目录
- 前言及准备:
- 一、红黑树接口
- 1.1 begin
- 1.2 end
- 1.3 查找
- 1.4 插入
- 1.5 左单旋和右单旋
- 二、树形迭代器(正向)
- 2.1 前置++
- 三、模拟实现set
- 四、模拟实现map
前言及准备:
set、map的底层结构是红黑树,它们的函数通过调用红黑树的接口来实现,红黑树一些接口需要通过树形迭代器来实现。set是k模型,map是kv模型,红黑树要不要写两份呢?答案是不需要,只用一份即可,通过仿函数来控制。
定义树的节点:
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{RBTreeNode<T>* _left;RBTreeNode<T>* _right;RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;T _data;Colour _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data):_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_parent(nullptr),_data(data),_col(RED){}
};
红黑树有3个指针域,数据域用T来表示,如果是set,那么传过来的是k模型;如果是map,是kv模型。新增的节点的颜色默认是红色(根节点除外)。
一、红黑树接口
1.1 begin
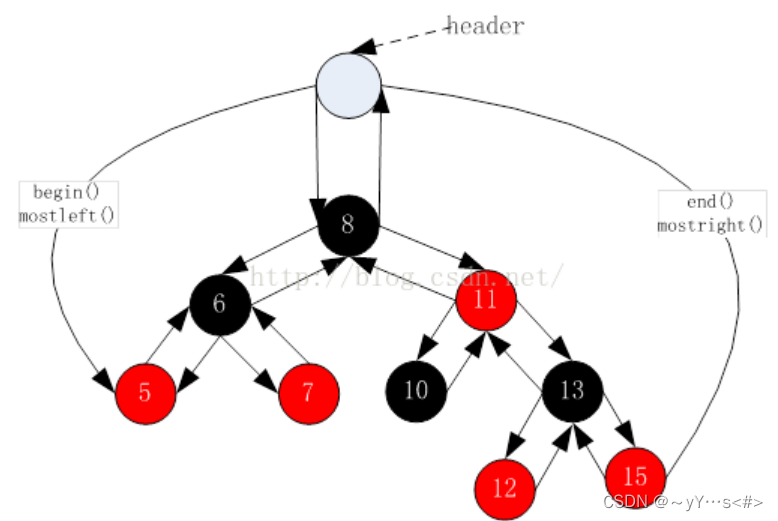
返回的是红黑树的第一个节点,注意,这里的第一个的顺序是按中序遍历来的,所以,第一个节点的位置是树的最左节点。
//返回的迭代器指向的数据可修改
iterator begin()
{Node* subLeft = _root;while (subLeft->_left){subLeft = subLeft->_left;}return iterator(subLeft);
}
//返回的迭代器指向的数据不可修改
const_iterator begin() const
{Node* subLeft = _root;while (subLeft->_left){subLeft = subLeft->_left;}return const_iterator(subLeft);
}
1.2 end
返回的是最后一个节点(最右侧节点)的下一个位置。由于这里实现的红黑树没有头节点,所以只能给nullptr来勉强实现这个迭代器。但是这样其实是不行的,因为对end()位置的迭代器进行 - - 操作,必须要能找最后一个元素,给nullptr就找不到了。如果有头节点,那么end()的位置应该是在头节点的位置。
iterator end()
{return iterator(nullptr);
}
const_iterator end() const
{return const_iterator(nullptr);
}
1.3 查找
查找的过程与之前写的二叉搜索树没有多大区别,要注意的是返回类型,找到了,返回的是该节点的迭代器,找不到就返回end()。
iterator Find(const K& key)
{KeyOfT kot;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < key){cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > key){cur = cur->_left;}else{return iterator(cur);}}return end();
}
咋知道是set还是map的数据进行比较,看传过来的类模板参数中的仿函数是set的还是map的。当然,这里只需写好就行,不用关心传过来的是什么,set和map的仿函数内部已经确定好了。
说明一下:
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
这是该红黑树的类模板,K是Find()函数中要对比的数据类型,T是节点的数据域,可能是k模型,也有可能是kv模型。怎么确定呢?通过第三个类模板参数——仿函数来确定。仿函数传的是set的,就是k模型;仿函数传的是map的,就是kv模型。仿函数内部具体实现下面再说。
1.4 插入
为了接近STL库中的insert函数,返回类型是pair,即插入成功,返回该节点的迭代器和true;插入失败,说明该节点已经存在,返回该节点的迭代器和false。
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)
{//为空if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;//根节点都是黑色的,特殊处理return make_pair(iterator(_root), true);}//非空KeyOfT kot;Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return make_pair(iterator(cur), false);}}//插入新节点cur = new Node(data);//红色的if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data)){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;Node* newnode = cur;//调整颜色while (parent && parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;//爷爷节点//父节点在爷爷节点的左边,那么叔叔节点在右边if (parent == grandfather->_left){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;//情况一:叔叔存在且为红if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){grandfather->_col = RED;uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;cur = grandfather;//爷爷不是根,向上更新parent = cur->_parent;}//情况二:叔叔不存在/存在且为黑else{//单旋if (cur == parent->_left){RotateR(grandfather);//右单旋parent->_col = BLACK;//变色grandfather->_col = RED;}//左右双旋 // cur == parent->_rightelse{RotateL(parent);//先左单旋RotateR(grandfather);//再右单旋grandfather->_col = RED;//变色cur->_col = BLACK;}}}else//父节点在右边,叔叔在左边{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;//情况一:叔叔存在且为红if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){grandfather->_col = RED;uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;cur = grandfather;//爷爷不是根,向上更新parent = cur->_parent;}//情况二:叔叔不存在/存在且为黑else{//单旋if (cur == parent->_right){RotateL(grandfather);//左单旋parent->_col = BLACK;//变色grandfather->_col = RED;}//右左双旋 // cur == parent->_leftelse{RotateR(parent);//先右单旋RotateL(grandfather);//再左单旋grandfather->_col = RED;//变色cur->_col = BLACK;}break;//经过情况二后跳出}}}_root->_col = BLACK;//统一处理,根必须是黑的return make_pair(iterator(newnode), true);
}
1.5 左单旋和右单旋
这两个就是之前的,这里不作重复叙述了
//左单旋
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subRL;//不为空if (subRL){subRL->_parent = parent;}subR->_left = parent;Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = subR;//处理parent如果为根if (parent == _root){_root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}//不为根,处理与ppnode的连接else{if (ppnode->_left == parent){ppnode->_left = subR;}else{ppnode->_right = subR;}subR->_parent = ppnode;}
}//右单旋
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;//不为空if (subLR){subLR->_parent = parent;}subL->_right = parent;Node* ppnode = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (parent == _root){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (ppnode->_left == parent){ppnode->_left = subL;}else{ppnode->_right = subL;}subL->_parent = ppnode;}
}
二、树形迭代器(正向)
2.1 前置++
首先要清楚的是++到下一个节点位置是按中序遍历走的,主要有两种情况:
- 该节点有右子树
- 该节点没有右子树
1️⃣有右子树
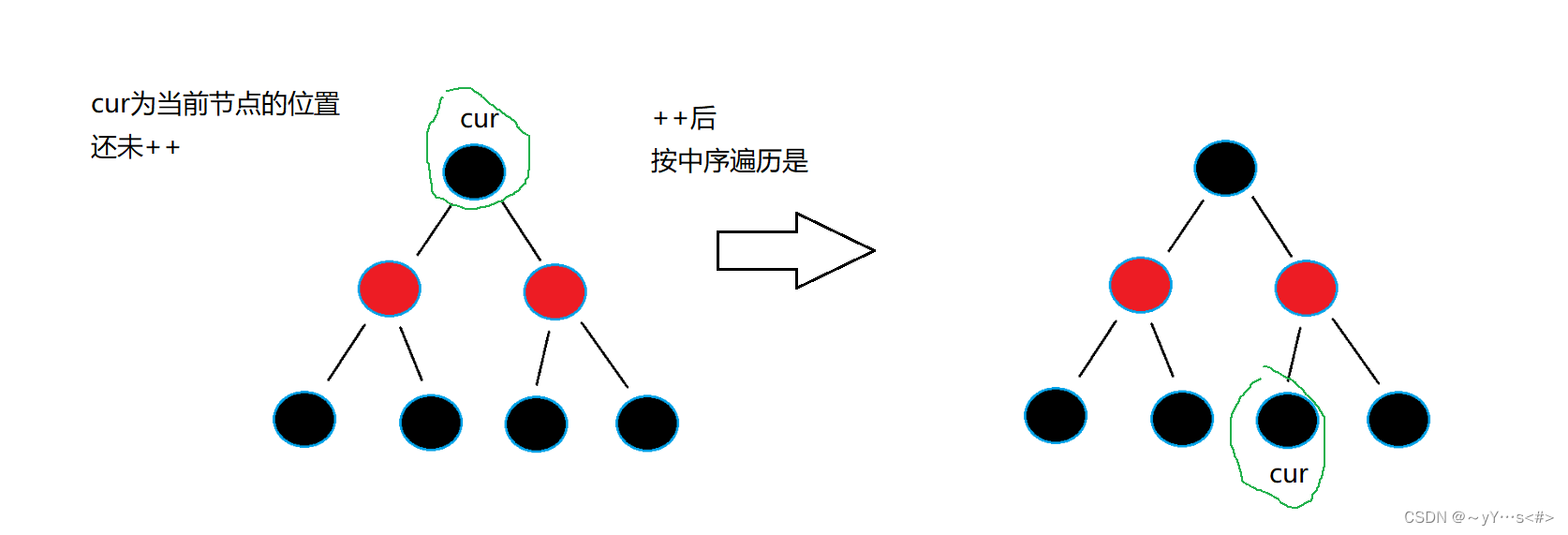
总结:有右子树++后的下一个节点是右子树的最左节点
2️⃣没有右子树
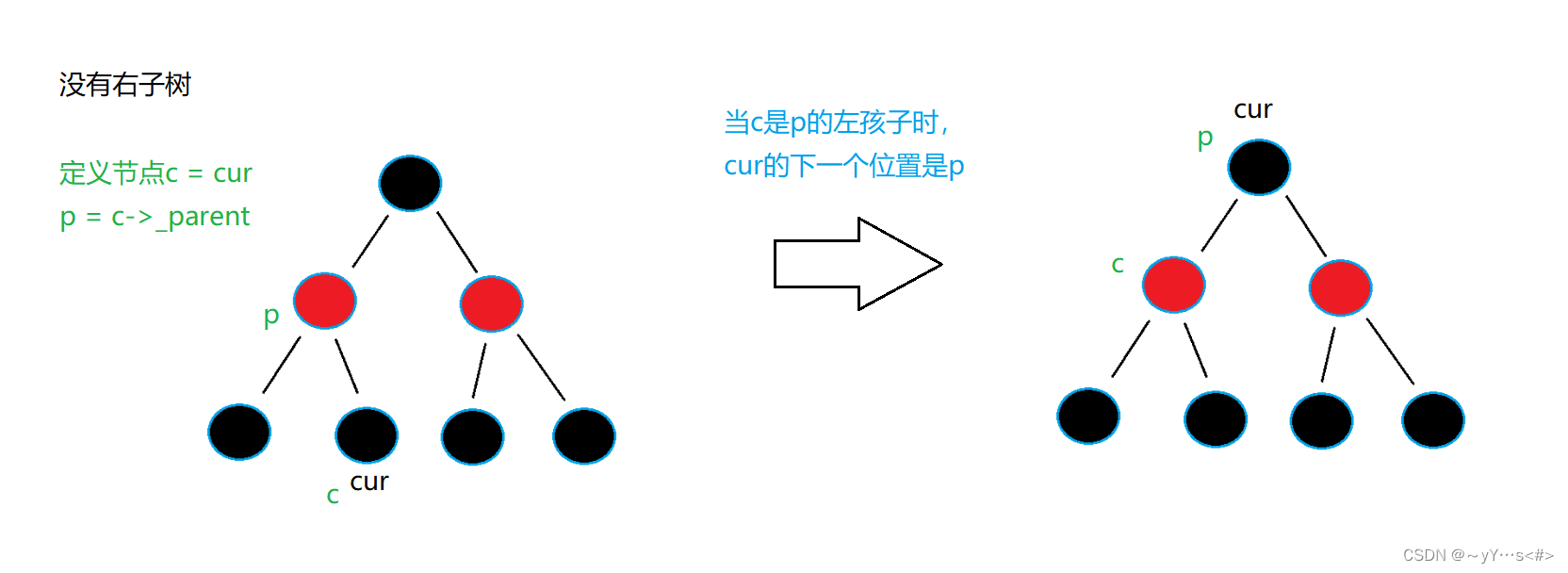
总结:没有右子树++后下一个节点是祖先节点中左孩子是当前节点(原来节点的位置)或者左孩子是当前节点的父亲的那个祖先
有点弯,再来图捋一捋:
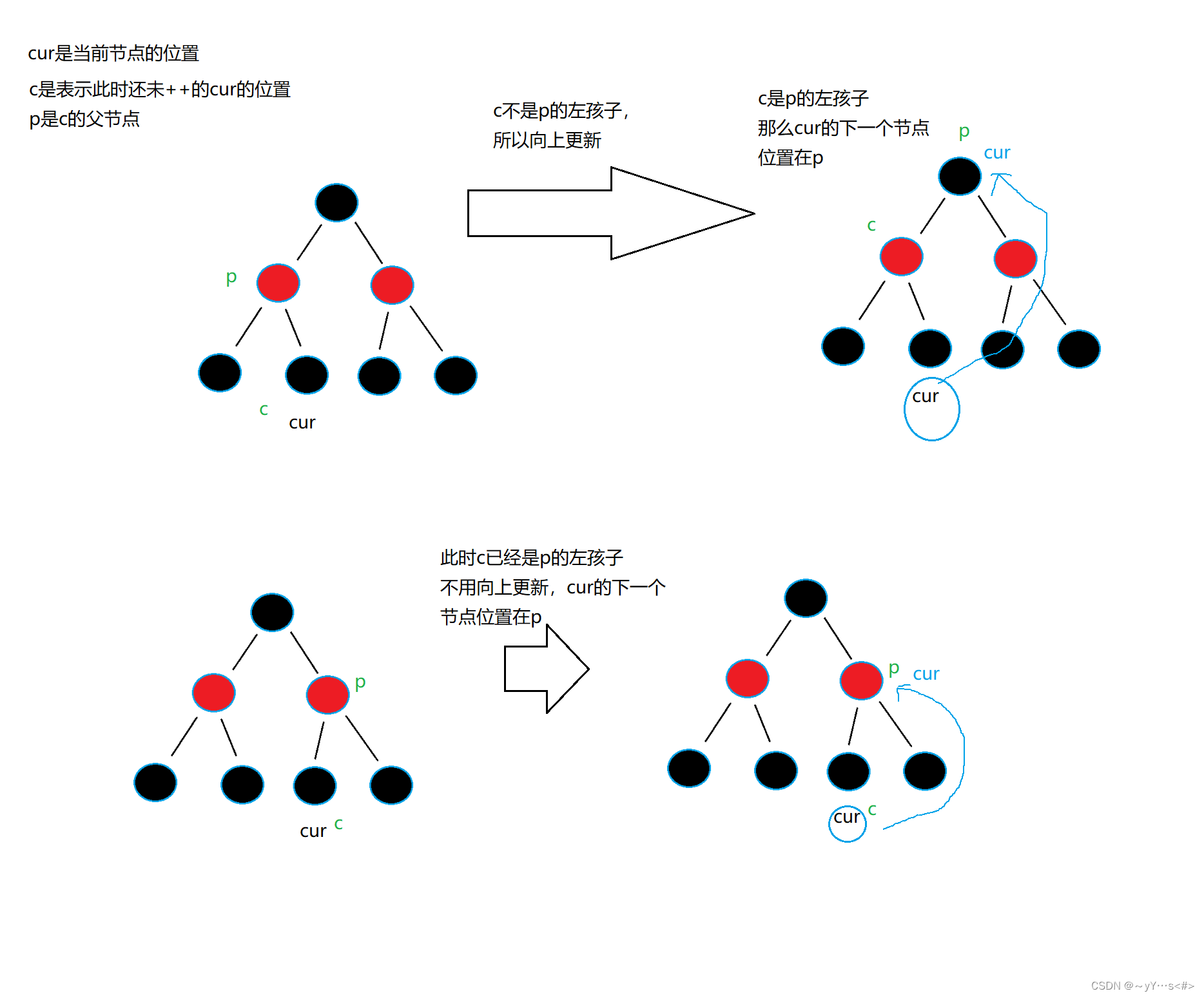
前置- -的逻辑与前置++刚好相反
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct RBTreeIterator
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;RBTreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}//前置++Self& operator++(){//右子树存在if (_node->_right){//下一个节点在右子树的最左边Node* subLeft = _node->_right;while (subLeft->_left){subLeft = subLeft->_left;}_node = subLeft;}//右子树不存在else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;//cur是parent的左子树,parent就是下一个while (parent && parent->_right == cur){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}//前置--Self& operator--()//与前置++的逻辑相反{//左子树存在if (_node->_left){//下一个节点是左子树的最右一个Node* subRight = _node->_left;while (subRight->_right){subRight = subRight->_right;}_node = subRight;}//左子树不存在else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;//cur是parent的右子树时parent就是下一个while (parent && parent->_left == cur){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){ return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;}
};
三、模拟实现set
set是k模型,仿函数返回的只有key值。其他接口调用红黑树的
template<class K>
class set
{//仿函数struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};
public:typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;//迭代器iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}const_iterator end() const{return _t.end();}//插入pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const K& key){return _t.Insert(key);}//查找iterator Find(const K& key){_t.Find(key);}
private:RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
四、模拟实现map
map是kv模型,仿函数返回的取kv中的key值。其他接口调用红黑树的,除此之外,多了一个operator[]
template<class K, class V>
class map
{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;//迭代器iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}const_iterator end() const{return _t.end();}//插入pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _t.Insert(kv);}//查找iterator Find(const K& key){_t.Find(key);}//operator[]V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> ret = Insert(make_pair(key, V()));return ret.first->second;}
private:RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};



![[论文笔记] Gradient Surgery for Multi-Task Learning](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/4c22f40956d649389468b6e89cbddd6b.png)