系列文章目录
提示:这里是该系列文章的所有文章的目录
第一章: (一)QCustomPlot常见属性设置、多曲线绘制、动态曲线绘制、生成游标、矩形放大等功能实现
第二章: (二)QCustomPlot生成热力图/矩阵颜色图
第三章: (三)Qt+QCustomPlot生成上下方向/不同颜色的条形图(柱形图)
第四章 :(四)QCustomPlot柱形图动态显示实例开发
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- 前言
- 一、模拟数据生成静态热力图
- 二、改变Z值生成动态效果
- 三、基于前文增加的代码总结/下载链接
- 总结
前言
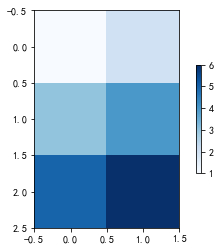
本文主要讲述了使用QCustomPlot图形库实现热力图的方法,这里的热力图也叫颜色图,本文实现了一个10x10矩阵的热力图,具体实现方式查看代码。文中实例是在上一篇文章实例基础上进行修改的,所以文中放置主要代码,需要完整代码可通过文末百度网盘链接进行下载。
项目效果
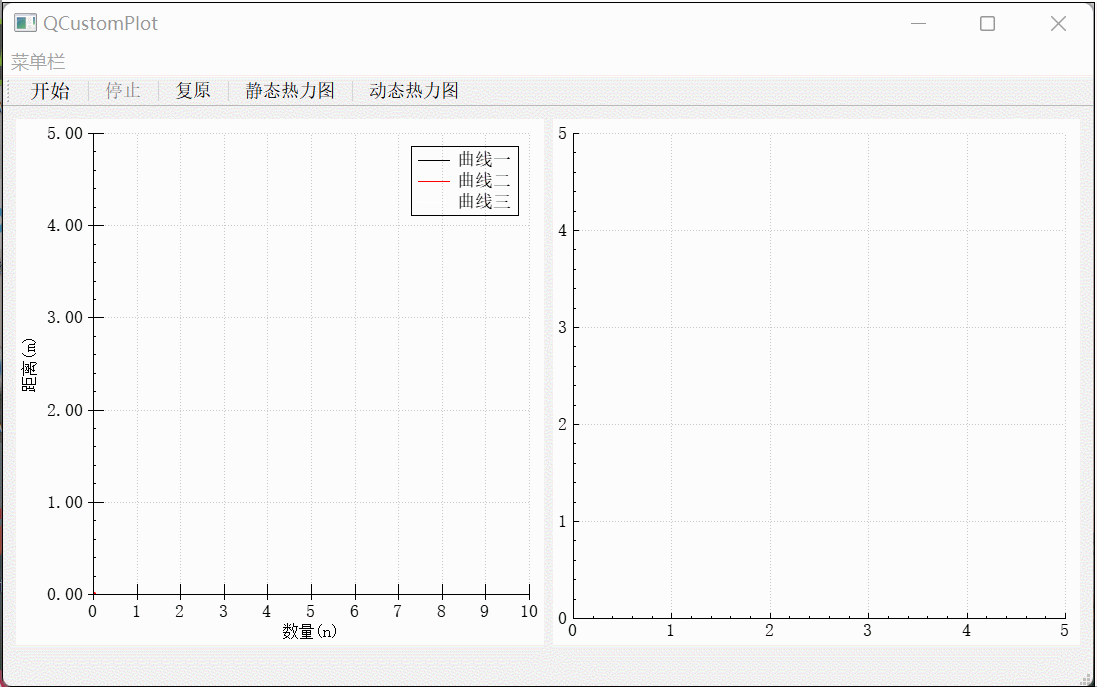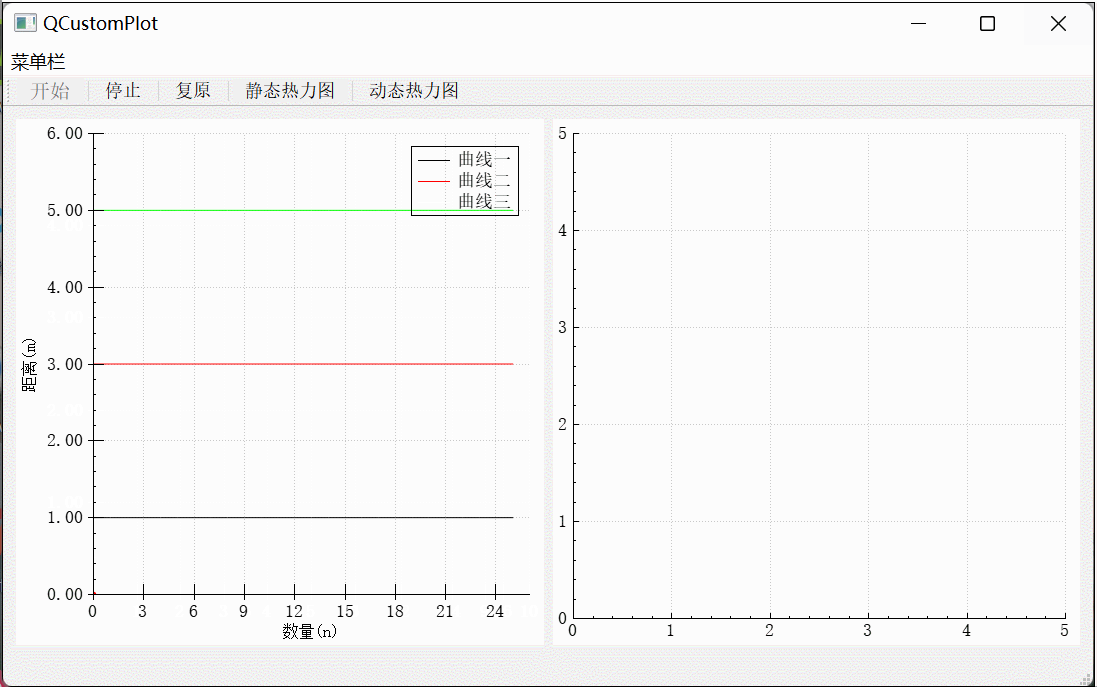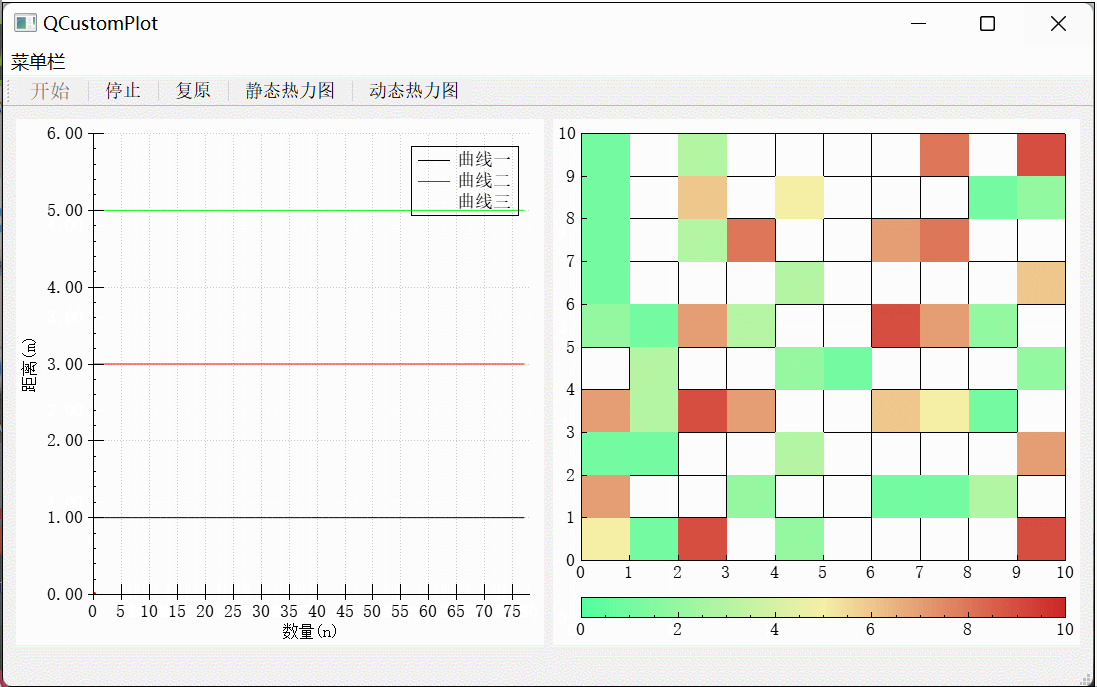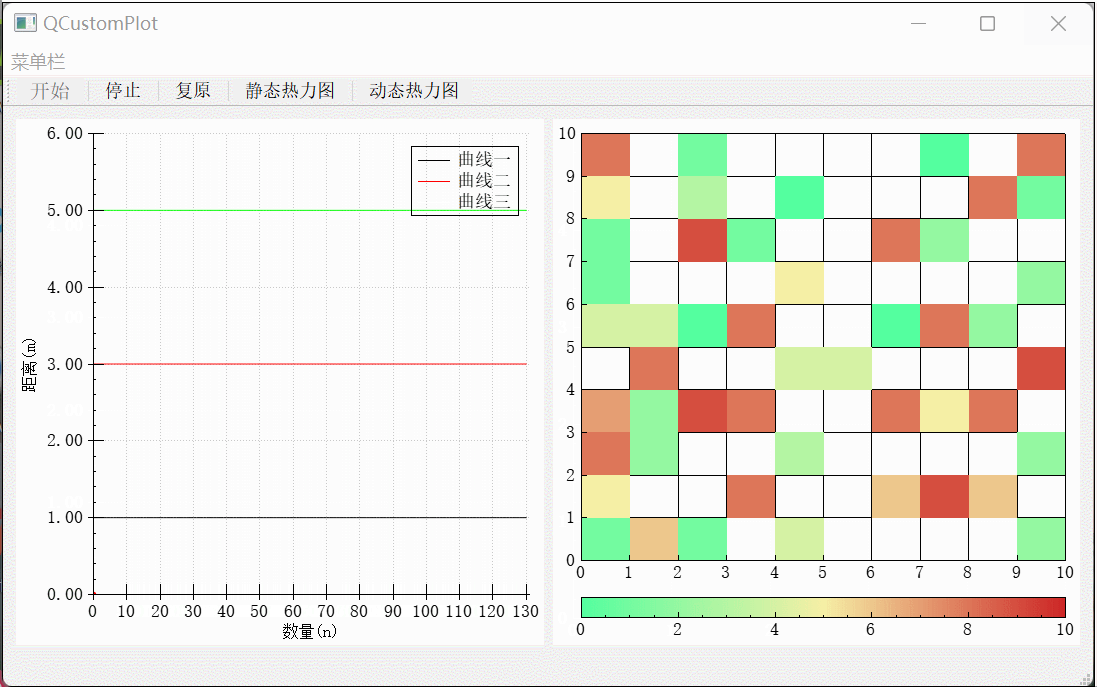
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
一、模拟数据生成静态热力图
1.创建QCPColorMap热力图及QCPColorScale色条
void MainWindow::setupHeatMap(QCustomPlot *customPlot)
{//x轴设置QSharedPointer<QCPAxisTickerFixed> intTicker_X(new QCPAxisTickerFixed);intTicker_X->setTickStep(1); //设置刻度之间的步长为1intTicker_X->setScaleStrategy(QCPAxisTickerFixed::ssMultiples); //设置缩放策略customPlot->xAxis->setTicker(intTicker_X); //应用自定义整形ticker,防止使用放大功能时出现相同的x刻度值customPlot->xAxis->ticker()->setTickCount(11); //刻度数量customPlot->xAxis->setNumberFormat("f"); //x轴刻度值格式customPlot->xAxis->setNumberPrecision(0); //刻度值精度//customPlot->xAxis->setLabel("X轴"); //设置标签customPlot->xAxis->setLabelFont(QFont(font().family(),8)); //设置标签字体大小customPlot->xAxis->setRange(0,10,Qt::AlignLeft); //设置x轴范围customPlot->xAxis->setSubTicks(false); //设置子刻度隐藏//customPlot->xAxis->setSubTickLength(2,0); //子刻度长度customPlot->xAxis->setTickLength(5,0); //主刻度长度customPlot->xAxis->grid()->setPen(QPen(Qt::black)); //设置主刻度线网格线显示,设置为Qt::NoPen就不会显示customPlot->xAxis->grid()->setSubGridVisible(false); //设置子刻度网格线是否可见//y轴设置QSharedPointer<QCPAxisTickerFixed> intTicker_Y(new QCPAxisTickerFixed);intTicker_Y->setTickStep(1);intTicker_Y->setScaleStrategy(QCPAxisTickerFixed::ssMultiples);customPlot->yAxis->setTicker(intTicker_Y);customPlot->yAxis->ticker()->setTickCount(11);customPlot->yAxis->setNumberFormat("f");customPlot->yAxis->setNumberPrecision(0);//customPlot->yAxis->setLabel("Y轴");customPlot->yAxis->setLabelFont(QFont(font().family(),8));customPlot->yAxis->setRange(0,10,Qt::AlignLeft);customPlot->yAxis->setSubTicks(false);//customPlot->yAxis->setSubTickLength(2,0);customPlot->yAxis->setTickLength(5,0);customPlot->yAxis->grid()->setPen(QPen(Qt::black));customPlot->yAxis->grid()->setSubGridVisible(false);//模拟数据:{行,列,值}QVector<QVector<double>> data ={{0,0,5},{0,1,1},{0,2,9},{0,3,0},{0,4,2},{0,5,0},{0,6,0},{0,7,0},{0,8,0},{0,9,9},{1,0,7},{1,1,0},{1,2,0},{1,3,2},{1,4,0},{1,5,0},{1,6,1},{1,7,1},{1,8,3},{1,9,0},{2,0,1},{2,1,1},{2,2,0},{2,3,0},{2,4,3},{2,5,0},{2,6,0},{2,7,0},{2,8,0},{2,9,7},{3,0,7},{3,1,3},{3,2,9},{3,3,7},{3,4,0},{3,5,0},{3,6,6},{3,7,5},{3,8,1},{3,9,0},{4,0,0},{4,1,3},{4,2,0},{4,3,0},{4,4,2},{4,5,1},{4,6,0},{4,7,0},{4,8,0},{4,9,2},{5,0,2},{5,1,1},{5,2,7},{5,3,3},{5,4,0},{5,5,0},{5,6,9},{5,7,7},{5,8,2},{5,9,0},{6,0,1},{6,1,0},{6,2,0},{6,3,0},{6,4,3},{6,5,0},{6,6,0},{6,7,0},{6,8,0},{6,9,6},{7,0,1},{7,1,0},{7,2,3},{7,3,8},{7,4,0},{7,5,0},{7,6,7},{7,7,8},{7,8,0},{7,9,0},{8,0,1},{8,1,0},{8,2,6},{8,3,0},{8,4,5},{8,5,0},{8,6,0},{8,7,0},{8,8,1},{8,9,2},{9,0,1},{9,1,0},{9,2,3},{9,3,0},{9,4,0},{9,5,0},{9,6,0},{9,7,8},{9,8,0},{9,9,9},};QCPColorMap *heatmap = new QCPColorMap(customPlot->xAxis,customPlot->yAxis); //构造一个颜色图heatmap->data()->setSize(10,10); //设置颜色图数据维度,代表你的数据矩阵(10x10),这里可以理解为有多少个小方块heatmap->data()->setRange(QCPRange(0.5,9.5), QCPRange(0.5,9.5)); //颜色图在x、y轴上的范围,这里可以查看下setRange函数定义for(int x=0;x<10;x++){for(int y=0;y<10;y++){int z = data.at(10 * y + x).at(2);if(z){heatmap->data()->setCell(x, y, z); //如果z不为0,则设置颜色值的位置}else{heatmap->data()->setAlpha(x, y, 0); //z为0,设置为透明,根据需求来设置}}}QCPColorScale *colorScale = new QCPColorScale(customPlot); //构造一个色条colorScale->setType(QCPAxis::atBottom); //水平显示customPlot->plotLayout()->addElement(1, 0, colorScale); //在颜色图下面显示heatmap->setColorScale(colorScale); //设置色条QCPColorGradient gradient; //色条使用的颜色渐变gradient.setColorStopAt(0.0, QColor("#54ff9f")); //设置渐变在指定位置的颜色(从0到1),最小为0.0gradient.setColorStopAt(0.5, QColor("#f6efa6")); //设置色条分段的颜色gradient.setColorStopAt(1.0, QColor("#cd2626")); //设置色条结束时的颜色,最大为1.0heatmap->setGradient(gradient); //设置颜色渐变//heatmap->rescaleDataRange(); //自动计算数据范围,数据范围决定了哪些数据值映射到QCPColorGradient的颜色渐变当中heatmap->setDataRange(QCPRange(0, 10)); //设置数据范围heatmap->setInterpolate(false); //禁用插值,界面显示小方块//保持色条与轴矩形边距一致QCPMarginGroup *marginGroup = new QCPMarginGroup(customPlot);customPlot->axisRect()->setMarginGroup(QCP::msLeft | QCP::msRight, marginGroup);colorScale->setMarginGroup(QCP::msLeft | QCP::msRight, marginGroup);//刷新界面customPlot->replot(QCustomPlot::rpQueuedReplot);
}
二、改变Z值生成动态效果
1.定时器内随机改变Z值
//热力图刷新定时器
void MainWindow::slot_mapTimeOut()
{auto *colorMap = static_cast<QCPColorMap *>(cusHeatMap->plottable(0));int keySize = colorMap->data()->keySize();int valueSize = colorMap->data()->valueSize();for(int x=0;x<keySize;x++){for (int y=0;y<valueSize;y++){//if(colorMap->data()->alpha(x,y)) //判断当前是否透明//{//如果之前有设置透明,依然会透明colorMap->data()->setCell(x,y, QRandomGenerator::global()->bounded(0,10)); //0-10直接随机值,可查看bounded定义//}}}cusHeatMap->replot(QCustomPlot::rpQueuedReplot); //括号内参数作用是避免重复绘制
}
三、基于前文增加的代码总结/下载链接
1.mainwindow.h
class MainWindow : public QMainWindow
{Q_OBJECTpublic:...void InitHeatMap();void setupHeatMap(QCustomPlot *customplot);private slots:...void slot_mapTimeOut();void on_action_heatMap_triggered();void on_action_heatMap_2_triggered();private:...//热力图QCustomPlot *cusHeatMap;QTimer *mapTimer;}
2.mainwindow.cpp
//构造函数中添加InitHeatMap();
void MainWindow::InitHeatMap()
{cusHeatMap = new QCustomPlot();cusHeatMap = ui->widget_color;//热力图刷新定时器mapTimer = new QTimer();connect(mapTimer,SIGNAL(timeout()),this,SLOT(slot_mapTimeOut()));
}void MainWindow::setupHeatMap(QCustomPlot *customPlot)
{//该函数内容见前文...
}void MainWindow::slot_mapTimeOut()
{//该函数内容见前文...
}void MainWindow::on_action_heatMap_triggered()
{setupHeatMap(cusHeatMap);
}void MainWindow::on_action_heatMap_2_triggered()
{mapTimer->start(1000); //开启定时器实现动态热力图效果
}
3.mainwindow.ui
4.完整代码百度网盘链接
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1aIvEe6pMI15M9K2H0FWRJQ
提取码:xxcj
总结
本文示例使用QCustomPlot绘制热力图的时候,可以发现所用的数据格式为{x,y,z},其中了x、y两个位置可以看作矩阵的x行y列,还有一个z数值,z数值对应着色条中渐变的颜色取值,需要注意的是渐变在指定位置的颜色是有范围的(0-1),可以使用heatmap->data()->setAlpha(x,y,z)将指定位置数据设为透明。
本系列文章下一篇:(三)Qt+QCustomPlot生成上下方向/不同颜色的条形图(柱形图)
hello:
共同学习,共同进步,如果还有相关问题,可在评论区留言进行讨论。
参考博客:QCustomPlot之热力图(十四)