异常NoSuchElementException,而peek和poll返回特殊值null;在队列为满时,add会抛出异常IllegalStateException,而offer只是返回false。
除了Queue,LinkedList还可以当成栈,栈也是一种常用的数据结构,与队列相反,它的特点是先进后出、后进先出,类似于一个储物箱,放的时候是一件件往上放,拿的时候则只能从上面开始拿。Java中没有单独的栈接口,栈相关方法包括在了表示双端队列的接口Deque中,主要有三个方法:
void push(E e);
E pop();
E peek();
解释如下。
push表示入栈,在头部添加元素,栈的空间可能是有限的,如果栈满了,push会抛出异常IllegalStateException。pop表示出栈,返回头部元素,并且从栈中删除,如果栈为空,会抛出异常NoSuchElementException。peek查看栈头部元素,不修改栈,如果栈为空,返回null。
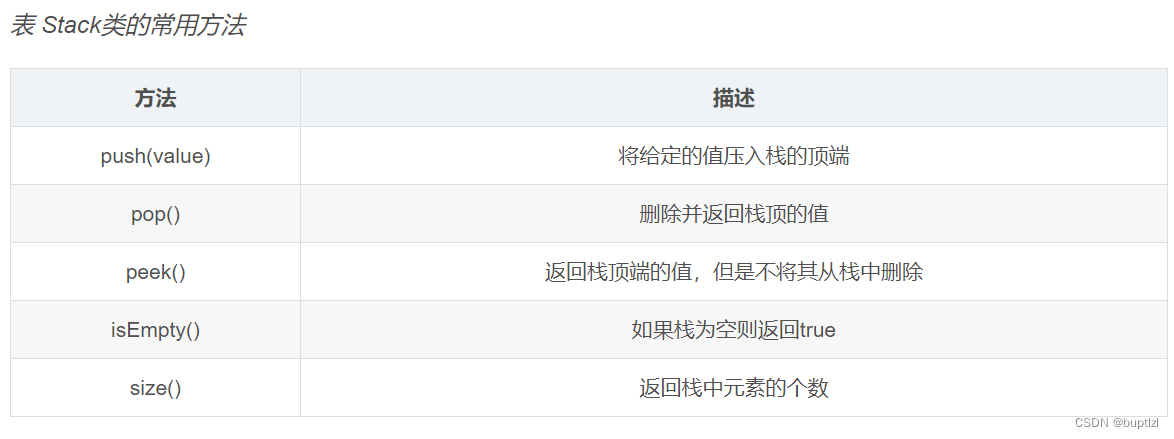
讲到栈,Java中有一个类Stack,单词意思就是栈,它也实现了栈的一些方法,如push/pop/peek等,但它没有实现Deque接口,它是Vector的子类,它增加的这些方法也通过synchronized实现了线程安全,具体就不介绍了。不需要线程安全的情况下,推荐使用LinkedList或ArrayDeque。
栈和队列都是在两端进行操作,栈只操作头部,队列两端都操作,但尾部只添加、头部只查看和删除。结合队列和栈,有一个更为通用的操作两端的接口Deque。Deque扩展了Queue,包括了栈的操作方法,此外,它还有如下更为明确的操作两端的方法:
void addFirst(E e);
void addLast(E e);
E getFirst();
E getLast();
boolean offerFirst(E e);
boolean offerLast(E e);
E peekFirst();
E peekLast();
E pollFirst();
E pollLast();
E removeFirst();
E removeLast();
xxxFirst操作头部,xxxLast操作尾部。与队列类似,每种操作有两种形式,区别也是在队列为空或满时处理不同。为空时,getXXX/removeXXX会抛出异常,而peekXXX/pollXXX会返回null。队列满时,addXXX会抛出异常,offerXXX只是返回false。
栈和队列只是双端队列的特殊情况,它们的方法都可以使用双端队列的方法替代,不过,使用不同的名称和方法,概念上更为清晰。
Deque接口还有一个迭代器方法,可以从后往前遍历:
/*** Returns an iterator over the elements in this deque in reverse* sequential order. The elements will be returned in order from* last (tail) to first (head).** @return an iterator over the elements in this deque in reverse* sequence*/Iterator<E> descendingIterator();
简单总结下:LinkedList的用法是比较简单的,与ArrayList用法类似,支持List接口,只是,LinkedList增加了一个接口Deque,可以把它看作队列、栈、双端队列,方便地在两端进行操作。如果只是用作List,那应该用ArrayList还是LinkedList呢?我们需要了解LinkedList的实现原理,根据实际需要再作决定。
2.2 实现原理
1、内部组成
我们知道,ArrayList内部是数组,元素在内存是连续存放的,但LinkedList不是。LinkedList直译就是链表,确切地说,它的内部实现是双向链表,每个元素在内存都是单独存放的,元素之间通过链接连在一起,类似于小朋友之间手拉手一样。
为了实现链表,LinkedList定义了一个s私有静态内部类 – 节点(Node),代码如下所示:
private static class Node<E> {E item;Node<E> next;Node<E> prev;Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {this.item = element;this.next = next;this.prev = prev;}}
节点包括实际的元素E item,但同时有两个链接,分别指向前一个节点(前驱,Node<E> prev)和后一个节点(后继,Node<E> next)。
LinkedList内部组成就是如下三个实例变量:
transient int size = 0;/*** Pointer to first node.*/
transient Node<E> first;/*** Pointer to last node.*/
transient Node<E> last;
size表示链表长度,默认为 0 0 0,first指向头节点,last指向尾节点,初始值都为null。
LinkedList的所有public方法内部操作的都是这三个实例变量,具体是怎么操作的?链接关系是如何维护的?我们看一些主要的方法,分别分析。
2、add 方法
add方法代码如下:
/*** Appends the specified element to the end of this list.** <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.** @param e element to be appended to this list* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})*/public boolean add(E e) {linkLast(e);return true;}
代码中,主要调用了linkLast方法,代码如下:
/*** Links e as last element.*/void linkLast(E e) {final Node<E> l = last;final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);last = newNode;if (l == null)first = newNode;elsel.next = newNode;size++;modCount++;}
linkLast代码的基本步骤如下。
-
创建一个新的节点
newNode。l和last指向原来的尾节点,如果原来链表为空,则为null。代码为:final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); -
修改尾节点
last,指向新的最后节点newNode。代码为:last = newNode; -
修改前节点的后向链接,如果原来链表为空,则让头节点指向新节点,否则让前一个节点的
next指向新节点。代码为:if (l == null)first = newNode; elsel.next = newNode; -
增加链表大小和修改计数器。代码为:
size++; modCount++;
接下来,通过图示加深LinkedList添加元素过程的理解:
List<String> list = new LinkedList<String>();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
执行完List<String> list = new LinkedList<String>()后,LinkedList内部结果如下所示:

添加a后,LinkedList内部结果如下所示:

添加b后,LinkedList内部结果如下所示:

可以看出,与ArrayList不同,LinkedList的内存是按需分配的,不需要预先分配多余的内存,添加元素只需分配新元素的空间,然后调节几个链接即可。
3、根据索引访问元素 get
LinkedList像ArrayList一样,支持根据索引值访问元素,代码如下:
/*** Returns the element at the specified position in this list.** @param index index of the element to return* @return the element at the specified position in this list* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}*/public E get(int index) {checkElementIndex(index);return node(index).item;}
checkElementIndex检查索引位置的有效性,如果无效,则抛出异常,代码为:
private void checkElementIndex(int index) {if (!isElementIndex(index))throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));}/*** Tells if the argument is the index of an existing element.*/private boolean isElementIndex(int index) {return index >= 0 && index < size;}
如果index有效,则传入参数index调用node方法查找对应的节点,其item属性就指向实际元素内容,node方法的代码为:
/*** Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.*/Node<E> node(int index) {// assert isElementIndex(index);if (index < (size >> 1)) {Node<E> x = first;for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)x = x.next;return x;} else {Node<E> x = last;for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)x = x.prev;return x;}}
size>>1等于size/2,如果索引位置在前半部分(index<(size>>1)),则从头节点开始查找,否则,从尾节点开始查找。可以看出,与ArrayList明显不同,ArrayList中数组元素连续存放,可以根据索引直接定位,而在LinkedList中,则必须从头或尾顺着链接查找,效率比较低。
4、根据内容查找元素索引 indexOf
/*** Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.* More formally, returns the lowest index {@code i} such that* {@code Objects.equals(o, get(i))},* or -1 if there is no such index.** @param o element to search for* @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element*/public int indexOf(Object o) {int index = 0;if (o == null) {for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {if (x.item == null)return index;index++;}} else {for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {if (o.equals(x.item))return index;index++;}}return -1;}
代码也很简单,从头节点顺着链接往后找,如果要找的是null,则找第一个item为null的节点,否则使用equals方法进行比较。
5、插入元素 add(int, E)
add()在尾部添加元素,如果在头部或者中间插入元素呢?可以使用add(int index, E element)方法,代码如下:
/*** Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).** @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted* @param element element to be inserted* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}*/public void add(int index, E element) {checkPositionIndex(index);if (index == size)linkLast(element);elselinkBefore(element, node(index));}
如果index为size,添加到最后面,一般情况,是插入到index对应节点的前面,调用方法为linkBefore,它的代码为:
/*** Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.*/void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {// assert succ != null;final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);succ.prev = newNode;if (pred == null)first = newNode;elsepred.next = newNode;size++;modCount++;}
参数succ表示后继节点,变量pred表示前驱节点,目标是在pred和succ中间插入一个节点。插入步骤是:
-
新建一个节点
newNode,前驱为pred,后继为succ。代码为:final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); -
让后继的前驱指向新节点。代码为:
succ.prev = newNode; -
让前驱的后继指向新节点,如果前驱为空,那么修改头节点指向新节点。代码为:
if (pred == null)first = newNode; elsepred.next = newNode; -
增加长度和修改计数器。
我们通过图示来进行介绍。还是上面的例子,比如,插入一个元素:
list.add(1, "c");
内存结构如下图所示:

可以看出,在中间插入元素,LinkedList只需按需分配内存,修改前驱和后继节点的链接,而ArrayList则可能需要分配很多额外空间,且移动所有后续元素。
6、删除元素 remove(int) 和 remove(Object)
我们再来看删除元素,首先看remove(int),代码如下为:
public E remove(int index) {checkElementIndex(index);return unlink(node(index));}
remove(Object),代码如下:
public boolean remove(Object o) {if (o == null) {for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {if (x.item == null) {unlink(x);return true;}}} else {for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {if (o.equals(x.item)) {unlink(x);return true;}}}return false;}
查看代码,可以知道,删除某个节点时,都是先找到待删除的节点,随后调用unlink(Node)方法,代码如下:
E unlink(Node<E> x) {// assert x != null;final E element = x.item;final Node<E> next = x.next;final Node<E> prev = x.prev;if (prev == null) {first = next;} else {prev.next = next;x.prev = null;}if (next == null) {last = prev;} else {next.prev = prev;x.next = null;}x.item = null;size--;modCount++;return element;}
删除x节点,基本思路就是让x的前驱和后继直接链接起来,next是x的后继,prev是x的前驱,具体分为两步。
- 让
x的前驱的后继指向x的后继。如果x没有前驱,说明删除的是头节点,则修改头节点指向x的后继。 - 让
x的后继的前驱指向x的前驱。如果x没有后继,说明删除的是尾节点,则修改尾节点指向x的前驱。
通过图示进行说明。还是上面的例子,如果删除一个元素:
list.remove(1);
内存结构如下图所示:

2.3 LinkedList 特点分析
用法上,LinkedList是一个List,但也实现了Deque接口,可以作为队列、栈和双端队列使用。实现原理上,LinkedList内部是一个双向链表,并维护了长度、头节点和尾节点,这决定了它有如下特点。
- 按需分配空间,不需要预先分配很多空间。
- 不可以随机访问,按照索引位置访问效率比较低,必须从头或尾顺着链接找,效率为 O ( N 2 ) O(\frac{N}{2}) O(2N)。
- 不管列表是否已排序,只要是按照内容查找元素,效率都比较低,必须逐个比较,效率为 O ( N ) O(N) O(N)。
- 在两端添加、删除元素的效率很高,为 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)。
- 在中间插入、删除元素,要先定位,效率比较低,为 O ( N ) O(N) O(N),但修改本身的效率很高,效率为 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)。
理解了LinkedList和ArrayList的特点,就能比较容易地进行选择了,如果列表长度未知,添加、删除操作比较多,尤其经常从两端进行操作,而按照索引位置访问相对比较少,则LinkedList是比较理想的选择。
马俊昌.Java编程的逻辑[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2018. ↩︎
尚硅谷教育.剑指Java:核心原理与应用实践[M].北京:电子工业出版社,2023. ↩︎